环境说明
代码示例的运行环境是 AS下的 Andorid JNI工程,方便MAC开发环境下,使得C++工程可以使用epoll,可以不用在MAC环境下搭linux开发环境。(PS: mac下采用kqueue机制,没有epoll)
代码示例
关键的代码,AS的JNI模板工程下的native-lib.cpp文件
代码功能简介:
一个写线程每隔3秒住管道写一个字符,另一个读线程通道监听epoll事件,从管道读一个字符。
管道的读取端注删事读事件到epoll实例中,当写线程住管道写数据后,读线程可以在事件拉取的循环周期中epoll_wait到可读事件,然后从管道中读出数据
#include <jni.h>
#include <string>
#include <thread>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <android/log.h>
using namespace std;
static char *TAG = "PIPE_AND_EPOLL";
static int MAX_EVENTS_SIZE = 1024;
void pipeAndEpoll() {
int pipeFd[2]; //pipeFd[0]是管道读取端,pipeFd[1]是管道写入端
int result = pipe(pipeFd);
if (result == -1) {
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_WARN, TAG, "pipe fail");
return;
}
int epollFd = epoll_create(1024);
if (epollFd == -1) {
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_WARN, TAG, "epoll_create fail");
return;
}
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.data.fd = pipeFd[0];
//水平触发方式,监听可读事件,即管道有数据可以读取了
ev.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;
//监听事件
result = epoll_ctl(epollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, pipeFd[0], &ev);
if (result == -1) {
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_WARN, TAG, "epoll_ctl fail");
return;
}
//写线程,每隔三秒住管道写一个字符
thread writeThread{[epollFd, pipeFd] {
char buffer[]{'A'};
while (true) {
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(3));
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO, TAG, "write:%d", buffer[0]);
write(pipeFd[1], buffer, 1);
}
}};
writeThread.detach();
//读线程,每隔1秒尝试去读一个字符
thread readThread{[epollFd, pipeFd] {
struct epoll_event events[MAX_EVENTS_SIZE];
char buffer[1];
while (true) {
//等待注册的事件发生,1秒内没有事件发生就返回,count为零
int count = epoll_wait(epollFd, events, MAX_EVENTS_SIZE, 1000);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if ((events[i].data.fd == pipeFd[0]) && (events[0].events & EPOLLIN)) {
read(pipeFd[0], buffer, 1);
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO, TAG, "read :%d", buffer[0]);
}
}
if (count == 0) {
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO, TAG, "No events yet");
}
}
}};
readThread.detach();
}
extern "C" JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_com_example_myapplication_MainActivity_stringFromJNI(
JNIEnv *env,
jobject /* this */) {
std::string hello = "Hello from C++";
pipeAndEpoll();
return env->NewStringUTF(hello.c_str());
}
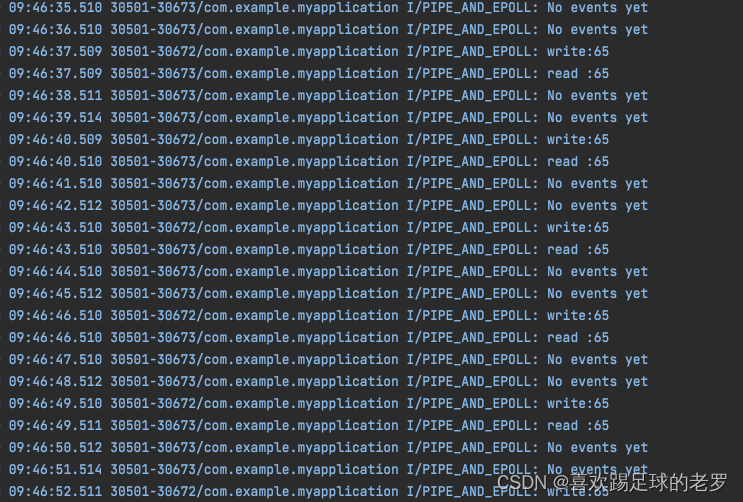
运行效果如下
总结
PIPE
// 1、创建管道实例,pipe[0]读取端,pipe[1]写入端
int pipeFd[2]; //pipeFd[0]是管道读取端,pipeFd[1]是管道写入端
int result = pipe(pipeFd);
// 2、调用write(pipe[1])写数据,read(pipe[0])读数据
write(pipeFd[1], buffer, 1);
read(pipeFd[0], buffer, 1);
// 3、pipe方法创建的是匿名管道
EPOLL
//1、创建epoll实例,epoll实例的文件句柄需要保存进来,注册事件与拉取事件方法需要传epoll实例
int epollFd = epoll_create(1024)
//2、注册某个fd的某些事件到epoll实例中
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.data.fd = pipeFd[0];
ev.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET; //水平触发方式,监听可读事件,即管道有数据可以读取了
result = epoll_ctl(epollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, pipeFd[0], &ev);
//3、拉取事件,
int count = epoll_wait(epollFd, events, MAX_EVENTS_SIZE, 1000);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if ((events[i].data.fd == pipeFd[0]) && (events[0].events & EPOLLIN)) {
read(pipeFd[0], buffer, 1);
}
}
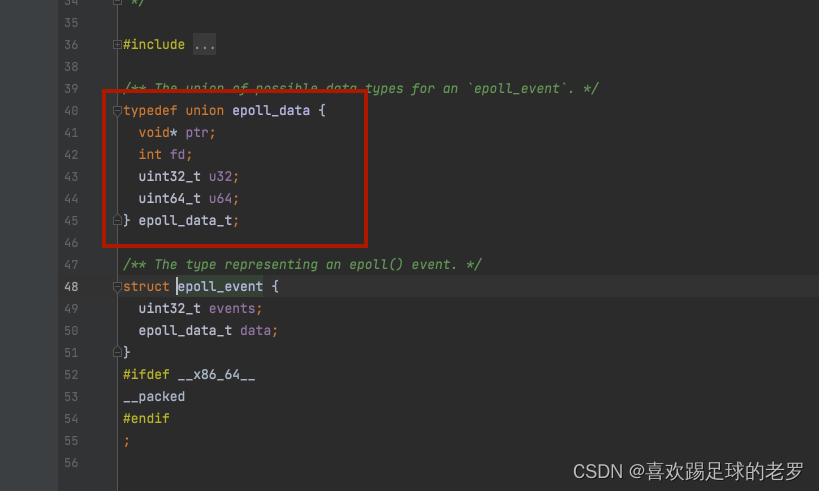
// epoll_event结构体有几个扩字段可以用来保存相关的上下文,事件触发时可以获取到相关的参数
头文件
PIPE
操作管道的pipe、write、read接口在 <unistd.h> 头文件,可以在这里查询这个API的具体内容

EPOLL
epoll相关的接口的头文件是<sys/epoll.h>, 接口使用文档在这里

参考文章
1、man7.org -查epoll_create这类系统接口的API文档
2、linux管道pipe详解
最后
以上就是爱撒娇裙子最近收集整理的关于【用示例学习与理解C++系列】pipe与epoll的使用环境说明代码示例总结头文件参考文章的全部内容,更多相关【用示例学习与理解C++系列】pipe与epoll内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复