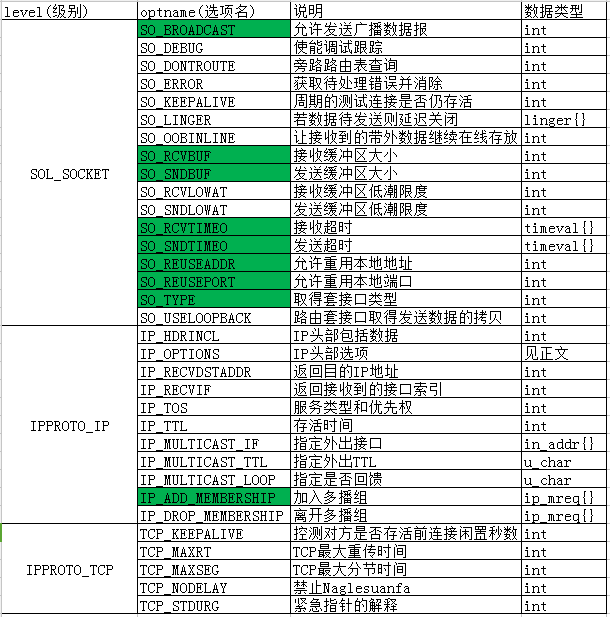
套接字机制提供两个套接字选项来控制套接字行为。一个接口用来控制选项,另一个接口允许查询一个选项的状态。
1 #include <sys/types.h> 2 #include <sys/socket.h> 3 4 int getsockopt(int sockfd, int level, int optname, void *optval, socklen_t *optlen); 5 int setsockopt(int sockfd, int level, int optname, const void *optval, socklen_t optlen); 6 返回值:若成功则返回0,若出错则返回-1
参数说明:
sockfd:必须指向一个打开的套接字描述符。
level:标识了选项应用的协议。
optname:要设置或获取套接字选项的名字。
optval:指向函数设置或获取值得地址,即保存选项值的缓存区。
optlen:指定了optval指向的对象的大小。
示例1:使用选项SO_RCVBUF和SO_SNDBUF获取缓冲区大小
server.c
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<sys/types.h> 4 #include<sys/socket.h> 5 #include<unistd.h> 6 #include<arpa/inet.h> 7 #include<netinet/in.h> 8 #include<string.h> 9 #include<errno.h> 10 11 #define N 64 12 #define err_log(log) do{ perror(log); exit(1);}while(0) 13 14 int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) 15 { 16 int sockfd, connectfd; 17 char buf[N]; 18 struct sockaddr_in serveraddr, clientaddr; 19 int optval; 20 socklen_t optlen = sizeof(optval); 21 socklen_t len = sizeof(clientaddr); 22 23 if(argc != 3) 24 { 25 fprintf(stderr, "Usage:%s serverip port", argv[0]); 26 return -1; 27 } 28 sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); 29 if(sockfd < 0) 30 err_log("fail to sockfd"); 31 32 serveraddr.sin_family = AF_INET; 33 serveraddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]); 34 serveraddr.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[2])); 35 36 if(getsockopt(sockfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &optval, &optlen) < 0) 37 err_log("fail to getsockopt"); 38 printf("SO_SNDBUF:%d Kn", optval/1024); 39 40 if(getsockopt(sockfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &optval, &optlen) < 0) 41 err_log("fail to getsockopt"); 42 printf("SO_RCVBUF:%d Kn", optval/1024); 43 44 if(bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&serveraddr, sizeof(serveraddr)) < 0) 45 err_log("fail to bind"); 46 if(listen(sockfd, 5) < 0) 47 err_log("fail to listen"); 48 if((connectfd = accept(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&clientaddr, &len)) < 0) 49 err_log("fail to connectfd"); 50 51 printf("client:%s--->%dn", inet_ntoa(clientaddr.sin_addr), ntohs(clientaddr.sin_port)); 52 53 while(1) 54 { 55 if(recv(connectfd, buf, N, 0) < 0) 56 err_log("fail to recv"); 57 if(strncmp(buf, "quit", 4) == 0) 58 break; 59 buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '�'; 60 printf("buf:%sn", buf); 61 strcat(buf, "+++***---"); 62 if(send(connectfd, buf, N, 0) < 0) 63 err_log("fail to send"); 64 } 65 close(connectfd); 66 close(sockfd); 67 return 0; 68 }
client.c
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<sys/types.h> 3 #include<sys/socket.h> 4 #include<unistd.h> 5 #include<arpa/inet.h> 6 #include<netinet/in.h> 7 #include<string.h> 8 #include<stdlib.h> 9 #include<errno.h> 10 11 #define N 64 12 #define err_log(log) do{perror(log); exit(1);}while(0) 13 14 int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) 15 { 16 int sockfd; 17 struct sockaddr_in serveraddr; 18 char buf[N]; 19 20 if(argc != 3) 21 { 22 fprintf(stderr, "Usage:%s serverip port.", argv[1]); 23 return -1; 24 } 25 sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); 26 if(sockfd < 0) 27 err_log("fail to sockfd"); 28 29 serveraddr.sin_family = AF_INET; 30 serveraddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]); 31 serveraddr.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[2])); 32 if(connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&serveraddr, sizeof(serveraddr)) < 0) 33 err_log("fail to connect"); 34 35 while(1) 36 { 37 printf("<client>"); 38 fgets(buf, N, stdin); 39 if(send(sockfd, buf, N, 0) < 0) 40 err_log("fail to send"); 41 if(strncmp(buf, "quit", 4) == 0) 42 break; 43 if(recv(sockfd, buf, N, 0) < 0) 44 err_log("fail to recv"); 45 printf("buf:%sn", buf); 46 } 47 close(sockfd); 48 return 0; 49 }
服务器运行结果:

客户端运行结果:
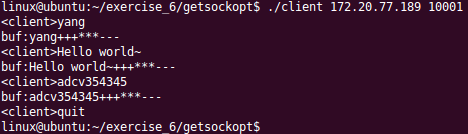
示例2:使用选项SO_RCVTIMEO超时接收
server.c
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<sys/types.h> 4 #include<sys/socket.h> 5 #include<unistd.h> 6 #include<netinet/in.h> 7 #include<arpa/inet.h> 8 #include<string.h> 9 #include<errno.h> 10 11 #define N 64 12 #define err_log(log) do{ perror(log); exit(1);}while(0) 13 14 int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) 15 { 16 int sockfd, connectfd; 17 char buf[N]; 18 struct sockaddr_in serveraddr, clientaddr; 19 socklen_t len = sizeof(clientaddr); 20 struct timeval tv; 21 socklen_t optlen = sizeof(tv); 22 23 if(argc != 3) 24 { 25 fprintf(stderr, "Usage:%s serverip port", argv[0]); 26 return -1; 27 } 28 29 sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); 30 if(sockfd < 0) 31 err_log("fail to sockfd"); 32 33 serveraddr.sin_family = AF_INET; 34 serveraddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]); 35 serveraddr.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[2])); 36 37 tv.tv_sec = 5; 38 tv.tv_usec = 0; 39 if(setsockopt(sockfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVTIMEO, &tv, optlen) < 0) 40 err_log("fail to setsockopt"); 41 42 if(bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&serveraddr, sizeof(serveraddr)) < 0) 43 err_log("fail to bind"); 44 45 if(listen(sockfd, 5) < 0) 46 err_log("fail to listen"); 47 48 if((connectfd = accept(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&clientaddr, &len)) < 0) 49 { 50 if(errno == 11) 51 { 52 printf("errno = %d--->%sn", errno, strerror(errno)); 53 } 54 else 55 { 56 err_log("fail to accept"); 57 } 58 } 59 printf("client:%s--->%dn", inet_ntoa(clientaddr.sin_addr), ntohs(clientaddr.sin_port)); 60 while(1) 61 { 62 if(recv(connectfd, buf, N, 0) < 0) 63 err_log("fail to recv"); 64 if(strncmp(buf, "quit", 4) == 0) 65 break; 66 buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '�'; 67 printf("buf:%sn", buf); 68 } 69 close(connectfd); 70 close(sockfd); 71 return 0; 72 }
client.c
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<sys/types.h> 4 #include<sys/socket.h> 5 #include<unistd.h> 6 #include<arpa/inet.h> 7 #include<netinet/in.h> 8 #include<string.h> 9 #include<errno.h> 10 11 #define N 64 12 #define err_log(log) do{perror(log); exit(1);}while(0) 13 14 int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) 15 { 16 int sockfd; 17 char buf[N]; 18 struct sockaddr_in serveraddr; 19 20 if(argc != 3) 21 { 22 fprintf(stderr, "Usage:%s serverip port.", argv[0]); 23 return -1; 24 } 25 26 sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); 27 if(sockfd < 0) 28 err_log("fail to sockfd"); 29 30 serveraddr.sin_family = AF_INET; 31 serveraddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]); 32 serveraddr.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[2])); 33 34 if(connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&serveraddr, sizeof(serveraddr)) < 0) 35 err_log("fail to connect"); 36 37 while(1) 38 { 39 printf("<client>"); 40 fgets(buf, N, stdin); 41 if(send(sockfd, buf, N, 0) < 0) 42 err_log("fail to send"); 43 if(strncmp(buf, "quit", 4) == 0) 44 break; 45 } 46 close(sockfd); 47 return 0; 48 }
运行程序如下:
(1)正常运行/退出
服务器端:
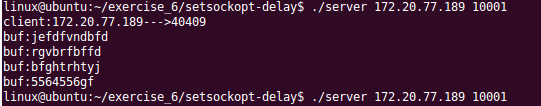
客服端:

(2)当正常发送/接收数据时,客户端停止发送,服务器端在设定5s后退出
服务器端:
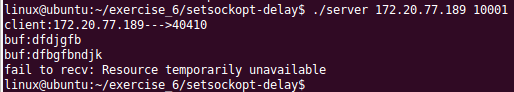
客户端:

(3)客户端不连接服务器,那么服务器会在设置的5s后退出
服务器端:
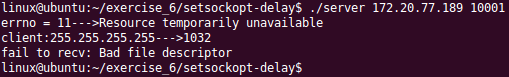
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/yangziwen0709/p/5025834.html
最后
以上就是大胆寒风最近收集整理的关于Linux setsockopt和getsockopt函数的用法分析的全部内容,更多相关Linux内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复