MySQL最全知识点总结
- 1. 为什么要使用数据库
- 2. 什么是数据库
- 3. 数据库管理系统
- 4. MySQL
- 4.1 MySQL历史简介
- 4.2 MySQL获取和安装
- 5. SQL
- 5.1 SQL语句概述
- 5.2 MySQL基本操作
- 6. MySQL开发工具使用
- 7. 查询语句【重点】DQL
- 7.1 基本格式
- 7.1.1 基本查询,字段表名
- 7.1.2 查询结果字段进行数据计算
- 7.1.3 去重查询 distinct
- 7.1.4 字段别名
- 7.2 排序查询 order by
- 7.2.1 单一条件排序
- 7.2.2 多字段条件排序
- 7.3 条件查询 where
- 7.3.1 基本格式
- 7.3.2 等值判断 =
- 7.3.3 不等值判定(> < >= <= != <>)
- 7.3.4 逻辑判断(and, or, not)
- 7.3.5 区间 between and
- 7.3.6 NULL值判断
- 7.3.7 枚举查询 in
- 7.3.8 模糊查询 like
- 7.3.9 分支结构查询
- 7.4 时间查询
- 7.5 字符串应用
- 7.6 内置方法
- 7.7 分组查询
- 7.8 分组过滤查询
- 7.9 限定查询
- 7.10 基本查询总结
- 7.11 子查询[重点,难点]
- 7.11.1 基本格式
- 7.11.2 子查询结果作为条件判断约束
- 7.11.3 子查询结果作为枚举限制 in
- 7.11.3 子查询结果作为一张表,从表内查询指定数据
- 7.11 合并查询[仅了解]
- 7.12 表连接查询【重点】
- 7.12.1 基本格式
- 7.12.2 笛卡尔乘积【避免】
- 7.12.3 内连接查询 inner join on 两张表
- 7.12.4 内连接查询 inner join on 四张表
- 7.12.5 内连接查询 inner join on 五张表
- 7.12.6 左外连接 left join on
- 7.12.7 右外连接 right join on
- 8. DML语句
- 8.1 增加 insert
- 8.2 修改 update 【慎用】
- 8.3 删除 delete【慎用】
- 8.4 truncate 清空整表数据
- 9. 库表操作
- 9.1 创建数据库
- 9.2 删除数据库
- 9.3 修改数据库
- 9.4 数据类型
- 9.4.1 数值类型
- 9.4.2 日期类型
- 9.4.3 字符串类型
- 9.5 创建表
- 10. 数据约束
- 10.1 默认值 default
- 10.2 非空 not null
- 10.3 唯一 unique
- 10.4 主键 primary key
- 10.5 自增长 auto_increment
1. 为什么要使用数据库
Java程序在运行的过程中对于数据进行存储操作,变量,对象,数组,集合,双边队列...数据是保存到内存中,数据存储是瞬时的,程序退出,电脑异常。都会导致数据丢失并且不可逆。
文件存储数据,XML,JSON,其他文件。可操作性比较差,API繁琐,不同的文件有不同的解析方式,而且在内存占用和效率问题上很难达到两全程度。
存在的一些问题:
1. 文件保存的数据没有数据类型区分,都是字符串。
2. 数据存储量是较小的,有一定限制的。
3. 没有安全限制。
4. 文件操作没有备份,回滚,数据保护机制
2. 什么是数据库
数据库按照特定的数据结构,来进行数据的组织,存储,管理和查询,数据库软件。可以长期存储,有安全限制,数据恢复,并且数据存储可拓展
数据库分类:
网状结构数据库
层次结构数据库
关系结构数据库【重点】
Oracle,MySQL,DB2,SQL Server
通过表结构方式来进行数据的存储操作。--> XLS表格
非关系型数据库
MongDB Redis
使用哈希表结构方式,Key-Value数据存储方式
ES
ElastecSearch
3. 数据库管理系统
数据库管理系统
DataBase Management System
DBMS
操作和管理数据大型软件,用于管理,建立,使用和查询数据。
Oracle
贼牛皮,安全性,稳定性,数据存储复杂程度....可以完全符合工业要求
贵
DB2
IBM公司,不是很多见
SQL Server
MS公司推出的关系型数据库
SQLite
轻量级数据库,源码1W行C语言,手机通讯录
4. MySQL
4.1 MySQL历史简介
MySQL数据库默认编码集 Latin1 ==> 西欧
瑞典的一个公司开发的!! MySQL AB公司
MySQL支持插件!!!
社区
InnoDB跨时代的存储引擎
MySQL性能是非常不错的!!!
美国小鹰号航空母舰数据存储都是使用MySQL
MySQL 隶属于Oracle公司,免费提供使用的数据库软件。目前流行的版本是 MySQL 5.5 5.6 5.7,最新版本是8.0
实际开发中我们要考虑稳定性,兼容性,普适性
4.2 MySQL获取和安装
【详见】 Windows下安装MySQL5.7
5. SQL
5.1 SQL语句概述
SQL是数据库通用查询数据,不管是MySQL,Oracle,SQL Server都是支持标准SQL语句。不同数据库都会有自己特定的一些SQL语言。
SQL简单来分类
C Create
R Read
U Update
D Delete
5.2 MySQL基本操作
cmd > mysql -hlocalhost -uroot -p123456
# mysql指目前需要操作连接的数据库
# -hlocalhost -h host端口,当前数据库所处的服务器ip地址,域名或者主机名
# localhost 表示本地,如果是本地连接可以省略
# -uroot -u user用户 root表示用户
# -p -password 密码
# 推荐方式
cmd > mysql -uroot -p
Enter password: ******
-- 展示当前数据库中所有的数据表
mysql > show databases;
-- 创建数据库
-- CREATE DATABASE DBName;
mysql > create database nzgp2001;
-- 创建数据库过程修改编码集
mysql > create database nzgp2002 character set latin1;
mysql > create database nzgp2003 character set gbk;
-- 查看创建数据库的详细内容
mysql > show create database nzgp2001;
-- 修改数据库的编码集
mysql > alter database nzgp2002 character set gbk;
-- 删除对应数据库
mysql > drop database nzgp2002;
-- 选择使用数据库
mysql > use nzgp2001;
-- 让MySQL告知当前使用的数据库是哪一个
# 让MySQL告知当前使用的数据库是哪一个
mysql > select database();
6. MySQL开发工具使用
Navivcat for MySQL 非常不错
SQLyog 小海豚
MySQL WorkBench 免费,MySQL官网提供
IDEA Java IDE提供了数据库操作支持
7. 查询语句【重点】DQL
7.1 基本格式
select 查询内容 from 从哪里查;
-- 查询内容 字段名 列明
-- 从哪里查 表名
7.1.1 基本查询,字段表名
-- * 所有字段全部展示
-- 不建议,如果采用select * 方式整个数据库数据的时间非常长,浪费资源
select * from t_employees;
-- 查询指定的字段
select EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME from t_employees;
7.1.2 查询结果字段进行数据计算
-- 查询员工ID号,员工的名字(FristName LastName) 用户年限
select EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME, SALARY * 12
from t_employees;
-- 这里允许使用+ - * / 可以完成字段和字段直接的算术运算
-- %在SQL语句中不是取余,而是占位符!!
7.1.3 去重查询 distinct
-- 查询结果中存在相同内容,第二个数据不要
select distinct MANAGER_ID
from t_employees;
-- 不去重
select MANAGER_ID
from t_employees;
7.1.4 字段别名
-- 字段名 as '别名'
select EMPLOYEE_ID as 'ID', FIRST_NAME as '名', LAST_NAME as '姓', SALARY * 12 as '年薪'
from t_employees;
7.2 排序查询 order by
规则 效果
asc 指定条件升序
desc 指定条件降序
-- 基本格式
select fieldName from tbName order by fieldName asc/desc;
-- 在查询结果展示中,按照执行的字段作为标记完成升序和降序
7.2.1 单一条件排序
select EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, SALARY -- 查询展示的字段有哪些
from t_employees -- 从哪里查询
order by SALARY asc ; -- order by 指定字段要求排序 升序
select EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, SALARY -- 查询展示的字段有哪些
from t_employees -- 从哪里查询
order by SALARY desc ; -- order by 指定字段要求排序 降序
7.2.2 多字段条件排序
-- 第一条件是工资降序,当第一条件出现一致情况下,使用第二条件进行二次排序
select EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, SALARY -- 查询展示的字段有哪些
from t_employees -- 从哪里查询
order by SALARY desc, EMPLOYEE_ID desc; -- order by 指定字段要求排序 工资降序 ID降序
7.3 条件查询 where
7.3.1 基本格式
select fieldName from tbName where condition;
-- 从指定数据表中,按照where之后指定条件,查询对应的字段数据
-- where条件是一个是一个boolean类型结果
7.3.2 等值判断 =
-- Java等于判断是用的是 == 或者更严谨的情况,会使用 equals
-- 数据库中使用 = 在where条件之后是一个等值判断
-- 查询在员工表内容,工资等于11000 对应的id号,名,和工资
select EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, SALARY
from t_employees
where SALARY = 11000;
7.3.3 不等值判定(> < >= <= != <>)
-- 查询在员工表内容,工资大于10000 对应的id号,名,和工资
select EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, SALARY
from t_employees
where SALARY > 10000;
-- 查询在员工表内容,工资大于10000 对应的id号,名,和工资
select EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, SALARY
from t_employees
where SALARY >= 10000;
-- 查询在员工表内容,部门ID不等于80 对应的id号,名,工资和部门ID
select EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, SALARY, DEPARTMENT_ID
from t_employees
where DEPARTMENT_ID <> 80;
-- 查询在员工表内容,部门ID不等于80 对应的id号,名,工资和部门ID
select EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, SALARY, DEPARTMENT_ID
from t_employees
where DEPARTMENT_ID != 80;
7.3.4 逻辑判断(and, or, not)
-- 查询在员工表内容,要求工资大于10000并且部门编号为80 对应的ID号,名,工资和部门ID
select EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, SALARY, DEPARTMENT_ID
from t_employees
where SALARY > 10000 and DEPARTMENT_ID = 80;
-- 查询在员工表内容,要求工资小于2500或者部门编号为90 对应的ID号,名,工资和部门ID
select EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, SALARY, DEPARTMENT_ID
from t_employees
where SALARY < 2500 or DEPARTMENT_ID = 90;
7.3.5 区间 between and
-- 要求between min and max 在min <==> max范围以内,而且要求小值之前,大值不然会报
-- 错,这里区间范围是包含指定的边界
-- 区间范围
select EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, SALARY
from t_employees
where SALARY between 8000 and 10000;
7.3.6 NULL值判断
-- is null 指定当前的字段是null
-- is not null 指定当前字段不是null
-- 找出所有提成为null的数据
select FIRST_NAME, COMMISSION_PCT
from t_employees
where COMMISSION_PCT is null;
-- 找出所有提成不是null的数据
select FIRST_NAME, COMMISSION_PCT
from t_employees
where COMMISSION_PCT is not null;
7.3.7 枚举查询 in
-- 查询部门编号为60, 70, 90员工名字和对应部门编号
-- in查询效率较低,推荐使用多条件拼接完成查询操作
select FIRST_NAME, DEPARTMENT_ID
from t_employees
where DEPARTMENT_ID in(70, 60, 90);
7.3.8 模糊查询 like
-- LIKE
-- _ 匹配一个字符
-- % 匹配任意长度字符
-- 查询FIRST_NAME,要求FIRST_NAME字段D字母开头后面有4个字符
select FIRST_NAME
from t_employees
where FIRST_NAME like 'D____';
-- -- 查询FIRST_NAME,要求FIRST_NAME字段带有D字母就可以,而且不区分大小写
select FIRST_NAME
from t_employees
where FIRST_NAME like '%D%';
7.3.9 分支结构查询
case
when condition1 then ret1
when condition2 then ret2
when condition3 then ret3
end
-- 从case开始,到end结束。满足条件对应一个结果,类似于Java中的switch case
-- 查询姓名,工资已经对应工资划分的等级LEVEL
select FIRST_NAME, SALARY,
case
when SALARY >= 10000 then 'A'
when SALARY >= 8000 and SALARY < 10000 then 'B'
when SALARY >= 6000 and SALARY < 8000 then 'C'
when SALARY >= 4000 and SALARY < 6000 then 'D'
else 'E'
end as 'LEVEL'
from t_employees;
7.4 时间查询
-- 语法
select 时间函数([参数列表]);
-- 查询时间情况下,得到的是一个单列单表(虚表)
时间函数 功能描述
sysdate() 当前系统时间(年,月,日, 时,分,秒)
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() 当前系统时间(日,月,年,时,分,秒)
curdate() 当前日期
curtime() 当前时间
week() 指定日期是这一年的第几周
hour() 指定日期是今天第几个小时
minite() 指定日期是小时的第几分钟
second() 指定日期是分钟的第几秒
select sysdate();
select CURRENT_TIMESTAMP();
select curdate();
select curtime();
select week('2019-11-23');
select now();
select second(sysdate());
select minute(sysdate());
select hour(sysdate());
7.5 字符串应用
方法 功能描述
concat(str1, str2, str3...) 拼接多个字符串
insert(str, pos, len, newStr) 在指定字符串位置pos,长度限制len,插入新字符串
lower(str) 大写转小写
upper(str) 小写转大写
substring(str,pos, len) 指定字符串,从pos位置开始,长度限制len
select concat('你好', ' MySQL', ' Oracle公司产品');
select insert('ABCDEFG', 3, 3, '你好');
select upper('abcdefg');
select lower('ABCDEF');
select substring('ABCDEFG', 2, 5);
7.6 内置方法
方法 功能描述
sum() 指定字段一列总会
avg() 指定字段一列平均值
max() 指定字段一列中的最大值
min() 指定字段一列中的最小值
count() 指定字段有多少行
-- 工资总和
select sum(SALARY)
from t_employees;
-- 工资平均数
select avg(SALARY)
from t_employees;
-- 工资最大值
select max(SALARY)
from t_employees;
-- 工资最小值
select min(SALARY)
from t_employees;
-- 当前有多少员工计数
select count(*)
from t_employees;
-- 当前有多少员工计数
-- count(1) 蜜汁比count(*) 快一点
select count(1)
from t_employees;
-- 统计有多少人有绩效
select count(COMMISSION_PCT)
from t_employees;
7.7 分组查询
select fieldName
from tbName
where condition_
group by 分组要求;
-- group by是一个分组关键字
-- 查询各部门人数是多少
-- 1. 需要按照department_id进行分组
-- 2. 计数需要使用count, 根据用户的employee_id进行计数操作
select department_id, count(employee_id)
from t_employees
group by department_id;
-- 查询各部门的平均工资
-- 1. 需要按照department_id进行分组
-- 2. 平均工资使用avg方法计算
select department_id, avg(salary)
from t_employees
group by department_id;
-- 查询各部门,各岗位的人数
-- 1. 需要按照department_id进行分组
-- 2. 需要按照岗位job_id进行分组
-- 3. 记录人数,count(employee_id)
select department_id, job_id, count(employee_id)
from t_employees
group by department_id, job_id;
-- [42000][1055] Expression #1 of SELECT list is not in GROUP BY
-- clause and contains nonaggregated column 'company.t_employees.department_id'
-- which is not functionally dependent on columns in GROUP BY clause;
-- this is incompatible with sql_mode=only_full_group_by
-- 如果使用group by要求分组字段一定是查询要求字段,这里需要根据查询结果进行分组
select department_id
from t_employees
group by job_id;
7.8 分组过滤查询
select fieldName
from tbName
where condition_
group by 分组要求
having 过滤规则;
-- having是在 group by 之后的条件过滤
-- 查询指定100,50,30,80最高工资
-- 1. 需要按照department_id进行分组
-- 2. 最高工资
-- 3. 限制manager_id = 100
-- 4. 限制department_id号为100,50,30,80
select department_id, max(salary)
from t_employees
where manager_id = 100
group by department_id
having department_id in (100, 50, 30, 80);
7.9 限定查询
select fieldName
from tbName
limit 限制;
-- limit [offset_start], row_count
-- 查询员工表中前10个数据,员工first_name, employee_id
select employee_id, first_name
from t_employees
limit 10;
-- 查询员工表中10个数据,要求offset为3,员工first_name, employee_id
-- 起始行从0开始
select employee_id, first_name
from t_employees
limit 3,10;
-- 【重点】
-- limit核心用法,分页查询
-- pageCount 当前是第几页
-- itemCount 一页展示多少个元素
-- select * from tbName limit (pageCount - 1) * itemCount, itemCount;
-- 展示第一页10条数据
select employee_id, first_name
from t_employees
limit 0, 10;
-- 展示第二页10条数据
select employee_id, first_name
from t_employees
limit 10, 10;
-- 展示第三页10条数据
select employee_id, first_name
from t_employees
limit 20, 10;
7.10 基本查询总结
select fieldName
from tbName
where condition_
group by 分组
having 分组过滤
order by 排序 [asc/desc]
limit offset, count;
-- from 数据来源,从那张表中查询数据
-- group by 分组
-- having 分组之后条件约束
-- select 查询指定的字段
-- order by 排序要求
-- limit 限制结果行数
7.11 子查询[重点,难点]
7.11.1 基本格式
select fieldName
from tbName
where (子查询结果);
7.11.2 子查询结果作为条件判断约束
-- 查询工资高于Jack的员工id和姓名
-- 1. 找出Jack的工资
-- 2. 得到Jack工资,作为条件查询对应的员工信息
select salary
from t_employees
where first_name = 'Jack';
select employee_id, first_name
from t_employees
where salary > 8400;
-- 整合为子查询
-- 条件判断
select employee_id, first_name
from t_employees
where salary > (select salary
from t_employees
where first_name = 'Jack');
7.11.3 子查询结果作为枚举限制 in
-- 查询和Jack同部门的员工信息
-- 1. 找出Jack的部门编号
select department_id
from t_employees
where first_name = 'Jack';
-- 2. 根据Jack的部门编号,使用in枚举查询,限制条件
select employee_id, first_name
from t_employees
where department_id in (80);
-- 整合为子查询
select employee_id, first_name
from t_employees
where department_id in (select department_id
from t_employees
where first_name = 'Jack');
7.11.3 子查询结果作为一张表,从表内查询指定数据
-- 查询员工表中工资前五名的员工信息
-- 1. 找到员工的id,first_name,工资降序
select employee_id, first_name
from t_employees
order by salary desc;
select employee_id, first_name
from (select employee_id, first_name
from t_employees
order by salary desc) as temp
limit 5;
7.11 合并查询[仅了解]
union
-- 合并,要求查询要求的字段个数一致
-- 去重
select employee_id, first_name
from t_employees
union
select job_id, job_title
from t_jobs;
-- 合并,要求查询要求的字段个数一致
-- 不去重
select department_id, first_name
from t_employees
union all
select manager_id, department_name
from t_departments;
7.12 表连接查询【重点】
7.12.1 基本格式
select fieldName
from tbName1
连接符 tbName2
on 条件
7.12.2 笛卡尔乘积【避免】
-- 笛卡尔乘积,没有约束条件,数据库匹配发生相乘关系,结果也不是预期结果
-- 无意义结果
select employee_id, first_name
from t_employees
inner join t_jobs;
7.12.3 内连接查询 inner join on 两张表
-- 查询所有部门部门名,和对应的员工信息id和first_name
select t_departments.department_name,
t_employees.employee_id,
t_employees.first_name -- 查询内容
from t_employees -- 从员工表中查询
inner join t_departments -- 内连接部门表
on t_employees.department_id = t_departments.department_id;
-- 条件限制员工表中的部门Id = 部门表中的部门id
-- 查询所有部门部门名,和对应的员工信息id和first_name
-- 给予表格一个别名,方便使用
select d.department_name,
e.employee_id,
e.first_name -- 查询内容
from t_employees e-- 从员工表中查询
inner join t_departments d-- 内连接部门表
on e.department_id = d.department_id; -- 条件限制员工表中的部门Id = 部门表中的部门id
7.12.4 内连接查询 inner join on 四张表
-- 查询所有员工对应的ID号,名字,部门名称,和国家对应名字
select te.employee_id, te.first_name, td.department_name, tc.country_name
from t_employees te
inner join t_departments td on te.department_id = td.department_id
inner join t_locations tl on td.location_id = tl.location_id
inner join t_countries tc on tl.country_id = tc.country_id;
7.12.5 内连接查询 inner join on 五张表
-- 查询所有员工对应的ID号,名字,工作职称,部门名称,和国家对应名字
select te.employee_id, te.first_name, tj.job_title, td.department_name, tc.country_name
from t_employees te
inner join t_jobs tj on te.job_id = tj.job_id
inner join t_departments td on te.department_id = td.department_id
inner join t_locations tl on td.location_id = tl.location_id
inner join t_countries tc on tl.country_id = tc.country_id;
7.12.6 左外连接 left join on
-- 左外连接 左表是主表,要求左表完整显示,右表匹配左表数据,如果右表没有数据匹配,显示null
-- 查询所有的员工信息ID,first_ame,已经对应的部门名字
select te.employee_id, te.first_name, td.department_name
from t_employees te
left join t_departments td on te.department_id = td.department_id;
7.12.7 右外连接 right join on
-- 右外连接查询,右表是主表,要求右表完整展示,左表匹配右表数据,如果左表没有数据匹配,显示null
-- 查询所有部门对应员工信息,员工信息没有显示null
select td.department_name,te.employee_id, te.first_name
from t_employees te
right join t_departments td on te.department_id = td.department_id;
8. DML语句
8.1 增加 insert
create table person(
id int,
name varchar(30),
salary float(8, 2),
age int
);
-- 规矩插入
insert into person(id, name, salary, age) VALUE (1, '骚磊', 100.5, 16);
-- 省略所有的字段名,按照字段顺序添加
insert into person value (2, '茂林', 20.5, 50);
-- 指定字段数据插入
insert into person(name, age) value ('骚杰', 66);
-- 禁止字段数据类型和插入数据类型不一致!!!
insert into person(name, age) value ('66', '23333333');
insert into person(name, age) value ('66', '你在整一个试试???');
8.2 修改 update 【慎用】
-- Unsafe query: 'Update' statement without 'where' updates all table rows at once
-- 没有任何约束的情况下,当前指定数据表中的所有数据行全部执行修改操作
-- 一定要带有where条件约束
update person set id = 10;
-- OK
update person set id = 10 where name = '骚磊';
-- 可以同时修改多个数据,不同的字段赋值操作使用 逗号隔开
update person set id = 20, age = 10, salary = 200000.01 where name = '骚磊';
8.3 删除 delete【慎用】
-- Unsafe query: 'Delete' statement without 'where' clears all data in the table
delete from person;
-- 根据条件约束删除是允许的
delete from person where name = '66';
8.4 truncate 清空整表数据
-- 清空整表数据,并且会影响到一定数据约束,例如auto_increment 自增长
truncate table person;
9. 库表操作
9.1 创建数据库
-- dbName数据库的名字,可以约束编码集[是情况而定]
create database dbName [character set charset];
9.2 删除数据库
sql -- 删除指定数据库 drop database dbName;
9.3 修改数据库
-- 修改数据库编码集
alter database dbname character set utf8;
9.4 数据类型
9.4.1 数值类型
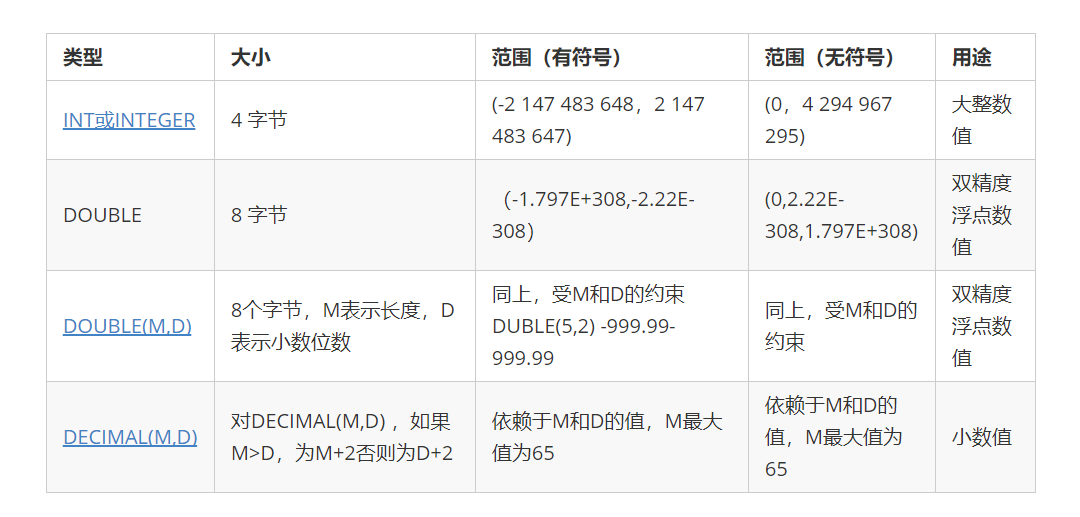
9.4.2 日期类型
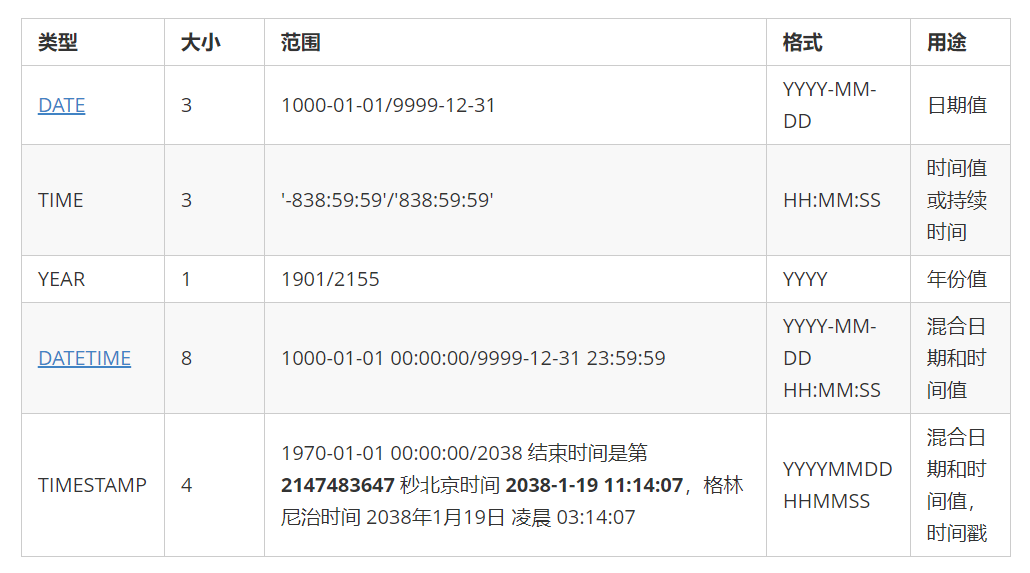
9.4.3 字符串类型
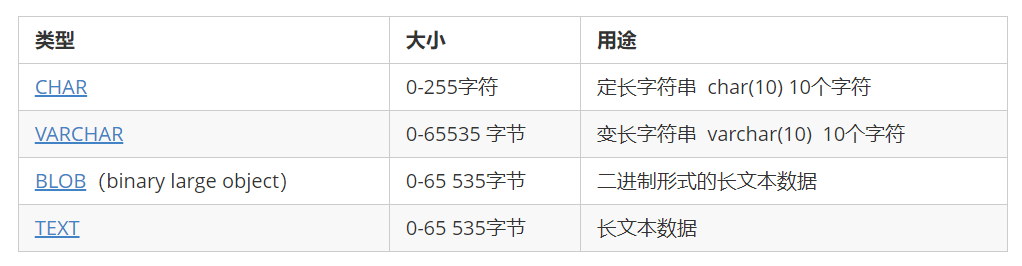
- CHAR和VARCHAR类型类似,但它们保存和检索的方式不同。它们的最大长度和是否尾部空格被保留等方面也不同。在存储或检索过程中不进行大小写转换。
- BINARY和VARBINARY类类似于CHAR和VARCHAR,不同的是它们包含二进制字符串而不要非二进制字符串。也就是说,它们包含字节字符串而不是字符字符串。这说明它们没有字符集,并且排序和比较基于列值字节的数值值。
- BLOB是一个二进制大对象,可以容纳可变数量的数据。有4种BLOB类型:TINYBLOB、BLOB、MEDIUMBLOB和LONGBLOB。它们只是可容纳值的最大长度不同。
- 有4种TEXT类型:TINYTEXT、TEXT、MEDIUMTEXT和LONGTEXT。
9.5 创建表
-- 1. 选择使用的数据库
create table tbName
(
fieldName1 fieldType1,
fieldName2 fieldType2,
fieldName3 fieldType3,
fieldName4 fieldType4
);
-- 可以加入约束,字符集和存储引擎
10. 数据约束
10.1 默认值 default
-- 创建数据表的过程中,指定字段可以带有默认值,如果用户没有指定数据的情况下,当前
-- 字段会采用默认值方式来进行数据赋值操作。
-- default
create table person1
(
id int,
name varchar(50),
country varchar(50) default 'PRC' -- 默认值字段
);
desc person1;
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| name | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| country | varchar(50) | YES | | PRC | |
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
-- 不给予带有默认值字段对应的数据,会采用默认值方式赋值当前子弹
insert into person1(id, name) value (1, '骚磊');
-- 给予当前带有默认值字段数据赋值操作,会采用给予的数据赋值当前字段
insert into person1(id, name, country) value (2, '航海中路彭于晏', '中华人民共和国');
10.2 非空 not null
-- not null 非空,要求当前字段必须有对应的数据,如果没有赋值报错
-- NN
-- 实际使用中必要字段!!!
create table person2
(
id int,
name varchar(50) not null,
country varchar(50) default 'PRC' -- 默认值字段
);
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| name | varchar(50) | NO | | NULL | |
| country | varchar(50) | YES | | PRC | |
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
insert into person2(id, name) VALUE (1, '46号技师');
-- ERROR Field 'name' doesn't have a default value
insert into person2(id) VALUE (2);
10.3 唯一 unique
-- 字段使用unique约束,当前字段中保存的数据在当前表内不可以重复
create table person3
(
id int unique,
name varchar(50) not null,
country varchar(50) default 'PRC' -- 默认值字段
);
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | YES | UNI | NULL | |
| name | varchar(50) | NO | | NULL | |
| country | varchar(50) | YES | | PRC | |
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
insert into person3(id, name) value (1, '哆啦A磊');
-- ERROR Duplicate entry '1' for key 'id'
-- 对应当前ID值已经存在,不能再次插入相同id数据
insert into person3(id, name) value (1, '老骚');
-- id使用unique限制唯一,但是null不作为唯一判断范围以内
insert into person3(name) value ('老骚');
insert into person3(name) value ('超超');
insert into person3(id, name) value (null, '贱贱的我就长大了');
insert into person3(id, name, country) value (null, '贱贱的我就长大了',null);
10.4 主键 primary key
-- 主要要求唯一,非空!!!
-- primary key 主键
-- 主键一般用于在开发中涉及到数据的唯一性参照物,但是不能使用带有业务逻辑要求数据作为
-- 主键,例如 性别 年龄 工资....
create table person4
(
id int primary key,
name varchar(50) not null,
country varchar(50) default 'PRC' -- 默认值字段
);
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | varchar(50) | NO | | NULL | |
| country | varchar(50) | YES | | PRC | |
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
insert into person4(id, name) value (1, '骚磊');
-- ERROR Duplicate entry '1' for key 'PRIMARY'
-- 对应使用primary key修饰的主键id已存在。
insert into person4(id, name) value (1, '骚磊');
-- ERROR Field 'id' doesn't have a default value
insert into person4(name) value ('骚磊');
-- ERROR Column 'id' cannot be null
insert into person4(id, name) value (null, '骚磊');
10.5 自增长 auto_increment
-- 自增长修饰字段会在数据添加的过程中自动赋值叠加操作
-- auto_increment修饰的字段必须是一个Key
-- AI ==> auto_increment
create table person5
(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(50) not null,
country varchar(50) default 'PRC' -- 默认值字段
);
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(50) | NO | | NULL | |
| country | varchar(50) | YES | | PRC | |
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
-- 自增长字段会从1开始
insert into person5(name) value ('郭德纲'); -- id = 1
insert into person5(name) value ('于谦'); -- id = 2
-- 自增长可以指定数值,而且存在影响自增长计数情况
insert into person5(id, name) value (5, '高峰'); -- id = 5
insert into person5(name) value ('栾云平'); -- id = 6
-- 自增长可以指定数值,而且存在影响自增长计数情况
insert into person5(id, name) value (8,'岳云鹏'); -- id = 8
insert into person5(name) value ('孙越'); -- id = 9
-- 指定id为7,但是当前id数据小于自增长,不影响自增长结果 数据保存排序
insert into person5(id, name) value (7, '郭麒麟'); -- id = 7
insert into person5(name) value ('阎鹤祥'); -- id = 10;
-- 删除数据
delete from person5 where id = 7;
delete from person5 where id = 10;
-- 被删除的id可以指定使用
insert into person5(id, name) value (7, '郭麒麟'); -- id = 7
-- delete删除不会印象自增长计数
insert into person5(name) value ('阎鹤祥'); -- id = 11
delete from person5 where id = 11;
-- 清空数据表,同时会重置自增长
truncate person5;
-- 数据库彻底关闭,会影响到自增长保存
作业
1. 大作业!!!
2. 复习整理项目
3. 复习反射和注解!!!
最后
以上就是美好发卡最近收集整理的关于【MySQL】MySQL最全知识点总结10. 数据约束的全部内容,更多相关【MySQL】MySQL最全知识点总结10.内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复