1、对于长时依赖问题
循环神经网络难以记忆长时间的信息。
LSTM长短时记忆网络能在一定程度上解决长时依赖问题。
2、输入门、遗忘门和输出门
输入门控制着网络的输入
遗忘门控制着记忆单元
输出门控制着网络的输出
遗忘门的作用就是决定以前的哪些记忆将被保留,哪些记忆将被遗忘,正是由于遗忘门的作用,LSTM有了长期记忆的功能。对于给定的功能,遗忘门能够自己学习保留多少以前的记忆。
3、遗忘门——记忆衰减系数
C_{t-1}作为上一步t-1时刻网络中的记忆单元,传入t时刻的网络之后,第一步就是决定他的遗忘程度,将t时刻前面的记忆状态乘上一个0~1的系数进行衰减,接着加上t时刻学到的记忆作为更新之后的记忆传出网络。
记忆衰减系数f_{t}计算过程如下:
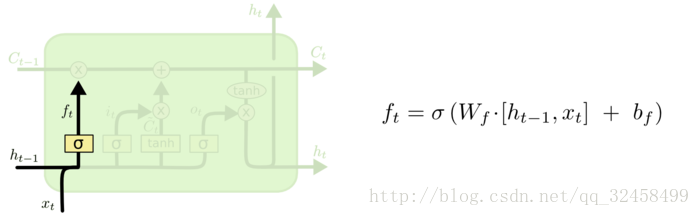
首先将t-1时刻的网络输出h_{t-1}和这一步的网络输入x_{t}结合起来,然后作用线性变换,最后再经过sigmoid激活函数,将结果映射到0~1作为记忆衰减系数。
**f_{t}为遗忘门
4、t时刻学到记忆的计算过程
当前时刻学到的记忆C~_[t}是通过当前输入和上一时刻输出的线性变换和tanh激活函数得到的。过程如下:
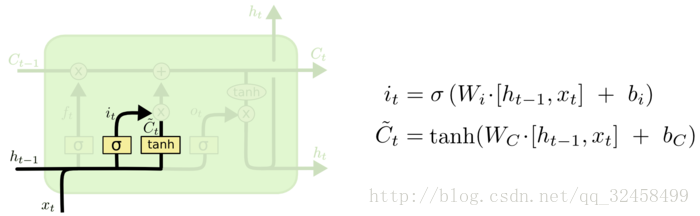
其中,对于该时刻学到的记忆也有一个衰减系数i_{t},这个系数跟上面方式相同,使用线性变换再使用sigmoid激活函数,将结果映射到0~1之间。
**i_{t}为输入门
5、当前时刻的记忆状态C_{t}的计算过程
最后将t-1时刻的衰减系数乘t-1时刻的记忆,加上该时刻t学到的记忆乘以它对应的衰减系数,便得到了当前t时刻的记忆状态。计算过程如下:
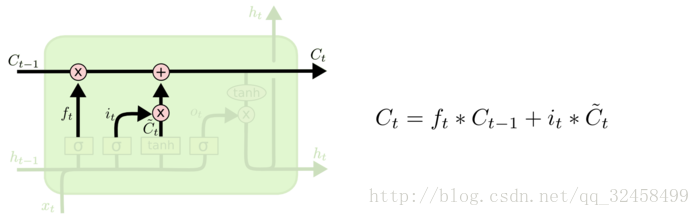
6、计算当前时刻的输出h_{t}
当前时刻t的网络输出h_{t}取决于当前时刻t的记忆状态和t时刻的输入、t-1时刻的输出,具体计算过程如下:
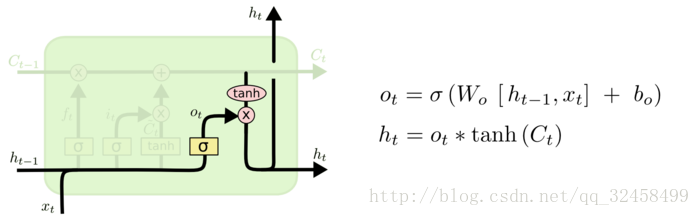
采用类似于计算记忆衰减系数的方法计算得到输出门的系数o_{t},这个系数决定了输出的多少。
**o_{t}为输出门
LSTM和传统循环神经网络最大的不同就是它使用了输入门、遗忘门和输出门来控制网络实现长时记忆的功能。
下面给出使用LSTM实现词性判断的pytorch代码:
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch import nn, optim
from torch.autograd import Variable
training_data = [("The dog ate the apple".split(),
["DET", "NN", "V", "DET", "NN"]),
("Everybody read that book".split(), ["NN", "V", "DET",
"NN"])]
word_to_idx = {}
tag_to_idx = {}
for context, tag in training_data:
for word in context:
if word not in word_to_idx:
word_to_idx[word] = len(word_to_idx)
for label in tag:
if label not in tag_to_idx:
tag_to_idx[label] = len(tag_to_idx)
alphabet = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
character_to_idx = {}
for i in range(len(alphabet)):
character_to_idx[alphabet[i]] = i
class CharLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_char, char_dim, char_hidden):
super(CharLSTM, self).__init__()
self.char_embedding = nn.Embedding(n_char, char_dim)
self.char_lstm = nn.LSTM(char_dim, char_hidden, batch_first=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.char_embedding(x)
_, h = self.char_lstm(x)
return h[0]
class LSTMTagger(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_word, n_char, char_dim, n_dim, char_hidden, n_hidden,
n_tag):
super(LSTMTagger, self).__init__()
self.word_embedding = nn.Embedding(n_word, n_dim)
self.char_lstm = CharLSTM(n_char, char_dim, char_hidden)
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(n_dim + char_hidden, n_hidden, batch_first=True)
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_tag)
def forward(self, x, word):
char = torch.FloatTensor()
for each in word:
char_list = []
for letter in each:
char_list.append(character_to_idx[letter.lower()])
char_list = torch.LongTensor(char_list)
char_list = char_list.unsqueeze(0)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
tempchar = self.char_lstm(Variable(char_list).cuda())
else:
tempchar = self.char_lstm(Variable(char_list))
tempchar = tempchar.squeeze(0)
char = torch.cat((char, tempchar.cpu().data), 0)
char = char.squeeze(1)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
char = char.cuda()
char = Variable(char)
x = self.word_embedding(x)
x = torch.cat((x, char), 1)
x = x.unsqueeze(0)
x, _ = self.lstm(x)
x = x.squeeze(0)
x = self.linear1(x)
y = F.log_softmax(x)
return y
model = LSTMTagger(
len(word_to_idx), len(character_to_idx), 10, 100, 50, 128, len(tag_to_idx))
if torch.cuda.is_available():
model = model.cuda()
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-2)
def make_sequence(x, dic):
idx = [dic[i] for i in x]
idx = Variable(torch.LongTensor(idx))
return idx
for epoch in range(300):
print('*' * 10)
print('epoch {}'.format(epoch + 1))
running_loss = 0
for data in training_data:
word, tag = data
word_list = make_sequence(word, word_to_idx)
tag = make_sequence(tag, tag_to_idx)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
word_list = word_list.cuda()
tag = tag.cuda()
# forward
out = model(word_list, word)
loss = criterion(out, tag)
running_loss += loss.data[0]
# backward
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print('Loss: {}'.format(running_loss / len(data)))
print()
input = make_sequence("Everybody ate the apple".split(), word_to_idx)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
input = input.cuda()
out = model(input, "Everybody ate the apple".split())
print(out)最后
以上就是单纯豌豆最近收集整理的关于LSTM的全部内容,更多相关LSTM内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复