list
list是一个具有头结点的双向循环链表,结构较为复杂,但是非常高效。
现在我创建一个list对象
首先需要包头文件:
#include <list>
std::list<int> l1;这个例子中,我实例化出了一个存int类型的对象。
接下来我参考cpulscpuls.com,介绍接口的用法:
一:数据操作:
1.assign:
①: void assign (size_type n, const value_type& val);
②: template <class InputIterator>
void assign (InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
①:
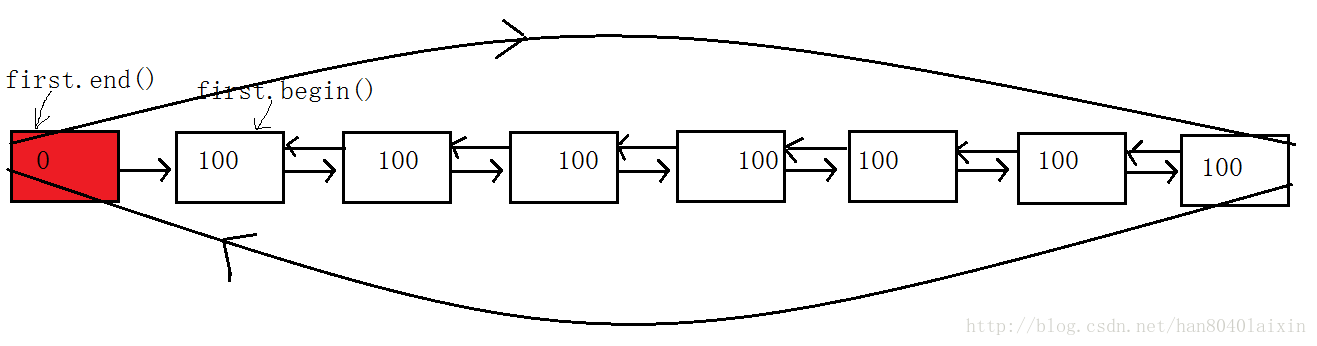
std::list<int> first;
first.assign(7, 100);//在first存了7个100 此时,first里存有7个100
给出first的结构:
②:
std::list<int> second;
second.assign(first.begin(), first.end()); //插入一段从first的begin到end结束的区间那么此时,second也里存有7个100(左闭右开)
int myints[] = { 1776, 7, 4 };//定义一个数组:1776 7 4
first.assign(myints, myints + 3);//插入从myints到myints+1这段区间此时,first里清除7个100,而是存有1776 7 4。
2.push_front:头插
void push_front (const value_type& val); std::list<int> mylist(2, 100);//100 100
mylist.push_front(200);//200 100 100
mylist.push_front(300);//300 200 100 1003.pop_front:头删
void pop_front(); std::list<int> mylist(2, 100);//100 100
mylist.pop_front();//1004.push_back:尾插
void push_back (const value_type& val); std::list<int> mylist;
mylist.push_back(1);
mylist.push_back(2);
mylist.push_back(3);
mylist.push_back(4);此时,mylist里存有1 2 3 4四个数据。
5.pop_back:尾删
void pop_back();删除尾上的数据,较容易
6.insert:
①: iterator insert (iterator position, const value_type& val);
②: void insert (iterator position, size_type n, const value_type& val);
③: template <class InputIterator>
void insert (iterator position, InputIterator first, InputIterator last);①:
std::list<int> mylist;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; ++i) mylist.push_back(i); // 1 2 3 4 5
std::list<int>::iterator it = mylist.begin();//迭代器it指向1
++it;//那么it指向2
mylist.insert(it, 10); //在it前插入10此时,mylist里存有1 10 2 3 4 5
②:
mylist.insert(it, 2, 20); //在it前插入两个20那么此时,mylist里存有 1 10 20 20 2 3 4 5
③:
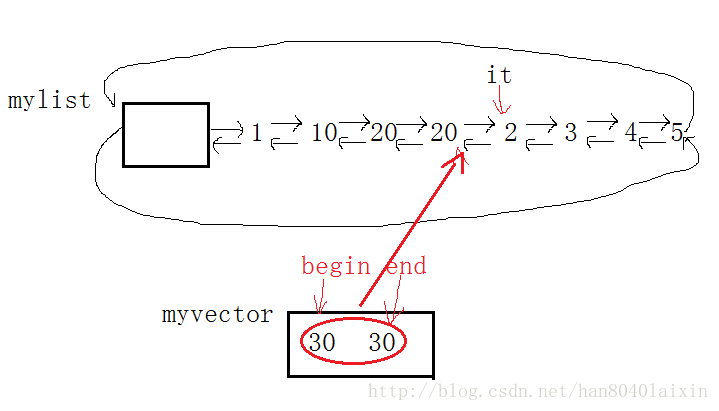
std::vector<int> myvector(2, 30);//创建一个myvector对象,存有30 30
mylist.insert(it, myvector.begin(), myvector.end());//在it前插入一段已myvector的begin开始到end结束的区间此时,mylist里存有1 10 20 20 30 30 2 3 4 5
7.erase:注意,删除后返回的是下一个位置
iterator erase (iterator position);
iterator erase (iterator first, iterator last);①:
std::list<int> mylist;
std::list<int>::iterator it1, it2;
for (int i = 1; i<10; ++i) mylist.push_back(i * 10);// 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
it1 = it2 = mylist.begin(); //it1和it2都行指向10
advance(it2, 6); //it2指向70
++it1; //it1指向20
it1 = mylist.erase(it1); // 10 30 40 50 60 70 80 90,删除了20并且返回30给it1
it2 = mylist.erase(it2); // 10 30 40 50 60 80 90删除了70并且返回80给t2②:
++it1; //it1指向40
--it2; //it2指向60
mylist.erase(it1, it2); // 10 30 60 80 90,删除了40到60这段区间(左闭右开),并且返回下一个,也就是608.swap:交换
void swap (list& x); std::list<int> mylist(5, 10);//10 10 10 10 10
std::list<int> anotherlist(6, 6);//6 6 6 6 6 6
mylist.swap(anotherlist);经过swap:
mylist: 6 6 6 6 6 6
anotherlist: 10 10 10 10 10
9.resize:改变size的函数,并且还具有初始化的能力
void resize (size_type n, value_type val = value_type()); std::list<int> mylist;
for (int i = 1; i<10; ++i) mylist.push_back(i);//1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
mylist.resize(5);//1 2 3 4 5
mylist.resize(8, 100);//1 2 3 4 5 100 100 100
mylist.resize(12);//1 2 3 4 5 100 100 100 0 0 0 0.当n<size,直接删除后面的数据
.当n>size,多出来的值会初始化:
(1):当写死了类型的值val,那么就会void clear();补val
(2):若没有写,那么就调用该类型默认构造函数补。10.clear:清空
void clear();清空链表,较简单
二:迭代器
1.begin和end:返回迭代器的开始和结束,如果const对象调用,则返回const迭代器
iterator begin();
const_iterator begin() const;
iterator end();
const_iterator end() const;注意,带头双向链表的begin是第一个节点,end不是最后一个节点而是头结点,只有这样,在左闭右开的原则下,从begin到end才能访问到所有有效节点。
int myints[] = {75,23,65,42,13};//数组:75 23 65 42 13
std::list<int> mylist (myints,myints+5);//mylist存有:75 23 65 42 13
for (std::list<int>::iterator it=mylist.begin(); it != mylist.end(); ++it)
//it从begin到end
std::cout << ' ' << *it;
std::cout << endl;输出: 75 23 65 42 13
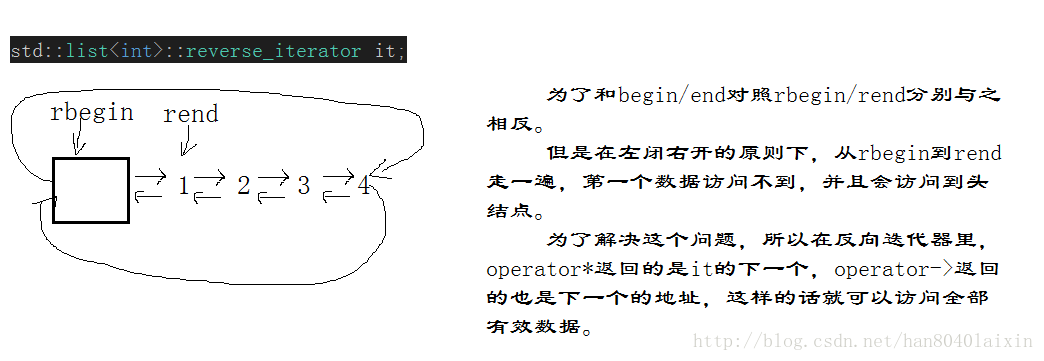
2.rbegin和rend:反向迭代器的开始和结束,如果const对象调用,则返回const迭代器。
reverse_iterator rbegin();
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const;
reverse_iterator rend();
const_reverse_iterator rend() const;它的rbegin/rend与begin/end正好相反。
std::list<int> mylist;
for (int i=1; i<=5; ++i) mylist.push_back(i);// 1 2 3 4 5
for (std::list<int>::reverse_iterator rit=mylist.rbegin(); rit!=mylist.rend(); ++rit)
std::cout << ' ' << *rit;//那么会从最后依次赋值分别为5 4 3 2 1
std::cout << 'n';输出:5 4 3 2 1
三:容量
1.empty:判断是否空,空则返回1,否则返回0
bool empty() const; std::vector<int> first;
cout << first.empty() << endl;//1
first.push_back(1);
cout << first.empty() << endl;//02.size:返回链表的有效数据个数
size_type size() const; std::list<int> myints;
std::cout << "0. size: " << myints.size() << 'n';//0
for (int i=0; i<10; i++) myints.push_back(i);//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
std::cout << "1. size: " << myints.size() << 'n';//10
myints.insert (myints.begin(),10,100);//在1前面插入10个100
std::cout << "2. size: " << myints.size() << 'n';//20
myints.pop_back();//删除一个
std::cout << "3. size: " << myints.size() << 'n';//19输出:
0. size: 0
1. size: 10
2. size: 20
3. size: 19
3.max_size:
size_type max_size() const;返回列表容器可以容纳的最大元素数.
四:元素访问
front和back:
front:对列表容器中第一个元素的引用。如果列表对象是const,函数返回一个const_reference。否则,它返回一个引用。
back:对列表容器中最后一个元素的引用。如果列表对象是const,函数返回一个const_reference。否则,它返回一个引用。
reference front();
const_reference front() const;
reference back();
const_reference back() const; std::list<int> mylist;
mylist.push_back(77);
mylist.push_back(22);//现在front为77, back为22
mylist.front() -= mylist.back();//front减等back
std::cout << "mylist.front() is now " << mylist.front() << 'n';输出:mylist.front() is now 55
五:操作
1.splice:连接
①:void splice (iterator position, list& x);
②:void splice (iterator position, list& x, iterator i);
③:void splice (iterator position, list& x, iterator first, iterator last);①:将x的所有元素转移到容器中。
std::list<int> mylist1, mylist2;
std::list<int>::iterator it;
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; ++i)
mylist1.push_back(i); // mylist1: 1 2 3 4
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i)
mylist2.push_back(i * 10); //mylist2: 10 20 30
it = mylist1.begin();
++it; //it为2
mylist1.splice(it, mylist2); 从it开始,粘接mylist2的数据此时, mylist1: 1 10 20 30 2 3 4
②:将由x指向的元素转移到容器中
mylist2.splice(mylist2.begin(), mylist1, it);//将mylist1的it指向的元素转移到mylist2的begin
此时: mylist1: 1 10 20 30 3 4
mylist2: 2
③:将范围(第一,最后)从x转移到容器中。
it = mylist1.begin();
std::advance(it, 3); // it现在为30
mylist1.splice(mylist1.begin(), mylist1, it, mylist1.end());//将it到end的数据,也就是(30 3 4)转移到了容器的前面此时:mylist1: 30 3 4 1 10 20
2.remove:有则删,没有则不做什么
void remove (const value_type& val);
int myints[] = { 17, 89, 7, 14 };
std::list<int> mylist(myints, myints + 4);
mylist.remove(89);//有89,删除这个节点
mylist.remove(99);//没有99,不做什么
for (std::list<int>::iterator it = mylist.begin(); it != mylist.end(); ++it)
std::cout << ' ' << *it;
std::cout << 'n';输出:17 7 14
3.remove_if
template <class Predicate>
void remove_if (Predicate pred);bool single_digit(const int& value) //判断value是否小于10
{
return (value<10);
}
struct is_odd
{
bool operator() (const int& value)//判断value是否为奇数
{
return (value % 2) == 1;
}
};
int main()
{
int myints[] = { 15, 36, 7, 17, 20, 39, 4, 1 };
std::list<int> mylist(myints, myints + 8); // 15 36 7 17 20 39 4 1
mylist.remove_if(single_digit);//函数功能是判断是否大于10,所以删除了所有小于10的数
//15 36 17 20 39
mylist.remove_if(is_odd());//类的仿函数功能是判断是否为奇数,所以删除了所有奇数
//36 20
return 0;
}参数可以是类,函数等,删除所有参数里判断为真的值。
4.unique
①:void unique();
②:template <class BinaryPredicate>
void unique (BinaryPredicate binary_pred);①:删除重复数据的节点,只能删除连续的,所以删除之前可以先进行排序
int main()
{
double mydoubles[] = { 12.15, 2.72, 73.0, 12.77, 3.14,12.77, 73.35, 72.25, 15.3, 72.25 };
std::list<double> mylist(mydoubles, mydoubles + 10);
mylist.sort();//2.72, 3.14, 12.15, 12.77, 12.77,15.3, 72.25, 72.25, 73.0, 73.35
mylist.unique();//删除掉了重复的:2.72, 3.14, 12.15, 12.771,5.3, 72.25, 73.0, 73.35
return 0;
}二:参数可以是函数,类等,删除参数里内容判断为真的连续的数据:
bool same_integral_part(double first, double second)//判读转为整数位是否相等
{
return (int(first) == int(second));
}
mylist.unique(same_integral_part); // 2.72, 3.14, 12.15,5.3, 72.25, 73.0
删除掉了连续的整数位相等的数据。
5.merge:合并
①:void merge (list& x);
②:template <class Compare>
void merge (list& x, Compare comp);bool mycomparison(double first, double second)//判断first的整数位是否小于second的整数位
{
return (int(first)<int(second));
}
int main()
{
std::list<double> first, second;
first.push_back(3.1);
first.push_back(2.2);
first.push_back(2.9);
second.push_back(3.7);
second.push_back(7.1);
second.push_back(1.4);
first.sort();//2.2 2.9 3.1
second.sort();//1.4 3.7 7.1
first.merge(second);//①first:1.4 2.2 2.9 3.1 3.7 7.1
second.push_back(2.1);//second:2.1
first.merge(second, mycomparison);//②first:1.4 2.2 2.9 2.1 3.1 3.7 7.1
//判断2.1是否小于first各个数据,从1.4开始,直到遇见3.1,2.1的整数位小于3.1的整数位,所以将2.1插入3.1之前
return 0;
}6.sort:缺省从小到大
①:void sort();
②:template <class Compare>
void sort (Compare comp);7.reverse:从两边到中间交换数据
void reverse(); std::list<int> mylist;
for (int i = 1; i<10; ++i) mylist.push_back(i);
//1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
mylist.reverse();
//9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1最后
以上就是高兴大门最近收集整理的关于STL-list的使用 详细说明的全部内容,更多相关STL-list的使用内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。

![【leetcode]189.轮转数组(C语言实现)【leetcode]189.轮转数组(C语言实现)1.第一种办法:基本旋转2.第二种办法:额外开辟一个数组3.第三种方法:三逆置结束语](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg10.png)






发表评论 取消回复