1. 使用线程池好处
每次都new Thread的弊端如下:
每次new Thread新建对象性能差。
线程缺乏统一管理,可能无限制新建线程,相互之间竞争,及可能占用过多系统资源导致死机或oom。
缺乏更多功能,如定时执行、定期执行、线程中断。
线程池的好处在于:
重用存在的线程,减少对象创建、消亡的开销,性能佳。
可有效控制最大并发线程数,提高系统资源的使用率,同时避免过多资源竞争,避免堵塞。
提供定时执行、定期执行、单线程、并发数控制等功能。
2. 概述
Java里面线程池的顶级接口是Executor,但是严格意义上讲Executor并不是一个线程池,而只是一个执行线程的工具。真正的线程池接口是ExecutorService和ScheduledExecutorService,实现为ThreadPoolExecutor和ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor。
3. ThreadPoolExecutor
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {}- corePoolSize
线程池的核心线程数。在没有设置allowCoreThreadTimeOut为true的情况下,核心线程会在线程池中一直存活,即使处于闲置状态。 - maximumPoolSize
线程池允许创建的最大线程数。如果队列满了,并且已创建的线程数小于最大线程数,则线程池会再创建新的线程执行任务。值得注意的是如果使用了无界的任务队列这个参数就没什么效果。
- 如果运行的线程少于 corePoolSize,则 Executor始终首选添加新的线程,而不进行排队。(如果当前运行的线程小于corePoolSize,则任务根本不会存放,添加到queue中,而是直接抄家伙(thread)开始运行)
- 如果运行的线程等于或多于 corePoolSize,则 Executor始终首选将请求加入队列,而不添加新的线程。
- 如果无法将请求加入队列,则创建新的线程,除非创建此线程超出 maximumPoolSize,在这种情况下,任务将被拒绝。
- keepAliveTime
非核心线程闲置时的超时时长。超过该时长,非核心线程就会被回收。若allowCoreThreadTimeOut属性为true时,该时长同样会作用于核心线程。 - unit
keepAliveTime的时间单位。 - workQueue
线程池中的任务队列,通过线程池的execute()方法提交的Runnable对象会存储在该队列中。 可选子类:
- threadFactory
线程工厂,为线程池提供创建新线程的功能。ThreadFactory是一个接口。Executors中提供了DefaultThreadFactory。 - RejectedExecutionHandler
the handler to use when execution is blocked because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached。当任务无法被执行时(超过线程最大容量maximum并且queue已经被排满了)的处理策略。默认为AbortPolicy,直接抛出异常。当队列和线程池都满了,说明线程池处于饱和状态,那么必须采取一种策略处理提交的新任务。

4. ThreadPoolExecutor执行规则
- 先判断线程数量是否达到核心线程数。如果没有直接启动一个核心线程来执行任务。否则执行2.
- 判断任务队列是否已满。如果没满则插入到任务队列等待。否则执行3.
- 判断线程数量是否达到最大线程数maxiumPoolSize。如果没有则直接开启非核心线程执行任务。否则执行4.
- 拒绝执行此任务,调用handler.rejectedExecution来进行处理。
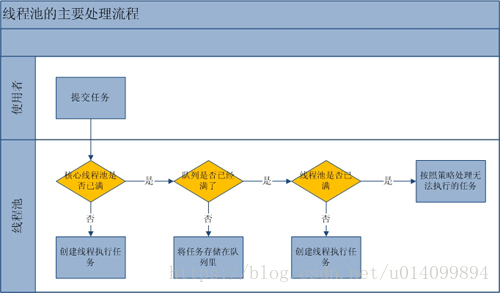
5. 示例:
public static Executor createExecutor(int threadPoolSize, int threadPriority) {
BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>();
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(threadPoolSize, threadPoolSize, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, taskQueue,
createThreadFactory(threadPriority, "pool-"));
}
private static ThreadFactory createThreadFactory(int threadPriority, String threadNamePrefix) {
return new DefaultThreadFactory(threadPriority, threadNamePrefix);
}
//代码来自UniversalImageLoader。支持设置线程优先级。
private static class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
private final int threadPriority;
DefaultThreadFactory(int threadPriority, String threadNamePrefix) {
this.threadPriority = threadPriority;
group = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
namePrefix = threadNamePrefix + poolNumber.getAndIncrement() + "-thread-";
}
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r, namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(), 0);//重命名线程,方便排查问题。
if (t.isDaemon()) t.setDaemon(false);
t.setPriority(threadPriority);//设置线程优先级
return t;
}
}6. Executors提供的线程池
- FixedThreadPool
线程数量固定的线程池,无限的任务队列,只有核心线程。最多只有nThreads个任务在并行处理,之后都在排队等待。
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}- CachedThreadPool
适合执行大量耗时较少的任务。没有核心线程,即没有任务时,它几乎不占用任何系统资源。These pools will typically improve the performance of programs that execute many short-lived asynchronous tasks.
SynchronousQueue不缓存任何一个任务,当即执行。
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}- ScheduledThreadPool
Creates a thread pool that can schedule commands to run after a given delay, or to execute periodically.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor源码解析
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
10L, MILLISECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}- SingleThreadExecutor
确保所有的任务都在一个线程中按顺序执行,使得这些任务之间不需要处理线程同步问题。Creates an Executor that uses a single worker thread operating off an unbounded queue.
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}7. 实用中
- Android中,可以根据需要自己创建线程池。frameWork提供的AsyncTask确实不好用。
- 设置线程的优先级
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority (int priority)
priority:【-20, 19】,高优先级 -> 低优先级.
THREAD_PRIORITY_DEFAULT,默认的线程优先级,值为0
THREAD_PRIORITY_LOWEST,最低的线程级别,值为19
THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND 后台线程建议设置这个优先级,值为10
THREAD_PRIORITY_MORE_FAVORABLE 相对THREAD_PRIORITY_DEFAULT稍微优先,值为-1
THREAD_PRIORITY_LESS_FAVORABLE 相对THREAD_PRIORITY_DEFAULT稍微落后一些,值为1
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//A Linux priority level, from -20 for highest scheduling priority to 19 for lowest scheduling priority.-20最高,19最低
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
}
};也可以使用PriorityBlockingQueue来实现调度任务优先级。
参考:
聊聊并发,JAVA线程池的分析和使用
Java自带线程池和队列详解
Trinea的介绍new Thread的弊端及Java四种线程池的使用
使用线程池处理异步任务
最后
以上就是含糊大炮最近收集整理的关于多线程 线程池ThreadPoolExecutor介绍的全部内容,更多相关多线程内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。






![[线程]glib库线程池代码分析](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg8.png)

发表评论 取消回复