文章目录
- 1. ContextLoaderListener
- 2. initWebApplicationContext
- 3. configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext
- 4. Servlet.init
SpringMVC 系列
请求debug
1. ContextLoaderListener
这里主要是为了搞清楚SpringMVC的IOC启动过程
ContextLoaderListener可以指定在Web应用程序启动时载入Ioc容器,正是通过ContextLoader来实现的,可以说是Ioc容器的初始化工作。
如果要使用ContextLoaderListener,请在web.xml中加入一下代码:
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
那么如果环境没问题,debug启动查看调用栈:
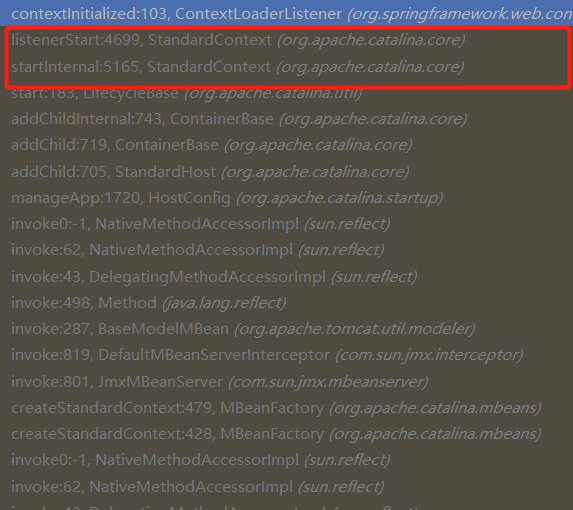
从调用栈可见,SpringMVC的ContextLoaderListener调用时机为Context启动时。
那么将监听器删除会怎么样?
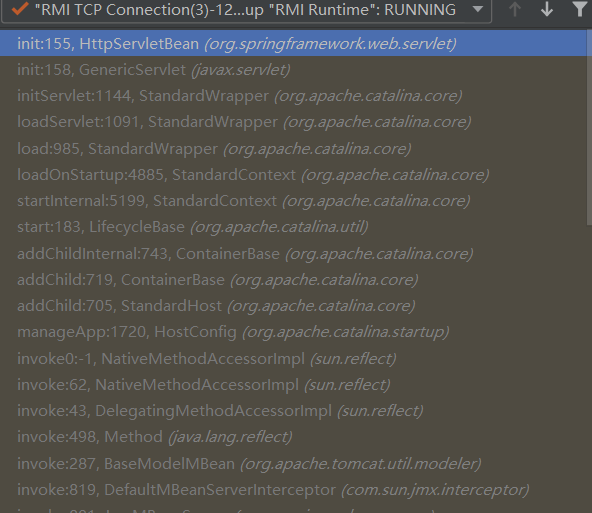
调用属于Wrapper的初始化方法。
其实结论就是:可以不配置ContextLoaderListener,其次,ContextLoaderListener可以去默认加载WEB/INFO下符合某些命名规则的配置文件。
假如配置了ContextLoaderListener,ContextLoaderListener会先一步创建IOC。
2. initWebApplicationContext
我们就来看看org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener#contextInitialized:
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader#initWebApplicationContext
/**
*为给定的servlet上下文初始化Spring的web应用程序上下文,
*使用在构建时提供的应用程序上下文,或创建一个新的上下文
*根据“{@link #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM contextClass}”和
* "{@link #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM contextConfigLocation}"
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the new WebApplicationContext
* @see #ContextLoader(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM
*/
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//在本地实例变量中存储上下文,以保证这一点
//它在ServletContext关闭时可用。
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
//上下文还没有刷新->提供诸如此类的服务
//设置父上下文,设置应用程序上下文id,等等
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
//上下文实例是在没有显式父元素>的情况下注入的
//确定根web应用程序上下文的父节点(如果有的话)。
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
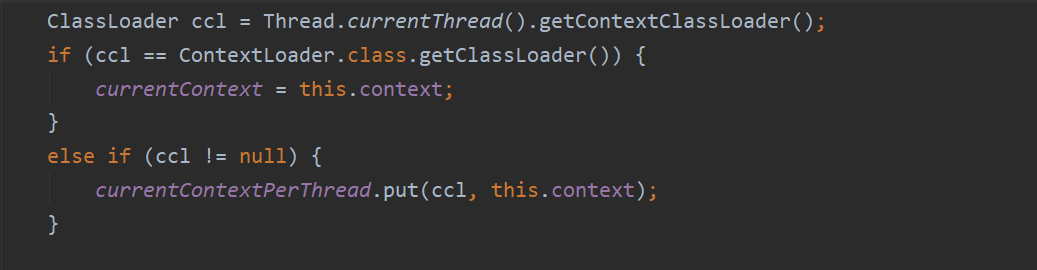
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
}
这个方法主要做了这些事:
- WebApplicationContext是否存在
在配置文件中只允许声明一次ServletContextListener,多次声明会扰乱Spring的执行逻辑。避免重复创建,检测Context是否存在有其必要性。
String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
至于为什么会从servletContext获取,因为,WebApplicationContext创建后会以k-v形式放入servletContext,便于全局获取。key为如上,应用名+.ROOT。
- 创建WebApplicationContext 实例
/**
*实例化这个加载器的根WebApplicationContext
*默认上下文类或自定义上下文类(如果指定)。
该实现期望自定义上下文来实现
* {@link ConfigurableWebApplicationContext}接口。
*可以在子类中被重写。
另外,{@link #customizeContext}在刷新之前被调用
*上下文,允许子类对上下文执行自定义修改。
* @param sc current servlet context
* @return the root WebApplicationContext
* @see ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
*/
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
/**
返回要使用的WebApplicationContext实现类
*默认的XmlWebApplicationContext或自定义上下文类,如果指定。
* @param 当前servlet上下文
* @return 要使用的WebApplicationContext实现类
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
*/
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}
其次还得注意一下,ContextLoader下的静态代码块:
static {
//从属性文件加载默认策略实现。
//这是目前严格内部的,不打算定制
//由应用程序开发人员。
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}

通过读取读取ContextLoader.properties文件的内的全限定类名,并反射创建一个WebApplicationContext实例。
- 将WebApplicationContext引用存入Context

4. 映射当前的类加载器与创建的实例到全局变量currentContextPerThread中
3. configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
wac.setServletContext(sc);
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// wac环境的#initPropertySources在任何情况下都会被调用
//刷新;是否在这里迫切地确保servlet属性源就绪
//在#refresh之前的任何后处理或初始化中使用
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
customizeContext(sc, wac);
wac.refresh();
}
刷新容器。
4. Servlet.init
再来看看之前的Tomcat调用容器的Wrapper的初始化方法。
org.springframework.web.servlet.HttpServletBean#init
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#initServletBean
/**
*覆盖{@link HttpServletBean}的方法,在任何bean属性之后调用
创建这个servlet的WebApplicationContext。
*/
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
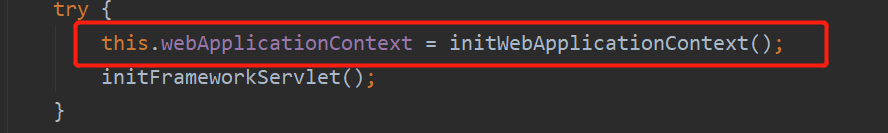
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
//留给子类实现
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
其主要工作委托给:
这个方法的主要功能就是创建或者刷新WebApplication实例,并对Servlet功能所使用的变量进行初始化。
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
//上下文还没有刷新->提供诸如此类的服务
//设置父上下文,设置应用程序上下文id,等等
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
//上下文实例被注入时没有设置显式父元素>
//根应用程序上下文(如果有的话);可能是空)作为父
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
//在构造时没有注入上下文实例->看看是否有
//已在servlet上下文中注册。如果存在,它是假设的
//父上下文(如果有的话)已经设置,并且
//用户已经执行了任何初始化,比如设置上下文id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
//这个servlet没有定义上下文实例->创建一个本地实例
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
//上下文不是带有refresh的ConfigurableApplicationContext
//在构建时注入的支持或上下文已经存在
//刷新->在这里手动触发初始onRefresh。
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
//将上下文作为servlet上下文属性发布。
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
那么接下来就会重点讲刷新:
onRefresh交由最终子类DispatcherServlet实现:
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#onRefresh
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
初始化servlet使用的策略对象。
为了进一步初始化策略对象,>可能会在子类中被重写。
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
这些就是SpringMVC源码部分的内容了,感兴趣的可以去深究。
最后
以上就是个性睫毛最近收集整理的关于java源码 - Spring5.x(7)之 SpringMVC的全部内容,更多相关java源码内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复