引言
对IO进行最简单的读写操作,设备驱动都非常的简单。像I2C、SPI、LCD 等这些复杂外设的驱动就不能这么去写了,Linux 系统要考虑到驱动的可重用性,因此提出了驱动的分离与分层这样的软件思路,在这个思路下诞生了我们将来最常打交道的 platform 设备驱动,也叫做平台设备驱动。我们就来学习一下 Linux 下的驱动分离,以及 platform 框架下的设备驱动该如何编写。
一、Linux 驱动的分离
对于 Linux 这样一个成熟、庞大、复杂的操作系统,代码的重用性非常重要,否则的话就会在 Linux 内核中存在大量无意义的重复代码。尤其是驱动程序,因为驱动程序占用了 Linux 内核代码量的大头,如果不对驱动程序加以管理,任由重复的代码肆意增加,那么用不了多久 Linux 内核的文件数量就庞大到无法接受的地步。
比如 I2C、SPI 等等都会采用驱动分隔的方式来简化驱动的开发。在实际的驱动开发中,一般 I2C 主机控制器驱动已经由半导体厂家编写好了,而设备驱动一般也由设备器件的厂家编写好了,我们只需要提供设备信息即可,比如 I2C 设备的话提供设备连接到了哪个 I2C 接口上,I2C 的速度是多少等等。相当于将设备信息从设备驱动中剥离开来,驱动使用标准方法去获取到设备信息(比如从设备树中获取到设备信息),然后根据获取到的设备信息来初始化设备。
这样就相当于驱动只负责驱动,设备只负责设备,想办法将两者进行匹配即可。这个就是 Linux 中的总线(bus)、驱动(driver)和设备(device)模型,也就是常说的驱动分离。总线就是驱动和设备信息的月老,负责给两者牵线搭桥。
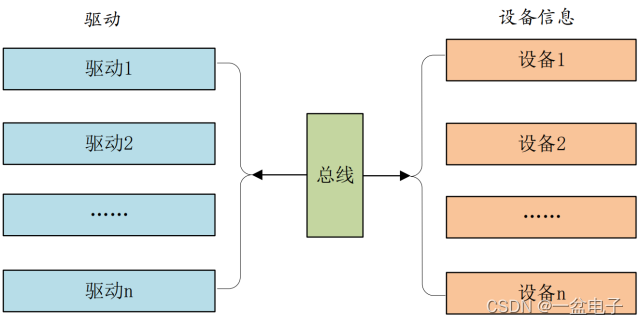
二、platform 平台驱动模型简介
1、platform 总线
Linux系统内核使用bus_type结构体表示总线,此结构体定义在文件include/linux/device.h,bus_type 结构体内容如下:
struct bus_type {
const char *name; /* 总线名字 */
const char *dev_name;
struct device *dev_root;
struct device_attribute *dev_attrs;
const struct attribute_group **bus_groups; /* 总线属性 */
const struct attribute_group **dev_groups; /* 设备属性 */
const struct attribute_group **drv_groups; /* 驱动属性 */
int (*match)(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv);
int (*uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);
int (*probe)(struct device *dev);
int (*remove)(struct device *dev);
void (*shutdown)(struct device *dev);
int (*online)(struct device *dev);
int (*offline)(struct device *dev);
int (*suspend)(struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct device *dev);
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
const struct iommu_ops *iommu_ops;
struct subsys_private *p;
struct lock_class_key lock_key;
};
match 函数,此函数是完成设备和驱动之间匹配的,总线就是使用 match 函数来根据注册的设备来查找对应的驱动,或者根据注册的驱动来查找相应的设备,因此每一条总线都必须实现此函数。
match 函数有两个参数:dev 和 drv,这两个参数分别为 device 和 device_driver 类型,也就是设备和驱动。
platform 总线是 bus_type 的一个具体实例,定义在文件 drivers/base/platform.c,platform 总线定义如下:
struct bus_type platform_bus_type = {
.name = "platform",
.dev_groups = platform_dev_groups,
.match = platform_match,
.uevent = platform_uevent,
.pm = &platform_dev_pm_ops,
};
platform_bus_type 就是 platform 平台总线,其中 platform_match 就是匹配函数。我们来看一下驱动和设备是如何匹配的,platform_match 函数定义在文件 drivers/base/platform.c 中,函数内容如下所示:
static int platform_match(struct device *dev,struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);
struct platform_driver *pdrv = to_platform_driver(drv);
/*When driver_override is set,only bind to the matching driver*/
if (pdev->driver_override)
return !strcmp(pdev->driver_override, drv->name);
/* Attempt an OF style match first */
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then try ACPI style match */
if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then try to match against the id table */
if (pdrv->id_table)
return platform_match_id(pdrv->id_table, pdev) != NULL;
/* fall-back to driver name match */
return (strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name) == 0);
}
驱动和设备的匹配有四种方法:
(1)OF 类型的匹配,也就是设备树采用的匹配方式,of_driver_match_device 函数定义在文件 include/linux/of_device.h 中。device_driver 结构体(表示设备驱动)中有个名为of_match_table的成员变量,此成员变量保存着驱动的compatible匹配表,设备树中的每个设备节点的 compatible 属性会和 of_match_table 表中的所有成员比较,查看是否有相同的条目,如果有的话就表示设备和此驱动匹配,设备和驱动匹配成功以后 probe 函数就会执行。
(2)ACPI匹配方式。
(3)id_table匹配,每个 platform_driver 结构体有一个 id_table 成员变量,顾名思义,保存了很多 id 信息。这些 id 信息存放着这个 platform 驱动所支持的驱动类型。通过查找id_table中name是否与设备名相同的项,如果存在的话,则匹配成功。
(4)id_table 不存在的话就直接比较驱动和设备的 name 字段,看看是不是相等,如果相等的话就匹配成功。
2、platform 驱动
platform_driver 结 构 体 表 示 platform 驱动,此结构体定义在文件include/linux/platform_device.h 中,内容如下:
struct platform_driver {
int (*probe)(struct platform_device *);
int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);
void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);
int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);
struct device_driver driver;
const struct platform_device_id *id_table;
bool prevent_deferred_probe;
};
probe 函数,当驱动与设备匹配成功以后 probe 函数就会执行,非常重要的函数!!一般驱动的提供者会编写,如果自己要编写一个全新的驱动,那么 probe 就需要自行实现。 driver 成员,为 device_driver 结构体变量,Linux 内核里面大量使用到了面向对象的思维,device_driver 相当于基类,提供了最基础的驱动框架。plaform_driver 继承了这个基类,然后在此基础上又添加了一些特有的成员变量。
id_table 是个表(也就是数组),每个元素的类型为 platform_device_id,platform_device_id 结构体内容如下:
struct platform_device_id {
char name[PLATFORM_NAME_SIZE];
kernel_ulong_t driver_data; //私有数据
};
device_driver 结构体定义在 include/linux/device.h,device_driver 结构体内容如下:
struct device_driver {
const char *name;
struct bus_type *bus;
struct module *owner;
const char *mod_name; /* used for built-in modules */
bool suppress_bind_attrs; /* disables bind/unbind via sysfs */
const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;
const struct acpi_device_id *acpi_match_table;
int (*probe) (struct device *dev);
int (*remove) (struct device *dev);
void (*shutdown) (struct device *dev);
int (*suspend) (struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume) (struct device *dev);
const struct attribute_group **groups;
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
struct driver_private *p;
};
of_match_table 就是采用设备树的时候驱动使用的匹配表,同样是数组,每个匹配项都为 of_device_id 结构体类型,此结构体定义在文件 include/linux/mod_devicetable.h 中,内 容如下:
struct of_device_id {
char name[32];
char type[32];
char compatible[128];
const void *data;
};
compatible 非常重要,因为对于设备树而言,就是通过设备节点的 compatible 属性值和 of_match_table 中每个项目的 compatible 成员变量进行比较,如果有相等的就表示设备和此驱动匹配成功。
在编写 platform 驱动的时候,首先定义一个 platform_driver 结构体变量,然后实现结构体中的各个成员变量,重点是实现匹配方法以及 probe 函数。当驱动和设备匹配成功以后 probe函数就会执行,具体的驱动程序在 probe 函数里面编写,比如字符设备驱动等等。
当我们定义并初始化好 platform_driver 结构体变量以后,需要在驱动入口函数里面调用platform_driver_register函数向Linux内核注册一个platform 驱动,platform_driver_register 函数原型如下所示:
int platform_driver_register (struct platform_driver *driver)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
driver:要注册的 platform 驱动。
返回值:负数,失败;0,成功。
还需要在驱动卸载函数中通过 platform_driver_unregister 函数卸载 platform 驱动,platform_driver_unregister 函数原型如下:
void platform_driver_unregister(struct platform_driver *drv)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
drv:要卸载的 platform 驱动。
返回值:无。
3、platform 设备
如果内核支持设备树的话就不要再使用 platform_device 来描述设备了,因为改用设备树去描述了。当然了,你如果一定要用 platform_device 来描述设备信息的话也是可以的。platform_device 结构体定义在文件include/linux/platform_device.h 中,结构体内容如下:
struct platform_device {
const char *name;
int id;
bool id_auto;
struct device dev;
u32 num_resources;
struct resource *resource;
const struct platform_device_id *id_entry;
char *driver_override; /* Driver name to force a match */
/* MFD cell pointer */
struct mfd_cell *mfd_cell;
/* arch specific additions */
struct pdev_archdata archdata;
};
name 表示设备名字,要和所使用的 platform 驱动的 name 字段相同,否则的话设
备就无法匹配到对应的驱动。
num_resources 表示资源数量,一般为第 28 行 resource 资源的大小。
resource 表示资源,也就是设备信息,比如外设寄存器等。Linux 内核使用 resource
结构体表示资源,resource 结构体内容如下:
struct resource {
resource_size_t start;
resource_size_t end;
const char *name;
unsigned long flags;
struct resource *parent, *sibling, *child;
};
start 和 end 分别表示资源的起始和终止信息,对于内存类的资源,就表示内存起始和终止地址,name 表示资源名字,flags 表示资源类型,可选的资源类型都定义在了文件include/linux/ioport.h 里面,如下所示:
#define IORESOURCE_BITS 0x000000ff /* Bus-specific bits */
#define IORESOURCE_TYPE_BITS 0x00001f00 /* Resource type */
#define IORESOURCE_IO 0x00000100 /* PCI/ISA I/O ports */
#define IORESOURCE_MEM 0x00000200
#define IORESOURCE_REG 0x00000300 /* Register offsets */
#define IORESOURCE_IRQ 0x00000400
#define IORESOURCE_DMA 0x00000800
#define IORESOURCE_BUS 0x00001000
......
/* PCI control bits. Shares IORESOURCE_BITS with above PCI ROM. */
#define IORESOURCE_PCI_FIXED (1<<4) /* Do not move resource */
在以前不支持设备树的Linux版本中,用户需要编写platform_device变量来描述设备信息,然后使用 platform_device_register 函数将设备信息注册到 Linux 内核中,此函数原型如下所示:
int platform_device_register(struct platform_device *pdev)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
pdev:要注册的 platform 设备。
返回值:负数,失败;0,成功。
如果不再使用 platform 的话可以通过 platform_device_unregister 函数注销掉相应的 platform设备,platform_device_unregister 函数原型如下:
void platform_device_unregister(struct platform_device *pdev)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
pdev:要注销的 platform 设备。
返回值:无。
三、程序编写
1、platform 设备与驱动程序编写
leddevice.c 和 leddriver.c 这两个文件,这两个文件分别为 LED灯的 platform 设备文件和 LED 灯的 platform 的驱动文件。在 leddevice.c 中输入如下所示内容:
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/ide.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/semaphore.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <asm/mach/map.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
/*
* 寄存器地址定义
*/
#define CCM_CCGR1_BASE (0X020C406C)
#define SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03_BASE (0X020E0068)
#define SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03_BASE (0X020E02F4)
#define GPIO1_DR_BASE (0X0209C000)
#define GPIO1_GDIR_BASE (0X0209C004)
#define REGISTER_LENGTH 4
/* @description : 释放flatform设备模块的时候此函数会执行
* @param - dev : 要释放的设备
* @return : 无
*/
static void led_release(struct device *dev)
{
printk("led device released!rn");
}
/*
* 设备资源信息,也就是LED0所使用的所有寄存器
*/
static struct resource led_resources[] = {
[0] = {
.start = CCM_CCGR1_BASE,
.end = (CCM_CCGR1_BASE + REGISTER_LENGTH - 1),
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
},
[1] = {
.start = SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03_BASE,
.end = (SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03_BASE + REGISTER_LENGTH - 1),
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
},
[2] = {
.start = SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03_BASE,
.end = (SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03_BASE + REGISTER_LENGTH - 1),
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
},
[3] = {
.start = GPIO1_DR_BASE,
.end = (GPIO1_DR_BASE + REGISTER_LENGTH - 1),
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
},
[4] = {
.start = GPIO1_GDIR_BASE,
.end = (GPIO1_GDIR_BASE + REGISTER_LENGTH - 1),
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
},
};
/*
* platform设备结构体
*/
static struct platform_device leddevice = {
.name = "imx6ul-led",
.id = -1,
.dev = {
.release = &led_release,
},
.num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(led_resources),
.resource = led_resources,
};
/*
* @description : 设备模块加载
* @param : 无
* @return : 无
*/
static int __init leddevice_init(void)
{
return platform_device_register(&leddevice);
}
/*
* @description : 设备模块注销
* @param : 无
* @return : 无
*/
static void __exit leddevice_exit(void)
{
platform_device_unregister(&leddevice);
}
module_init(leddevice_init);
module_exit(leddevice_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
leddevice.c 文件编写完成以后就编写 leddriver.c 这个 platform 驱动文件,在 leddriver.c 里面输入如下内容:
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/ide.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/semaphore.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <asm/mach/map.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#define LEDDEV_CNT 1 /* 设备号长度 */
#define LEDDEV_NAME "platled" /* 设备名字 */
#define LEDOFF 0
#define LEDON 1
/* 寄存器名 */
static void __iomem *IMX6U_CCM_CCGR1;
static void __iomem *SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03;
static void __iomem *SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03;
static void __iomem *GPIO1_DR;
static void __iomem *GPIO1_GDIR;
/* leddev设备结构体 */
struct leddev_dev{
dev_t devid; /* 设备号 */
struct cdev cdev; /* cdev */
struct class *class; /* 类 */
struct device *device; /* 设备 */
int major; /* 主设备号 */
};
struct leddev_dev leddev; /* led设备 */
/*
* @description : LED打开/关闭
* @param - sta : LEDON(0) 打开LED,LEDOFF(1) 关闭LED
* @return : 无
*/
void led0_switch(u8 sta)
{
u32 val = 0;
if(sta == LEDON){
val = readl(GPIO1_DR);
val &= ~(1 << 3);
writel(val, GPIO1_DR);
}else if(sta == LEDOFF){
val = readl(GPIO1_DR);
val|= (1 << 3);
writel(val, GPIO1_DR);
}
}
/*
* @description : 打开设备
* @param - inode : 传递给驱动的inode
* @param - filp : 设备文件,file结构体有个叫做private_data的成员变量
* 一般在open的时候将private_data指向设备结构体。
* @return : 0 成功;其他 失败
*/
static int led_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
filp->private_data = &leddev; /* 设置私有数据 */
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : 向设备写数据
* @param - filp : 设备文件,表示打开的文件描述符
* @param - buf : 要写给设备写入的数据
* @param - cnt : 要写入的数据长度
* @param - offt : 相对于文件首地址的偏移
* @return : 写入的字节数,如果为负值,表示写入失败
*/
static ssize_t led_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
{
int retvalue;
unsigned char databuf[1];
unsigned char ledstat;
retvalue = copy_from_user(databuf, buf, cnt);
if(retvalue < 0) {
return -EFAULT;
}
ledstat = databuf[0]; /* 获取状态值 */
if(ledstat == LEDON) {
led0_switch(LEDON); /* 打开LED灯 */
}else if(ledstat == LEDOFF) {
led0_switch(LEDOFF); /* 关闭LED灯 */
}
return 0;
}
/* 设备操作函数 */
static struct file_operations led_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = led_open,
.write = led_write,
};
/*
* @description : flatform驱动的probe函数,当驱动与
* 设备匹配以后此函数就会执行
* @param - dev : platform设备
* @return : 0,成功;其他负值,失败
*/
static int led_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{
int i = 0;
int ressize[5];
u32 val = 0;
struct resource *ledsource[5];
printk("led driver and device has matched!rn");
/* 1、获取资源 */
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
ledsource[i] = platform_get_resource(dev, IORESOURCE_MEM, i); /* 依次MEM类型资源 */
if (!ledsource[i]) {
dev_err(&dev->dev, "No MEM resource for always onn");
return -ENXIO;
}
ressize[i] = resource_size(ledsource[i]);
}
/* 2、初始化LED */
/* 寄存器地址映射 */
IMX6U_CCM_CCGR1 = ioremap(ledsource[0]->start, ressize[0]);
SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03 = ioremap(ledsource[1]->start, ressize[1]);
SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03 = ioremap(ledsource[2]->start, ressize[2]);
GPIO1_DR = ioremap(ledsource[3]->start, ressize[3]);
GPIO1_GDIR = ioremap(ledsource[4]->start, ressize[4]);
val = readl(IMX6U_CCM_CCGR1);
val &= ~(3 << 26); /* 清除以前的设置 */
val |= (3 << 26); /* 设置新值 */
writel(val, IMX6U_CCM_CCGR1);
/* 设置GPIO1_IO03复用功能,将其复用为GPIO1_IO03 */
writel(5, SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03);
writel(0x10B0, SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03);
/* 设置GPIO1_IO03为输出功能 */
val = readl(GPIO1_GDIR);
val &= ~(1 << 3); /* 清除以前的设置 */
val |= (1 << 3); /* 设置为输出 */
writel(val, GPIO1_GDIR);
/* 默认关闭LED1 */
val = readl(GPIO1_DR);
val |= (1 << 3) ;
writel(val, GPIO1_DR);
/* 注册字符设备驱动 */
/*1、创建设备号 */
if (leddev.major) { /* 定义了设备号 */
leddev.devid = MKDEV(leddev.major, 0);
register_chrdev_region(leddev.devid, LEDDEV_CNT, LEDDEV_NAME);
} else { /* 没有定义设备号 */
alloc_chrdev_region(&leddev.devid, 0, LEDDEV_CNT, LEDDEV_NAME); /* 申请设备号 */
leddev.major = MAJOR(leddev.devid); /* 获取分配号的主设备号 */
}
/* 2、初始化cdev */
leddev.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_init(&leddev.cdev, &led_fops);
/* 3、添加一个cdev */
cdev_add(&leddev.cdev, leddev.devid, LEDDEV_CNT);
/* 4、创建类 */
leddev.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, LEDDEV_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(leddev.class)) {
return PTR_ERR(leddev.class);
}
/* 5、创建设备 */
leddev.device = device_create(leddev.class, NULL, leddev.devid, NULL, LEDDEV_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(leddev.device)) {
return PTR_ERR(leddev.device);
}
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : platform驱动的remove函数,移除platform驱动的时候此函数会执行
* @param - dev : platform设备
* @return : 0,成功;其他负值,失败
*/
static int led_remove(struct platform_device *dev)
{
iounmap(IMX6U_CCM_CCGR1);
iounmap(SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03);
iounmap(SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03);
iounmap(GPIO1_DR);
iounmap(GPIO1_GDIR);
cdev_del(&leddev.cdev);/* 删除cdev */
unregister_chrdev_region(leddev.devid, LEDDEV_CNT); /* 注销设备号 */
device_destroy(leddev.class, leddev.devid);
class_destroy(leddev.class);
return 0;
}
/* platform驱动结构体 */
static struct platform_driver led_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "imx6ul-led", /* 驱动名字,用于和设备匹配 */
},
.probe = led_probe,
.remove = led_remove,
};
/*
* @description : 驱动模块加载函数
* @param : 无
* @return : 无
*/
static int __init leddriver_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&led_driver);
}
/*
* @description : 驱动模块卸载函数
* @param : 无
* @return : 无
*/
static void __exit leddriver_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&led_driver);
}
module_init(leddriver_init);
module_exit(leddriver_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
2、测试 APP 编写
#include "stdio.h"
#include "unistd.h"
#include "sys/types.h"
#include "sys/stat.h"
#include "fcntl.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "string.h"
#define LEDOFF 0
#define LEDON 1
/*
* @description : main主程序
* @param - argc : argv数组元素个数
* @param - argv : 具体参数
* @return : 0 成功;其他 失败
*/
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd, retvalue;
char *filename;
unsigned char databuf[2];
if(argc != 3){
printf("Error Usage!rn");
return -1;
}
filename = argv[1];
/* 打开led驱动 */
fd = open(filename, O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0){
printf("file %s open failed!rn", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
databuf[0] = atoi(argv[2]); /* 要执行的操作:打开或关闭 */
retvalue = write(fd, databuf, sizeof(databuf));
if(retvalue < 0){
printf("LED Control Failed!rn");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
retvalue = close(fd); /* 关闭文件 */
if(retvalue < 0){
printf("file %s close failed!rn", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
3、Makefile
KERNELDIR := /home/sh/Desktop/MUL/zimage
CURRENT_PATH := $(shell pwd)
obj-m := leddevice.o leddriver.o
ARCH=arm
CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf-
build: kernel_modules
kernel_modules:
$(MAKE) -j32 -C $(KERNELDIR) ARCH=$(ARCH) CROSS_COMPILE=$(CROSS_COMPILE) M=$(CURRENT_PATH) modules
clean:
$(MAKE) -j32 -C $(KERNELDIR) ARCH=$(ARCH) CROSS_COMPILE=$(CROSS_COMPILE) M=$(CURRENT_PATH) clean
三、运行测试
输入如下命令加载 leddevice.ko 和 leddriver.ko 驱动模块:
insmod leddevice.ko //加载驱动
insmod leddriver.ko //加载驱动
驱动模块和设备模块加载成功以后 platform 总线就会进行匹配,当驱动和设备匹配成功后,就会输出如下图所示一行语句:

在/sys/bus/platform/devices/和/sys/bus/platform/drivers/目录下,都存在一个名字“imx6ul-led”的文件,否则说明我们的设备模块加载失败。


驱动和设备匹配成功以后就可以测试 LED 灯驱动了,输入如下命令打开 LED 灯:
/ledApp /dev/platled 1 //打开 LED 灯
在输入如下命令关闭 LED 灯:
./ledApp /dev/platled 0 //关闭 LED 灯
观察一下 LED 灯能否打开和关闭,如果可以的话就说明驱动工作正常,如果要卸载驱动的话输入如下命令即可:
rmmod leddevice.ko
rmmod leddriver.ko
最后
以上就是鳗鱼花瓣最近收集整理的关于I.MX6ULL ARM驱动开发---platfrom设备驱动引言一、Linux 驱动的分离二、platform 平台驱动模型简介三、程序编写三、运行测试的全部内容,更多相关I.MX6ULL内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复