第一种情况
String作为key
/*
* 使用HashMap存储数据并遍历(字符串作为key)
*/
public class HashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,String> hm = new HashMap<String,String>();
hm.put("gky001", "龚二丫");
hm.put("gky002", "龚二狗");
hm.put("gky003", "龚村花");
//遍历Map对象
//方法一,获取所有的key,通过key得到value并返回
Set<String> keys = hm.keySet();
for (String key : keys) {
String value = hm.get(key);
System.out.println("key:"+key+"---"+"value:"+value);
}
System.out.println("########################");
//方法二,获取所有的结婚证对象,通过结婚证对象来获取丈夫老婆
Set<Map.Entry<String,String>> entrys = hm.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : entrys) {
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("丈夫:"+key+"---"+"老婆:"+value);
}
}
}
运行结果
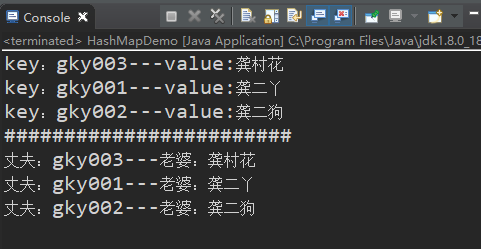
第二种情况
自定义对象作为key
既然是自定义对象,首先创建一个类
名字,年龄,重写toString方法,方便输出
public class Student5 {
String name;
int age;
public Student5(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student5 [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
接着
/*
* 使用HashMap存储数据并遍历(自定义对象作为key)
*/
public class HashMapDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Map对象
HashMap<Student5,String> hm = new HashMap<Student5,String>();
//创建key对象
Student5 s = new Student5("闫狗蛋",22);
Student5 s2 = new Student5("张全蛋",33);
//添加映射关系
hm.put(s, "gky001");
hm.put(s2, "gky002");
//遍历
//方法1
Set<Student5> keys = hm.keySet();
for (Student5 key : keys) {
String value = hm.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
System.out.println("#########################");
//方法2
Set<Map.Entry<Student5, String>> entrys = hm.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Student5, String> entry : entrys) {
Student5 key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
}
}
运行结果
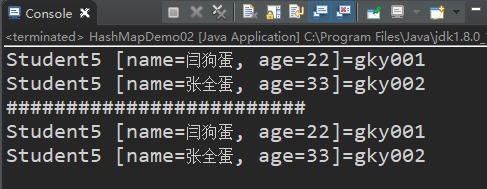
此时假如添加一个重复对象,结果会怎样呢?
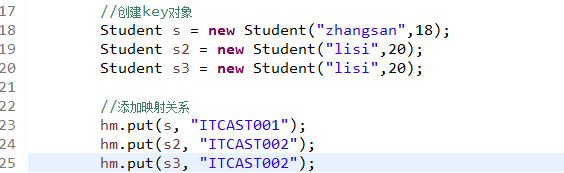
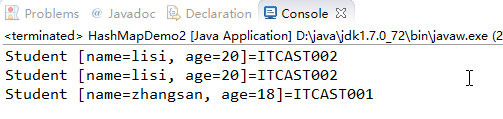
为什么没去重呢?
这就和以前学的是一个道理,需要在Student5类中重写hashCode和equals方法。然后就能去重了
最后
以上就是魁梧汽车最近收集整理的关于HashMap储存数据并遍历的全部内容,更多相关HashMap储存数据并遍历内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复