1. 背景
1.1. 注册中心是什么
注册中心可以说是微服务架构中的”通讯录“,它记录了服务和服务地址的映射关系。在分布式架构中,服务会注册到这里,当服务需要调用其它服务时,就到这里找到服务的地址,进行调用。
1.2. 为什么需要注册中心
在分布式系统中,服务可能有上千个,然后每个服务都有好几个实例,如果通过 ip + port 进行服务之间通信则会使系统变得难维护,并且还需要考虑其他复杂的问题:
- 服务注册后,如何被及时发现
- 服务宕机后,如何及时下线
- 服务如何有效的水平扩展
- 如何获取服务列表
- 注册中心如何实现自身的高可用
2. Eureka
2.1. 世面上的流行的注册中心
| 组件名称 | 组件简介 |
|---|---|
| Zookeeper | zookeeper是一个分布式协调工具,可以实现注册中心功能 |
| Eureka | springcloud的注册中心 |
| Consul | Consul 简化了分布式环境中的服务的注册和发现流程,国外比较流行 |
| Nacos | Nacos 致力于帮助您发现、配置和管理微服务。SpringCloudAlibaba |
2.2. Eureka
https://github.com/Netflix/eureka
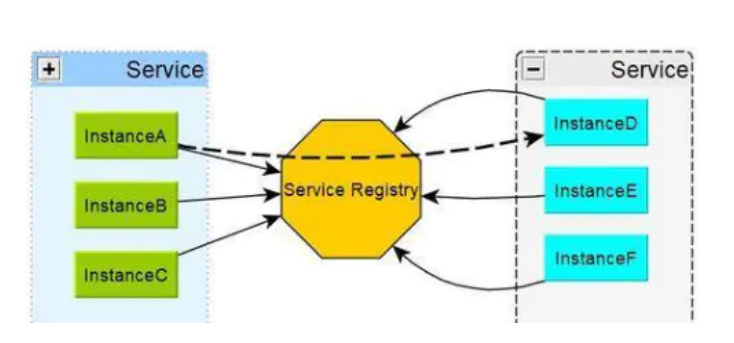
服务注册中心(可以是一个集群),对外暴露自己的地址
注册中心有 Eureka Service, Eureka Client,Eureka Client又分为提供者和消费者;
(某一个服务既可以是提供者也可以是消费者)
服务提供者
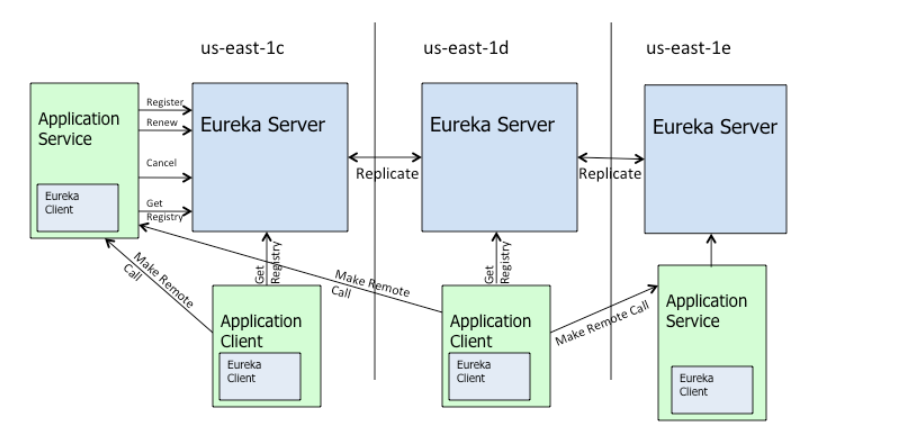
- 服务注册: 启动的时候会通过发送REST请求的方式将自己注册到Eureka Server上,同时带上了自身服务的一些元数据信息。
- 服务续约: 在注册完服务之后,服务提供者会维护一个心跳(默认30S) 用来持续告诉Eureka Server: "我还活着 ”
- 服务下线: 当服务实例进行正常的关闭操作时,它会触发一个服务下线的REST请求 给Eureka Server, 告诉服务注册中心:“我要下线了 ”。
服务消费者
- 获取服务: 服务消费者(Eureka Client)在启动的时候,会发送一个REST请求给Eureka Server,获 取上面注册的服务清单,并且缓存在Eureka Client本地,默认缓存30秒 (eureka.client.registryFetchIntervalSeconds)。同时,为了性能考虑,Eureka Server也会维护一份只读的服务清单缓存,该缓存每隔30秒更新一次。
- 服务调用: 服务消费者在获取服务清单后,通过服务名可以获得具体提供服务的实例名和该实例的元数据信息。在进行服务调用的时候,优先访问同处一个Zone中的服务提供方。
Eureka Server(服务注册中心)
-
失效剔除:【在关闭自我保护才有效】 默认每隔一段时间(默认为60秒) 将当前清单中超时(默认为90秒)没有续约的服务剔除出去。
-
自我保护: EurekaServer 在运行期间,如果在15分钟内超过85%的客户端节点都没有正常的心跳(通常由于网络不稳定导致)。 Eureka Server会将当前的实例注册信息保护起来, 让这些实例不会过期,尽可能保护这些注册信息。此时会出现以下几种情况:
- Eureka Server不再从注册列表中移除因为长时间没收到心跳而应该过期的服务。
- Eureka Server仍然能够接受新服务的注册和查询请求,但是不会被同步到其它节点上,保证当前节点依然可用。
- 当网络稳定时,当前Eureka Server新的注册信息会被同步到其它节点中。
因此Eureka Server可以很好的应对因网络故障导致部分节点失联的情况,而不会像ZK那样如果有一半不可用的情况会导 致整个集群不可用而变成瘫痪。
3.1. 服务注册
3.1.1. Eureka-Client
啥时候会被注册
- 当客户端刚刚启动的时候
- 当客户端的instance信息发生改动
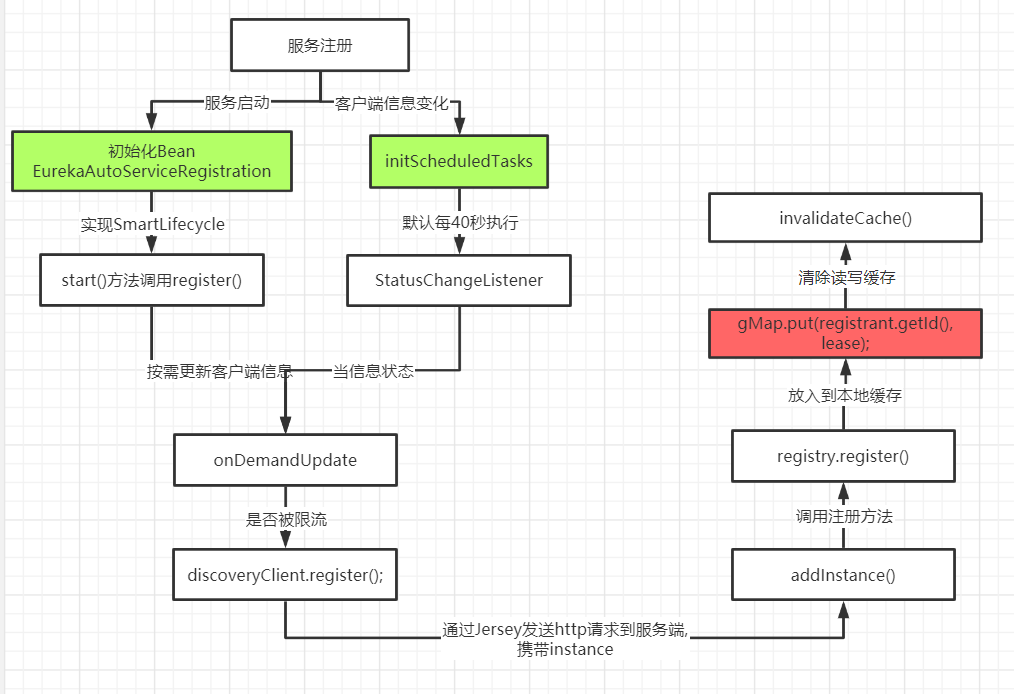
当我们的客户端引入了Eureka-Client,当主方法启动时,@SpringBootApplication会扫描所有的META-INF/spring.factories文件下的 xxxAutoConfiguration。这时候 EurekaClientAutoConfiguration 也会被加载。
上面这段代码,很简单,就是实例化了一个Bean,主要是这个Bean实现了SmartLifecycle, 当重写方法 isAutoStartup() 返回值为true,会启动start()方法。
下面可以详细看看这个代码。
EurekaClientAutoConfiguration.java
@Bean
public EurekaAutoServiceRegistration eurekaAutoServiceRegistration(ApplicationContext context, EurekaServiceRegistry registry, EurekaRegistration registration) {
// 重点代码
return new EurekaAutoServiceRegistration(context, registry, registration);
}
EurekaAutoServiceRegistration.java
public class EurekaAutoServiceRegistration implements AutoServiceRegistration, SmartLifecycle, Ordered {
@Override
public void start() {
// ...
// 该实例还未启动
if (!this.running.get() && this.registration.getNonSecurePort() > 0) {
// 重点;自动去注册服务
this.serviceRegistry.register(this.registration);
// 发布 节点注册事件
this.context.publishEvent(
new InstanceRegisteredEvent<>(this, this.registration.getInstanceConfig()));
this.running.set(true);
}
}
@Override
public boolean isAutoStartup() {
return true;
}
}
InstanceInfoReplicator.java
public boolean onDemandUpdate() {
if (rateLimiter.acquire(burstSize, allowedRatePerMinute)) {
if (!scheduler.isShutdown()) {
scheduler.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// ...
// 调用run方法
InstanceInfoReplicator.this.run();
}
});
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
public void run() {
try {
// 刷新实例信息。
discoveryClient.refreshInstanceInfo();
Long dirtyTimestamp = instanceInfo.isDirtyWithTime();
if (dirtyTimestamp != null) {
// 注册自己的服务
discoveryClient.register();
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(dirtyTimestamp);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
} finally {
Future next = scheduler.schedule(this, replicationIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next);
}
}
第二种是当我们客户端instance信息发生变化
private void initScheduledTasks() {
//省略, 刷新缓存的定时器
// 监听instance的状态变更
instanceInfoReplicator = new InstanceInfoReplicator(
this,
instanceInfo,
clientConfig.getInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds(),
2); // burstSize
statusChangeListener = new ApplicationInfoManager.StatusChangeListener() {
@Override
public String getId() {
return "statusChangeListener";
}
@Override
public void notify(StatusChangeEvent statusChangeEvent) {
// ...
// 调用方法
instanceInfoReplicator.onDemandUpdate();
}
};
if (clientConfig.shouldOnDemandUpdateStatusChange()) {
applicationInfoManager.registerStatusChangeListener(statusChangeListener);
}
instanceInfoReplicator.start(clientConfig.getInitialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds());
}
总结 :服务注册分为2种。
第一种: 当应用启动的时候,如果应用开启了自动注册(默认开启), 那么在自动配置类加载的时候,会通过EurekaAutoServiceRegistration实例化的时候,去改变instance的status,然后调用注册。
第二种: 主要应用于启动之后,当应用的信息发生改变之后,每40每秒执行一次的线程,检测到了,也会自动去注册一次。
DiscoveryClient.register()
DiscoveryClient.java
boolean register() throws Throwable {
EurekaHttpResponse<Void> httpResponse;
try {
//发起HTTP请求
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.register(instanceInfo);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 204;
}
使用的Jersey框架来完成http的请求调用
AbstractJerseyEurekaHttpClient.java
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Void> register(InstanceInfo info) {
// 请求url
String urlPath = "apps/" + info.getAppName();
ClientResponse response = null;
try {
Builder resourceBuilder = jerseyClient.resource(serviceUrl).path(urlPath).getRequestBuilder();
addExtraHeaders(resourceBuilder);
response = resourceBuilder
.header("Accept-Encoding", "gzip")
.type(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_TYPE)
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
// post请求;请求参数
.post(ClientResponse.class, info);
return anEurekaHttpResponse(response.getStatus()).headers(headersOf(response)).build();
} finally {
// ...
}
}
POST 请求 Eureka-Server 的 apps/${APP_NAME} 接口,参数为 InstanceInfo ,实现注册实例信息的注册。
3.1.2. Eureka-Service
ApplicationResource.java
@POST
@Consumes({"application/json", "application/xml"})
public Response addInstance(InstanceInfo info,
@HeaderParam(PeerEurekaNode.HEADER_REPLICATION) String isReplication) {
// 参数校验
// ...
// 重点代码
registry.register(info, "true".equals(isReplication));
return Response.status(204).build();
}
浏览器发送 localhost:7001/eureka/apps
<applications>
<versions__delta>1</versions__delta>
# applicaitons的组成的hash
<apps__hashcode>UP_3_</apps__hashcode>
<application>
# 应用名
<name>CLOUD-PROVIDER-PAYMENT</name>
# 实例
<instance>
# 实例ID需要唯一
<instanceId>LAPTOP-RHVGCSK0:payment:8001</instanceId>
<hostName>192.168.31.193</hostName>
<app>CLOUD-PROVIDER-PAYMENT</app>
<ipAddr>192.168.31.193</ipAddr>
<status>UP</status>
<overriddenstatus>UNKNOWN</overriddenstatus>
<port enabled="true">8001</port>
<securePort enabled="false">443</securePort>
<countryId>1</countryId>
<dataCenterInfo class="com.netflix.appinfo.InstanceInfo$DefaultDataCenterInfo">
<name>MyOwn</name>
</dataCenterInfo>
<leaseInfo>
<renewalIntervalInSecs>30</renewalIntervalInSecs>
<durationInSecs>90</durationInSecs>
<registrationTimestamp>1617633199552</registrationTimestamp>
<lastRenewalTimestamp>1617633829600</lastRenewalTimestamp>
<evictionTimestamp>0</evictionTimestamp>
<serviceUpTimestamp>1617633199552</serviceUpTimestamp>
</leaseInfo>
<metadata>
<management.port>8001</management.port>
</metadata>
<homePageUrl>http://192.168.31.193:8001/</homePageUrl>
<statusPageUrl>http://192.168.31.193:8001/actuator/info</statusPageUrl>
<healthCheckUrl>http://192.168.31.193:8001/actuator/health</healthCheckUrl>
<vipAddress>cloud-provider-payment</vipAddress>
<secureVipAddress>cloud-provider-payment</secureVipAddress>
<isCoordinatingDiscoveryServer>false</isCoordinatingDiscoveryServer>
<lastUpdatedTimestamp>1617633199552</lastUpdatedTimestamp>
<lastDirtyTimestamp>1617633199491</lastDirtyTimestamp>
<actionType>ADDED</actionType>
</instance>
</application>
<application>
<name>ORDER80</name>
# 多个实例
<instance>
<instanceId>LAPTOP-RHVGCSK0:order:80</instanceId>
<hostName>192.168.31.193</hostName>
<app>ORDER80</app>
<ipAddr>192.168.31.193</ipAddr>
<status>UP</status>
<port enabled="true">80</port>
<securePort enabled="false">443</securePort>
<countryId>1</countryId>
<leaseInfo>
<renewalIntervalInSecs>30</renewalIntervalInSecs>
<durationInSecs>90</durationInSecs>
<registrationTimestamp>1617633135195</registrationTimestamp>
<lastRenewalTimestamp>1617633825249</lastRenewalTimestamp>
<evictionTimestamp>0</evictionTimestamp>
<serviceUpTimestamp>1617633135195</serviceUpTimestamp>
</leaseInfo>
<metadata>
<management.port>80</management.port>
</metadata>
<homePageUrl>http://192.168.31.193:80/</homePageUrl>
<statusPageUrl>http://192.168.31.193:80/actuator/info</statusPageUrl>
<healthCheckUrl>http://192.168.31.193:80/actuator/health</healthCheckUrl>
<vipAddress>order80</vipAddress>
<secureVipAddress>order80</secureVipAddress>
<isCoordinatingDiscoveryServer>false</isCoordinatingDiscoveryServer>
<lastUpdatedTimestamp>1617633135195</lastUpdatedTimestamp>
<lastDirtyTimestamp>1617633135119</lastDirtyTimestamp>
<actionType>ADDED</actionType>
</instance>
<instance>
<instanceId>LAPTOP-RHVGCSK0:order:81</instanceId>
<hostName>192.168.31.193</hostName>
<app>ORDER80</app>
<ipAddr>192.168.31.193</ipAddr>
<status>UP</status>
<overriddenstatus>UNKNOWN</overriddenstatus>
<port enabled="true">81</port>
<securePort enabled="false">443</securePort>
<countryId>1</countryId>
<dataCenterInfo class="com.netflix.appinfo.InstanceInfo$DefaultDataCenterInfo">
<name>MyOwn</name>
</dataCenterInfo>
<leaseInfo>
<renewalIntervalInSecs>30</renewalIntervalInSecs>
<durationInSecs>90</durationInSecs>
<registrationTimestamp>1617631878936</registrationTimestamp>
<lastRenewalTimestamp>1617633829226</lastRenewalTimestamp>
<evictionTimestamp>0</evictionTimestamp>
<serviceUpTimestamp>1617631878937</serviceUpTimestamp>
</leaseInfo>
<metadata>
<management.port>81</management.port>
</metadata>
<homePageUrl>http://192.168.31.193:81/</homePageUrl>
<statusPageUrl>http://192.168.31.193:81/actuator/info</statusPageUrl>
<healthCheckUrl>http://192.168.31.193:81/actuator/health</healthCheckUrl>
<vipAddress>order80</vipAddress>
<secureVipAddress>order80</secureVipAddress>
<isCoordinatingDiscoveryServer>false</isCoordinatingDiscoveryServer>
<lastUpdatedTimestamp>1617631878937</lastUpdatedTimestamp>
<lastDirtyTimestamp>1617631878931</lastDirtyTimestamp>
<actionType>ADDED</actionType>
</instance>
</application>
</applications>
上面的register方法,最终调用的是PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl的方法
PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.java
@Override
public void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) {
// 实例注册
super.register(info, leaseDuration, isReplication);
// 复制到同等服务节点上去
replicateToPeers(Action.Register, info.getAppName(), info.getId(), info, null, isReplication);
}
需要先了解一下Lease这个对象,因为Eureka-Server最终处理注册信息的时候,都会转化为这个对象来处理。
public class Lease<T> {
// 默认的过期时间 90s
public static final int DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS = 90;
// 实例信息
private T holder;
// 服务剔除是时间,当服务下线的时候,会过来更新这个时间戳registrationTimestamp
private long evictionTimestamp;
// 服务注册的时间
private long registrationTimestamp;
// 服务启动时间 ,当客户端在注册的时候,instanceInfo的status为UP的时候,则更新这个 时间戳
private long serviceUpTimestamp;
// Make it volatile so that the expiration task would see this quicker
// 最后更新时间,每次续约的时候,都会更新这个时间戳,在判断实例是否过期时,需要用到这个属性。
private volatile long lastUpdateTimestamp;
// 过期时间
private long duration;
/**
* 服务是否过期
*/
public boolean isExpired(long additionalLeaseMs) {
return (evictionTimestamp > 0 || System.currentTimeMillis() > (lastUpdateTimestamp + duration + additionalLeaseMs));
}
服务注册重要代码
// eureka的注册表
private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> registry
= new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>>();
public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) {
try {
// 上读锁
read.lock();
// 通过服务名从本地MAP里面获取当前服务列表。
Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(registrant.getAppName());
REGISTER.increment(isReplication);
// 如果第一次进来,那么gMap为空,则创建一个ConcurrentHashMap放入到registry里面去
if (gMap == null) {
final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gNewMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>();
// putIfAbsent方法主要是在向ConcurrentHashMap中添加键—值对的时候,它会先判断该键值对是否已经存在。
// 如果不存在(新的entry),那么会向map中添加该键值对,并返回null。
// 如果已经存在,那么不会覆盖已有的值,直接返回已经存在的值。
// 线程安全操作
gMap =
registry.putIfAbsent(registrant.getAppName(), gNewMap);
// 表明map中确实不存在,则设置gMap为最新创建的那个
if (gMap == null) {
gMap = gNewMap;
}
}
// 从MAP中查询已经存在的Lease信息 (比如第二次来)
Lease<InstanceInfo> existingLease = gMap.get(registrant.getId());
// 构建一个最新的Lease信息
Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = new Lease<InstanceInfo>(registrant, leaseDuration);
if (existingLease != null) {
// 如果该实例是第一次启动,设置启动启动
lease.setServiceUpTimestamp(existingLease.getServiceUpTimestamp());
}
// 放入本地Map中
gMap.put(registrant.getId(), lease);
// 设置注册类型为添加
registrant.setActionType(ActionType.ADDED);
// 最近变更记录队列,记录了实例的每次变化, 用于注册信息的增量获取、
recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(lease));
registrant.setLastUpdatedTimestamp();
// 清除读写缓存
invalidateCache(registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getVIPAddress(), registrant.getSecureVipAddress());
} finally {
read.unlock();
}
3.2. 拉取服务列表
3.2.1. Eureka-Client
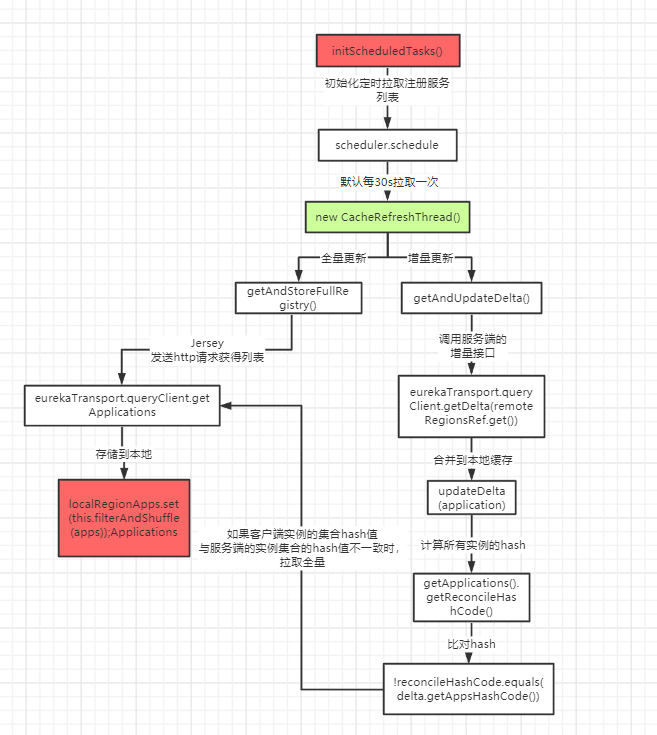
还是在 initScheduledTasks() 初始化所有的定时任务 这个方法中:
private void initScheduledTasks() {
if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
// registry cache refresh timer
// 拉取服务30秒;每30秒刷新一次
int registryFetchIntervalSeconds = clientConfig.getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds();
int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"cacheRefresh",
scheduler,
cacheRefreshExecutor,
registryFetchIntervalSeconds,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new CacheRefreshThread()
),
registryFetchIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
// 其他代码
}
定时更新服务注册列表线程CacheRefreshThread
class CacheRefreshThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
refreshRegistry();
}
}
@VisibleForTesting
void refreshRegistry() {
try {
// ...
// 重要代码,拉取服务列表
boolean success = fetchRegistry(remoteRegionsModified);
if (success) {
registrySize = localRegionApps.get().size();
lastSuccessfulRegistryFetchTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
}
}
}
由上可以看到,系统在启动的时候,初始化了一个定时器,每30秒一次,用来刷新本地缓存信息。
获得实例信息
/**
* 客户端的服务列表
*/
private final AtomicReference<Applications> localRegionApps = new AtomicReference<Applications>();
private boolean fetchRegistry(boolean forceFullRegistryFetch) {
Stopwatch tracer = FETCH_REGISTRY_TIMER.start();
try {
// 取出之前获取的服务列表
Applications applications = getApplications();
// 判断多个条件,确定是否触发全量更新,如下任一个满足都会全量更新:
// 1. 是否禁用增量
// 2. 是否对某个region特别关注
// 3. 外部传参是否要全量拉取
// 4. 本地缓存服务列表是否为empty
if (clientConfig.shouldDisableDelta()
|| (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress()))
|| forceFullRegistryFetch
|| (applications == null)
|| (applications.getRegisteredApplications().size() == 0)
|| (applications.getVersion() == -1)) //Client application does not have latest library supporting delta
{
// 拉取全量信息
getAndStoreFullRegistry();
} else {
// 拉取并更新增量信息
getAndUpdateDelta(applications);
}
// 重新计算hash值
applications.setAppsHashCode(applications.getReconcileHashCode());
logTotalInstances();
} catch (Throwable e) {
} finally {
if (tracer != null) {
tracer.stop();
}
}
return true;
}
全量获取
private final AtomicReference<Applications> localRegionApps = new AtomicReference<Applications>();
private void getAndStoreFullRegistry() throws Throwable {
long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get();
Applications apps = null;
EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress() == null
?
// 全量获取
eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications(remoteRegionsRef.get())
: eurekaTransport.queryClient.getVip(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress(), remoteRegionsRef.get());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) {
apps = httpResponse.getEntity();
}
if (apps == null) {
logger.error("The application is null for some reason. Not storing this information");
} else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) {
// 设置到本地缓存里面去
localRegionApps.set(this.filterAndShuffle(apps));
} else {
// ...
}
}
增量获取
DiscoveryClient.java
private void getAndUpdateDelta(Applications applications) throws Throwable {
long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get();
// 增量获取信息
Applications delta = null;
EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = eurekaTransport.queryClient.getDelta(remoteRegionsRef.get());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) {
delta = httpResponse.getEntity();
}
// 增量获取为空,则全量返回
if (delta == null) {
getAndStoreFullRegistry();
}
// CAS
else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) {
String reconcileHashCode = "";
// 这里设置原子锁的原因是怕某次调度网络请求时间过长,导致同一时间有多线程拉取到增量信息并发修改
if (fetchRegistryUpdateLock.tryLock()) {
try {
// 将获取到的增量信息和本地缓存信息合并
updateDelta(delta);
// 计算本地的hash; ${status}_${count}_;DOWN _2_UP_100_
reconcileHashCode = getReconcileHashCode(applications);
} finally {
fetchRegistryUpdateLock.unlock();
}
} else {
// ..
}
// 如果本地的hash与service的hash不一致,全量去拉取
if (!reconcileHashCode.equals(delta.getAppsHashCode()) || clientConfig.shouldLogDeltaDiff()) {
reconcileAndLogDifference(delta, reconcileHashCode); // this makes a remoteCall
}
} else {
// ...
}
}
- 发起http请求,将服务端的客户端变化的信息拉取过来,如: register, cancle, modify 有过这些操作的数据
- 上锁,防止某次调度网络请求时间过长,导致同一时间有多线程拉取到增量信息并发修改
- 将请求过来的增量数据和本地的数据做合并
- 计算hashCode
- 如果hashCode不一致,增量更新错误,则又会去服务端发起一次全量获取
获取注册信息
ApplicationsResource.java
@Path("/{version}/apps")
public class ApplicationsResource {
// 省略代码
@GET
public Response getContainers(@PathParam("version") String version,
@HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT) String acceptHeader,
@HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT_ENCODING) String acceptEncoding,
@HeaderParam(EurekaAccept.HTTP_X_EUREKA_ACCEPT) String eurekaAccept,
@Context UriInfo uriInfo,
@Nullable @QueryParam("regions") String regionsStr) {
// ...
// 构建全量数据缓存key
Key cacheKey = new Key(Key.EntityType.Application,
ResponseCacheImpl.ALL_APPS,
keyType, CurrentRequestVersion.get(), EurekaAccept.fromString(eurekaAccept), regions
);
Response response;
// 重点代码
response = Response.ok(responseCache.get(cacheKey))
.build();
return response;
}
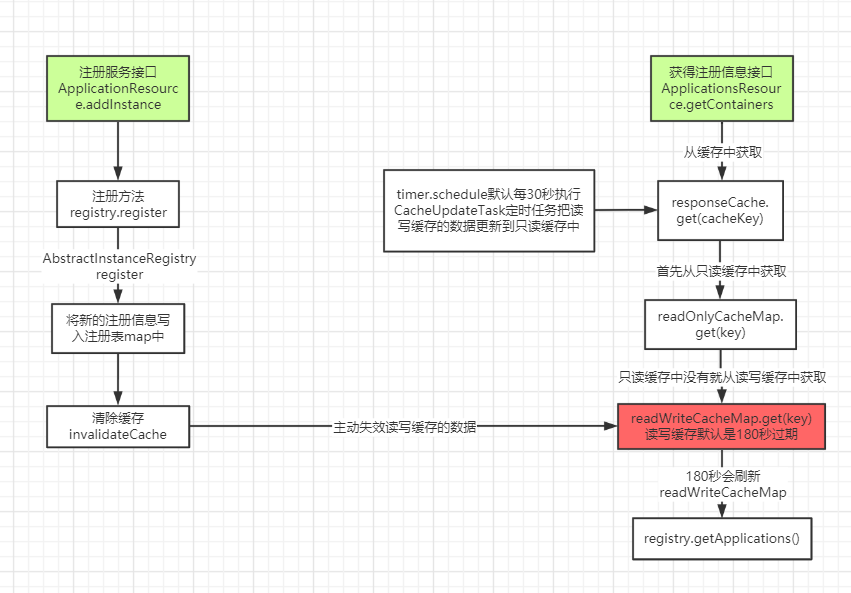
responseCache.get(cacheKey)从缓存中获取
// ...
Value getValue(final Key key, boolean useReadOnlyCache) {
Value payload = null;
try {
// 是否使用只读缓存,默认为true
if (useReadOnlyCache) {
// 从缓存中获取数据
final Value currentPayload = readOnlyCacheMap.get(key);
// 如果不为空,直接返回数据
if (currentPayload != null) {
payload = currentPayload;
}
// 如果为空
else {
// 从读写读写中获取
payload = readWriteCacheMap.get(key);
// 同时将数据放入只读缓存中
readOnlyCacheMap.put(key, payload);
}
} else {
// 从读写读写中获取
payload = readWriteCacheMap.get(key);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
}
return payload;
}
// 只读缓存
private final ConcurrentMap<Key, Value> readOnlyCacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<Key, Value>();
// 读写缓存
private final LoadingCache<Key, Value> readWriteCacheMap;
// 在构造器中实现逻辑
ResponseCacheImpl(EurekaServerConfig serverConfig, ServerCodecs serverCodecs, AbstractInstanceRegistry registry) {
this.serverConfig = serverConfig;
this.serverCodecs = serverCodecs;
// 是否使用只读缓存,默认为true
this.shouldUseReadOnlyResponseCache = serverConfig.shouldUseReadOnlyResponseCache();
this.registry = registry;
// 缓存更新的时间间隔,默认为30s
long responseCacheUpdateIntervalMs = serverConfig.getResponseCacheUpdateIntervalMs();
// 读写缓存构造,使用Google的CacheBuilder缓存
this.readWriteCacheMap =
CacheBuilder.newBuilder().initialCapacity(1000)
// 过期180s
.expireAfterWrite(serverConfig.getResponseCacheAutoExpirationInSeconds(), TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.removalListener(new RemovalListener<Key, Value>() {
@Override
public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification<Key, Value> notification) {
Key removedKey = notification.getKey();
}
})
// 缓存加载器,当缓存不存在时,会自动执行load方法,进行缓存加载。同时返回缓存数据
.build(new CacheLoader<Key, Value>() {
@Override
public Value load(Key key) throws Exception {
// 加载数据
Value value = generatePayload(key);
return value;
}
});
// 是否使用只读缓存,如果使用,此处则启动一个定时器,默认每隔30s用来复制readWriteCacheMap 的数据至readOnlyCacheMap
if (shouldUseReadOnlyResponseCache) {
timer.schedule(getCacheUpdateTask(),
new Date(((System.currentTimeMillis() / responseCacheUpdateIntervalMs) * responseCacheUpdateIntervalMs)
+ responseCacheUpdateIntervalMs),
responseCacheUpdateIntervalMs);
}
}
private TimerTask getCacheUpdateTask() {
return new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 遍历只读缓存中的key
for (Key key : readOnlyCacheMap.keySet()) {
try {
CurrentRequestVersion.set(key.getVersion());
// 从读写缓存中获得数据
Value cacheValue = readWriteCacheMap.get(key);
// 从只读缓存中获得数据
Value currentCacheValue = readOnlyCacheMap.get(key);
// 如果两者不一致,以读写缓存为准,覆盖只读缓存的数据
if (cacheValue != currentCacheValue) {
readOnlyCacheMap.put(key, cacheValue);
}
} catch (Throwable th) {
}
}
}
};
}
总结:
在拉取注册的时候:
- 首先从ReadOnlyCacheMap里查缓存的注册表;
- 若没有,就找ReadWriteCacheMap里缓存的注册表;
- 如果还没有,就从内存中获取实际的注册表数据。
在注册表发生时候:
- 会在内存中更新变更的注册表数据,同时过期掉ReadWriteCacheMap;
- 此过程不会影响ReadOnlyCacheMap提供人家查询注册表;
- ReadOnlyCacheMap 默认30秒会从ReadWriteCacheMap中更新数据;
- ReadWriteCacheMap 默认是180秒数据会失效。
- 下次有服务拉取列表或者是ReadOnlyCacheMap更新时, 如果缓存没有命中,都会去注册表重新获取最新的值。
多级缓存的优点:
- 尽可能保证了内存注册表数据不会出现频繁的读写冲突问题;
- 进一步保证了对eurekaService的大量请求,都是快速走纯内存。【如我们公司】
参考文档 :
https://github.com/Netflix/eureka
https://www.iocoder.cn/categories/Eureka/
最后
以上就是酷酷身影最近收集整理的关于注册中心eureka的介绍及源码探索1. 背景2. Eureka的全部内容,更多相关注册中心eureka的介绍及源码探索1.内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复