#define module_param(name, type, perm)
module_param_named(name, name, type, perm)
最后的 module_param 字段是一个权限值,,表示此参数在sysfs文件系统中所对应的文件节点的属性。你应当使用 <linux/stat.h> 中定义的值. 这个值控制谁可以存取这些模块参数在 sysfs 中的表示.当perm为0时,表示此参数不存在 sysfs文件系统下对应的文件节点。 否则, 模块被加载后,在/sys/module/ 目录下将出现以此模块名命名的目录, 带有给定的权限.。
权限在include/linux/stat.h中有定义
比如:
#define S_IRWXU 00700
#define S_IRUSR 00400
#define S_IWUSR 00200
#define S_IXUSR 00100
#define S_IRWXG 00070
#define S_IRGRP 00040
#define S_IWGRP 00020
#define S_IXGRP 00010
#define S_IRWXO 00007
#define S_IROTH 00004
#define S_IWOTH 00002
#define S_IXOTH 00001
使用 S_IRUGO 作为参数可以被所有人读取, 但是不能改变; S_IRUGO|S_IWUSR 允许 root 来改变参数. 注意, 如果一个参数被 sysfs 修改, 你的模块看到的参数值也改变了, 但是你的模块没有任何其他的通知. 你应当不要使模块参数可写, 除非你准备好检测这个改变并且因而作出反应.
#include <linux/kernel.h>#include <linux/module.h>#include <linux/init.h>#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
static int test;module_param(test, int, 0644);
static int __init hello_init(void){printk(KERN_INFO"Hello welcome! test = %d n", test);return 0;}
static void __exit hello_exit(void){printk(KERN_INFO"Goodbey !n");}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Test");MODULE_AUTHOR("Mchgloak");
module_init(hello_init);module_exit(hello_exit);
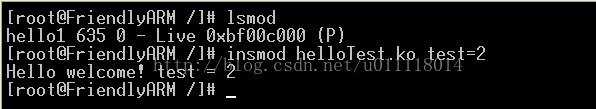
最后
以上就是高大悟空最近收集整理的关于Linux内核编程(二) —— 接受参数的模块的全部内容,更多相关Linux内核编程(二)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复