实现功能:检测出串行输入数据4位Data二进制序列0101,当检测到该序列的时候,out=1,否则out=0
(1)给出状态编码,画出状态图
(2)门电路实现
(3)verilog实现
首先规定Q3Q2Q1为刚输入的三位数,接下来要输入的数是A,Z为输入A以后的状态机的输出结果,则可以画出状态转换图如下:

然后根据状态图,我们可以得到状态表:

从而推导出激励方程,根据卡诺图化简得到序列检测的门级检测电路如下:

(3)根据状态图写出verilog代码:
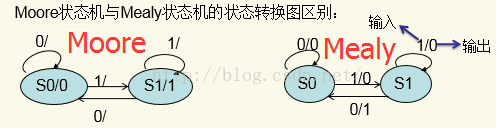
mealy型状态机的输出与其输入以及当前状态有关:
module xuliejiance(input clk,rst,q output out); reg [2:0]state,nexts; parameter s1=3'd0, s2=3'd1,s3=3'd2,s4=3'd3,s5=3'd4, s6=3'd5,s7=3'd6,s8=3'd7; always@(posedge clk ir negedge rst) begin if(~rst) state<=3'd0; else state<=nextstate; end always@(q,state) case(state) 0:if(q==1) nextstate=3'd1; else nextstate=3'd0; 1:if(q==1) nextstate=3'd3; else nextstate=3'd2; 2:if(q==1) nextstate=3'd5; else nextstate=3'd4; 3:if(q==1) nextstate=3'd5; else nextstate=3'd6; 4:if(q==1) nextstate=3'd0; else nextstate=3'd1; 5:if(q==1) nextstate=3'd0; else nextstate=3'd3; 6:if(q==1) nextstate=3'd0; else nextstate=3'd4; 7:if(q==1) nextstate=3'd7; else nextstate=3'd6; default: nextstate<=3'd0; endcase assign out=(state==3'd2)&&(x==0); endmodule
moore型状态机的输出只与其当前状态有关:
module xuliejiance( input clk,rst,q, output out); reg [2:0] state,nextstate; parameter s0=3'd0,s1=3'd1,s2=3'd2,s3=3'd3,s4=3'd4; always @(posedge clk or negedge rst) begin if(~rst) state<=3'd0; else state<=nextstate; end always@(*) begin case(state) s0: begin if(q==0) nextstate=s1; else nextstate=s0; end s1: begin if(q==1) nextstate=s2; else nextstate=s0; end s2: begin if(q==1) nextstate=s2; else nextstate=s3; end s3: begin if(q==1) nextstate=s4; else nextstate=s0; end s4: begin if(q==1) nextstate=s0; else nextstate=s1; end end assign out=(state==s4)?1:0; endmodule
以上写的都是两段式的状态机的实现,此外我们可以用更加正式的三段式的状态机实现
以下是一个可以用与参考的状态机的东西:
我们以1101序列检测器为例:
1101序列检测器Mealy状态机状态转移图

1101序列检测器Moore状态机状态转移图

我们以Mealy状态机为例
一段式状态机(部分核心代码):

两段式状态机(部分核心代码):

三段式状态机(部分核心代码):

转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/Dinging006/p/9539194.html
最后
以上就是自由大白最近收集整理的关于FPGA 状态机-序列检测器verilog的全部内容,更多相关FPGA内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复