一、集合概述
1.1 集合的由来
我们学习的是面向对象语言,而面向对象语言对事物的描述是通过对象体现的,为了方便对多个对象进行操作,我们就必须把这多个对象进行存储。而要想存储多个对象,就不能是一个基本的变量,而应该是一个容器类型的变量,在我们目前所学过的知识里面,有哪些是容器类型的呢?数组和StringBuffer。但是呢?StringBuffer的结果是一个字符串,不一定满足我们的要求,所以我们只能选择数组,这就是对象数组。而对象数组又不能适应变化的需求,因为数组的长度是固定的,这个时候,为了适应变化的需求,Java就提供了集合类供我们使用。
1.2 数组和集合的区别
【长度区别】
数组的长度固定
集合长度可变
【内容不同】
数组存储的是同一种类型的元素
而集合可以存储不同类型的元素
【元素的数据类型问题】
数组可以存储基本数据类型,也可以存储引用数据类型
集合只能存储引用类型
1.3 集合的继承体系
刚说过集合是存储多个元素的,但是呢,存储多个元素我们也是有不同需求的:比如说,我要这多个元素中不能有相同的元素,再比如说,我要这多个元素按照某种规则排序一下。针对不同的需求,Java就提供了不同的集合类,这样呢,Java就提供了很多个集合类。这多个集合类的数据结构不同,结构不同不重要的,重要的是你要能够存储东西,并且还要能够使用这些东西,比如说判断,获取等。既然这样,那么,这多个集合类是有共性的内容的,我们把这些集合类的共性内容不断的向上提取,最终就能形成集合的继承体系结构。
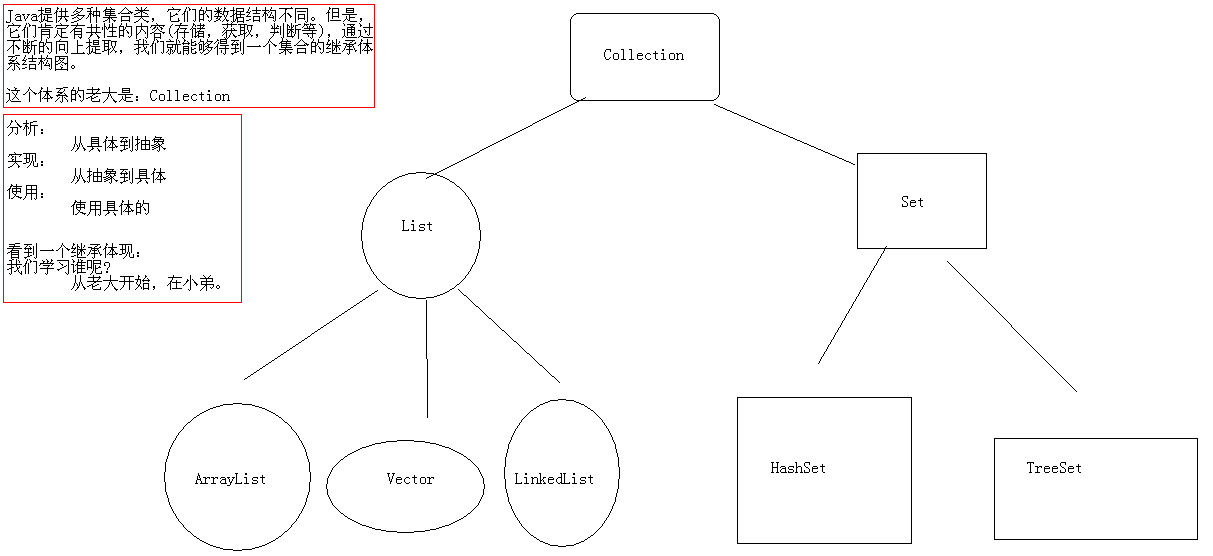
因为Collection是集合继承体系中的根接口,所以我们先来学习Collection。
Collection 是层次结构中的根接口。Collection 表示一组对象,这些对象也称为 collection 的元素。一些 collection 允许有重复的元素,而另一些则不允许。一些 collection 是有序的,而另一些则是无序的。
二、Collection的基本功能
2.1 添加功能
- boolean add(Object obj):添加一个元素
- boolean addAll(Collection c):添加一个集合的元素
public class CollectionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建集合1 // Collection c1 = new Collection(); //错误,因为接口不能实例化 Collection c1 = new ArrayList(); c1.add("abc1"); c1.add("abc2"); c1.add("abc3"); c1.add("abc4"); // 创建集合2 Collection c2 = new ArrayList(); c2.add("abc5"); c2.add("abc6"); c2.add("abc7"); // boolean addAll(Collection c):添加一个集合的元素 System.out.println("addAll:" + c1.addAll(c2));//true System.out.println("c1" + c1);//[abc1, abc2, abc3, abc4, abc5, abc6, abc7] } }
2.2 删除功能
- void clear():移除所有元素
- boolean remove(Object o):移除一个元素
- boolean removeAll(Collection c):移除一个集合的元素,只要有一个元素被移除了,就返回true。
public class CollectionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建集合1 Collection c1 = new ArrayList(); c1.add("abc1"); c1.add("abc2"); c1.add("abc3"); c1.add("abc4"); // void clear():移除所有元素 // c1.clear(); // boolean remove(Object o):移除一个元素 // System.out.println("remove:" + c1.remove("abc1")); // System.out.println("remove:" + c1.remove("abc2")); // 创建集合2 Collection c2 = new ArrayList(); c2.add("abc2"); c2.add("abc3"); c2.add("abc7"); //boolean removeAll(Collection c):移除一个集合的元素 //只要有一个元素被移除了,就返回true。 System.out.println("removeAll:" + c1.removeAll(c2)); System.out.println("c1:" + c1);//[abc1, abc4] } }
2.3 判断功能
- boolean contains(Object o):判断集合中是否包含指定的元素
- boolean containsAll(Collection c):判断集合中是否包含指定的集合元素,只有包含所有的元素,才叫包含
- boolean isEmpty():判断集合是否为空
public class CollectionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建集合1 // Collection c1 = new Collection(); //错误,因为接口不能实例化 Collection c1 = new ArrayList(); c1.add("abc1"); c1.add("abc2"); c1.add("abc3"); c1.add("abc4"); // boolean contains(Object o):判断集合中是否包含指定的元素 // System.out.println("contains:"+c1.contains("abc1")); // System.out.println("contains:"+c1.contains("abc2")) // boolean isEmpty():判断集合是否为空 // System.out.println("isEmpty:"+c1.isEmpty()); // 创建集合2 Collection c2 = new ArrayList(); c2.add("abc2"); c2.add("abc3"); c2.add("abc7"); //boolean containsAll(Collection c):判断集合中是否包含指定的集合元素 //只有包含所有的元素,才叫包含 System.out.println("containsAll:" + c1.containsAll(c2));//false System.out.println("c1:" + c1); } }
2.4 长度功能
int size():元素的个数
public class CollectionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建集合对象 // Collection c = new Collection(); //错误,因为接口不能实例化 Collection c = new ArrayList(); c.add("hello"); c.add("world"); c.add("java"); //int size():元素的个数 System.out.println("size:"+c.size()); } }
注意:
数组求长度用length属性;
字符串求长度用length()方法
集合求长度用size()方法
public class Length_Size { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] strings = {"aaa","bbb","ccc"}; String string = "aaabbbccc"; List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); list.add(1); System.out.println("String[].length="+strings.length); System.out.println("String.length()="+string.length()); System.out.println("List.size()="+list.size()); } }
2.5 交集功能
boolean retainAll(Collection c):两个集合都有的元素
public class CollectionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建集合1 Collection c1 = new ArrayList(); c1.add("abc1"); c1.add("abc2"); c1.add("abc3"); c1.add("abc4"); // 创建集合2 Collection c2 = new ArrayList(); c2.add("abc2"); c2.add("abc3"); c2.add("abc7"); //boolean retainAll(Collection c):两个集合都有的元素?思考元素去哪了,返回的boolean又是什么意思呢? //假设有两个集合A,B。 //A对B做交集,最终的结果保存在A中,B不变。 //返回值表示的是A是否发生过改变。 System.out.println("retainAll:" + c1.retainAll(c2));//true System.out.println("c1:" + c1);//[abc2, abc3] System.out.println("c2:" + c2);//[abc2, abc3, abc7] } }
三、Collection集合的遍历
3.1 转成数组再遍历
Object[] toArray():把集合转成数组,可以实现集合的遍历
public class CollectionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建集合对象 Collection c = new ArrayList(); // 添加元素 c.add("hello"); c.add("world"); c.add("java"); // 遍历 // Object[] toArray():把集合转成数组,可以实现集合的遍历 Object[] objs = c.toArray(); for (int x = 0; x < objs.length; x++) { // System.out.println(objs[x]); // 我知道元素是字符串,我在获取到元素的的同时,还想知道元素的长度。 // System.out.println(objs[x] + "---" + objs[x].length()); // 上面的实现不了,原因是Object中没有length()方法 // 我们要想使用字符串的方法,就必须把元素还原成字符串 // 向下转型 String s = (String) objs[x]; System.out.println(s + "----" + s.length()); } } }
【练习】
用集合存储5个学生对象,并把学生对象进行遍历。
/* * 分析: * A:创建学生类 * B:创建集合对象 * C:创建学生对象 * D:把学生添加到集合 * E:把集合转成数组 * F:遍历数组 */ public class StudentDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建集合对象 Collection c = new ArrayList(); // 创建学生对象 Student s1 = new Student("林青霞", 27); Student s2 = new Student("风清扬", 30); Student s3 = new Student("令狐冲", 33); Student s4 = new Student("武鑫", 25); Student s5 = new Student("刘晓曲", 22); // 把学生添加到集合 c.add(s1); c.add(s2); c.add(s3); c.add(s4); c.add(s5); // 把集合转成数组 Object[] objs = c.toArray(); // 遍历数组 for (int x = 0; x < objs.length; x++) { // System.out.println(objs[x]); Student s = (Student) objs[x]; System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); } } }
3.2 使用Iterator迭代器遍历(重点)
Iterator iterator():迭代器,集合的专用遍历方式。
Iterator接口下有两个方法用于集合的遍历
- Object next():获取元素,并移动到下一个位置。
- boolean hasNext():如果仍有元素可以迭代,则返回 true。
public class IteratorDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建集合对象 Collection c = new ArrayList(); // 创建并添加元素 c.add("hello"); c.add("world"); c.add("java"); // Iterator iterator():迭代器,集合的专用遍历方式 Iterator it = c.iterator();// 实际返回的肯定是子类对象,这里是多态 while (it.hasNext()) { String s = (String) it.next(); System.out.println(s); } } }
【迭代器的使用图解】
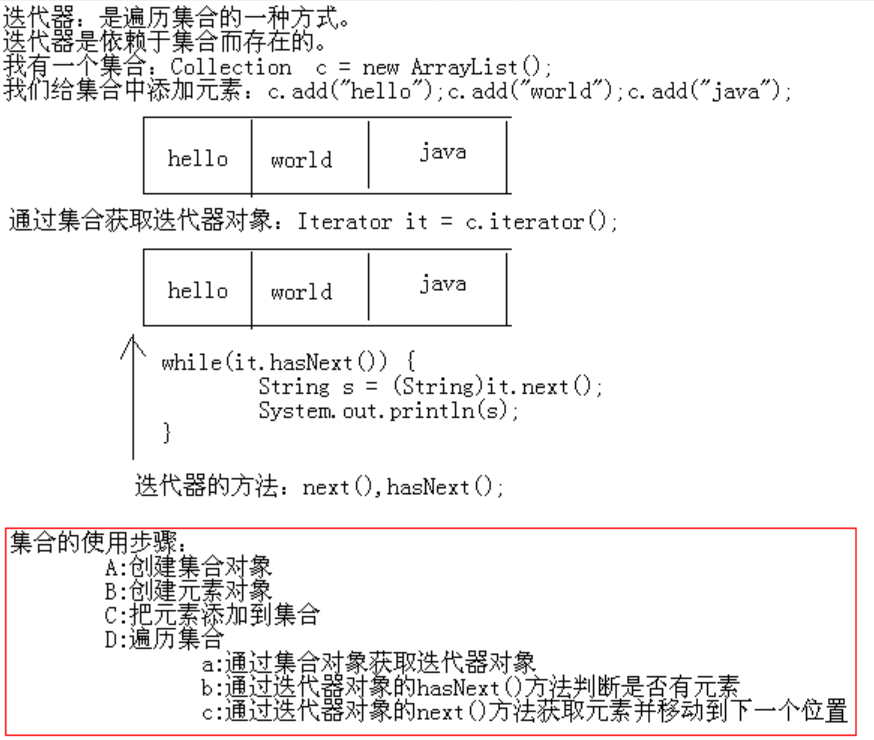
【迭代器的原理解析】
迭代器为什么不定义成一个类,而是一个接口?
假设迭代器定义的是一个类,这样我们就可以创建该类的对象,调用该类的方法来实现集合的遍历。但是呢,我们想想,Java中提供了很多的集合类,而这些集合类的数据结构是不同的。所以,存储的方式和遍历的方式应该是不同的,进而它们的遍历方式也应该不是一样的,最终,就没有定义迭代器类的。
而无论你是哪种集合,你都应该具备获取元素的操作,并且,最好再辅助于判断功能,这样,在获取前先判断,就更不容易出错。也就是说,判断功能和获取功能应该是一个集合遍历所具备的,而每种集合的方式又不太一样,所以我们把这两个功能给提取出来,并不提供具体实现,这种方式就是接口。
那么,真正的具体实现类在哪里呢?
在真正的具体的子类中,以内部类的方式体现的。
【迭代器的源码】
public interface Inteator { boolean hasNext(); Object next(); } public interface Iterable { Iterator iterator(); } public interface Collection extends Iterable { Iterator iterator(); } public interface List extends Collection { Iterator iterator(); } public class ArrayList implements List { public Iterator iterator() { return new Itr(); } private class Itr implements Iterator { public boolean hasNext() {} public Object next(){} } } Collection c = new ArrayList(); c.add("hello"); c.add("world"); c.add("java"); Iterator it = c.iterator(); //new Itr(); while(it.hasNext()) { String s = (String)it.next(); System.out.println(s); }
【练习】
用集合存储5个学生对象,并把学生对象进行遍历。用迭代器遍历。
public class IteratorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建集合对象 Collection c = new ArrayList(); // 创建学生对象 Student s1 = new Student("林青霞", 27); Student s2 = new Student("风清扬", 30); Student s3 = new Student("令狐冲", 33); Student s4 = new Student("武鑫", 25); Student s5 = new Student("刘晓曲", 22); // 把学生添加到集合中 c.add(s1); c.add(s2); c.add(s3); c.add(s4); c.add(s5); // 遍历 Iterator it = c.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { Student s = (Student) it.next(); System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); // NoSuchElementException 不要多次使用it.next()方法 // System.out.println(((Student) it.next()).getName() + "---" // + ((Student) it.next()).getAge()); } // System.out.println("----------------------------------"); // for循环改写 // for(Iterator it = c.iterator();it.hasNext();){ // Student s = (Student) it.next(); // System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); // } } }
注意:不要多次使用it.next()方法,因为每次使用都是访问一个对象。
四、集合的toString()方法源码解析
Collection c = new ArrayList(); c.add("hello"); c.add("world"); c.add("java"); System.out.println(c);
为什么c输出的不是地址值呢?
- Collection c = new ArrayList();
这是多态,所以输出c的toString()方法,其实是输出ArrayList的toString()
- 看ArrayList的toString()
而我们在ArrayList里面却没有发现toString()。 以后遇到这种情况,也不要担心,你认为有,它却没有,就应该去它父亲里面看看。 - toString()的方法源码
public String toString() { Iterator<E> it = iterator(); //集合本身调用迭代器方法,得到集合迭代器 if (! it.hasNext()) return "[]"; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append('['); for (;;) { E e = it.next(); //e=hello,world,java sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e); if (! it.hasNext()) //[hello, world, java] return sb.append(']').toString(); sb.append(',').append(' '); } }
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/yft-javaNotes/p/10854404.html
最后
以上就是安详白羊最近收集整理的关于JavaSE学习笔记(十五)—— 集合概述及Collection接口一、集合概述二、Collection的基本功能三、Collection集合的遍历四、集合的toString()方法源码解析的全部内容,更多相关JavaSE学习笔记(十五)——内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
![[JavaSE进阶笔记]day07 set集合,泛型](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg8.png)







发表评论 取消回复