tensorflow应用:双向LSTM神经网络手写数字识别
- 思路
- Python程序1.建模训练保存
- Tensorboard检查计算图及训练结果
- 打开训练好的模型进行预测
思路
将28X28的图片看成28行像素,按行展开成28时间步,每时间步间对识别都有影响,故用双向LSTM神经元,其实每列间对识别也有影响,用卷积神经网络也许更合理,这里只是学习LSTM的用法。应该也可以用两个双向LSTM神经网络进行联合预测,一个按行扫描,一个按列扫描。
Python程序1.建模训练保存
# coding=utf-8
import os
os.environ["TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL"]='2' # 只显示 warning 和 Error
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib import rnn
import numpy as np
###data (50000,784),(1000,784),(1000,784):
import pickle
import gzip
def load_data():
f = gzip.open('../data/mnist.pkl.gz', 'rb')
training_data, validation_data, test_data = pickle.load(f,encoding='bytes')
f.close()
return (training_data, validation_data, test_data)
def vectorized_result(j):
e = np.zeros(10)
e[j] = 1.0
return e
training_data, validation_data, test_data = load_data()
trainData_in=training_data[0][:50000]
trainData_out=[vectorized_result(j) for j in training_data[1][:50000]]
validData_in=validation_data[0]
validData_out=[vectorized_result(j) for j in validation_data[1]]
testData_in=test_data[0][:100]
testData_out=[vectorized_result(j) for j in test_data[1][:100]]
#define constants
#unrolled through 28 time steps 28行对应28个时间步:
TIME_STEPS=28
#hidden LSTM units
NUM_HIDDEN=128
#???rows of 28 pixels 每行28个像素:
NUM_INPUT=28
#learning rate for adam
LEARNING_RATE=0.001
#mnist is meant to be classified in 10 classes(0-9).
NUM_CLASSES=10
#size of batch
BATCH_SIZE=1024
TRAINING_EPOCHS=1#
#weights and biases of appropriate shape to accomplish above task
#out_weights=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([NUM_HIDDEN,NUM_CLASSES]))
#双向神经网络的权重为单向的2倍尺度:
out_weights=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2*NUM_HIDDEN,NUM_CLASSES]))
out_bias=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([NUM_CLASSES]))
#defining placeholders
#input image placeholder:
x_input=tf.placeholder("float",[None,TIME_STEPS,NUM_INPUT],name='x_input')
#input label placeholder:
y_desired=tf.placeholder("float",[None,NUM_CLASSES])
#processing the input tensor from [BATCH_SIZE,NUM_STEPS,NUM_INPUT] to "TIME_STEPS" number of [BATCH-SIZE,NUM_INPUT] tensors!:
#对输入的一个张量的第二维解包变成TIME_STEPS个张量!:
x_input_step=tf.unstack(x_input ,TIME_STEPS,1)
#defining the network:
#def BiRNN(x_input_step,out_weights,out_bias):
#lstm_layer=rnn.BasicLSTMCell(NUM_HIDDEN,forget_bias=1.0)
#正向神经元:
lstm_fw_cell=rnn.BasicLSTMCell(NUM_HIDDEN,forget_bias=1.0)
#反向神经元:
lstm_bw_cell=rnn.BasicLSTMCell(NUM_HIDDEN,forget_bias=1.0)
#outputs,_=rnn.static_rnn(lstm_layer,x_input_step,dtype="float32")
#构建双向LSTM网络:
outputs,_,_=rnn.static_bidirectional_rnn( lstm_fw_cell,lstm_bw_cell,x_input_step,dtype="float32")
#converting last output of dimension [batch_size,num_hidden] to [batch_size,num_classes] by out_weight multiplication
z_prediction= tf.add(tf.matmul(outputs[-1],out_weights),out_bias,name='z_prediction')
#z_prediction=BiRNN(x_input_step, out_weights, out_bias)
#注意!z_prediction经softmax归一化后才是最终的输出,用于和标签比较,下面的损失函数中用了softmax哈交叉熵,跳过了求y_output这一步:
y_output=tf.nn.softmax(z_prediction,name='y_output')
#loss_function:
loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(logits=z_prediction,labels=y_desired),name='loss')
#optimization
opt=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=LEARNING_RATE).minimize(loss)
#model evaluation
correct_prediction=tf.equal(tf.argmax(z_prediction,1),tf.argmax(y_desired,1))
accuracy=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
#以下汇总一些参数用于TensorBoard:
for value in [loss]:
tf.summary.scalar(value.op.name,value) #汇总的标签及值
summary_op=tf.summary.merge_all() #汇总合并
#initialize variables:
init=tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 生成一个写日志的writer,并将当前的tensorflow计算图写入日志。
# tensorflow提供了多种写日志文件的API
summary_writer=tf.summary.FileWriter(r'C:templog_simple_stats',sess.graph)
sess.run(init)
num_batches=int(len(trainData_in)/BATCH_SIZE)
for epoch in range(TRAINING_EPOCHS):
for i in range(num_batches):
batch_x=trainData_in[i*BATCH_SIZE:(i+1)*BATCH_SIZE]
batch_x=batch_x.reshape((BATCH_SIZE,TIME_STEPS,NUM_INPUT))#
batch_y=trainData_out[i*BATCH_SIZE:(i+1)*BATCH_SIZE]
#优化及日志结果!!!!!!:::::
_,summary=sess.run([opt,summary_op], feed_dict={x_input: batch_x, y_desired: batch_y})
#写日志,将结果添加到汇总:
summary_writer.add_summary(summary,global_step=epoch*num_batches+i)
if i %10==0:
acc=sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x_input:batch_x,y_desired:batch_y})
los=sess.run(loss,feed_dict={x_input:batch_x,y_desired:batch_y})
print('epoch:%4d,'%epoch,'%4d'%i)
print("Accuracy ",acc)
print("Loss ",los)
print("__________________")
print("Finished!")
print("Test Accuracy ",sess.run(accuracy,
feed_dict={x_input:testData_in.reshape((-1,TIME_STEPS,NUM_INPUT)),
y_desired:testData_out}))
saver=tf.train.Saver()
save_path=saver.save(sess,'../data')
print('Model saved to %s' % save_path)
summary_writer.close()
Tensorboard检查计算图及训练结果
在终端运行:
Tensorboard --logdir= C:templog_simple_stats
C:UsersliAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython36Scripts>tensorboard --logdir=C:templog_simple_stats
TensorBoard 1.10.0 at http://li-PC:6006 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
用谷歌浏览器打开http://li-pc:6006/
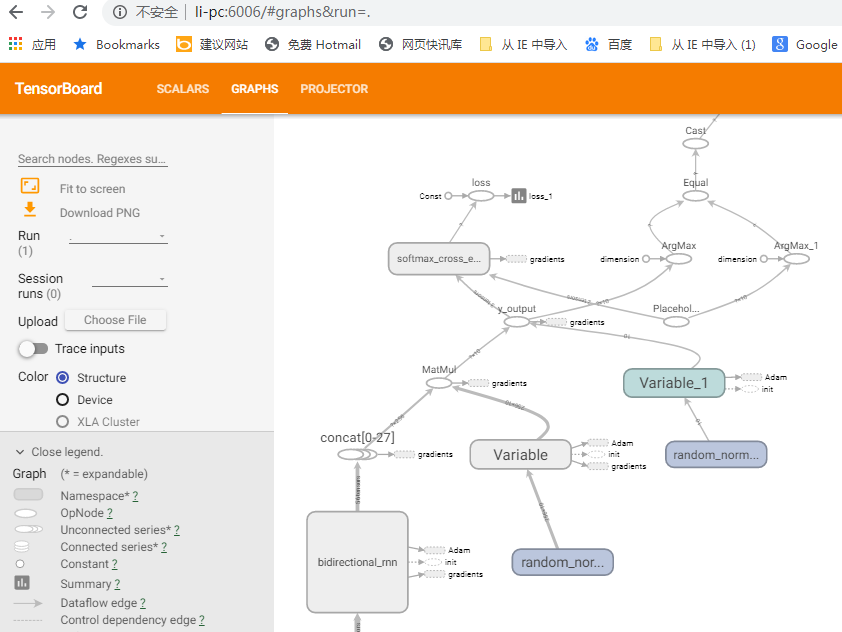
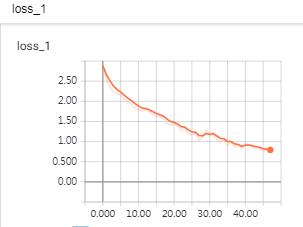
打开训练好的模型进行预测
# coding=utf-8
import os
os.environ["TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL"]='2' # 只显示 warning 和 Error
###data (50000,784),(1000,784),(1000,784):
import pickle
import gzip
import numpy as np
def load_data():
f = gzip.open('../data/mnist.pkl.gz', 'rb')
training_data, validation_data, test_data = pickle.load(f,encoding='bytes')
f.close()
return (training_data, validation_data, test_data)
def vectorized_result(j):
e = np.zeros(10)
e[j] = 1.0
return e
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#unrolled through 28 time steps 28行对应28个时间步:
TIME_STEPS=28
#???rows of 28 pixels 每行28个像素:
NUM_INPUT=28
training_data, validation_data, test_data = load_data()
testData_in=test_data[0]
testData_out=[vectorized_result(j) for j in test_data[1]]
sess=tf.InteractiveSession()
new_saver=tf.train.import_meta_graph('../data.meta')
new_saver.restore(sess, '../data')
tf.get_default_graph().as_graph_def()
x_input=sess.graph.get_tensor_by_name('x_input:0')
y_output=sess.graph.get_tensor_by_name('y_output:0')
try_input=testData_in[6]
try_desired=testData_out[6]
print(try_desired)
print(y_output.eval(feed_dict={x_input:
np.array([try_input]).reshape((-1,TIME_STEPS,NUM_INPUT))}))
try_input.resize(28,28)
plt.imshow(try_input,cmap='Greys_r')
plt.show()
[0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[[1.13495190e-07 7.10399399e-06 5.81623426e-05 1.16373285e-05
7.91627526e-01 5.11910184e-04 1.04986066e-04 1.08990945e-01
1.73597573e-03 9.69514474e-02]]
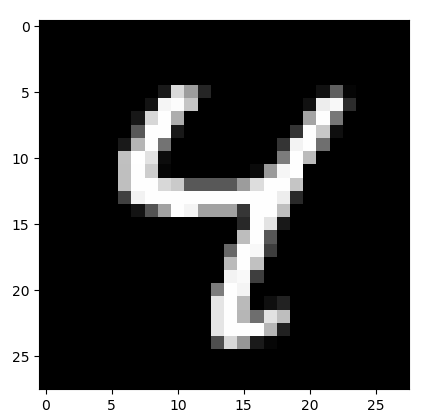
模型只进行了一轮训练,40次更新,40X1024个样本,就准确识别了手写数字4,判断为数字4的概率是 7.91627526e-01
最后
以上就是野性电源最近收集整理的关于tensorflow应用:双向LSTM神经网络手写数字识别的全部内容,更多相关tensorflow应用内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。


![[人工智能-深度学习-49]:循环神经网络 - RNN与NLP的关系以及RNN在人工神经网络中的位置](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg8.png)





发表评论 取消回复