BST
二叉查找树(BST):根节点大于等于左子树所有节点,小于等于右子树所有节点。
二叉查找树中序遍历有序。
1. 修剪二叉查找树
669. Trim a Binary Search Tree (Easy)
Leetcode / 力扣
Input:
3
/
0 4
2
/
1
L = 1
R = 3
Output:
3
/
2
/
1
题目描述:只保留值在 L ~ R 之间的节点
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int L, int R) {
if (root == null) return null;
if (root.val > R) return trimBST(root.left, L, R);
if (root.val < L) return trimBST(root.right, L, R);
root.left = trimBST(root.left, L, R);
root.right = trimBST(root.right, L, R);
return root;
}
2. 寻找二叉查找树的第 k 个元素
中序遍历解法:
private int cnt = 0;
private int val;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
inOrder(root, k);
return val;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode node, int k) {
if (node == null) return;
inOrder(node.left, k);
cnt++;
if (cnt == k) {
val = node.val;
return;
}
inOrder(node.right, k);
}
递归解法:
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
int leftCnt = count(root.left);
if (leftCnt == k - 1) return root.val;
if (leftCnt > k - 1) return kthSmallest(root.left, k);
return kthSmallest(root.right, k - leftCnt - 1);
}
private int count(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return 0;
return 1 + count(node.left) + count(node.right);
}
3. 把二叉查找树每个节点的值都加上比它大的节点的值
Input: The root of a Binary Search Tree like this:
5
/
2 13
Output: The root of a Greater Tree like this:
18
/
20 13
先遍历右子树。
private int sum = 0;
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
traver(root);
return root;
}
private void traver(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
traver(node.right);
sum += node.val;
node.val = sum;
traver(node.left);
}
4. 二叉查找树的最近公共祖先
_______6______
/
___2__ ___8__
/ /
0 4 7 9
/
3 5
For example, the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of nodes 2 and 8 is 6. Another example is LCA of nodes 2 and 4 is 2, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return root;
}
5. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
_______3______
/
___5__ ___1__
/ /
6 2 0 8
/
7 4
For example, the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of nodes 5 and 1 is 3. Another example is LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return left == null ? right : right == null ? left : root;
}
6. 从有序数组中构造二叉查找树
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return toBST(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode toBST(int[] nums, int sIdx, int eIdx){
if (sIdx > eIdx) return null;
int mIdx = (sIdx + eIdx) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mIdx]);
root.left = toBST(nums, sIdx, mIdx - 1);
root.right = toBST(nums, mIdx + 1, eIdx);
return root;
}
7. 根据有序链表构造平衡的二叉查找树
Given the sorted linked list: [-10,-3,0,5,9],
One possible answer is: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the following height balanced BST:
0
/
-3 9
/ /
-10 5
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return null;
if (head.next == null) return new TreeNode(head.val);
ListNode preMid = preMid(head);
ListNode mid = preMid.next;
preMid.next = null; // 断开链表
TreeNode t = new TreeNode(mid.val);
t.left = sortedListToBST(head);
t.right = sortedListToBST(mid.next);
return t;
}
private ListNode preMid(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;
ListNode pre = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return pre;
}
8. 在二叉查找树中寻找两个节点,使它们的和为一个给定值
Input:
5
/
3 6
/
2 4 7
Target = 9
Output: True
使用中序遍历得到有序数组之后,再利用双指针对数组进行查找。
应该注意到,这一题不能用分别在左右子树两部分来处理这种思想,因为两个待求的节点可能分别在左右子树中。
public boolean findTarget(TreeNode root, int k) {
List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
inOrder(root, nums);
int i = 0, j = nums.size() - 1;
while (i < j) {
int sum = nums.get(i) + nums.get(j);
if (sum == k) return true;
if (sum < k) i++;
else j--;
}
return false;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> nums) {
if (root == null) return;
inOrder(root.left, nums);
nums.add(root.val);
inOrder(root.right, nums);
}
9. 在二叉查找树中查找两个节点之差的最小绝对值
Input:
1
3
/
2
Output:
1
利用二叉查找树的中序遍历为有序的性质,计算中序遍历中临近的两个节点之差的绝对值,取最小值。
private int minDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private TreeNode preNode = null;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
inOrder(root);
return minDiff;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
inOrder(node.left);
if (preNode != null) minDiff = Math.min(minDiff, node.val - preNode.val);
preNode = node;
inOrder(node.right);
}
10. 寻找二叉查找树中出现次数最多的值
1
2
/
2
return [2].
答案可能不止一个,也就是有多个值出现的次数一样多。
private int curCnt = 1;
private int maxCnt = 1;
private TreeNode preNode = null;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> maxCntNums = new ArrayList<>();
inOrder(root, maxCntNums);
int[] ret = new int[maxCntNums.size()];
int idx = 0;
for (int num : maxCntNums) {
ret[idx++] = num;
}
return ret;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode node, List<Integer> nums) {
if (node == null) return;
inOrder(node.left, nums);
if (preNode != null) {
if (preNode.val == node.val) curCnt++;
else curCnt = 1;
}
if (curCnt > maxCnt) {
maxCnt = curCnt;
nums.clear();
nums.add(node.val);
} else if (curCnt == maxCnt) {
nums.add(node.val);
}
preNode = node;
inOrder(node.right, nums);
}
Trie
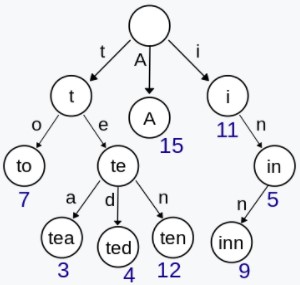
Trie,又称前缀树或字典树,用于判断字符串是否存在或者是否具有某种字符串前缀。
1. 实现一个 Trie
class Trie {
private class Node {
Node[] childs = new Node[26];
boolean isLeaf;
}
private Node root = new Node();
public Trie() {
}
public void insert(String word) {
insert(word, root);
}
private void insert(String word, Node node) {
if (node == null) return;
if (word.length() == 0) {
node.isLeaf = true;
return;
}
int index = indexForChar(word.charAt(0));
if (node.childs[index] == null) {
node.childs[index] = new Node();
}
insert(word.substring(1), node.childs[index]);
}
public boolean search(String word) {
return search(word, root);
}
private boolean search(String word, Node node) {
if (node == null) return false;
if (word.length() == 0) return node.isLeaf;
int index = indexForChar(word.charAt(0));
return search(word.substring(1), node.childs[index]);
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return startWith(prefix, root);
}
private boolean startWith(String prefix, Node node) {
if (node == null) return false;
if (prefix.length() == 0) return true;
int index = indexForChar(prefix.charAt(0));
return startWith(prefix.substring(1), node.childs[index]);
}
private int indexForChar(char c) {
return c - 'a';
}
}
2. 实现一个 Trie,用来求前缀和
Input: insert("apple", 3), Output: Null
Input: sum("ap"), Output: 3
Input: insert("app", 2), Output: Null
Input: sum("ap"), Output: 5
class MapSum {
private class Node {
Node[] child = new Node[26];
int value;
}
private Node root = new Node();
public MapSum() {
}
public void insert(String key, int val) {
insert(key, root, val);
}
private void insert(String key, Node node, int val) {
if (node == null) return;
if (key.length() == 0) {
node.value = val;
return;
}
int index = indexForChar(key.charAt(0));
if (node.child[index] == null) {
node.child[index] = new Node();
}
insert(key.substring(1), node.child[index], val);
}
public int sum(String prefix) {
return sum(prefix, root);
}
private int sum(String prefix, Node node) {
if (node == null) return 0;
if (prefix.length() != 0) {
int index = indexForChar(prefix.charAt(0));
return sum(prefix.substring(1), node.child[index]);
}
int sum = node.value;
for (Node child : node.child) {
sum += sum(prefix, child);
}
return sum;
}
private int indexForChar(char c) {
return c - 'a';
}
}
数学
素数分解
每一个数都可以分解成素数的乘积,例如 84 = 22 * 31 * 50 * 71 * 110 * 130 * 170 * …
整除
令 x = 2m0 * 3m1 * 5m2 * 7m3 * 11m4 * …
令 y = 2n0 * 3n1 * 5n2 * 7n3 * 11n4 * …
如果 x 整除 y(y mod x == 0),则对于所有 i,mi <= ni。
最大公约数最小公倍数
x 和 y 的最大公约数为:gcd(x,y) = 2min(m0,n0) * 3min(m1,n1) * 5min(m2,n2) * …
x 和 y 的最小公倍数为:lcm(x,y) = 2max(m0,n0) * 3max(m1,n1) * 5max(m2,n2) * …
1. 生成素数序列
埃拉托斯特尼筛法在每次找到一个素数时,将能被素数整除的数排除掉。
public int countPrimes(int n) {
boolean[] notPrimes = new boolean[n + 1];
int count = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
if (notPrimes[i]) {
continue;
}
count++;
// 从 i * i 开始,因为如果 k < i,那么 k * i 在之前就已经被去除过了
for (long j = (long) (i) * i; j < n; j += i) {
notPrimes[(int) j] = true;
}
}
return count;
}
2. 最大公约数
int gcd(int a, int b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}
最小公倍数为两数的乘积除以最大公约数。
int lcm(int a, int b) {
return a * b / gcd(a, b);
}
3. 使用位操作和减法求解最大公约数
编程之美:2.7
对于 a 和 b 的最大公约数 f(a, b),有:
- 如果 a 和 b 均为偶数,f(a, b) = 2*f(a/2, b/2);
- 如果 a 是偶数 b 是奇数,f(a, b) = f(a/2, b);
- 如果 b 是偶数 a 是奇数,f(a, b) = f(a, b/2);
- 如果 a 和 b 均为奇数,f(a, b) = f(b, a-b);
乘 2 和除 2 都可以转换为移位操作。
public int gcd(int a, int b) {
if (a < b) {
return gcd(b, a);
}
if (b == 0) {
return a;
}
boolean isAEven = isEven(a), isBEven = isEven(b);
if (isAEven && isBEven) {
return 2 * gcd(a >> 1, b >> 1);
} else if (isAEven && !isBEven) {
return gcd(a >> 1, b);
} else if (!isAEven && isBEven) {
return gcd(a, b >> 1);
} else {
return gcd(b, a - b);
}
}
进制转换
1. 7 进制
public String convertToBase7(int num) {
if (num == 0) {
return "0";
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
boolean isNegative = num < 0;
if (isNegative) {
num = -num;
}
while (num > 0) {
sb.append(num % 7);
num /= 7;
}
String ret = sb.reverse().toString();
return isNegative ? "-" + ret : ret;
}
Java 中 static String toString(int num, int radix) 可以将一个整数转换为 radix 进制表示的字符串。
public String convertToBase7(int num) {
return Integer.toString(num, 7);
}
2. 16 进制
Input:
26
Output:
"1a"
Input:
-1
Output:
"ffffffff"
负数要用它的补码形式。
public String toHex(int num) {
char[] map = {'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'};
if (num == 0) return "0";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (num != 0) {
sb.append(map[num & 0b1111]);
num >>>= 4; // 因为考虑的是补码形式,因此符号位就不能有特殊的意义,需要使用无符号右移,左边填 0
}
return sb.reverse().toString();
}
3. 26 进制
1 -> A
2 -> B
3 -> C
...
26 -> Z
27 -> AA
28 -> AB
因为是从 1 开始计算的,而不是从 0 开始,因此需要对 n 执行 -1 操作。
public String convertToTitle(int n) {
if (n == 0) {
return "";
}
n--;
return convertToTitle(n / 26) + (char) (n % 26 + 'A');
}
阶乘
1. 统计阶乘尾部有多少个 0
尾部的 0 由 2 * 5 得来,2 的数量明显多于 5 的数量,因此只要统计有多少个 5 即可。
对于一个数 N,它所包含 5 的个数为:N/5 + N/52 + N/53 + …,其中 N/5 表示不大于 N 的数中 5 的倍数贡献一个 5,N/52 表示不大于 N 的数中 52 的倍数再贡献一个 5 …。
public int trailingZeroes(int n) {
return n == 0 ? 0 : n / 5 + trailingZeroes(n / 5);
}
如果统计的是 N! 的二进制表示中最低位 1 的位置,只要统计有多少个 2 即可,该题目出自 编程之美:2.2 。和求解有多少个 5 一样,2 的个数为 N/2 + N/22 + N/23 + …
字符串加法减法
1. 二进制加法
67. Add Binary (Easy)
Leetcode / 力扣
a = "11"
b = "1"
Return "100".
public String addBinary(String a, String b) {
int i = a.length() - 1, j = b.length() - 1, carry = 0;
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
while (carry == 1 || i >= 0 || j >= 0) {
if (i >= 0 && a.charAt(i--) == '1') {
carry++;
}
if (j >= 0 && b.charAt(j--) == '1') {
carry++;
}
str.append(carry % 2);
carry /= 2;
}
return str.reverse().toString();
}
2. 字符串加法
字符串的值为非负整数。
public String addStrings(String num1, String num2) {
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
int carry = 0, i = num1.length() - 1, j = num2.length() - 1;
while (carry == 1 || i >= 0 || j >= 0) {
int x = i < 0 ? 0 : num1.charAt(i--) - '0';
int y = j < 0 ? 0 : num2.charAt(j--) - '0';
str.append((x + y + carry) % 10);
carry = (x + y + carry) / 10;
}
return str.reverse().toString();
}
相遇问题
1. 改变数组元素使所有的数组元素都相等
Input:
[1,2,3]
Output:
2
Explanation:
Only two moves are needed (remember each move increments or decrements one element):
[1,2,3] => [2,2,3] => [2,2,2]
每次可以对一个数组元素加一或者减一,求最小的改变次数。
这是个典型的相遇问题,移动距离最小的方式是所有元素都移动到中位数。理由如下:
设 m 为中位数。a 和 b 是 m 两边的两个元素,且 b > a。要使 a 和 b 相等,它们总共移动的次数为 b - a,这个值等于 (b - m) + (m - a),也就是把这两个数移动到中位数的移动次数。
设数组长度为 N,则可以找到 N/2 对 a 和 b 的组合,使它们都移动到 m 的位置。
解法 1
先排序,时间复杂度:O(NlogN)
public int minMoves2(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int move = 0;
int l = 0, h = nums.length - 1;
while (l <= h) {
move += nums[h] - nums[l];
l++;
h--;
}
return move;
}
解法 2
使用快速选择找到中位数,时间复杂度 O(N)
public int minMoves2(int[] nums) {
int move = 0;
int median = findKthSmallest(nums, nums.length / 2);
for (int num : nums) {
move += Math.abs(num - median);
}
return move;
}
private int findKthSmallest(int[] nums, int k) {
int l = 0, h = nums.length - 1;
while (l < h) {
int j = partition(nums, l, h);
if (j == k) {
break;
}
if (j < k) {
l = j + 1;
} else {
h = j - 1;
}
}
return nums[k];
}
private int partition(int[] nums, int l, int h) {
int i = l, j = h + 1;
while (true) {
while (nums[++i] < nums[l] && i < h) ;
while (nums[--j] > nums[l] && j > l) ;
if (i >= j) {
break;
}
swap(nums, i, j);
}
swap(nums, l, j);
return j;
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
多数投票问题
1. 数组中出现次数多于 n / 2 的元素
先对数组排序,最中间那个数出现次数一定多于 n / 2。
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length / 2];
}
可以利用 Boyer-Moore Majority Vote Algorithm 来解决这个问题,使得时间复杂度为 O(N)。可以这么理解该算法:使用 cnt 来统计一个元素出现的次数,当遍历到的元素和统计元素不相等时,令 cnt–。如果前面查找了 i 个元素,且 cnt == 0,说明前 i 个元素没有 majority,或者有 majority,但是出现的次数少于 i / 2,因为如果多于 i / 2 的话 cnt 就一定不会为 0。此时剩下的 n - i 个元素中,majority 的数目依然多于 (n - i) / 2,因此继续查找就能找出 majority。
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
int cnt = 0, majority = nums[0];
for (int num : nums) {
majority = (cnt == 0) ? num : majority;
cnt = (majority == num) ? cnt + 1 : cnt - 1;
}
return majority;
}
其它
1. 平方数
Input: 16
Returns: True
平方序列:1,4,9,16,…
间隔:3,5,7,…
间隔为等差数列,使用这个特性可以得到从 1 开始的平方序列。
public boolean isPerfectSquare(int num) {
int subNum = 1;
while (num > 0) {
num -= subNum;
subNum += 2;
}
return num == 0;
}
2. 3 的 n 次方
public boolean isPowerOfThree(int n) {
return n > 0 && (1162261467 % n == 0);
}
3. 乘积数组
For example, given [1,2,3,4], return [24,12,8,6].
给定一个数组,创建一个新数组,新数组的每个元素为原始数组中除了该位置上的元素之外所有元素的乘积。
要求时间复杂度为 O(N),并且不能使用除法。
public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] products = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(products, 1);
int left = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
left *= nums[i - 1];
products[i] *= left;
}
int right = 1;
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
right *= nums[i + 1];
products[i] *= right;
}
return products;
}
4. 找出数组中的乘积最大的三个数
Input: [1,2,3,4]
Output: 24
public int maximumProduct(int[] nums) {
int max1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE, max2 = Integer.MIN_VALUE, max3 = Integer.MIN_VALUE, min1 = Integer.MAX_VALUE, min2 = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int n : nums) {
if (n > max1) {
max3 = max2;
max2 = max1;
max1 = n;
} else if (n > max2) {
max3 = max2;
max2 = n;
} else if (n > max3) {
max3 = n;
}
if (n < min1) {
min2 = min1;
min1 = n;
} else if (n < min2) {
min2 = n;
}
}
return Math.max(max1*max2*max3, max1*min1*min2);
}
数组与矩阵
1. 把数组中的 0 移到末尾
For example, given nums = [0, 1, 0, 3, 12], after calling your function, nums should be [1, 3, 12, 0, 0].
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int idx = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
if (num != 0) {
nums[idx++] = num;
}
}
while (idx < nums.length) {
nums[idx++] = 0;
}
}
2. 改变矩阵维度
Input:
nums =
[[1,2],
[3,4]]
r = 1, c = 4
Output:
[[1,2,3,4]]
Explanation:
The row-traversing of nums is [1,2,3,4]. The new reshaped matrix is a 1 * 4 matrix, fill it row by row by using the previous list.
public int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] nums, int r, int c) {
int m = nums.length, n = nums[0].length;
if (m * n != r * c) {
return nums;
}
int[][] reshapedNums = new int[r][c];
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < c; j++) {
reshapedNums[i][j] = nums[index / n][index % n];
index++;
}
}
return reshapedNums;
}
3. 找出数组中最长的连续 1
public int findMaxConsecutiveOnes(int[] nums) {
int max = 0, cur = 0;
for (int x : nums) {
cur = x == 0 ? 0 : cur + 1;
max = Math.max(max, cur);
}
return max;
}
4. 有序矩阵查找
[
[ 1, 5, 9],
[10, 11, 13],
[12, 13, 15]
]
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) return false;
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int row = 0, col = n - 1;
while (row < m && col >= 0) {
if (target == matrix[row][col]) return true;
else if (target < matrix[row][col]) col--;
else row++;
}
return false;
}
5. 有序矩阵的 Kth Element
matrix = [
[ 1, 5, 9],
[10, 11, 13],
[12, 13, 15]
],
k = 8,
return 13.
解题参考:Share my thoughts and Clean Java Code
二分查找解法:
public int kthSmallest(int[][] matrix, int k) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int lo = matrix[0][0], hi = matrix[m - 1][n - 1];
while (lo <= hi) {
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n && matrix[i][j] <= mid; j++) {
cnt++;
}
}
if (cnt < k) lo = mid + 1;
else hi = mid - 1;
}
return lo;
}
堆解法:
public int kthSmallest(int[][] matrix, int k) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
PriorityQueue<Tuple> pq = new PriorityQueue<Tuple>();
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) pq.offer(new Tuple(0, j, matrix[0][j]));
for(int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) { // 小根堆,去掉 k - 1 个堆顶元素,此时堆顶元素就是第 k 的数
Tuple t = pq.poll();
if(t.x == m - 1) continue;
pq.offer(new Tuple(t.x + 1, t.y, matrix[t.x + 1][t.y]));
}
return pq.poll().val;
}
class Tuple implements Comparable<Tuple> {
int x, y, val;
public Tuple(int x, int y, int val) {
this.x = x; this.y = y; this.val = val;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Tuple that) {
return this.val - that.val;
}
}
6. 一个数组元素在 [1, n] 之间,其中一个数被替换为另一个数,找出重复的数和丢失的数
Input: nums = [1,2,2,4]
Output: [2,3]
Input: nums = [1,2,2,4]
Output: [2,3]
最直接的方法是先对数组进行排序,这种方法时间复杂度为 O(NlogN)。本题可以以 O(N) 的时间复杂度、O(1) 空间复杂度来求解。
主要思想是通过交换数组元素,使得数组上的元素在正确的位置上。
public int[] findErrorNums(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
while (nums[i] != i + 1 && nums[nums[i] - 1] != nums[i]) {
swap(nums, i, nums[i] - 1);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] != i + 1) {
return new int[]{nums[i], i + 1};
}
}
return null;
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
7. 找出数组中重复的数,数组值在 [1, n] 之间
要求不能修改数组,也不能使用额外的空间。
二分查找解法:
public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int l = 1, h = nums.length - 1;
while (l <= h) {
int mid = l + (h - l) / 2;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] <= mid) cnt++;
}
if (cnt > mid) h = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l;
}
双指针解法,类似于有环链表中找出环的入口:
public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int slow = nums[0], fast = nums[nums[0]];
while (slow != fast) {
slow = nums[slow];
fast = nums[nums[fast]];
}
fast = 0;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = nums[slow];
fast = nums[fast];
}
return slow;
}
8. 数组相邻差值的个数
Input: n = 3, k = 2
Output: [1, 3, 2]
Explanation: The [1, 3, 2] has three different positive integers ranging from 1 to 3, and the [2, 1] has exactly 2 distinct integers: 1 and 2.
题目描述:数组元素为 1~n 的整数,要求构建数组,使得相邻元素的差值不相同的个数为 k。
让前 k+1 个元素构建出 k 个不相同的差值,序列为:1 k+1 2 k 3 k-1 … k/2 k/2+1.
public int[] constructArray(int n, int k) {
int[] ret = new int[n];
ret[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1, interval = k; i <= k; i++, interval--) {
ret[i] = i % 2 == 1 ? ret[i - 1] + interval : ret[i - 1] - interval;
}
for (int i = k + 1; i < n; i++) {
ret[i] = i + 1;
}
return ret;
}
9. 数组的度
Input: [1,2,2,3,1,4,2]
Output: 6
题目描述:数组的度定义为元素出现的最高频率,例如上面的数组度为 3。要求找到一个最小的子数组,这个子数组的度和原数组一样。
public int findShortestSubArray(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> numsCnt = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> numsLastIndex = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> numsFirstIndex = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int num = nums[i];
numsCnt.put(num, numsCnt.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
numsLastIndex.put(num, i);
if (!numsFirstIndex.containsKey(num)) {
numsFirstIndex.put(num, i);
}
}
int maxCnt = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
maxCnt = Math.max(maxCnt, numsCnt.get(num));
}
int ret = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int num = nums[i];
int cnt = numsCnt.get(num);
if (cnt != maxCnt) continue;
ret = Math.min(ret, numsLastIndex.get(num) - numsFirstIndex.get(num) + 1);
}
return ret;
}
10. 对角元素相等的矩阵
1234
5123
9512
In the above grid, the diagonals are "[9]", "[5, 5]", "[1, 1, 1]", "[2, 2, 2]", "[3, 3]", "[4]", and in each diagonal all elements are the same, so the answer is True.
public boolean isToeplitzMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
for (int i = 0; i < matrix[0].length; i++) {
if (!check(matrix, matrix[0][i], 0, i)) {
return false;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
if (!check(matrix, matrix[i][0], i, 0)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean check(int[][] matrix, int expectValue, int row, int col) {
if (row >= matrix.length || col >= matrix[0].length) {
return true;
}
if (matrix[row][col] != expectValue) {
return false;
}
return check(matrix, expectValue, row + 1, col + 1);
}
11. 嵌套数组
Input: A = [5,4,0,3,1,6,2]
Output: 4
Explanation:
A[0] = 5, A[1] = 4, A[2] = 0, A[3] = 3, A[4] = 1, A[5] = 6, A[6] = 2.
One of the longest S[K]:
S[0] = {A[0], A[5], A[6], A[2]} = {5, 6, 2, 0}
题目描述:S[i] 表示一个集合,集合的第一个元素是 A[i],第二个元素是 A[A[i]],如此嵌套下去。求最大的 S[i]。
public int arrayNesting(int[] nums) {
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int j = i; nums[j] != -1; ) {
cnt++;
int t = nums[j];
nums[j] = -1; // 标记该位置已经被访问
j = t;
}
max = Math.max(max, cnt);
}
return max;
}
12. 分隔数组
Input: arr = [1,0,2,3,4]
Output: 4
Explanation:
We can split into two chunks, such as [1, 0], [2, 3, 4].
However, splitting into [1, 0], [2], [3], [4] is the highest number of chunks possible.
题目描述:分隔数组,使得对每部分排序后数组就为有序。
public int maxChunksToSorted(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null) return 0;
int ret = 0;
int right = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
right = Math.max(right, arr[i]);
if (right == i) ret++;
}
return ret;
}
双指针
双指针主要用于遍历数组,两个指针指向不同的元素,从而协同完成任务。
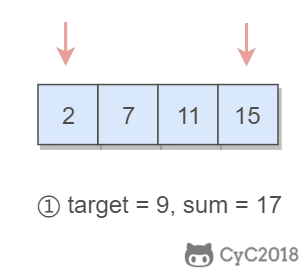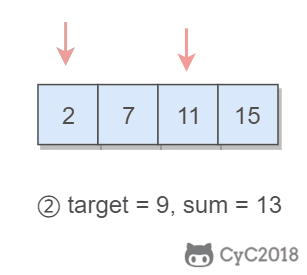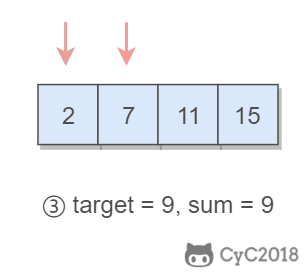
1. 有序数组的 Two Sum
Input: numbers={2, 7, 11, 15}, target=9
Output: index1=1, index2=2
题目描述:在有序数组中找出两个数,使它们的和为 target。
使用双指针,一个指针指向值较小的元素,一个指针指向值较大的元素。指向较小元素的指针从头向尾遍历,指向较大元素的指针从尾向头遍历。
- 如果两个指针指向元素的和 sum == target,那么得到要求的结果;
- 如果 sum > target,移动较大的元素,使 sum 变小一些;
- 如果 sum < target,移动较小的元素,使 sum 变大一些。
数组中的元素最多遍历一次,时间复杂度为 O(N)。只使用了两个额外变量,空间复杂度为 O(1)。
public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
if (numbers == null) return null;
int i = 0, j = numbers.length - 1;
while (i < j) {
int sum = numbers[i] + numbers[j];
if (sum == target) {
return new int[]{i + 1, j + 1};
} else if (sum < target) {
i++;
} else {
j--;
}
}
return null;
}
2. 两数平方和
Input: 5
Output: True
Explanation: 1 * 1 + 2 * 2 = 5
题目描述:判断一个非负整数是否为两个整数的平方和。
可以看成是在元素为 0~target 的有序数组中查找两个数,使得这两个数的平方和为 target,如果能找到,则返回 true,表示 target 是两个整数的平方和。
本题和 167. Two Sum II - Input array is sorted 类似,只有一个明显区别:一个是和为 target,一个是平方和为 target。本题同样可以使用双指针得到两个数,使其平方和为 target。
本题的关键是右指针的初始化,实现剪枝,从而降低时间复杂度。设右指针为 x,左指针固定为 0,为了使 02 + x2 的值尽可能接近 target,我们可以将 x 取为 sqrt(target)。
因为最多只需要遍历一次 0~sqrt(target),所以时间复杂度为 O(sqrt(target))。又因为只使用了两个额外的变量,因此空间复杂度为 O(1)。
public boolean judgeSquareSum(int target) {
if (target < 0) return false;
int i = 0, j = (int) Math.sqrt(target);
while (i <= j) {
int powSum = i * i + j * j;
if (powSum == target) {
return true;
} else if (powSum > target) {
j--;
} else {
i++;
}
}
return false;
}
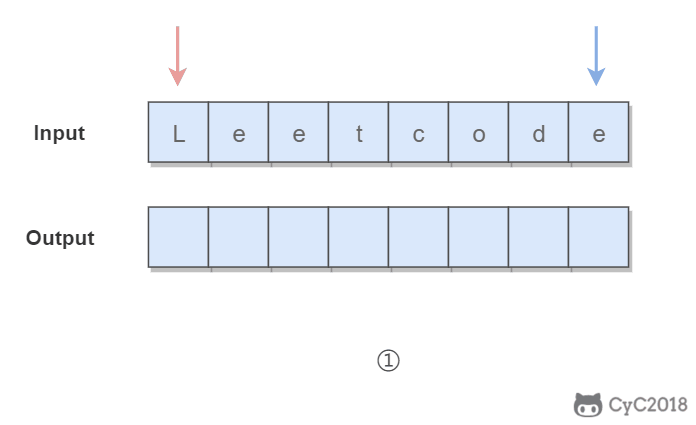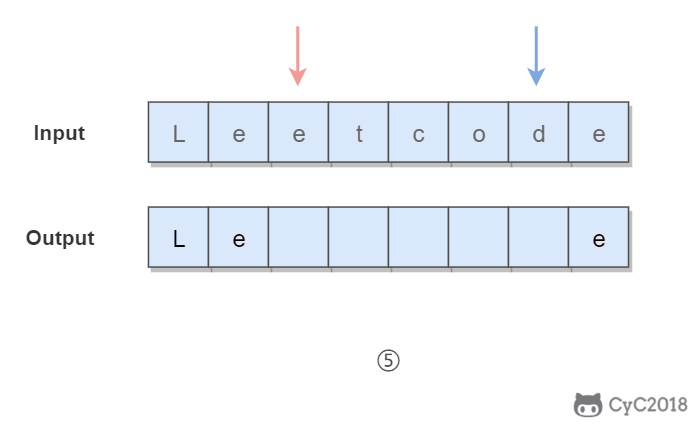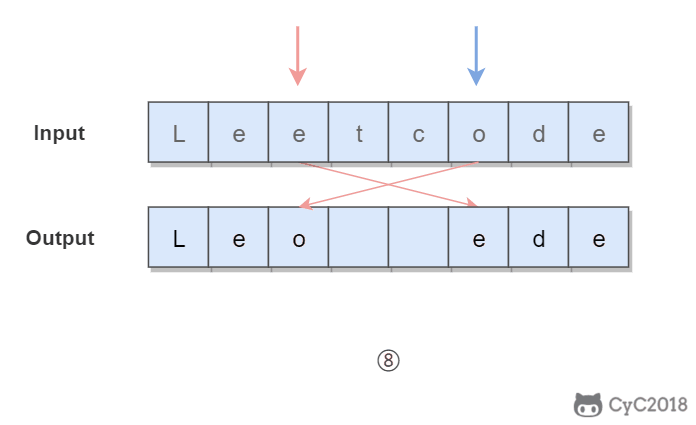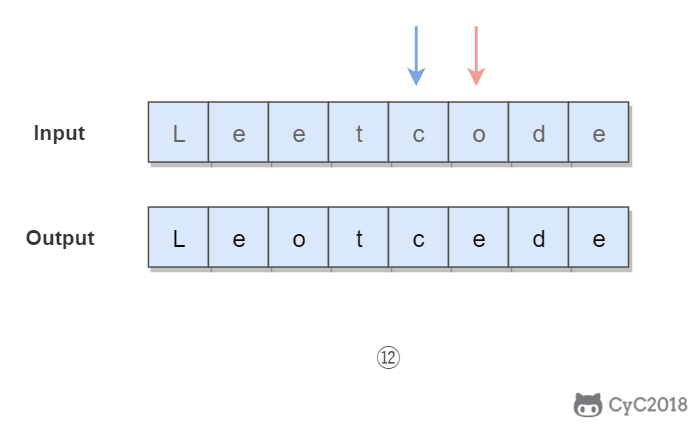
3. 反转字符串中的元音字符
Given s = "leetcode", return "leotcede".
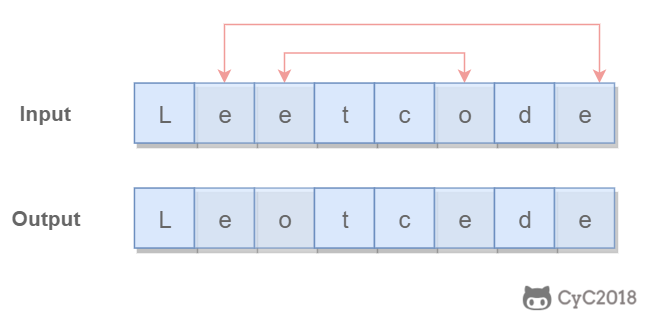
使用双指针,一个指针从头向尾遍历,一个指针从尾到头遍历,当两个指针都遍历到元音字符时,交换这两个元音字符。
为了快速判断一个字符是不是元音字符,我们将全部元音字符添加到集合 HashSet 中,从而以 O(1) 的时间复杂度进行该操作。
- 时间复杂度为 O(N):只需要遍历所有元素一次
- 空间复杂度 O(1):只需要使用两个额外变量
private final static HashSet<Character> vowels = new HashSet<>(
Arrays.asList('a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u', 'A', 'E', 'I', 'O', 'U'));
public String reverseVowels(String s) {
if (s == null) return null;
int i = 0, j = s.length() - 1;
char[] result = new char[s.length()];
while (i <= j) {
char ci = s.charAt(i);
char cj = s.charAt(j);
if (!vowels.contains(ci)) {
result[i++] = ci;
} else if (!vowels.contains(cj)) {
result[j--] = cj;
} else {
result[i++] = cj;
result[j--] = ci;
}
}
return new String(result);
}
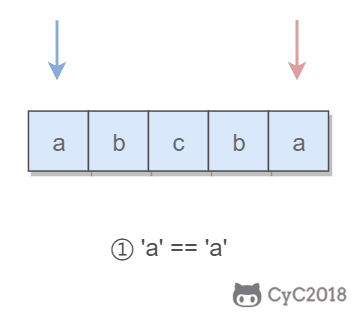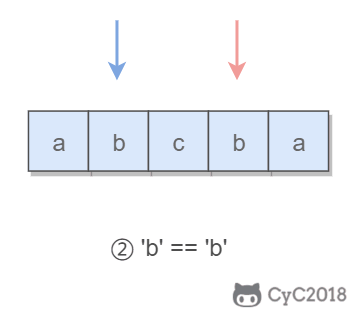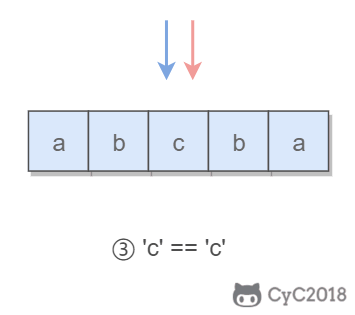
4. 回文字符串
Input: "abca"
Output: True
Explanation: You could delete the character 'c'.
题目描述:可以删除一个字符,判断是否能构成回文字符串。
所谓的回文字符串,是指具有左右对称特点的字符串,例如 “abcba” 就是一个回文字符串。
使用双指针可以很容易判断一个字符串是否是回文字符串:令一个指针从左到右遍历,一个指针从右到左遍历,这两个指针同时移动一个位置,每次都判断两个指针指向的字符是否相同,如果都相同,字符串才是具有左右对称性质的回文字符串。
本题的关键是处理删除一个字符。在使用双指针遍历字符串时,如果出现两个指针指向的字符不相等的情况,我们就试着删除一个字符,再判断删除完之后的字符串是否是回文字符串。
在判断是否为回文字符串时,我们不需要判断整个字符串,因为左指针左边和右指针右边的字符之前已经判断过具有对称性质,所以只需要判断中间的子字符串即可。
在试着删除字符时,我们既可以删除左指针指向的字符,也可以删除右指针指向的字符。
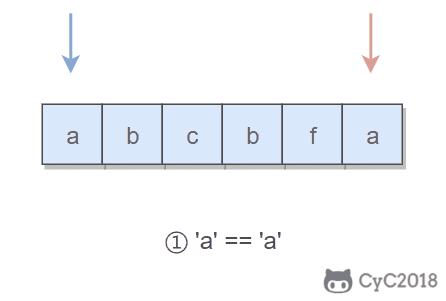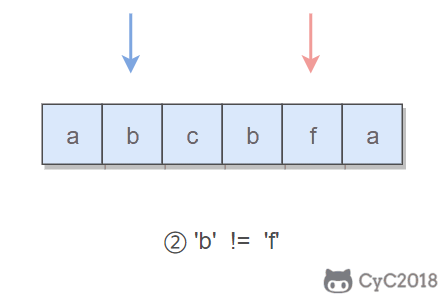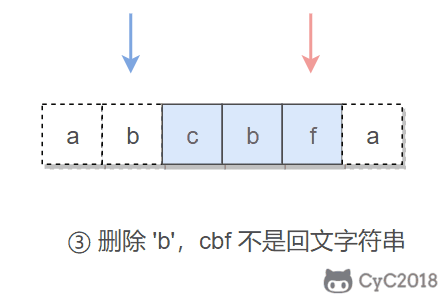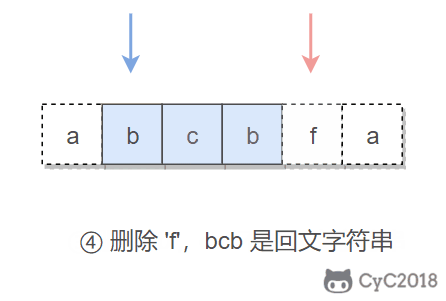
public boolean validPalindrome(String s) {
for (int i = 0, j = s.length() - 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) {
return isPalindrome(s, i, j - 1) || isPalindrome(s, i + 1, j);
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean isPalindrome(String s, int i, int j) {
while (i < j) {
if (s.charAt(i++) != s.charAt(j--)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
5. 归并两个有序数组
Input:
nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
题目描述:把归并结果存到第一个数组上。
需要从尾开始遍历,否则在 nums1 上归并得到的值会覆盖还未进行归并比较的值。
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int index1 = m - 1, index2 = n - 1;
int indexMerge = m + n - 1;
while (index2 >= 0) {
if (index1 < 0) {
nums1[indexMerge--] = nums2[index2--];
} else if (index2 < 0) {
nums1[indexMerge--] = nums1[index1--];
} else if (nums1[index1] > nums2[index2]) {
nums1[indexMerge--] = nums1[index1--];
} else {
nums1[indexMerge--] = nums2[index2--];
}
}
}
6. 判断链表是否存在环
141. Linked List Cycle (Easy)
使用双指针,一个指针每次移动一个节点,一个指针每次移动两个节点,如果存在环,那么这两个指针一定会相遇。
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode l1 = head, l2 = head.next;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null && l2.next != null) {
if (l1 == l2) {
return true;
}
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next.next;
}
return false;
}
7. 最长子序列
Input:
s = "abpcplea", d = ["ale","apple","monkey","plea"]
Output:
"apple"
题目描述:删除 s 中的一些字符,使得它构成字符串列表 d 中的一个字符串,找出能构成的最长字符串。如果有多个相同长度的结果,返回字典序的最小字符串。
通过删除字符串 s 中的一个字符能得到字符串 t,可以认为 t 是 s 的子序列,我们可以使用双指针来判断一个字符串是否为另一个字符串的子序列。
public String findLongestWord(String s, List<String> d) {
String longestWord = "";
for (String target : d) {
int l1 = longestWord.length(), l2 = target.length();
if (l1 > l2 || (l1 == l2 && longestWord.compareTo(target) < 0)) {
continue;
}
if (isSubstr(s, target)) {
longestWord = target;
}
}
return longestWord;
}
private boolean isSubstr(String s, String target) {
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < s.length() && j < target.length()) {
if (s.charAt(i) == target.charAt(j)) {
j++;
}
i++;
}
return j == target.length();
}
搜索
深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索广泛运用于树和图中,但是它们的应用远远不止如此。
BFS
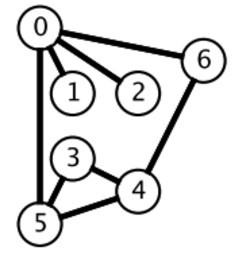
广度优先搜索一层一层地进行遍历,每层遍历都是以上一层遍历的结果作为起点,遍历一个距离能访问到的所有节点。需要注意的是,遍历过的节点不能再次被遍历。
第一层:
- 0 -> {6,2,1,5}
第二层:
- 6 -> {4}
- 2 -> {}
- 1 -> {}
- 5 -> {3}
第三层:
- 4 -> {}
- 3 -> {}
每一层遍历的节点都与根节点距离相同。设 di 表示第 i 个节点与根节点的距离,推导出一个结论:对于先遍历的节点 i 与后遍历的节点 j,有 di <= dj。利用这个结论,可以求解最短路径等 最优解 问题:第一次遍历到目的节点,其所经过的路径为最短路径。应该注意的是,使用 BFS 只能求解无权图的最短路径,无权图是指从一个节点到另一个节点的代价都记为 1。
在程序实现 BFS 时需要考虑以下问题:
- 队列:用来存储每一轮遍历得到的节点;
- 标记:对于遍历过的节点,应该将它标记,防止重复遍历。
1. 计算在网格中从原点到特定点的最短路径长度
[[1,1,0,1],
[1,0,1,0],
[1,1,1,1],
[1,0,1,1]]
题目描述:0 表示可以经过某个位置,求解从左上角到右下角的最短路径长度。
public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grids) {
if (grids == null || grids.length == 0 || grids[0].length == 0) {
return -1;
}
int[][] direction = {{1, -1}, {1, 0}, {1, 1}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, -1}, {-1, 0}, {-1, 1}};
int m = grids.length, n = grids[0].length;
Queue<Pair<Integer, Integer>> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new Pair<>(0, 0));
int pathLength = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
pathLength++;
while (size-- > 0) {
Pair<Integer, Integer> cur = queue.poll();
int cr = cur.getKey(), cc = cur.getValue();
if (grids[cr][cc] == 1) {
continue;
}
if (cr == m - 1 && cc == n - 1) {
return pathLength;
}
grids[cr][cc] = 1; // 标记
for (int[] d : direction) {
int nr = cr + d[0], nc = cc + d[1];
if (nr < 0 || nr >= m || nc < 0 || nc >= n) {
continue;
}
queue.add(new Pair<>(nr, nc));
}
}
}
return -1;
}
2. 组成整数的最小平方数数量
279. Perfect Squares (Medium)
Leetcode / 力扣
For example, given n = 12, return 3 because 12 = 4 + 4 + 4; given n = 13, return 2 because 13 = 4 + 9.
可以将每个整数看成图中的一个节点,如果两个整数之差为一个平方数,那么这两个整数所在的节点就有一条边。
要求解最小的平方数数量,就是求解从节点 n 到节点 0 的最短路径。
本题也可以用动态规划求解,在之后动态规划部分中会再次出现。
public int numSquares(int n) {
List<Integer> squares = generateSquares(n);
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] marked = new boolean[n + 1];
queue.add(n);
marked[n] = true;
int level = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
level++;
while (size-- > 0) {
int cur = queue.poll();
for (int s : squares) {
int next = cur - s;
if (next < 0) {
break;
}
if (next == 0) {
return level;
}
if (marked[next]) {
continue;
}
marked[next] = true;
queue.add(next);
}
}
}
return n;
}
/**
* 生成小于 n 的平方数序列
* @return 1,4,9,...
*/
private List<Integer> generateSquares(int n) {
List<Integer> squares = new ArrayList<>();
int square = 1;
int diff = 3;
while (square <= n) {
squares.add(square);
square += diff;
diff += 2;
}
return squares;
}
3. 最短单词路径
Input:
beginWord = "hit",
endWord = "cog",
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
Output: 5
Explanation: As one shortest transformation is "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog",
return its length 5.
Input:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
Output: 0
Explanation: The endWord "cog" is not in wordList, therefore no possible transformation.
题目描述:找出一条从 beginWord 到 endWord 的最短路径,每次移动规定为改变一个字符,并且改变之后的字符串必须在 wordList 中。
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
wordList.add(beginWord);
int N = wordList.size();
int start = N - 1;
int end = 0;
while (end < N && !wordList.get(end).equals(endWord)) {
end++;
}
if (end == N) {
return 0;
}
List<Integer>[] graphic = buildGraphic(wordList);
return getShortestPath(graphic, start, end);
}
private List<Integer>[] buildGraphic(List<String> wordList) {
int N = wordList.size();
List<Integer>[] graphic = new List[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
graphic[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (isConnect(wordList.get(i), wordList.get(j))) {
graphic[i].add(j);
}
}
}
return graphic;
}
private boolean isConnect(String s1, String s2) {
int diffCnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length() && diffCnt <= 1; i++) {
if (s1.charAt(i) != s2.charAt(i)) {
diffCnt++;
}
}
return diffCnt == 1;
}
private int getShortestPath(List<Integer>[] graphic, int start, int end) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] marked = new boolean[graphic.length];
queue.add(start);
marked[start] = true;
int path = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
path++;
while (size-- > 0) {
int cur = queue.poll();
for (int next : graphic[cur]) {
if (next == end) {
return path;
}
if (marked[next]) {
continue;
}
marked[next] = true;
queue.add(next);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
DFS
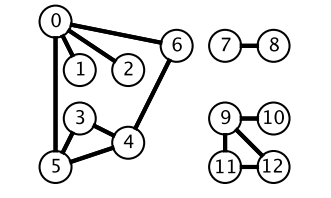
广度优先搜索一层一层遍历,每一层得到的所有新节点,要用队列存储起来以备下一层遍历的时候再遍历。
而深度优先搜索在得到一个新节点时立即对新节点进行遍历:从节点 0 出发开始遍历,得到到新节点 6 时,立马对新节点 6 进行遍历,得到新节点 4;如此反复以这种方式遍历新节点,直到没有新节点了,此时返回。返回到根节点 0 的情况是,继续对根节点 0 进行遍历,得到新节点 2,然后继续以上步骤。
从一个节点出发,使用 DFS 对一个图进行遍历时,能够遍历到的节点都是从初始节点可达的,DFS 常用来求解这种 可达性 问题。
在程序实现 DFS 时需要考虑以下问题:
- 栈:用栈来保存当前节点信息,当遍历新节点返回时能够继续遍历当前节点。可以使用递归栈。
- 标记:和 BFS 一样同样需要对已经遍历过的节点进行标记。
1. 查找最大的连通面积
[[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],
[0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]]
private int m, n;
private int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
m = grid.length;
n = grid[0].length;
int maxArea = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, dfs(grid, i, j));
}
}
return maxArea;
}
private int dfs(int[][] grid, int r, int c) {
if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n || grid[r][c] == 0) {
return 0;
}
grid[r][c] = 0;
int area = 1;
for (int[] d : direction) {
area += dfs(grid, r + d[0], c + d[1]);
}
return area;
}
2. 矩阵中的连通分量数目
Input:
11000
11000
00100
00011
Output: 3
可以将矩阵表示看成一张有向图。
private int m, n;
private int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
m = grid.length;
n = grid[0].length;
int islandsNum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] != '0') {
dfs(grid, i, j);
islandsNum++;
}
}
}
return islandsNum;
}
private void dfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j) {
if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || grid[i][j] == '0') {
return;
}
grid[i][j] = '0';
for (int[] d : direction) {
dfs(grid, i + d[0], j + d[1]);
}
}
3. 好友关系的连通分量数目
Input:
[[1,1,0],
[1,1,0],
[0,0,1]]
Output: 2
Explanation:The 0th and 1st students are direct friends, so they are in a friend circle.
The 2nd student himself is in a friend circle. So return 2.
题目描述:好友关系可以看成是一个无向图,例如第 0 个人与第 1 个人是好友,那么 M[0][1] 和 M[1][0] 的值都为 1。
private int n;
public int findCircleNum(int[][] M) {
n = M.length;
int circleNum = 0;
boolean[] hasVisited = new boolean[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!hasVisited[i]) {
dfs(M, i, hasVisited);
circleNum++;
}
}
return circleNum;
}
private void dfs(int[][] M, int i, boolean[] hasVisited) {
hasVisited[i] = true;
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
if (M[i][k] == 1 && !hasVisited[k]) {
dfs(M, k, hasVisited);
}
}
}
4. 填充封闭区域
For example,
X X X X
X O O X
X X O X
X O X X
After running your function, the board should be:
X X X X
X X X X
X X X X
X O X X
题目描述:使被 ‘X’ 包围的 ‘O’ 转换为 ‘X’。
先填充最外侧,剩下的就是里侧了。
private int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
private int m, n;
public void solve(char[][] board) {
if (board == null || board.length == 0) {
return;
}
m = board.length;
n = board[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dfs(board, i, 0);
dfs(board, i, n - 1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dfs(board, 0, i);
dfs(board, m - 1, i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'T') {
board[i][j] = 'O';
} else if (board[i][j] == 'O') {
board[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
}
private void dfs(char[][] board, int r, int c) {
if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n || board[r][c] != 'O') {
return;
}
board[r][c] = 'T';
for (int[] d : direction) {
dfs(board, r + d[0], c + d[1]);
}
}
5. 能到达的太平洋和大西洋的区域
Given the following 5x5 matrix:
Pacific ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
~ 1 2 2 3 (5) *
~ 3 2 3 (4) (4) *
~ 2 4 (5) 3 1 *
~ (6) (7) 1 4 5 *
~ (5) 1 1 2 4 *
* * * * * Atlantic
Return:
[[0, 4], [1, 3], [1, 4], [2, 2], [3, 0], [3, 1], [4, 0]] (positions with parentheses in above matrix).
左边和上边是太平洋,右边和下边是大西洋,内部的数字代表海拔,海拔高的地方的水能够流到低的地方,求解水能够流到太平洋和大西洋的所有位置。
private int m, n;
private int[][] matrix;
private int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) {
return ret;
}
m = matrix.length;
n = matrix[0].length;
this.matrix = matrix;
boolean[][] canReachP = new boolean[m][n];
boolean[][] canReachA = new boolean[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dfs(i, 0, canReachP);
dfs(i, n - 1, canReachA);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dfs(0, i, canReachP);
dfs(m - 1, i, canReachA);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (canReachP[i][j] && canReachA[i][j]) {
ret.add(Arrays.asList(i, j));
}
}
}
return ret;
}
private void dfs(int r, int c, boolean[][] canReach) {
if (canReach[r][c]) {
return;
}
canReach[r][c] = true;
for (int[] d : direction) {
int nextR = d[0] + r;
int nextC = d[1] + c;
if (nextR < 0 || nextR >= m || nextC < 0 || nextC >= n
|| matrix[r][c] > matrix[nextR][nextC]) {
continue;
}
dfs(nextR, nextC, canReach);
}
}
Backtracking
Backtracking(回溯)属于 DFS。
- 普通 DFS 主要用在 可达性问题 ,这种问题只需要执行到特点的位置然后返回即可。
- 而 Backtracking 主要用于求解 排列组合 问题,例如有 { ‘a’,‘b’,‘c’ } 三个字符,求解所有由这三个字符排列得到的字符串,这种问题在执行到特定的位置返回之后还会继续执行求解过程。
因为 Backtracking 不是立即返回,而要继续求解,因此在程序实现时,需要注意对元素的标记问题:
- 在访问一个新元素进入新的递归调用时,需要将新元素标记为已经访问,这样才能在继续递归调用时不用重复访问该元素;
- 但是在递归返回时,需要将元素标记为未访问,因为只需要保证在一个递归链中不同时访问一个元素,可以访问已经访问过但是不在当前递归链中的元素。
1. 数字键盘组合
17. Letter Combinations of a Phone Number (Medium)

Input:Digit string "23"
Output: ["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].
private static final String[] KEYS = {"", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
List<String> combinations = new ArrayList<>();
if (digits == null || digits.length() == 0) {
return combinations;
}
doCombination(new StringBuilder(), combinations, digits);
return combinations;
}
private void doCombination(StringBuilder prefix, List<String> combinations, final String digits) {
if (prefix.length() == digits.length()) {
combinations.add(prefix.toString());
return;
}
int curDigits = digits.charAt(prefix.length()) - '0';
String letters = KEYS[curDigits];
for (char c : letters.toCharArray()) {
prefix.append(c); // 添加
doCombination(prefix, combinations, digits);
prefix.deleteCharAt(prefix.length() - 1); // 删除
}
}
2. IP 地址划分
93. Restore IP Addresses(Medium)
Given "25525511135",
return ["255.255.11.135", "255.255.111.35"].
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
List<String> addresses = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder tempAddress = new StringBuilder();
doRestore(0, tempAddress, addresses, s);
return addresses;
}
private void doRestore(int k, StringBuilder tempAddress, List<String> addresses, String s) {
if (k == 4 || s.length() == 0) {
if (k == 4 && s.length() == 0) {
addresses.add(tempAddress.toString());
}
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.length() && i <= 2; i++) {
if (i != 0 && s.charAt(0) == '0') {
break;
}
String part = s.substring(0, i + 1);
if (Integer.valueOf(part) <= 255) {
if (tempAddress.length() != 0) {
part = "." + part;
}
tempAddress.append(part);
doRestore(k + 1, tempAddress, addresses, s.substring(i + 1));
tempAddress.delete(tempAddress.length() - part.length(), tempAddress.length());
}
}
}
3. 在矩阵中寻找字符串
For example,
Given board =
[
['A','B','C','E'],
['S','F','C','S'],
['A','D','E','E']
]
word = "ABCCED", -> returns true,
word = "SEE", -> returns true,
word = "ABCB", -> returns false.
private final static int[][] direction = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
private int m;
private int n;
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
if (word == null || word.length() == 0) {
return true;
}
if (board == null || board.length == 0 || board[0].length == 0) {
return false;
}
m = board.length;
n = board[0].length;
boolean[][] hasVisited = new boolean[m][n];
for (int r = 0; r < m; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < n; c++) {
if (backtracking(0, r, c, hasVisited, board, word)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean backtracking(int curLen, int r, int c, boolean[][] visited, final char[][] board, final String word) {
if (curLen == word.length()) {
return true;
}
if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n
|| board[r][c] != word.charAt(curLen) || visited[r][c]) {
return false;
}
visited[r][c] = true;
for (int[] d : direction) {
if (backtracking(curLen + 1, r + d[0], c + d[1], visited, board, word)) {
return true;
}
}
visited[r][c] = false;
return false;
}
4. 输出二叉树中所有从根到叶子的路径
1
/
2 3
5
["1->2->5", "1->3"]
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> paths = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return paths;
}
List<Integer> values = new ArrayList<>();
backtracking(root, values, paths);
return paths;
}
private void backtracking(TreeNode node, List<Integer> values, List<String> paths) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
values.add(node.val);
if (isLeaf(node)) {
paths.add(buildPath(values));
} else {
backtracking(node.left, values, paths);
backtracking(node.right, values, paths);
}
values.remove(values.size() - 1);
}
private boolean isLeaf(TreeNode node) {
return node.left == null && node.right == null;
}
private String buildPath(List<Integer> values) {
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < values.size(); i++) {
str.append(values.get(i));
if (i != values.size() - 1) {
str.append("->");
}
}
return str.toString();
}
5. 排列
[1,2,3] have the following permutations:
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
]
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> permutes = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> permuteList = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] hasVisited = new boolean[nums.length];
backtracking(permuteList, permutes, hasVisited, nums);
return permutes;
}
private void backtracking(List<Integer> permuteList, List<List<Integer>> permutes, boolean[] visited, final int[] nums) {
if (permuteList.size() == nums.length) {
permutes.add(new ArrayList<>(permuteList)); // 重新构造一个 List
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++) {
if (visited[i]) {
continue;
}
visited[i] = true;
permuteList.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(permuteList, permutes, visited, nums);
permuteList.remove(permuteList.size() - 1);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
6. 含有相同元素求排列
[1,1,2] have the following unique permutations:
[[1,1,2], [1,2,1], [2,1,1]]
数组元素可能含有相同的元素,进行排列时就有可能出现重复的排列,要求重复的排列只返回一个。
在实现上,和 Permutations 不同的是要先排序,然后在添加一个元素时,判断这个元素是否等于前一个元素,如果等于,并且前一个元素还未访问,那么就跳过这个元素。
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> permutes = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> permuteList = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums); // 排序
boolean[] hasVisited = new boolean[nums.length];
backtracking(permuteList, permutes, hasVisited, nums);
return permutes;
}
private void backtracking(List<Integer> permuteList, List<List<Integer>> permutes, boolean[] visited, final int[] nums) {
if (permuteList.size() == nums.length) {
permutes.add(new ArrayList<>(permuteList));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++) {
if (i != 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !visited[i - 1]) {
continue; // 防止重复
}
if (visited[i]){
continue;
}
visited[i] = true;
permuteList.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(permuteList, permutes, visited, nums);
permuteList.remove(permuteList.size() - 1);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
7. 组合
If n = 4 and k = 2, a solution is:
[
[2,4],
[3,4],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[1,3],
[1,4],
]
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> combinations = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> combineList = new ArrayList<>();
backtracking(combineList, combinations, 1, k, n);
return combinations;
}
private void backtracking(List<Integer> combineList, List<List<Integer>> combinations, int start, int k, final int n) {
if (k == 0) {
combinations.add(new ArrayList<>(combineList));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i <= n - k + 1; i++) { // 剪枝
combineList.add(i);
backtracking(combineList, combinations, i + 1, k - 1, n);
combineList.remove(combineList.size() - 1);
}
}
8. 组合求和
given candidate set [2, 3, 6, 7] and target 7,
A solution set is:
[[7],[2, 2, 3]]
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> combinations = new ArrayList<>();
backtracking(new ArrayList<>(), combinations, 0, target, candidates);
return combinations;
}
private void backtracking(List<Integer> tempCombination, List<List<Integer>> combinations,
int start, int target, final int[] candidates) {
if (target == 0) {
combinations.add(new ArrayList<>(tempCombination));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (candidates[i] <= target) {
tempCombination.add(candidates[i]);
backtracking(tempCombination, combinations, i, target - candidates[i], candidates);
tempCombination.remove(tempCombination.size() - 1);
}
}
}
9. 含有相同元素的组合求和
For example, given candidate set [10, 1, 2, 7, 6, 1, 5] and target 8,
A solution set is:
[
[1, 7],
[1, 2, 5],
[2, 6],
[1, 1, 6]
]
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> combinations = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backtracking(new ArrayList<>(), combinations, new boolean[candidates.length], 0, target, candidates);
return combinations;
}
private void backtracking(List<Integer> tempCombination, List<List<Integer>> combinations,
boolean[] hasVisited, int start, int target, final int[] candidates) {
if (target == 0) {
combinations.add(new ArrayList<>(tempCombination));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (i != 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && !hasVisited[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
if (candidates[i] <= target) {
tempCombination.add(candidates[i]);
hasVisited[i] = true;
backtracking(tempCombination, combinations, hasVisited, i + 1, target - candidates[i], candidates);
hasVisited[i] = false;
tempCombination.remove(tempCombination.size() - 1);
}
}
}
10. 1-9 数字的组合求和
Input: k = 3, n = 9
Output:
[[1,2,6], [1,3,5], [2,3,4]]
从 1-9 数字中选出 k 个数不重复的数,使得它们的和为 n。
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
List<List<Integer>> combinations = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
backtracking(k, n, 1, path, combinations);
return combinations;
}
private void backtracking(int k, int n, int start,
List<Integer> tempCombination, List<List<Integer>> combinations) {
if (k == 0 && n == 0) {
combinations.add(new ArrayList<>(tempCombination));
return;
}
if (k == 0 || n == 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = start; i <= 9; i++) {
tempCombination.add(i);
backtracking(k - 1, n - i, i + 1, tempCombination, combinations);
tempCombination.remove(tempCombination.size() - 1);
}
}
11. 子集
找出集合的所有子集,子集不能重复,[1, 2] 和 [2, 1] 这种子集算重复
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> subsets = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> tempSubset = new ArrayList<>();
for (int size = 0; size <= nums.length; size++) {
backtracking(0, tempSubset, subsets, size, nums); // 不同的子集大小
}
return subsets;
}
private void backtracking(int start, List<Integer> tempSubset, List<List<Integer>> subsets,
final int size, final int[] nums) {
if (tempSubset.size() == size) {
subsets.add(new ArrayList<>(tempSubset));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {
tempSubset.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(i + 1, tempSubset, subsets, size, nums);
tempSubset.remove(tempSubset.size() - 1);
}
}
12. 含有相同元素求子集
For example,
If nums = [1,2,2], a solution is:
[
[2],
[1],
[1,2,2],
[2,2],
[1,2],
[]
]
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> subsets = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> tempSubset = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] hasVisited = new boolean[nums.length];
for (int size = 0; size <= nums.length; size++) {
backtracking(0, tempSubset, subsets, hasVisited, size, nums); // 不同的子集大小
}
return subsets;
}
private void backtracking(int start, List<Integer> tempSubset, List<List<Integer>> subsets, boolean[] hasVisited,
final int size, final int[] nums) {
if (tempSubset.size() == size) {
subsets.add(new ArrayList<>(tempSubset));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (i != 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !hasVisited[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
tempSubset.add(nums[i]);
hasVisited[i] = true;
backtracking(i + 1, tempSubset, subsets, hasVisited, size, nums);
hasVisited[i] = false;
tempSubset.remove(tempSubset.size() - 1);
}
}
13. 分割字符串使得每个部分都是回文数
For example, given s = "aab",
Return
[
["aa","b"],
["a","a","b"]
]
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
List<List<String>> partitions = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> tempPartition = new ArrayList<>();
doPartition(s, partitions, tempPartition);
return partitions;
}
private void doPartition(String s, List<List<String>> partitions, List<String> tempPartition) {
if (s.length() == 0) {
partitions.add(new ArrayList<>(tempPartition));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (isPalindrome(s, 0, i)) {
tempPartition.add(s.substring(0, i + 1));
doPartition(s.substring(i + 1), partitions, tempPartition);
tempPartition.remove(tempPartition.size() - 1);
}
}
}
private boolean isPalindrome(String s, int begin, int end) {
while (begin < end) {
if (s.charAt(begin++) != s.charAt(end--)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
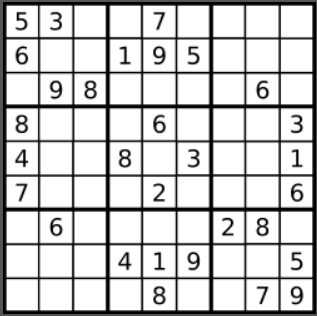
14. 数独
private boolean[][] rowsUsed = new boolean[9][10];
private boolean[][] colsUsed = new boolean[9][10];
private boolean[][] cubesUsed = new boolean[9][10];
private char[][] board;
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
this.board = board;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '.') {
continue;
}
int num = board[i][j] - '0';
rowsUsed[i][num] = true;
colsUsed[j][num] = true;
cubesUsed[cubeNum(i, j)][num] = true;
}
backtracking(0, 0);
}
private boolean backtracking(int row, int col) {
while (row < 9 && board[row][col] != '.') {
row = col == 8 ? row + 1 : row;
col = col == 8 ? 0 : col + 1;
}
if (row == 9) {
return true;
}
for (int num = 1; num <= 9; num++) {
if (rowsUsed[row][num] || colsUsed[col][num] || cubesUsed[cubeNum(row, col)][num]) {
continue;
}
rowsUsed[row][num] = colsUsed[col][num] = cubesUsed[cubeNum(row, col)][num] = true;
board[row][col] = (char) (num + '0');
if (backtracking(row, col)) {
return true;
}
board[row][col] = '.';
rowsUsed[row][num] = colsUsed[col][num] = cubesUsed[cubeNum(row, col)][num] = false;
}
return false;
}
private int cubeNum(int i, int j) {
int r = i / 3;
int c = j / 3;
return r * 3 + c;
}
15. N 皇后
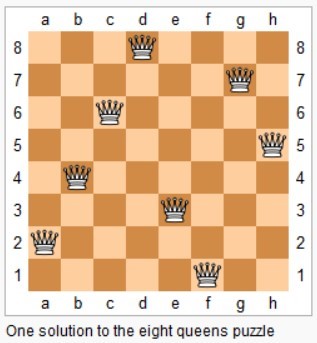
在 n*n 的矩阵中摆放 n 个皇后,并且每个皇后不能在同一行,同一列,同一对角线上,求所有的 n 皇后的解。
一行一行地摆放,在确定一行中的那个皇后应该摆在哪一列时,需要用三个标记数组来确定某一列是否合法,这三个标记数组分别为:列标记数组、45 度对角线标记数组和 135 度对角线标记数组。
45 度对角线标记数组的长度为 2 * n - 1,通过下图可以明确 (r, c) 的位置所在的数组下标为 r + c。
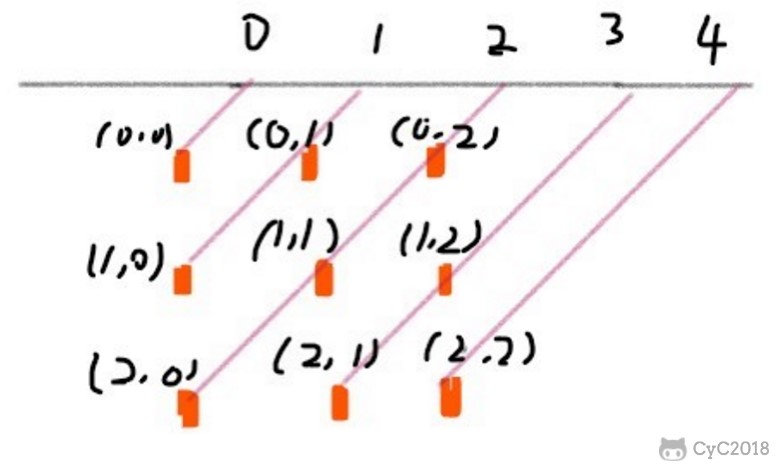
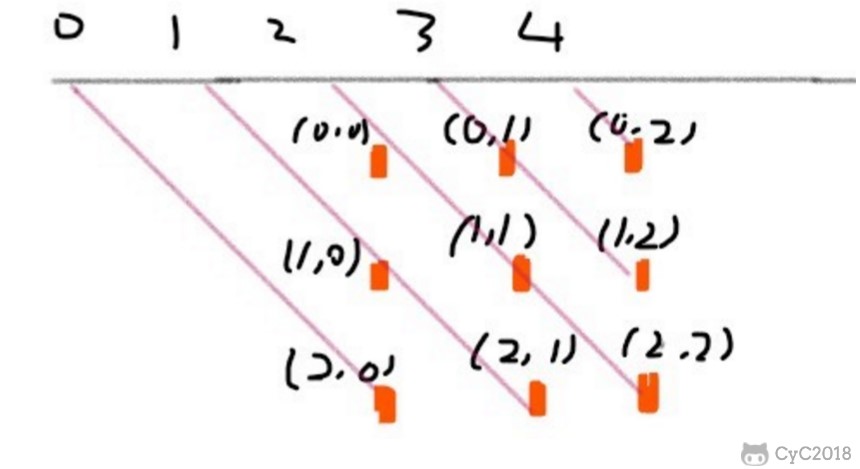
135 度对角线标记数组的长度也是 2 * n - 1,(r, c) 的位置所在的数组下标为 n - 1 - (r - c)。
private List<List<String>> solutions;
private char[][] nQueens;
private boolean[] colUsed;
private boolean[] diagonals45Used;
private boolean[] diagonals135Used;
private int n;
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
solutions = new ArrayList<>();
nQueens = new char[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(nQueens[i], '.');
}
colUsed = new boolean[n];
diagonals45Used = new boolean[2 * n - 1];
diagonals135Used = new boolean[2 * n - 1];
this.n = n;
backtracking(0);
return solutions;
}
private void backtracking(int row) {
if (row == n) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (char[] chars : nQueens) {
list.add(new String(chars));
}
solutions.add(list);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
int diagonals45Idx = row + col;
int diagonals135Idx = n - 1 - (row - col);
if (colUsed[col] || diagonals45Used[diagonals45Idx] || diagonals135Used[diagonals135Idx]) {
continue;
}
nQueens[row][col] = 'Q';
colUsed[col] = diagonals45Used[diagonals45Idx] = diagonals135Used[diagonals135Idx] = true;
backtracking(row + 1);
colUsed[col] = diagonals45Used[diagonals45Idx] = diagonals135Used[diagonals135Idx] = false;
nQueens[row][col] = '.';
}
}
贪心思想
保证每次操作都是局部最优的,并且最后得到的结果是全局最优的。
1. 分配饼干
Input: grid[1,3], size[1,2,4]
Output: 2
题目描述:每个孩子都有一个满足度 grid,每个饼干都有一个大小 size,只有饼干的大小大于等于一个孩子的满足度,该孩子才会获得满足。求解最多可以获得满足的孩子数量。
- 给一个孩子的饼干应当尽量小并且又能满足该孩子,这样大饼干才能拿来给满足度比较大的孩子。
- 因为满足度最小的孩子最容易得到满足,所以先满足满足度最小的孩子。
在以上的解法中,我们只在每次分配时饼干时选择一种看起来是当前最优的分配方法,但无法保证这种局部最优的分配方法最后能得到全局最优解。我们假设能得到全局最优解,并使用反证法进行证明,即假设存在一种比我们使用的贪心策略更优的最优策略。如果不存在这种最优策略,表示贪心策略就是最优策略,得到的解也就是全局最优解。
证明:假设在某次选择中,贪心策略选择给当前满足度最小的孩子分配第 m 个饼干,第 m 个饼干为可以满足该孩子的最小饼干。假设存在一种最优策略,可以给该孩子分配第 n 个饼干,并且 m < n。我们可以发现,经过这一轮分配,贪心策略分配后剩下的饼干一定有一个比最优策略来得大。因此在后续的分配中,贪心策略一定能满足更多的孩子。也就是说不存在比贪心策略更优的策略,即贪心策略就是最优策略。
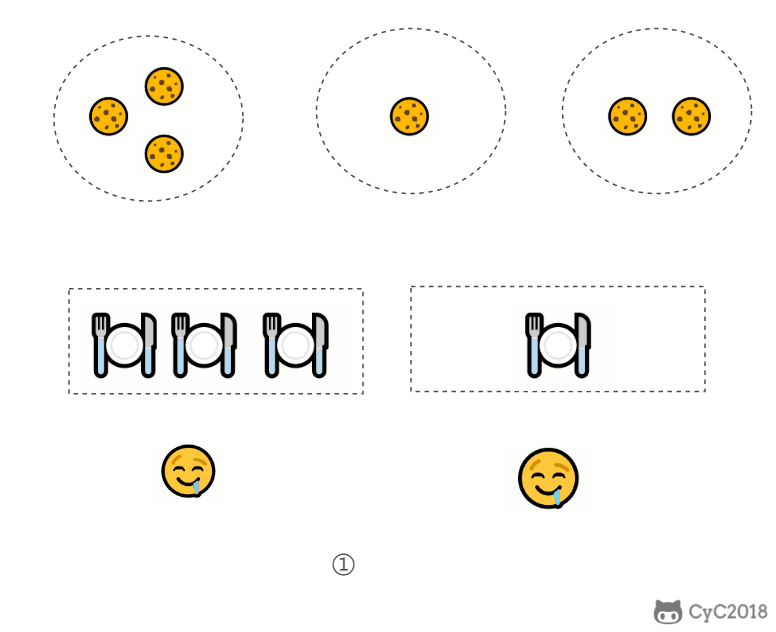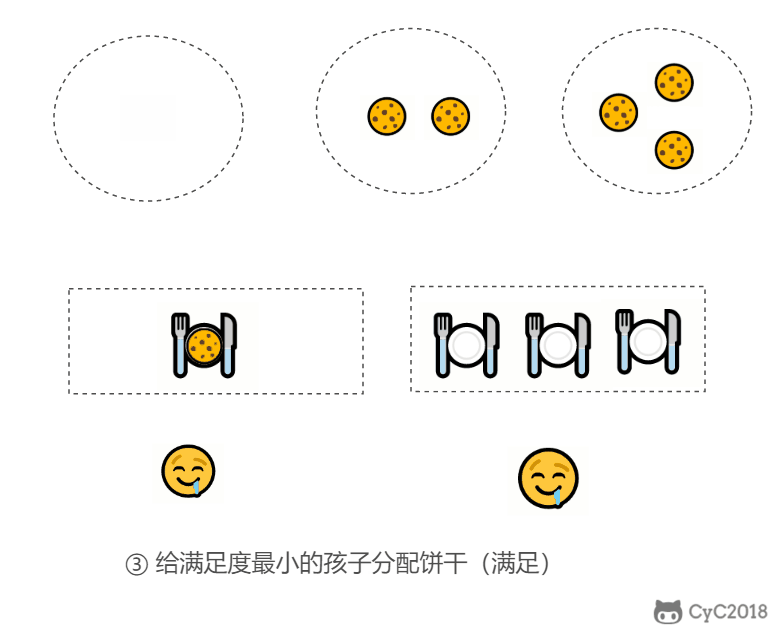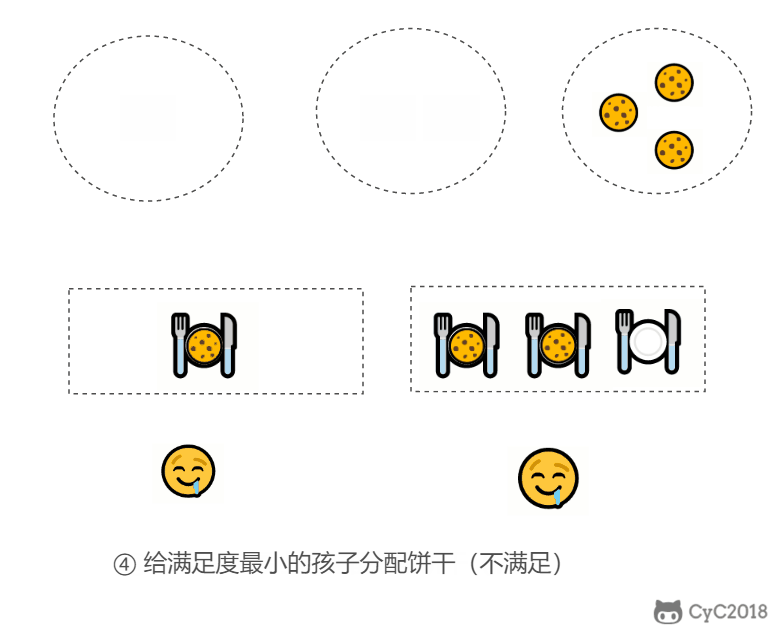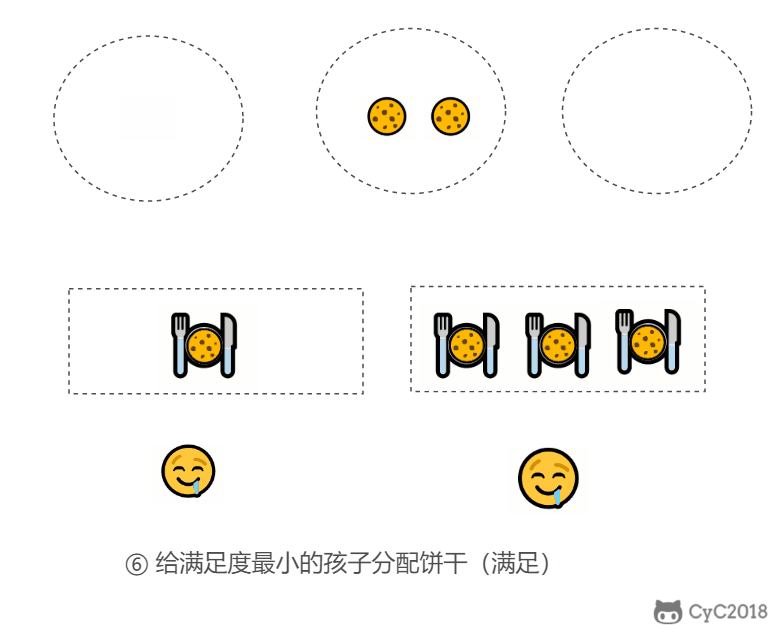
public int findContentChildren(int[] grid, int[] size) {
if (grid == null || size == null) return 0;
Arrays.sort(grid);
Arrays.sort(size);
int gi = 0, si = 0;
while (gi < grid.length && si < size.length) {
if (grid[gi] <= size[si]) {
gi++;
}
si++;
}
return gi;
}
2. 不重叠的区间个数
Input: [ [1,2], [1,2], [1,2] ]
Output: 2
Explanation: You need to remove two [1,2] to make the rest of intervals non-overlapping.
Input: [ [1,2], [2,3] ]
Output: 0
Explanation: You don't need to remove any of the intervals since they're already non-overlapping.
题目描述:计算让一组区间不重叠所需要移除的区间个数。
先计算最多能组成的不重叠区间个数,然后用区间总个数减去不重叠区间的个数。
在每次选择中,区间的结尾最为重要,选择的区间结尾越小,留给后面的区间的空间越大,那么后面能够选择的区间个数也就越大。
按区间的结尾进行排序,每次选择结尾最小,并且和前一个区间不重叠的区间。
public int eraseOverlapIntervals(int[][] intervals) {
if (intervals.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
Arrays.sort(intervals, Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o[1]));
int cnt = 1;
int end = intervals[0][1];
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++) {
if (intervals[i][0] < end) {
continue;
}
end = intervals[i][1];
cnt++;
}
return intervals.length - cnt;
}
使用 lambda 表示式创建 Comparator 会导致算法运行时间过长,如果注重运行时间,可以修改为普通创建 Comparator 语句:
Arrays.sort(intervals, new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return (o1[1] < o2[1]) ? -1 : ((o1[1] == o2[1]) ? 0 : 1);
}
});
实现 compare() 函数时避免使用 return o1[1] - o2[1]; 这种减法操作,防止溢出。
3. 投飞镖刺破气球
Input:
[[10,16], [2,8], [1,6], [7,12]]
Output:
2
题目描述:气球在一个水平数轴上摆放,可以重叠,飞镖垂直投向坐标轴,使得路径上的气球都被刺破。求解最小的投飞镖次数使所有气球都被刺破。
也是计算不重叠的区间个数,不过和 Non-overlapping Intervals 的区别在于,[1, 2] 和 [2, 3] 在本题中算是重叠区间。
public int findMinArrowShots(int[][] points) {
if (points.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
Arrays.sort(points, Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o[1]));
int cnt = 1, end = points[0][1];
for (int i = 1; i < points.length; i++) {
if (points[i][0] <= end) {
continue;
}
cnt++;
end = points[i][1];
}
return cnt;
}
4. 根据身高和序号重组队列
Input:
[[7,0], [4,4], [7,1], [5,0], [6,1], [5,2]]
Output:
[[5,0], [7,0], [5,2], [6,1], [4,4], [7,1]]
题目描述:一个学生用两个分量 (h, k) 描述,h 表示身高,k 表示排在前面的有 k 个学生的身高比他高或者和他一样高。
为了使插入操作不影响后续的操作,身高较高的学生应该先做插入操作,否则身高较小的学生原先正确插入的第 k 个位置可能会变成第 k+1 个位置。
身高 h 降序、个数 k 值升序,然后将某个学生插入队列的第 k 个位置中。
public int[][] reconstructQueue(int[][] people) {
if (people == null || people.length == 0 || people[0].length == 0) {
return new int[0][0];
}
Arrays.sort(people, (a, b) -> (a[0] == b[0] ? a[1] - b[1] : b[0] - a[0]));
List<int[]> queue = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] p : people) {
queue.add(p[1], p);
}
return queue.toArray(new int[queue.size()][]);
}
5. 买卖股票最大的收益
题目描述:一次股票交易包含买入和卖出,只进行一次交易,求最大收益。
只要记录前面的最小价格,将这个最小价格作为买入价格,然后将当前的价格作为售出价格,查看当前收益是不是最大收益。
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
if (n == 0) return 0;
int soFarMin = prices[0];
int max = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (soFarMin > prices[i]) soFarMin = prices[i];
else max = Math.max(max, prices[i] - soFarMin);
}
return max;
}
6. 买卖股票的最大收益 II
题目描述:可以进行多次交易,多次交易之间不能交叉进行,可以进行多次交易。
对于 [a, b, c, d],如果有 a <= b <= c <= d ,那么最大收益为 d - a。而 d - a = (d - c) + (c - b) + (b - a) ,因此当访问到一个 prices[i] 且 prices[i] - prices[i-1] > 0,那么就把 prices[i] - prices[i-1] 添加到收益中。
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int profit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1]) {
profit += (prices[i] - prices[i - 1]);
}
}
return profit;
}
7. 种植花朵
Input: flowerbed = [1,0,0,0,1], n = 1
Output: True
题目描述:flowerbed 数组中 1 表示已经种下了花朵。花朵之间至少需要一个单位的间隔,求解是否能种下 n 朵花。
public boolean canPlaceFlowers(int[] flowerbed, int n) {
int len = flowerbed.length;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len && cnt < n; i++) {
if (flowerbed[i] == 1) {
continue;
}
int pre = i == 0 ? 0 : flowerbed[i - 1];
int next = i == len - 1 ? 0 : flowerbed[i + 1];
if (pre == 0 && next == 0) {
cnt++;
flowerbed[i] = 1;
}
}
return cnt >= n;
}
8. 判断是否为子序列
392. Is Subsequence (Medium)
Leetcode / 力扣
s = "abc", t = "ahbgdc"
Return true.
public boolean isSubsequence(String s, String t) {
int index = -1;
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
index = t.indexOf(c, index + 1);
if (index == -1) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
9. 修改一个数成为非递减数组
Input: [4,2,3]
Output: True
Explanation: You could modify the first 4 to 1 to get a non-decreasing array.
题目描述:判断一个数组是否能只修改一个数就成为非递减数组。
在出现 nums[i] < nums[i - 1] 时,需要考虑的是应该修改数组的哪个数,使得本次修改能使 i 之前的数组成为非递减数组,并且 不影响后续的操作 。优先考虑令 nums[i - 1] = nums[i],因为如果修改 nums[i] = nums[i - 1] 的话,那么 nums[i] 这个数会变大,就有可能比 nums[i + 1] 大,从而影响了后续操作。还有一个比较特别的情况就是 nums[i] < nums[i - 2],修改 nums[i - 1] = nums[i] 不能使数组成为非递减数组,只能修改 nums[i] = nums[i - 1]。
public boolean checkPossibility(int[] nums) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length && cnt < 2; i++) {
if (nums[i] >= nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
cnt++;
if (i - 2 >= 0 && nums[i - 2] > nums[i]) {
nums[i] = nums[i - 1];
} else {
nums[i - 1] = nums[i];
}
}
return cnt <= 1;
}
10. 子数组最大的和
For example, given the array [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],
the contiguous subarray [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6.
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int preSum = nums[0];
int maxSum = preSum;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
preSum = preSum > 0 ? preSum + nums[i] : nums[i];
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, preSum);
}
return maxSum;
}
11. 分隔字符串使同种字符出现在一起
Input: S = "ababcbacadefegdehijhklij"
Output: [9,7,8]
Explanation:
The partition is "ababcbaca", "defegde", "hijhklij".
This is a partition so that each letter appears in at most one part.
A partition like "ababcbacadefegde", "hijhklij" is incorrect, because it splits S into less parts.
public List<Integer> partitionLabels(String S) {
int[] lastIndexsOfChar = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < S.length(); i++) {
lastIndexsOfChar[char2Index(S.charAt(i))] = i;
}
List<Integer> partitions = new ArrayList<>();
int firstIndex = 0;
while (firstIndex < S.length()) {
int lastIndex = firstIndex;
for (int i = firstIndex; i < S.length() && i <= lastIndex; i++) {
int index = lastIndexsOfChar[char2Index(S.charAt(i))];
if (index > lastIndex) {
lastIndex = index;
}
}
partitions.add(lastIndex - firstIndex + 1);
firstIndex = lastIndex + 1;
}
return partitions;
}
private int char2Index(char c) {
return c - 'a';
}
图
二分图
如果可以用两种颜色对图中的节点进行着色,并且保证相邻的节点颜色不同,那么这个图就是二分图。
1. 判断是否为二分图
Input: [[1,3], [0,2], [1,3], [0,2]]
Output: true
Explanation:
The graph looks like this:
0----1
| |
| |
3----2
We can divide the vertices into two groups: {0, 2} and {1, 3}.
Example 2:
Input: [[1,2,3], [0,2], [0,1,3], [0,2]]
Output: false
Explanation:
The graph looks like this:
0----1
| |
| |
3----2
We cannot find a way to divide the set of nodes into two independent subsets.
public boolean isBipartite(int[][] graph) {
int[] colors = new int[graph.length];
Arrays.fill(colors, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) { // 处理图不是连通的情况
if (colors[i] == -1 && !isBipartite(i, 0, colors, graph)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean isBipartite(int curNode, int curColor, int[] colors, int[][] graph) {
if (colors[curNode] != -1) {
return colors[curNode] == curColor;
}
colors[curNode] = curColor;
for (int nextNode : graph[curNode]) {
if (!isBipartite(nextNode, 1 - curColor, colors, graph)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
拓扑排序
常用于在具有先序关系的任务规划中。
1. 课程安排的合法性
2, [[1,0]]
return true
2, [[1,0],[0,1]]
return false
题目描述:一个课程可能会先修课程,判断给定的先修课程规定是否合法。
本题不需要使用拓扑排序,只需要检测有向图是否存在环即可。
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
List<Integer>[] graphic = new List[numCourses];
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
graphic[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] pre : prerequisites) {
graphic[pre[0]].add(pre[1]);
}
boolean[] globalMarked = new boolean[numCourses];
boolean[] localMarked = new boolean[numCourses];
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (hasCycle(globalMarked, localMarked, graphic, i)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean hasCycle(boolean[] globalMarked, boolean[] localMarked,
List<Integer>[] graphic, int curNode) {
if (localMarked[curNode]) {
return true;
}
if (globalMarked[curNode]) {
return false;
}
globalMarked[curNode] = true;
localMarked[curNode] = true;
for (int nextNode : graphic[curNode]) {
if (hasCycle(globalMarked, localMarked, graphic, nextNode)) {
return true;
}
}
localMarked[curNode] = false;
return false;
}
2. 课程安排的顺序
4, [[1,0],[2,0],[3,1],[3,2]]
There are a total of 4 courses to take. To take course 3 you should have finished both courses 1 and 2. Both courses 1 and 2 should be taken after you finished course 0. So one correct course order is [0,1,2,3]. Another correct ordering is[0,2,1,3].
使用 DFS 来实现拓扑排序,使用一个栈存储后序遍历结果,这个栈的逆序结果就是拓扑排序结果。
证明:对于任何先序关系:v->w,后序遍历结果可以保证 w 先进入栈中,因此栈的逆序结果中 v 会在 w 之前。
public int[] findOrder(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
List<Integer>[] graphic = new List[numCourses];
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
graphic[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] pre : prerequisites) {
graphic[pre[0]].add(pre[1]);
}
Stack<Integer> postOrder = new Stack<>();
boolean[] globalMarked = new boolean[numCourses];
boolean[] localMarked = new boolean[numCourses];
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (hasCycle(globalMarked, localMarked, graphic, i, postOrder)) {
return new int[0];
}
}
int[] orders = new int[numCourses];
for (int i = numCourses - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
orders[i] = postOrder.pop();
}
return orders;
}
private boolean hasCycle(boolean[] globalMarked, boolean[] localMarked, List<Integer>[] graphic,
int curNode, Stack<Integer> postOrder) {
if (localMarked[curNode]) {
return true;
}
if (globalMarked[curNode]) {
return false;
}
globalMarked[curNode] = true;
localMarked[curNode] = true;
for (int nextNode : graphic[curNode]) {
if (hasCycle(globalMarked, localMarked, graphic, nextNode, postOrder)) {
return true;
}
}
localMarked[curNode] = false;
postOrder.push(curNode);
return false;
}
并查集
并查集可以动态地连通两个点,并且可以非常快速地判断两个点是否连通。
1. 冗余连接
Input: [[1,2], [1,3], [2,3]]
Output: [2,3]
Explanation: The given undirected graph will be like this:
1
/
2 - 3
题目描述:有一系列的边连成的图,找出一条边,移除它之后该图能够成为一棵树。
public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) {
int N = edges.length;
UF uf = new UF(N);
for (int[] e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1];
if (uf.connect(u, v)) {
return e;
}
uf.union(u, v);
}
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}
private class UF {
private int[] id;
UF(int N) {
id = new int[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < id.length; i++) {
id[i] = i;
}
}
void union(int u, int v) {
int uID = find(u);
int vID = find(v);
if (uID == vID) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < id.length; i++) {
if (id[i] == uID) {
id[i] = vID;
}
}
}
int find(int p) {
return id[p];
}
boolean connect(int u, int v) {
return find(u) == find(v);
}
}
位运算
0. 原理
基本原理
0s 表示一串 0,1s 表示一串 1。
x ^ 0s = x x & 0s = 0 x | 0s = x
x ^ 1s = ~x x & 1s = x x | 1s = 1s
x ^ x = 0 x & x = x x | x = x
利用 x ^ 1s = ~x 的特点,可以将一个数的位级表示翻转;利用 x ^ x = 0 的特点,可以将三个数中重复的两个数去除,只留下另一个数。
1^1^2 = 2
利用 x & 0s = 0 和 x & 1s = x 的特点,可以实现掩码操作。一个数 num 与 mask:00111100 进行位与操作,只保留 num 中与 mask 的 1 部分相对应的位。
01011011 &
00111100
--------
00011000
利用 x | 0s = x 和 x | 1s = 1s 的特点,可以实现设值操作。一个数 num 与 mask:00111100 进行位或操作,将 num 中与 mask 的 1 部分相对应的位都设置为 1。
01011011 |
00111100
--------
01111111
位与运算技巧
n&(n-1) 去除 n 的位级表示中最低的那一位 1。例如对于二进制表示 01011011,减去 1 得到 01011010,这两个数相与得到 01011010。
01011011 &
01011010
--------
01011010
n&(-n) 得到 n 的位级表示中最低的那一位 1。-n 得到 n 的反码加 1,也就是 -n=~n+1。例如对于二进制表示 10110100,-n 得到 01001100,相与得到 00000100。
10110100 &
01001100
--------
00000100
n-(n&(-n)) 则可以去除 n 的位级表示中最低的那一位 1,和 n&(n-1) 效果一样。
移位运算
>> n 为算术右移,相当于除以 2n,例如 -7 >> 2 = -2。
11111111111111111111111111111001 >> 2
--------
11111111111111111111111111111110
>>> n 为无符号右移,左边会补上 0。例如 -7 >>> 2 = 1073741822。
11111111111111111111111111111001 >>> 2
--------
00111111111111111111111111111111
<< n 为算术左移,相当于乘以 2n。-7 << 2 = -28。
11111111111111111111111111111001 << 2
--------
11111111111111111111111111100100
mask 计算
要获取 111111111,将 0 取反即可,~0。
要得到只有第 i 位为 1 的 mask,将 1 向左移动 i-1 位即可,1<<(i-1) 。例如 1<<4 得到只有第 5 位为 1 的 mask :00010000。
要得到 1 到 i 位为 1 的 mask,(1<<i)-1 即可,例如将 (1<<4)-1 = 00010000-1 = 00001111。
要得到 1 到 i 位为 0 的 mask,只需将 1 到 i 位为 1 的 mask 取反,即 ~((1<<i)-1)。
Java 中的位操作
static int Integer.bitCount(); // 统计 1 的数量
static int Integer.highestOneBit(); // 获得最高位
static String toBinaryString(int i); // 转换为二进制表示的字符串
1. 统计两个数的二进制表示有多少位不同
Input: x = 1, y = 4
Output: 2
Explanation:
1 (0 0 0 1)
4 (0 1 0 0)
↑ ↑
The above arrows point to positions where the corresponding bits are different.
对两个数进行异或操作,位级表示不同的那一位为 1,统计有多少个 1 即可。
public int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
int z = x ^ y;
int cnt = 0;
while(z != 0) {
if ((z & 1) == 1) cnt++;
z = z >> 1;
}
return cnt;
}
使用 z&(z-1) 去除 z 位级表示最低的那一位。
public int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
int z = x ^ y;
int cnt = 0;
while (z != 0) {
z &= (z - 1);
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
可以使用 Integer.bitcount() 来统计 1 个的个数。
public int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
return Integer.bitCount(x ^ y);
}
2. 数组中唯一一个不重复的元素
Input: [4,1,2,1,2]
Output: 4
两个相同的数异或的结果为 0,对所有数进行异或操作,最后的结果就是单独出现的那个数。
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int ret = 0;
for (int n : nums) ret = ret ^ n;
return ret;
}
3. 找出数组中缺失的那个数
Input: [3,0,1]
Output: 2
题目描述:数组元素在 0-n 之间,但是有一个数是缺失的,要求找到这个缺失的数。
public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
ret = ret ^ i ^ nums[i];
}
return ret ^ nums.length;
}
4. 数组中不重复的两个元素
两个不相等的元素在位级表示上必定会有一位存在不同。
将数组的所有元素异或得到的结果为不存在重复的两个元素异或的结果。
diff &= -diff 得到出 diff 最右侧不为 0 的位,也就是不存在重复的两个元素在位级表示上最右侧不同的那一位,利用这一位就可以将两个元素区分开来。
public int[] singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int diff = 0;
for (int num : nums) diff ^= num;
diff &= -diff; // 得到最右一位
int[] ret = new int[2];
for (int num : nums) {
if ((num & diff) == 0) ret[0] ^= num;
else ret[1] ^= num;
}
return ret;
}
5. 翻转一个数的比特位
public int reverseBits(int n) {
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
ret <<= 1;
ret |= (n & 1);
n >>>= 1;
}
return ret;
}
如果该函数需要被调用很多次,可以将 int 拆成 4 个 byte,然后缓存 byte 对应的比特位翻转,最后再拼接起来。
private static Map<Byte, Integer> cache = new HashMap<>();
public int reverseBits(int n) {
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
ret <<= 8;
ret |= reverseByte((byte) (n & 0b11111111));
n >>= 8;
}
return ret;
}
private int reverseByte(byte b) {
if (cache.containsKey(b)) return cache.get(b);
int ret = 0;
byte t = b;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
ret <<= 1;
ret |= t & 1;
t >>= 1;
}
cache.put(b, ret);
return ret;
}
6. 不用额外变量交换两个整数
a = a ^ b;
b = a ^ b;
a = a ^ b;
7. 判断一个数是不是 2 的 n 次方
二进制表示只有一个 1 存在。
public boolean isPowerOfTwo(int n) {
return n > 0 && Integer.bitCount(n) == 1;
}
利用 1000 & 0111 == 0 这种性质,得到以下解法:
public boolean isPowerOfTwo(int n) {
return n > 0 && (n & (n - 1)) == 0;
}
8. 判断一个数是不是 4 的 n 次方
这种数在二进制表示中有且只有一个奇数位为 1,例如 16(10000)。
public boolean isPowerOfFour(int num) {
return num > 0 && (num & (num - 1)) == 0 && (num & 0b01010101010101010101010101010101) != 0;
}
也可以使用正则表达式进行匹配。
public boolean isPowerOfFour(int num) {
return Integer.toString(num, 4).matches("10*");
}
9. 判断一个数的位级表示是否不会出现连续的 0 和 1
693. Binary Number with Alternating Bits (Easy)
Leetcode / 力扣
Input: 10
Output: True
Explanation:
The binary representation of 10 is: 1010.
Input: 11
Output: False
Explanation:
The binary representation of 11 is: 1011.
对于 1010 这种位级表示的数,把它向右移动 1 位得到 101,这两个数每个位都不同,因此异或得到的结果为 1111。
public boolean hasAlternatingBits(int n) {
int a = (n ^ (n >> 1));
return (a & (a + 1)) == 0;
}
10. 求一个数的补码
Input: 5
Output: 2
Explanation: The binary representation of 5 is 101 (no leading zero bits), and its complement is 010. So you need to output 2.
题目描述:不考虑二进制表示中的首 0 部分。
对于 00000101,要求补码可以将它与 00000111 进行异或操作。那么问题就转换为求掩码 00000111。
public int findComplement(int num) {
if (num == 0) return 1;
int mask = 1 << 30;
while ((num & mask) == 0) mask >>= 1;
mask = (mask << 1) - 1;
return num ^ mask;
}
可以利用 Java 的 Integer.highestOneBit() 方法来获得含有首 1 的数。
public int findComplement(int num) {
if (num == 0) return 1;
int mask = Integer.highestOneBit(num);
mask = (mask << 1) - 1;
return num ^ mask;
}
对于 10000000 这样的数要扩展成 11111111,可以利用以下方法:
mask |= mask >> 1 11000000
mask |= mask >> 2 11110000
mask |= mask >> 4 11111111
public int findComplement(int num) {
int mask = num;
mask |= mask >> 1;
mask |= mask >> 2;
mask |= mask >> 4;
mask |= mask >> 8;
mask |= mask >> 16;
return (mask ^ num);
}
11. 实现整数的加法
a ^ b 表示没有考虑进位的情况下两数的和,(a & b) << 1 就是进位。
递归会终止的原因是 (a & b) << 1 最右边会多一个 0,那么继续递归,进位最右边的 0 会慢慢增多,最后进位会变为 0,递归终止。
public int getSum(int a, int b) {
return b == 0 ? a : getSum((a ^ b), (a & b) << 1);
}
12. 字符串数组最大乘积
Given ["abcw", "baz", "foo", "bar", "xtfn", "abcdef"]
Return 16
The two words can be "abcw", "xtfn".
题目描述:字符串数组的字符串只含有小写字符。求解字符串数组中两个字符串长度的最大乘积,要求这两个字符串不能含有相同字符。
本题主要问题是判断两个字符串是否含相同字符,由于字符串只含有小写字符,总共 26 位,因此可以用一个 32 位的整数来存储每个字符是否出现过。
public int maxProduct(String[] words) {
int n = words.length;
int[] val = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (char c : words[i].toCharArray()) {
val[i] |= 1 << (c - 'a');
}
}
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if ((val[i] & val[j]) == 0) {
ret = Math.max(ret, words[i].length() * words[j].length());
}
}
}
return ret;
}
13. 统计从 0 ~ n 每个数的二进制表示中 1 的个数
338. Counting Bits (Medium)
Leetcode / 力扣
对于数字 6(110),它可以看成是 4(100) 再加一个 2(10),因此 dp[i] = dp[i&(i-1)] + 1;
public int[] countBits(int num) {
int[] ret = new int[num + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= num; i++){
ret[i] = ret[i&(i-1)] + 1;
}
return ret;
}
栈和队列
1. 用栈实现队列
栈的顺序为后进先出,而队列的顺序为先进先出。使用两个栈实现队列,一个元素需要经过两个栈才能出队列,在经过第一个栈时元素顺序被反转,经过第二个栈时再次被反转,此时就是先进先出顺序。
class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> in = new Stack<>();
private Stack<Integer> out = new Stack<>();
public void push(int x) {
in.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
in2out();
return out.pop();
}
public int peek() {
in2out();
return out.peek();
}
private void in2out() {
if (out.isEmpty()) {
while (!in.isEmpty()) {
out.push(in.pop());
}
}
}
public boolean empty() {
return in.isEmpty() && out.isEmpty();
}
}
2. 用队列实现栈
在将一个元素 x 插入队列时,为了维护原来的后进先出顺序,需要让 x 插入队列首部。而队列的默认插入顺序是队列尾部,因此在将 x 插入队列尾部之后,需要让除了 x 之外的所有元素出队列,再入队列。
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> queue;
public MyStack() {
queue = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
queue.add(x);
int cnt = queue.size();
while (cnt-- > 1) {
queue.add(queue.poll());
}
}
public int pop() {
return queue.remove();
}
public int top() {
return queue.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
}
3. 最小值栈
class MinStack {
private Stack<Integer> dataStack;
private Stack<Integer> minStack;
private int min;
public MinStack() {
dataStack = new Stack<>();
minStack = new Stack<>();
min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
public void push(int x) {
dataStack.add(x);
min = Math.min(min, x);
minStack.add(min);
}
public void pop() {
dataStack.pop();
minStack.pop();
min = minStack.isEmpty() ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : minStack.peek();
}
public int top() {
return dataStack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
对于实现最小值队列问题,可以先将队列使用栈来实现,然后就将问题转换为最小值栈,这个问题出现在 编程之美:3.7。
4. 用栈实现括号匹配
"()[]{}"
Output : true
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if (c == '(' || c == '{' || c == '[') {
stack.push(c);
} else {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
char cStack = stack.pop();
boolean b1 = c == ')' && cStack != '(';
boolean b2 = c == ']' && cStack != '[';
boolean b3 = c == '}' && cStack != '{';
if (b1 || b2 || b3) {
return false;
}
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
5. 数组中元素与下一个比它大的元素之间的距离
Input: [73, 74, 75, 71, 69, 72, 76, 73]
Output: [1, 1, 4, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0]
在遍历数组时用栈把数组中的数存起来,如果当前遍历的数比栈顶元素来的大,说明栈顶元素的下一个比它大的数就是当前元素。
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
int n = temperatures.length;
int[] dist = new int[n];
Stack<Integer> indexs = new Stack<>();
for (int curIndex = 0; curIndex < n; curIndex++) {
while (!indexs.isEmpty() && temperatures[curIndex] > temperatures[indexs.peek()]) {
int preIndex = indexs.pop();
dist[preIndex] = curIndex - preIndex;
}
indexs.add(curIndex);
}
return dist;
}
6. 循环数组中比当前元素大的下一个元素
Input: [1,2,1]
Output: [2,-1,2]
Explanation: The first 1's next greater number is 2;
The number 2 can't find next greater number;
The second 1's next greater number needs to search circularly, which is also 2.
与 739. Daily Temperatures (Medium) 不同的是,数组是循环数组,并且最后要求的不是距离而是下一个元素。
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] next = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(next, -1);
Stack<Integer> pre = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n * 2; i++) {
int num = nums[i % n];
while (!pre.isEmpty() && nums[pre.peek()] < num) {
next[pre.pop()] = num;
}
if (i < n){
pre.push(i);
}
}
return next;
}
字符串
1. 字符串循环移位包含
编程之美 3.1
s1 = AABCD, s2 = CDAA
Return : true
给定两个字符串 s1 和 s2,要求判定 s2 是否能够被 s1 做循环移位得到的字符串包含。
s1 进行循环移位的结果是 s1s1 的子字符串,因此只要判断 s2 是否是 s1s1 的子字符串即可。
2. 字符串循环移位
编程之美 2.17
s = "abcd123" k = 3
Return "123abcd"
将字符串向右循环移动 k 位。
将 abcd123 中的 abcd 和 123 单独翻转,得到 dcba321,然后对整个字符串进行翻转,得到 123abcd。
3. 字符串中单词的翻转
程序员代码面试指南
s = "I am a student"
Return "student a am I"
将每个单词翻转,然后将整个字符串翻转。
4. 两个字符串包含的字符是否完全相同
s = "anagram", t = "nagaram", return true.
s = "rat", t = "car", return false.
可以用 HashMap 来映射字符与出现次数,然后比较两个字符串出现的字符数量是否相同。
由于本题的字符串只包含 26 个小写字符,因此可以使用长度为 26 的整型数组对字符串出现的字符进行统计,不再使用 HashMap。
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
int[] cnts = new int[26];
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
cnts[c - 'a']++;
}
for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {
cnts[c - 'a']--;
}
for (int cnt : cnts) {
if (cnt != 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
5. 计算一组字符集合可以组成的回文字符串的最大长度
409. Longest Palindrome (Easy)
Input : "abccccdd"
Output : 7
Explanation : One longest palindrome that can be built is "dccaccd", whose length is 7.
使用长度为 256 的整型数组来统计每个字符出现的个数,每个字符有偶数个可以用来构成回文字符串。
因为回文字符串最中间的那个字符可以单独出现,所以如果有单独的字符就把它放到最中间。
public int longestPalindrome(String s) {
int[] cnts = new int[256];
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
cnts[c]++;
}
int palindrome = 0;
for (int cnt : cnts) {
palindrome += (cnt / 2) * 2;
}
if (palindrome < s.length()) {
palindrome++; // 这个条件下 s 中一定有单个未使用的字符存在,可以把这个字符放到回文的最中间
}
return palindrome;
}
6. 字符串同构
Given "egg", "add", return true.
Given "foo", "bar", return false.
Given "paper", "title", return true.
记录一个字符上次出现的位置,如果两个字符串中的字符上次出现的位置一样,那么就属于同构。
public boolean isIsomorphic(String s, String t) {
int[] preIndexOfS = new int[256];
int[] preIndexOfT = new int[256];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char sc = s.charAt(i), tc = t.charAt(i);
if (preIndexOfS[sc] != preIndexOfT[tc]) {
return false;
}
preIndexOfS[sc] = i + 1;
preIndexOfT[tc] = i + 1;
}
return true;
}
7. 回文子字符串个数
Input: "aaa"
Output: 6
Explanation: Six palindromic strings: "a", "a", "a", "aa", "aa", "aaa".
从字符串的某一位开始,尝试着去扩展子字符串。
private int cnt = 0;
public int countSubstrings(String s) {
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
extendSubstrings(s, i, i); // 奇数长度
extendSubstrings(s, i, i + 1); // 偶数长度
}
return cnt;
}
private void extendSubstrings(String s, int start, int end) {
while (start >= 0 && end < s.length() && s.charAt(start) == s.charAt(end)) {
start--;
end++;
cnt++;
}
}
8. 判断一个整数是否是回文数
要求不能使用额外空间,也就不能将整数转换为字符串进行判断。
将整数分成左右两部分,右边那部分需要转置,然后判断这两部分是否相等。
public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
if (x == 0) {
return true;
}
if (x < 0 || x % 10 == 0) {
return false;
}
int right = 0;
while (x > right) {
right = right * 10 + x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
return x == right || x == right / 10;
}
9. 统计二进制字符串中连续 1 和连续 0 数量相同的子字符串个数
Input: "00110011"
Output: 6
Explanation: There are 6 substrings that have equal number of consecutive 1's and 0's: "0011", "01", "1100", "10", "0011", and "01".
public int countBinarySubstrings(String s) {
int preLen = 0, curLen = 1, count = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(i - 1)) {
curLen++;
} else {
preLen = curLen;
curLen = 1;
}
if (preLen >= curLen) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
最后
以上就是俊逸裙子最近收集整理的关于200个经典面试题(算法思想+数据结构)_2数学数组与矩阵双指针搜索贪心思想图位运算栈和队列字符串的全部内容,更多相关200个经典面试题(算法思想+数据结构)_2数学数组与矩阵双指针搜索贪心思想图位运算栈和队列字符串内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复