我是靠谱客的博主 奋斗烤鸡,这篇文章主要介绍Spring Boot之 CommandLineRunner、ApplicationRunner和@PostConstruct,现在分享给大家,希望可以做个参考。
在使用Spring Boot开发的工作中,我们经常会需要遇到一种功能需求,比如在服务启动时候,去加载一些配置,去请求一下其他服务的接口。Spring Boot给我们提供了三种常用的实现方法:
第一种是实现CommandLineRunner接口,
第二种是实现ApplicationRunner接口
第三种是使用注解:@PostConstruct
1、CommandLineRunner
1、CommandLineRunner执行的时间节点是在Application完成初始化工作之后。
2、CommandLineRunner在有多个实现的时候,可以使用@order注解指定执行先后顺序。
3、源码在:org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#run(),可以看看
我们先看一下CommandLineRunner的源码:
package org.springframework.boot;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface CommandLineRunner {
void run(String... args) throws Exception;
}
SpringApplication源码:
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = this.createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
context = this.createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
this.prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
this.refreshContext(context);
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable var10) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(var10);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
return context;
} catch (Throwable var9) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null);
throw new IllegalStateException(var9);
}
}
callRunners方法源码:
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
Iterator var4 = (new LinkedHashSet(runners)).iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
Object runner = var4.next();
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
this.callRunner((ApplicationRunner)runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
this.callRunner((CommandLineRunner)runner, args);
}
}
}
我们写一个例子实现:
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Component
@Order(1)
public class CommandLineRunnerTest implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("----CommandLineRunnerTest1 start---"+ Arrays.toString(args));
}
}
2、ApplicationRunner
ApplicationRunner跟CommandLineRunner是区别是在run方法里接收的参数不同,CommandLineRuner接收的参数是String... args,而ApplicationRunner的run方法的参数是ApplicationArguments
看看ApplicationRunner的源码:
package org.springframework.boot;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationRunner {
void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception;
}
我们写一个例子实现:
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
@Component
@Order(1)
public class ApplicationRunnerTest implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("---ApplicationRunnerTest start----");
List<String> nonOptionArgs = args.getNonOptionArgs();
System.out.println("[非选项参数]>>> " + nonOptionArgs);
Set<String> optionNames = args.getOptionNames();
for(String optionName: optionNames) {
System.out.println("[选项参数]>>> name:" + optionName
+ ";value:" + args.getOptionValues(optionName));
}
}
}
3、@PostConstruct
@PostConstruct是在javaEE5的时候引入的,它并不是Spring提供的,但是Spring有对@PostConstruct的实现。并且是在对象加载完之后执行。
先看注解源码
@Documented
@Retention (RUNTIME)
@Target(METHOD)
public @interface PostConstruct {
}
我们写一个例子实现:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
@Component
public class PostConstructTest {
@PostConstruct
public void start(){
System.out.println("---PostConstruct start---");
}
}
运行代码输出结果 :
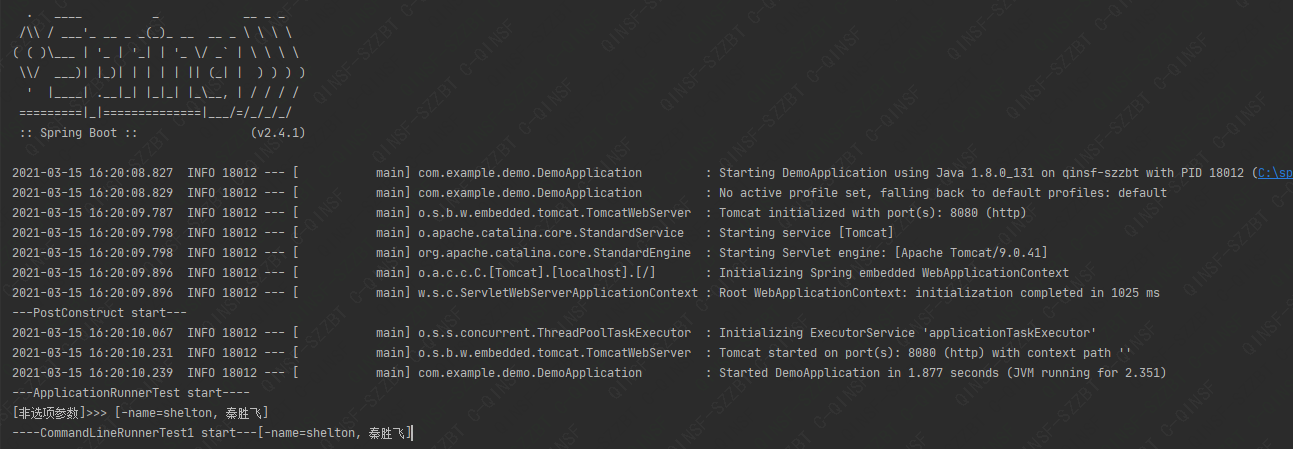
5、源码
https://gitee.com/Qinux/command-line-runner-demo.git
微信公众号:一凡码农
欢迎交流
最后
以上就是奋斗烤鸡最近收集整理的关于Spring Boot之 CommandLineRunner、ApplicationRunner和@PostConstruct的全部内容,更多相关Spring内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复