今天写的代码在用到vector的迭代器的时候出现了错误,后面写了一个测试的code并查阅了相关资料,找到了问题。测试的code是这样的:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> int_array;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
int_array.push_back(i);
}
for (auto it = int_array.begin(); it != int_array.end(); it++) {
cout << (*it) << 't';
}
cout << endl;
for (auto it = int_array.begin(); it != int_array.end(); it++) {
if(*it%4==0)
int_array.erase(it);
}
for (auto it = int_array.begin(); it != int_array.end(); it++) {
cout << (*it) << 't';
}
cout << endl;
cin.get();
return 0;
}
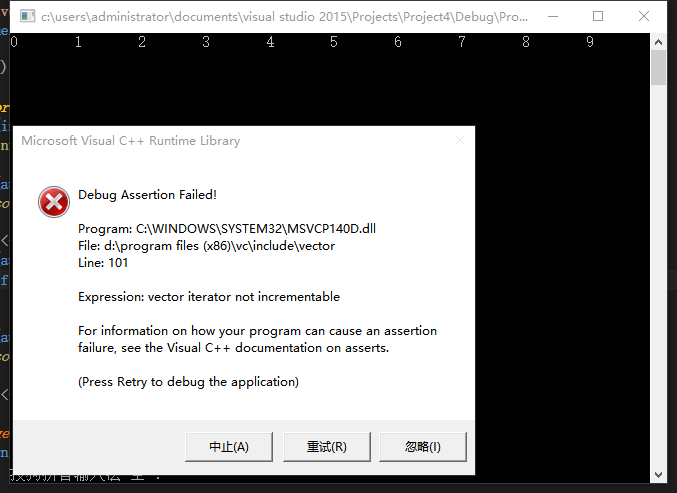
错误显而易见,vector迭代器不是可递增的,为什么呢?
因为vector是序列式容器,顺序容器内存是连续分配,删除一个元素会导致后面所有的元素会向前移动一个位置。所以删除序列式容器当前的iterator会使后面所有元素的iterator都失效。不过我们可以这样做来解决:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> int_array;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
int_array.push_back(i);
}
for (auto it = int_array.begin(); it != int_array.end(); it++) {
cout << (*it) << 't';
}
cout << endl;
for (auto it = int_array.begin(); it != int_array.end(); ) {
if (*it % 4 == 0) {
it=int_array.erase(it);
}
else {
it++;
}
}
for (auto it = int_array.begin(); it != int_array.end(); it++) {
cout << (*it) << 't';
}
cout << endl;
cin.get();
return 0;
}
因为erase方法可以返回下一个有效的iterator,所以当删除的时候,避免递增,而是把erase的返回值赋予iterator,这样就可以了。
而这样的错误与解决方法对map这些关联式的容器也是成立的,因为map的实现是靠RB-Tree,当删除是,需要调整树的结构来符合定义,所以迭代器也会失效啦。
最后
以上就是清秀白云最近收集整理的关于STL iterator失效的全部内容,更多相关STL内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复