1.容器简介
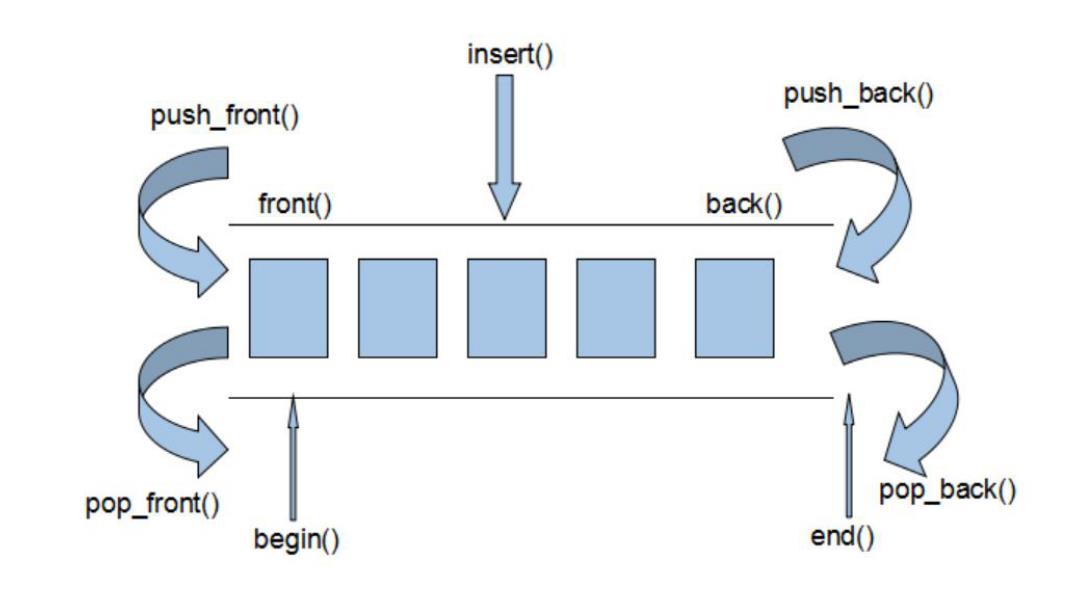
deque是一种具有队列和栈的性质的数据结构。双端队列中的元素可以从两端弹出,其限定插入和删除操作在表的两端进行。其操作示意图如下:
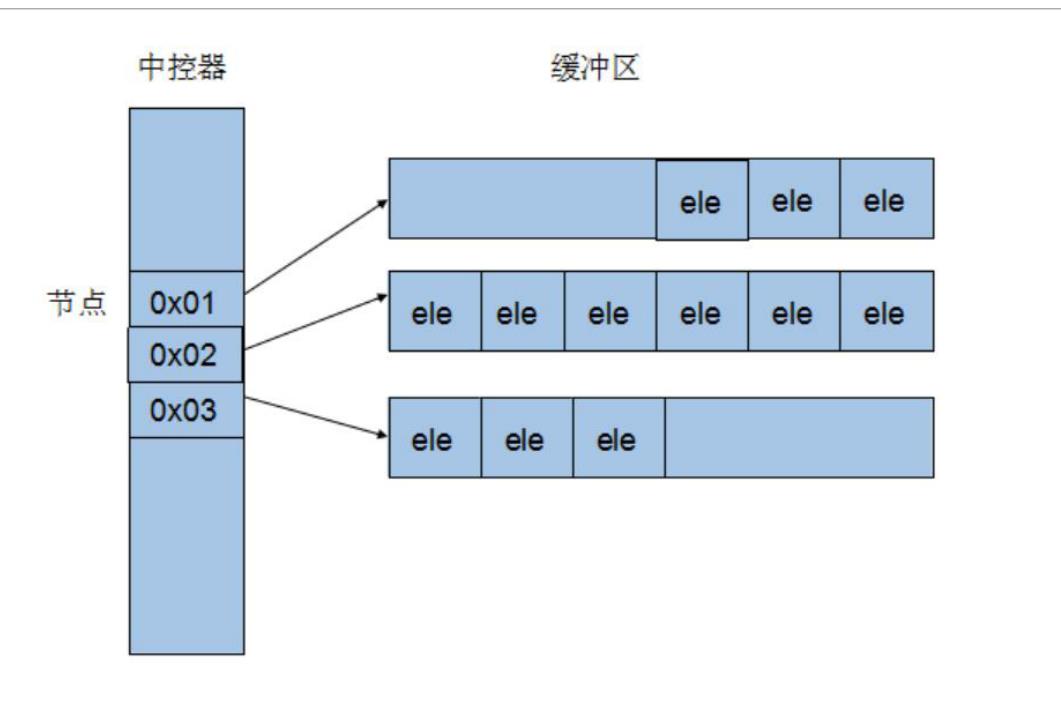
相比于vector,deque没有容量的概念,因为它是动态的以分段连续空间组合而成,随时可以增加一段新的空间并链接起来,换句话说,像 vector 那样,”旧空间不足而重新配置一块更大空间,然后复制元素,再释放旧空间”这样的事情在 deque 身上是不会发生的。deque在内存中是分段连续的,有中央控制,维持整体连续的假象。中控器中每一个节点都是一个指针,指向真正的缓存区。其内存结构如下图:
由于这种分段连续的内存分配方式,使用sort对其排序速度较慢。
2.构造函数
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
int main ()
{
unsigned int i;
// constructors used in the same order as described above:
std::deque<int> first; // empty deque of ints
std::deque<int> second (4,100); // four ints with value 100
std::deque<int> third (second.begin(),second.end()); // iterating through second
std::deque<int> fourth (third); // a copy of third
// the iterator constructor can be used to copy arrays:
int myints[] = {16,2,77,29};
std::deque<int> fifth (myints, myints + sizeof(myints) / sizeof(int) );
std::cout << "The contents of fifth are:";
for (std::deque<int>::iterator it = fifth.begin(); it!=fifth.end(); ++it)
std::cout << ' ' << *it;
std::cout << 'n';
return 0;
}运行结果:
The contents of fifth are: 16 2 77 29
3.成员函数
迭代器:
| begin() | 指向第一个元素位置 |
| end() | 指向最后一个元素后一个位置 |
| rbegin() | 指向第一个元素之前一个位置 |
| rend() | 指向最后一个元素位置 |
容量相关:
| size() | 返回容器大小 |
| max_size() | 返回容器最大容量 |
| empty() | 判断容器是否为空 |
| resize() | 改变容器大小 |
成员访问:
| 使用[ ]方式访问 |
| 使用.at()方式访问 |
| front() 返回第一个元素 |
| back() 返回最后一个元素 |
容器调整:
| assign | 重新给容器分配元素 |
| push_back | 向容器末尾插入元素 |
| push_front | 向元素开头插入元素 |
| pop_back | 删除末尾元素 |
| pop_front | 删除开头元素 |
| insert | 向指定位置插入元素,返回值为指向最后一个插入位置的迭代器 |
| erase | 删除元素 |
| swap | 交换两个容器 |
| clear | 清空容器 |
| emplace | 向指定位置插入元素,只能插入单个元素 |
| emplace_front | 在容器开头插入元素(效率比push_front高) |
| emplace_back | 在容器末尾插入元素 |
assign有三种分配方式:
范围:void assign (InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
值:void assign (size_type n, const value_type& val);
初始化的列表:void assign (initializer_list<value_type> il);
insert使用:
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
int main ()
{
std::deque<int> mydeque;
// set some initial values:
for (int i=1; i<6; i++) mydeque.push_back(i); // 1 2 3 4 5
std::deque<int>::iterator it = mydeque.begin();
++it;
it = mydeque.insert (it,10); // 1 10 2 3 4 5
// "it" now points to the newly inserted 10
mydeque.insert (it,2,20); // 1 20 20 10 2 3 4 5
// "it" no longer valid!
it = mydeque.begin()+2;
std::vector<int> myvector (2,30);
mydeque.insert (it,myvector.begin(),myvector.end());
// 1 20 30 30 20 10 2 3 4 5
std::cout << "mydeque contains:";
for (it=mydeque.begin(); it!=mydeque.end(); ++it)
std::cout << ' ' << *it;
std::cout << 'n';
return 0;
}运行结果:
mydeque contains: 1 20 30 30 20 10 2 3 4 5
4.其他函数
也可以使用STL的一些通用函数,比如
- swap(deque1,deque2)交换两个容器,
- 重载了==,!=,>,<,<=,>=比较运算符,
- sort(deque.begin(),deque().end())对其进行排序 ,
- 等
最后
以上就是愤怒小笼包最近收集整理的关于c++ deque(双端队列)使用指南的全部内容,更多相关c++内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复