在前面的文章介绍了,如何使用服务注册发现组件: Eureka,并给出使用示例。本文在此基础上,将会讲解 Eureka 客户端实现的内幕,结合源码深入实现的细节,知其所以然。客户端需要重点关注以下几点:
- 从Eureka Server中拉取注册表信息
- 全量拉取注册表信息
- 增量式拉取注册表信息
- 注册表缓存刷新定时器与续租(心跳)定时器
- 服务注册与服务按需注册
- 服务实例的下线
本文摘录于笔者出版的书籍 《Spring Cloud 微服务架构进阶》
Eureka Client 结构
在Finchley版本的SpringCloud中,不需要添加任何的额外的注解就可以登记为Eureka Client,只需要在pom文件中添加spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client的依赖。
为了跟踪Eureka的运行机制,读者可以打开SpringBoot的Debug模式来查看更多的输出日志:
logging:
level:
org.springframework: DEBUG
查看spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-client的src/main/resource.META-INF/spring.factories,查看Eureka Client有哪些自动配置类:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaClientConfigServerAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaClientAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.eureka.RibbonEurekaAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration
排除掉与配置中心相关的自动配置类,从中可以找到三个与Eureka Client密切相关的自动配置类:
- EurekaClientAutoConfiguration
- RibbonEurekaAutoConfiguration
- EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration
下面将对这些类进行分析,看看一个正常的Eureka Client需要做哪一些初始化配置。
EurekaClientAutoConfiguration
Eureke Client的自动配置类,负责了Eureka Client中关键的bean的配置和初始化,以下是其内比较重要的bean的介绍与作用。
EurekaClientConfig
提供了Eureka Client注册到Eureka Server所需要的配置信息,SpringCloud为其提供了一个默认配置类的EurekaClientConfigBean,可以在配置文件中通过前缀eureka.client+属性名进行覆盖。
ApplicationInfoManager
该类管理了服务实例的信息类InstanceInfo,其内包括Eureka Server上的注册表所需要的信息,代表了每个Eureka Client提交到注册中心的数据,用以供服务发现。同时管理了实例的配置信息EurekaInstanceConfig,SpringCloud提供了一个EurekaInstanceConfigBean的配置类进行默认配置,也可以在配置文件application.yml中通过eureka.instance+属性名进行自定义配置。
EurekaInstanceConfigBean
继承了EurekaInstanceConfig接口,是Eureka Client注册到服务器上需要提交的关于服务实例自身的相关信息,主要用于服务发现:
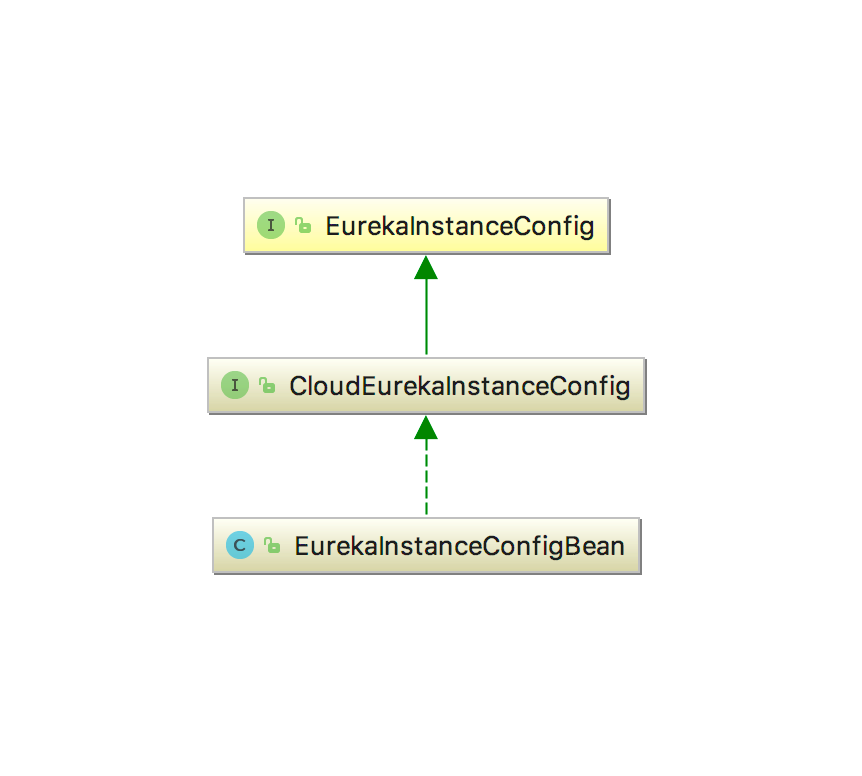
通常这些信息在配置文件中的eureka.instance前缀下进行设置,SpringCloud通过EurekaInstanceConfigBean配置类提供了相关的默认配置。以下是一些比较关键的属性,这些信息都将注册到注册中心上。
public class EurekaInstanceConfigBean implements CloudEurekaInstanceConfig, EnvironmentAware {
// 服务实例的应用名
private String appname;
// 服务实例的Id,通常和appname共同唯一标记一个服务实例
private String instanceId;
// 自定义添加的元数据,由用户使用以适配扩展业务需求
private Map<String, String> metadataMap;
// 如果服务实例部署在AWS上,该类将持有服务实例部署所在的数据中心的准确信息
private DataCenterInfo dataCenterInfo;
// 服务实例的Ip地址
private String ipAddress;
// 服务实例主页地址
private String homePageUrl;
// 服务实例健康检查地址
private String healthCheckUrlPath;
// 服务实例的状态地址
private String statusPageUrlPath
.....
}
DiscoveryClient
这是SpringCloud定义的用来服务发现的顶级接口,在Netflix Eureka或者consul都有相应的具体实现类,提供的方法如下:
public interface DiscoveryClient {
// 获取实现类的描述
String description();
// 通过服务Id获取服务实例的信息
List<ServiceInstance> getInstances(String serviceId);
// 获取所有的服务实例的Id
List<String> getServices();
}
其在Eureka方面的实现的相关的类结构图:
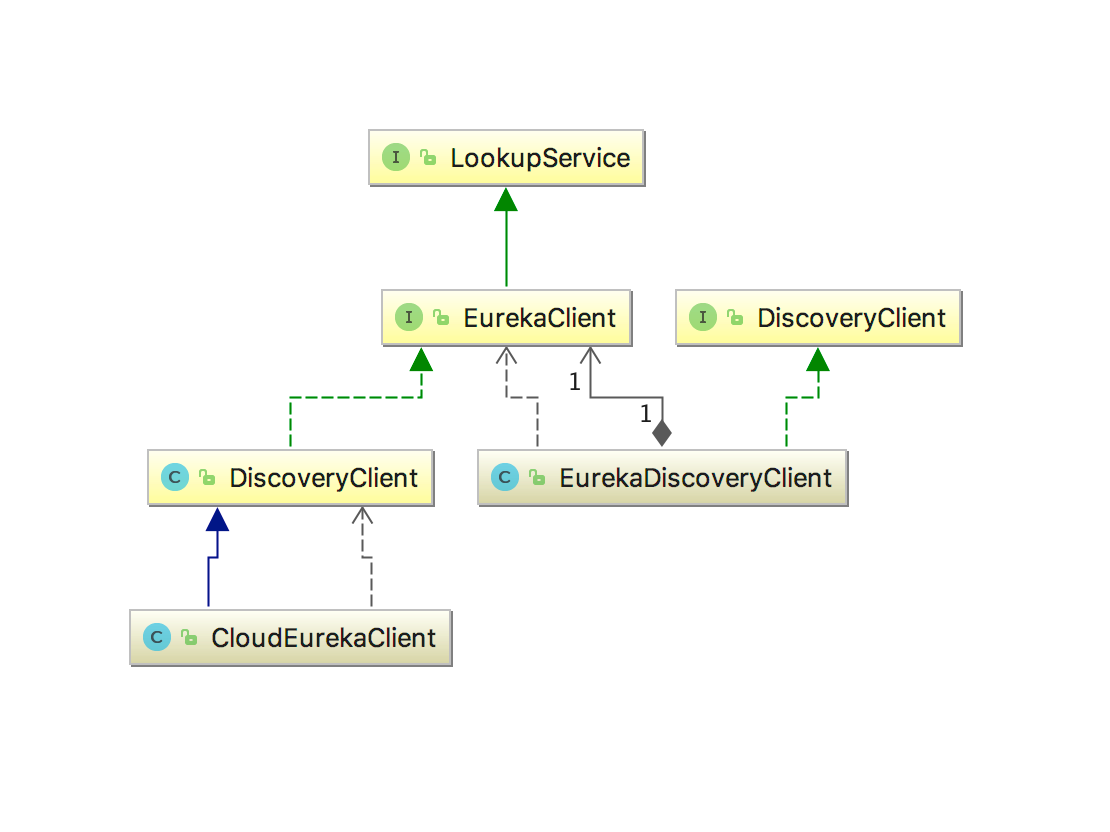
EurekaDiscoveryClient继承了DiscoveryClient,但是通过查看EurekaDiscoveryClient中的代码,会发现它是通过组合类EurekaClient实现接口的功能,如下的getInstance接口:
@Override
public List<ServiceInstance> getInstances(String serviceId) {
List<InstanceInfo> infos = this.eurekaClient.getInstancesByVipAddress(serviceId,false);
List<ServiceInstance> instances = new ArrayList<>();
for (InstanceInfo info : infos) {
instances.add(new EurekaServiceInstance(info));
}
return instances;
}
EurekaClient来自于com.netflix.discovery包中,其默认实现为com.netflix.discovery.DiscoveryClient,这属于eureka-client的源代码,它提供了Eureka Client注册到Server上、续租,下线以及获取Server中注册表信息等诸多关键功能。SpringCloud通过组合方式调用了Eureka中的的服务发现方法,关于EurekaClient的详细代码分析将放在客户端核心代码中介绍。为了适配spring-cloud,spring提供了一个CloudEurekaClient继承了com.netflix.discovery.DiscoveryClient,同时覆盖了onCacheRefreshed防止在spring-boot还没初始化时调用该接口出现NullPointException。
上述的几个配置类之间的关系非常紧密,数据之间存在一定的耦合,所以下面介绍一下它们之间的关系
首先是EurekaInstanceConfig,代码位于EurekaClientAutoConfiguration
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EurekaInstanceConfig.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public EurekaInstanceConfigBean eurekaInstanceConfigBean(InetUtils inetUtils, ManagementMetadataProvider managementMetadataProvider) {
// 从配置文件中读取属性
String hostname = getProperty("eureka.instance.hostname");
boolean preferIpAddress = Boolean.parseBoolean(getProperty("eureka.instance.prefer-ip-address"));
String ipAddress = getProperty("eureka.instance.ipAddress");
boolean isSecurePortEnabled = Boolean.parseBoolean(getProperty("eureka.instance.secure-port-enabled"));
String serverContextPath = env.getProperty("server.context-path", "/");
int serverPort = Integer.valueOf(env.getProperty("server.port", env.getProperty("port", "8080")));
Integer managementPort = env.getProperty("management.server.port", Integer.class);// nullable. should be wrapped into optional
String managementContextPath = env.getProperty("management.server.context-path");// nullable. should be wrapped into optional
Integer jmxPort = env.getProperty("com.sun.management.jmxremote.port", Integer.class);//nullable
EurekaInstanceConfigBean instance = new EurekaInstanceConfigBean(inetUtils);
// 设置非空属性
instance.setNonSecurePort(serverPort);
instance.setInstanceId(getDefaultInstanceId(env));
instance.setPreferIpAddress(preferIpAddress);
if (StringUtils.hasText(ipAddress)) {
instance.setIpAddress(ipAddress);
}
if(isSecurePortEnabled) {
instance.setSecurePort(serverPort);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(hostname)) {
instance.setHostname(hostname);
}
String statusPageUrlPath = getProperty("eureka.instance.status-page-url-path");
String healthCheckUrlPath = getProperty("eureka.instance.health-check-url-path");
if (StringUtils.hasText(statusPageUrlPath)) {
instance.setStatusPageUrlPath(statusPageUrlPath);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(healthCheckUrlPath)) {
instance.setHealthCheckUrlPath(healthCheckUrlPath);
}
ManagementMetadata metadata = managementMetadataProvider.get(instance, serverPort, serverContextPath, managementContextPath, managementPort);
.....
return instance;
}
从上面的代码可以发现,EurekaInstanceConfig的属性主要通过EurekaInstanceConfigBean的实现提供,同时也会尝试从配置文件中读取一部分配置,在例如eureka.instance.hostname、eureka.instance.status-page-url-path、eureka.instance.health-check-url-path等等,它代表了应用实例的应该具备的信息,然后这部分信息会被封装成InstanceInfo,被注册到Eureka Server中。
InstanceInfo是通过InstanceInfoFactory(org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka)封装EurekaInstanceConfig中的属性创建的,其中InstanceInfo的属性基本是volatile,保证了内存中的该类信息的一致性和原子性。
代码位于InstanceInfoFactory。
public InstanceInfo create(EurekaInstanceConfig config) {
LeaseInfo.Builder leaseInfoBuilder = LeaseInfo.Builder.newBuilder()
.setRenewalIntervalInSecs(config.getLeaseRenewalIntervalInSeconds())
.setDurationInSecs(config.getLeaseExpirationDurationInSeconds());
// 创建服务实例的信息用来注册到eureka server上
InstanceInfo.Builder builder = InstanceInfo.Builder.newBuilder();
String namespace = config.getNamespace();
if (!namespace.endsWith(".")) {
namespace = namespace + ".";
}
builder.setNamespace(namespace).setAppName(config.getAppname())
.setInstanceId(config.getInstanceId())
.setAppGroupName(config.getAppGroupName())
.setDataCenterInfo(config.getDataCenterInfo())
.setIPAddr(config.getIpAddress()).setHostName(config.getHostName(false))
.setPort(config.getNonSecurePort())
.enablePort(InstanceInfo.PortType.UNSECURE,
config.isNonSecurePortEnabled())
.setSecurePort(config.getSecurePort())
.enablePort(InstanceInfo.PortType.SECURE, config.getSecurePortEnabled())
.setVIPAddress(config.getVirtualHostName())
.setSecureVIPAddress(config.getSecureVirtualHostName())
.setHomePageUrl(config.getHomePageUrlPath(), config.getHomePageUrl())
.setStatusPageUrl(config.getStatusPageUrlPath(),
config.getStatusPageUrl())
.setHealthCheckUrls(config.getHealthCheckUrlPath(),
config.getHealthCheckUrl(), config.getSecureHealthCheckUrl())
.setASGName(config.getASGName());
....
InstanceInfo instanceInfo = builder.build();
instanceInfo.setLeaseInfo(leaseInfoBuilder.build());
return instanceInfo;
}
接着是ApplicationInfoManager,代码位于EurekaClientAutoConfiguration。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ApplicationInfoManager.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public ApplicationInfoManager eurekaApplicationInfoManager(EurekaInstanceConfig config) {
InstanceInfo instanceInfo = new InstanceInfoFactory().create(config);
return new ApplicationInfoManager(config, instanceInfo);
}
通过组合EurekaInstanceConfig和InstanceInfo创建了ApplicationInfoManager,属于应用信息管理器。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EurekaClientConfig.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public EurekaClientConfigBean eurekaClientConfigBean() {
EurekaClientConfigBean client = new EurekaClientConfigBean();
if ("bootstrap".equals(propertyResolver.getProperty("spring.config.name"))) {
// We don't register during bootstrap by default, but there will be another
// chance later.
client.setRegisterWithEureka(false);
}
return client;
}
前面有讲到,EurekaClientConfig持有Eureka Client与Eureka Server进行交互的关键性配置信息,类似serviceUrl(Server地址),EurekaClient通过EurekaClientConfig中配置信息与Eureka Server进行服务注册与发现。
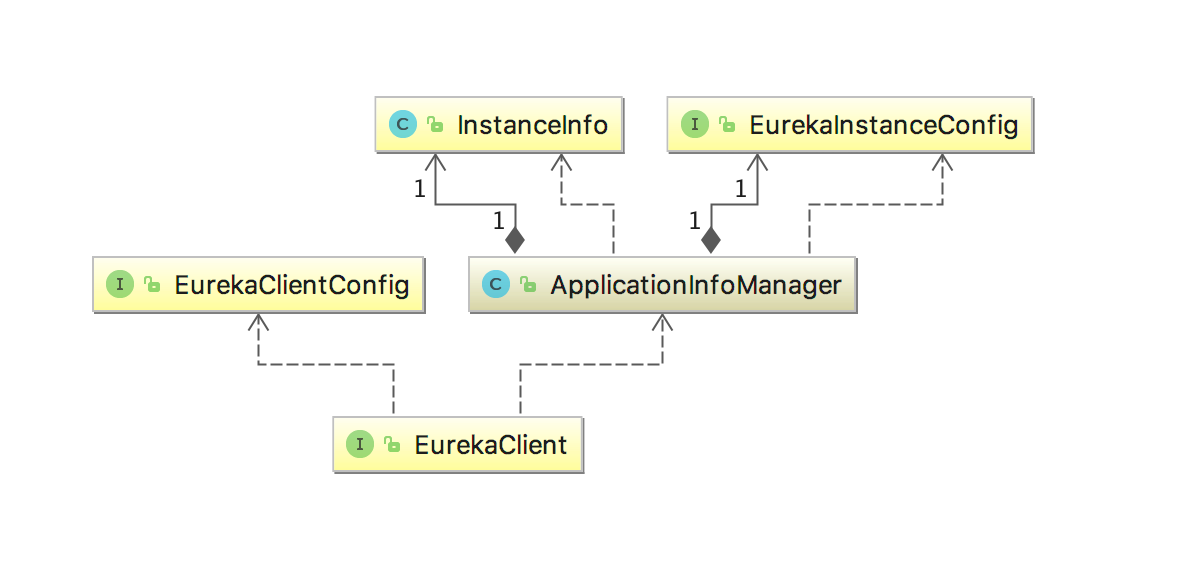
最后是EurekaClient,通过ApplicationInfoManager与EurekaClientConfig组合创建,即EurekaClient同时持有了client的服务实例信息用于服务发现,与Eureka Server注册的配置用于服务注册。
@Bean(destroyMethod = "shutdown")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EurekaClient.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public EurekaClient eurekaClient(ApplicationInfoManager manager, EurekaClientConfig config){
return new CloudEurekaClient(manager, config, this.optionalArgs, this.context);
}
整体的类结构如下
EurekaRegistration、EurekaServiceRegistry、EurekaAutoServiceRegistration
这是SpringCloud适配Eureka所加的将服务注册到服务注册中心的相关类,先来看一下相关的类结构
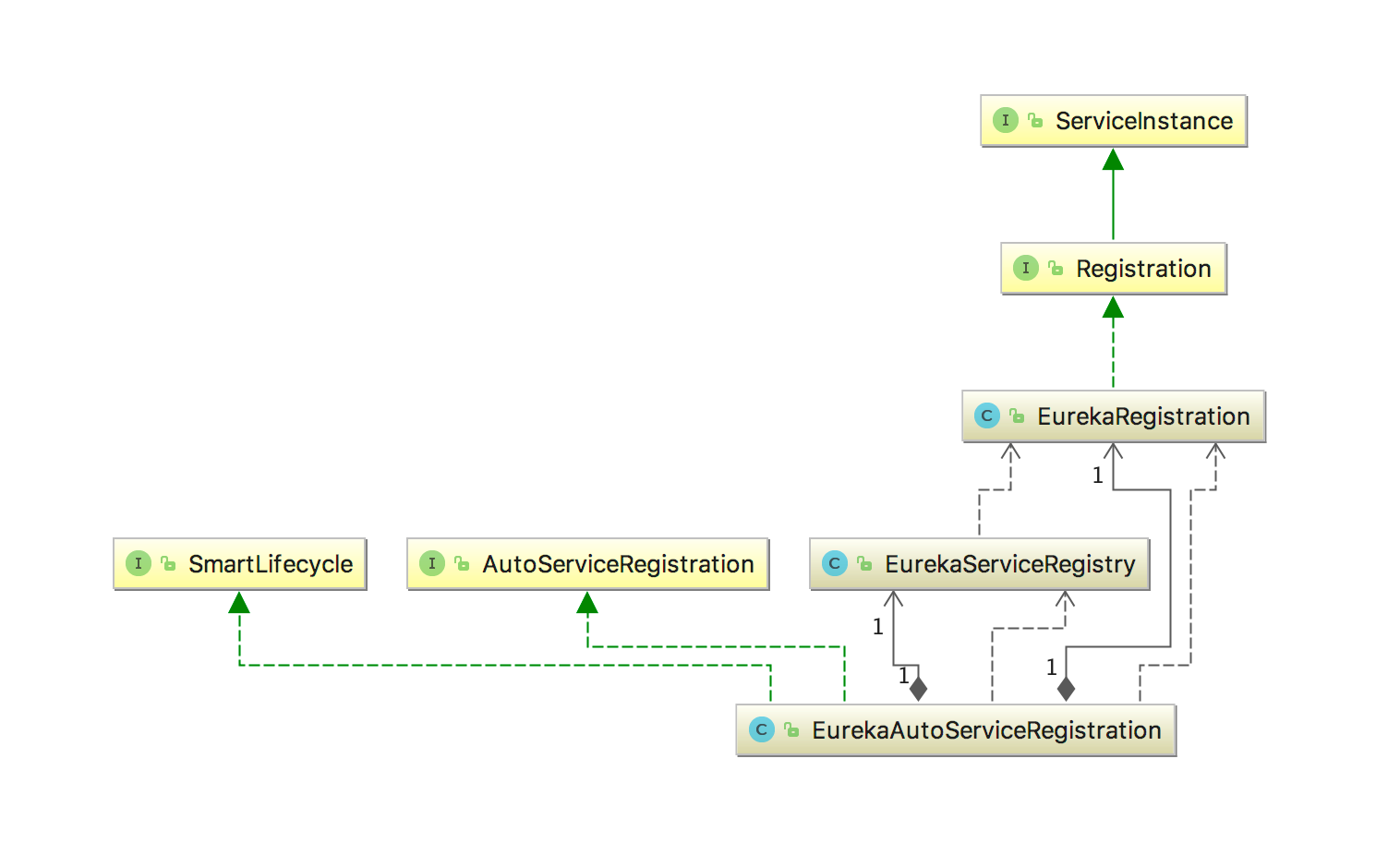
Registration继承了ServiceInstance,代表了一个被注册到服务发现系统的一个服务实例,必须具备的信息如hostname和port等,Registration是ServiceInstance的一个门面类
public interface ServiceInstance {
//获取服务实例的serviceId
String getServiceId();
//获取服务实例的hostname
String getHost();
//获取服务实例的端口号
int getPort();
boolean isSecure();
//获取服务实例的uri地址
URI getUri();
//获取服务实例的元数据key-value对
Map<String, String> getMetadata();
}
对应Eureka,EurekaRegistration实现了Registration,查看其中的代码,只是照搬了EurekaInstanceConfigBean中的配置信息,同时注入了EurekaClient,为Eureka Client的服务注册提供实现。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(AutoServiceRegistrationProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public EurekaRegistration eurekaRegistration(EurekaClient eurekaClient, CloudEurekaInstanceConfig instanceConfig, ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, ObjectProvider<HealthCheckHandler> healthCheckHandler) {
return EurekaRegistration.builder(instanceConfig)
.with(applicationInfoManager)
.with(eurekaClient)
.with(healthCheckHandler)
.build();
}
ServiceRegistry里面提供了将服务实例注册到服务注册中心的相关接口:
public interface ServiceRegistry<R extends Registration> {
//注册服务实例,registration当中通常有关于服务实例的信息,例如hostname和port
void register(R registration);
//注销服务实例
void deregister(R registration);
//关闭ServiceRegistry,通常在服务关闭的时候被调用
void close();
//设置服务实例的状态
void setStatus(R registration, String status);
//获取服务实例的状态
<T> T getStatus(R registration);
}
其中在EurekaServiceRegistry的注册和下线的实现如下:
@Override
public void register(EurekaRegistration reg) {
// 初始化EurekaRegistration中的EurekaClient,如果为null
maybeInitializeClient(reg);
// 修改服务的状态为UP
reg.getApplicationInfoManager()
.setInstanceStatus(reg.getInstanceConfig().getInitialStatus());
// 设置健康检查
reg.getHealthCheckHandler().ifAvailable(healthCheckHandler ->
reg.getEurekaClient().registerHealthCheck(healthCheckHandler));
}
private void maybeInitializeClient(EurekaRegistration reg) {
reg.getApplicationInfoManager().getInfo();
reg.getEurekaClient().getApplications();
}
@Override
public void deregister(EurekaRegistration reg) {
if (reg.getApplicationInfoManager().getInfo() != null) {
// 设置服务的状态为DOWN
reg.getApplicationInfoManager().setInstanceStatus(InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus.DOWN);
}
}
在上面的代码中可以发现,对服务的注册和下线仅仅是修改了服务当前的状态,其实在EurekaClient的接口实现类中有专门对InstanceStatus状态修改的监听,当服务实例的信息改变时就会触发不同的事件进行处理。
EurekaAutoServiceRegistration,顾名思义,就是服务实例的自动注册,由前面的类图可知,该类继承了SmartLifecycle的接口,这是org.springframework.context包中的相关类,说明EurekaAutoServiceRegistration类受到了Spring的生命周期的管理。
...
@EventListener(ServletWebServerInitializedEvent.class)
public void onApplicationEvent(ServletWebServerInitializedEvent event) {
int localPort = event.getWebServer().getPort();
if (this.port.get() == 0) {
log.info("Updating port to " + localPort);
this.port.compareAndSet(0, localPort);
start();
}
}
@EventListener(ContextClosedEvent.class)
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextClosedEvent event) {
if( event.getApplicationContext() == context ) {
stop();
}
}
在上述代码中,该类监听了ServletWebServerInitializedEvent和ContextClosedEvent两个事件,即在应用初始化阶段调用start()和应用上下文关闭阶段调用stop(),其实就是在应用启动和关闭时分别进行服务的注册和下线的自动操作。
EurekaAutoServiceRegistration的服务注册和下线是直接调用了EurekaServiceRegistry中的方法。
@Override
public void start() {
// only set the port if the nonSecurePort or securePort is 0 and this.port != 0
if (this.port.get() != 0) {
if (this.registration.getNonSecurePort() == 0) {
this.registration.setNonSecurePort(this.port.get());
}
if (this.registration.getSecurePort() == 0 && this.registration.isSecure()) {
this.registration.setSecurePort(this.port.get());
}
}
if (!this.running.get() && this.registration.getNonSecurePort() > 0) {
// 注册服务
this.serviceRegistry.register(this.registration);
this.context.publishEvent(
new InstanceRegisteredEvent<>(this, this.registration.getInstanceConfig()));
this.running.set(true);
}
}
@Override
public void stop() {
// 服务下线
this.serviceRegistry.deregister(this.registration);
this.running.set(false);
}
EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration
EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration只做了两件事,监听了RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent事件以及注入EurekaHealthCheckHandler接口的实现类。
RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent事件一般在spring管理的bean被刷新的时候被抛出,此时说明应用环境的配置和参数有可能发生变化,于是需要重新注册服务,防止注册中心的服务实例信息与本地信息不一致。
@EventListener(RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent.class)
public void onApplicationEvent(RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent event) {
// 保证了一个刷新事件发生后client的重新注册
if(eurekaClient != null) {
eurekaClient.getApplications();
}
if (autoRegistration != null) {
// 重新注册防止本地信息与注册表中的信息不一致
this.autoRegistration.stop();
this.autoRegistration.start();
}
}
RibbonEurekaAutoConfiguration
Eureka中配置负载均衡的配置类,具体关于Ribbon的内容将在其他章节进行讲解,这里就略过
客户端核心代码
包结构
主要的代码位于eureka-client中,项目的module为eureka-client,版本为v1.8.7,这是Finchley版本的Spring Cloud所依赖的eureka版本
包结构如下
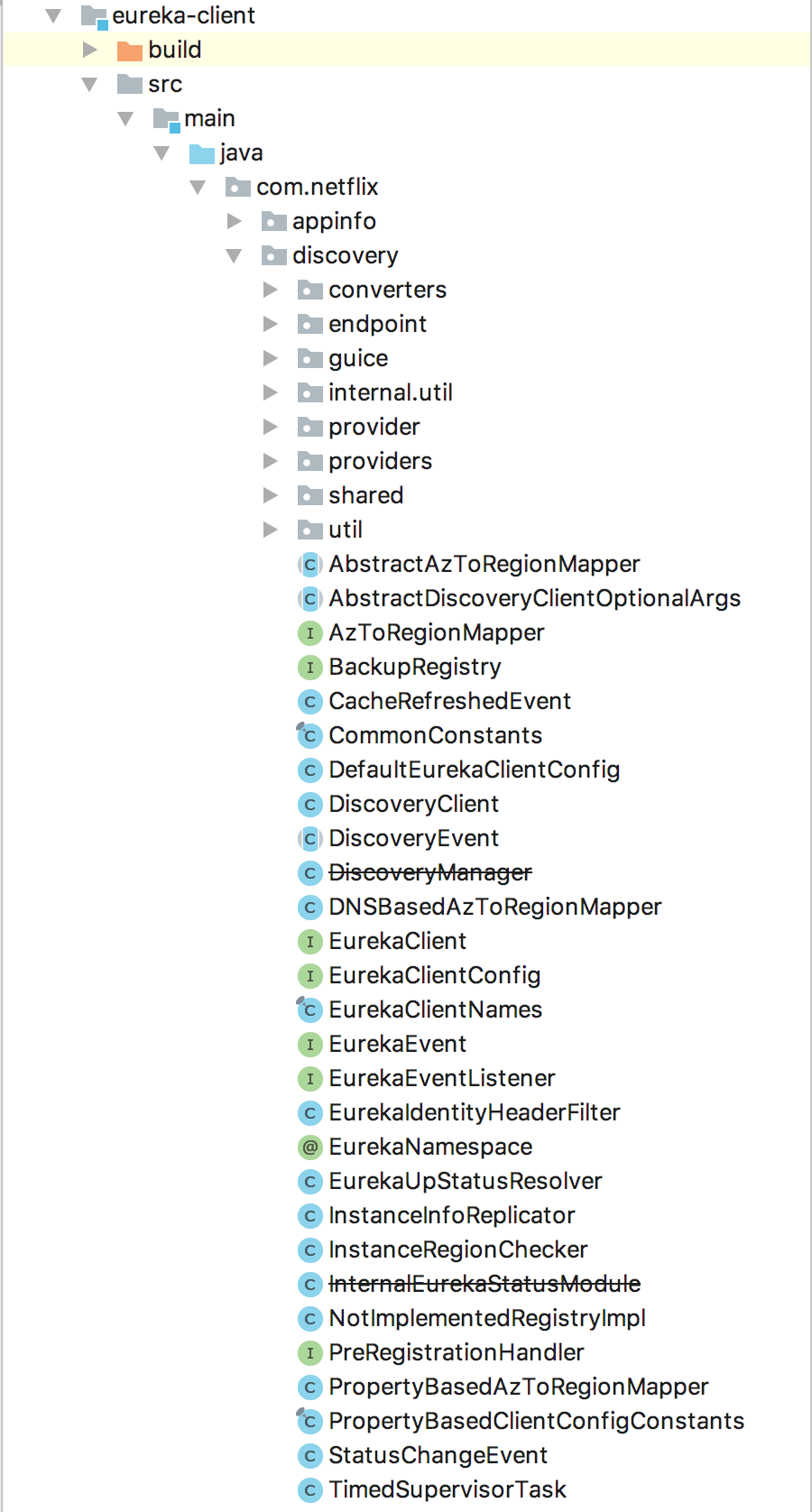
简要的包介绍:
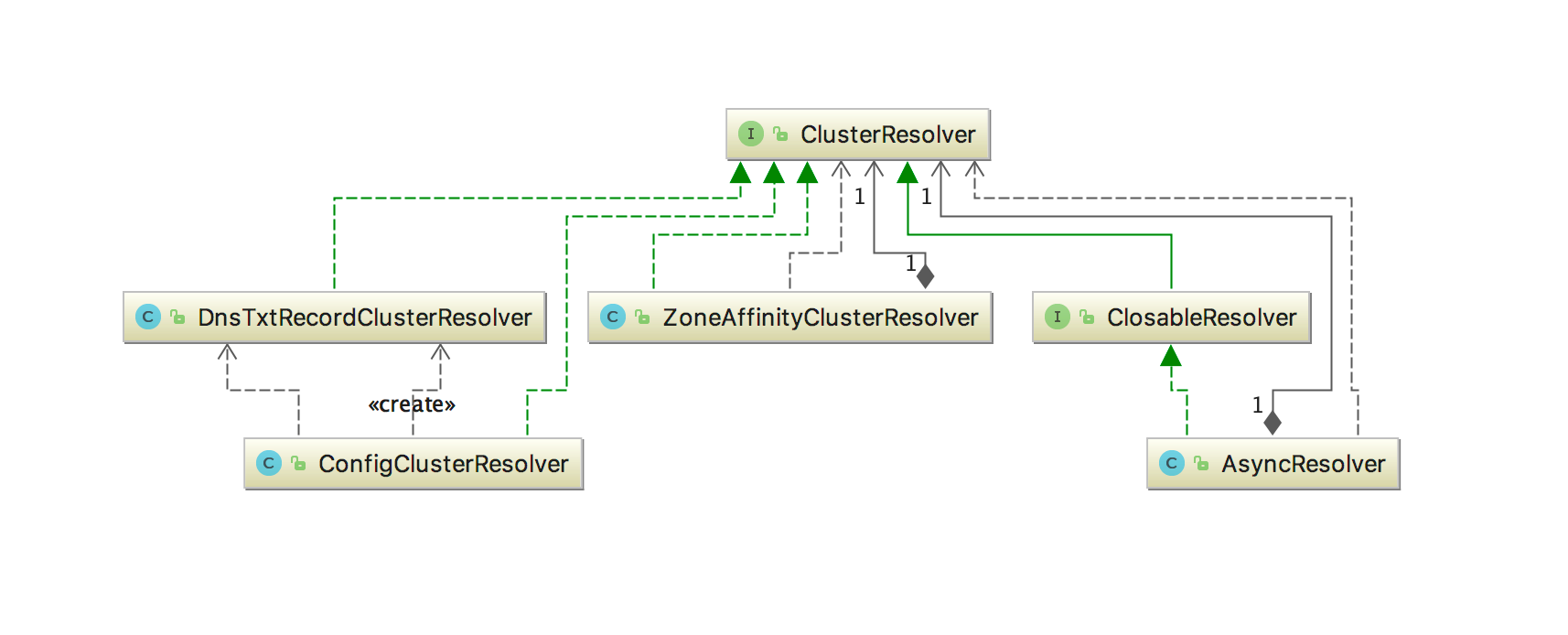
com.netflix.appinfo: 主要是关于eureka-client的配置信息类,如上面提及的EurekaInstanceConfig,InstanceInfo,其中也包含了类似AmazonInfo、DataCenterInfo等与AWS中的架构适配密切相关的接口,在此不做详解的介绍,有兴趣读者可以自行去了解。com.netflix.discovery: 主要实现Eureka-Client的服务发现和服务注册功能。com.netflix.discovery.converters: 主要解决Eureka服务之间的数据传输的编码与解码,支持JSON、XML等格式。com.netflix.discovery.guice:Google的guice依赖注入配置包,类似Spring的configuration。com.netflix.discovery.provider: 提供的Jersey中请求与响应的序列化与反序列化实现,默认实现是DefaultJerseyProvider。com.netflix.discovery.providers: 目前只有DefaultEurekaClientConfigProvider,提供EurekaClientConfig工厂生成方法。com.netflix.discovery.shared: Eureka Client与Eureka Server共享重用的方法。com.netflix.discovery.shared.dns: DNS解析器。com.netflix.discovery.shared.resolver: Euraka Endpoint解析器,EurekaEndpoint指的是服务端点,一般指的是Eureka Server的访问地址,默认实现为DefaultEndpoint,ClusterResolver将配置的Eureka Server地址解析为EurekaEndpoint,这里面用到了委托者设计模式,类图如下,有很明显的请求委托的处理过程。com.netflix.discovery.shared.transport: Eureka Client与Eureka Server之间进行HTTP通信的客户端以及通信的request和response的封装类。
DiscoveryClient
DiscoveryClient可以说是Eureka Client的核心类,负责了与Eureka Server交互的关键逻辑,具备了以下的职能:
- 注册服务实例到Eureka Server中;
- 更新与Eureka Server的契约;
- 在服务关闭时从Eureka Server中取消契约;
- 查询在Eureka Server中注册的服务/实例的列表。
DiscoverClient的核心类图如下:
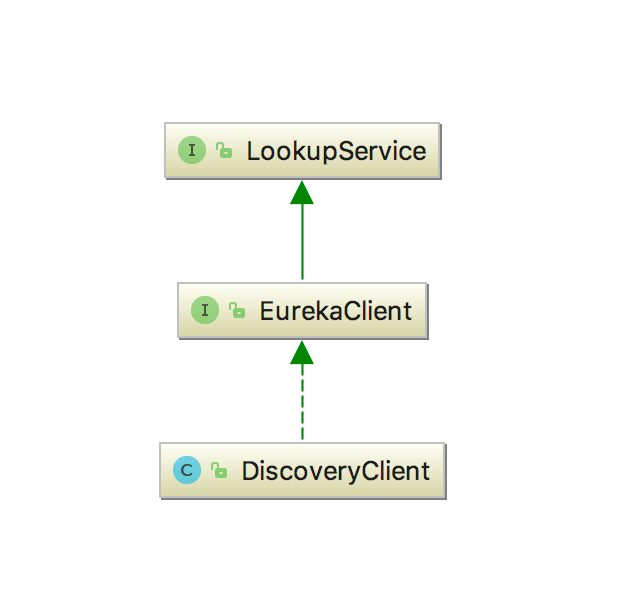
DiscoveryClient的顶层接口为LookupService,主要的目的是为了发现活跃中的服务实例。
public interface LookupService<T> {
//根据服务实例注册的appName来获取,获取一个封装有相同appName的服务实例信息的容器
Application getApplication(String appName);
//返回当前注册的所有的服务实例信息
Applications getApplications();
//根据服务实例的id获取
List<InstanceInfo> getInstancesById(String id);
//获取下一个可能的Eureka Server来处理当前对注册表信息的处理,一般是通过循环的方式来获取下一个Server
InstanceInfo getNextServerFromEureka(String virtualHostname, boolean secure);
}
Application中持有一个特定应用的多个实例的列表,可以理解成同一个服务的集群信息,它们都挂在同一个服务名appName下,InstanceInfo代表一个服务实例,部分代码如下:
public class Application {
private static Random shuffleRandom = new Random();
//服务名
private String name;
@XStreamOmitField
private volatile boolean isDirty = false;
@XStreamImplicit
private final Set<InstanceInfo> instances;
private final AtomicReference<List<InstanceInfo>> shuffledInstances;
private final Map<String, InstanceInfo> instancesMap;
.....
}
为了保证原子性操作以及数据的唯一性,防止脏数据,Application中对InstanceInfo的操作都是同步操作,感受一下Application.addInstance方法。
public void addInstance(InstanceInfo i) {
instancesMap.put(i.getId(), i);
synchronized (instances) {
instances.remove(i);
instances.add(i);
isDirty = true;
}
}
通过同步代码块,保证每次只有有一个线程对instances进行修改,同时注意instancesMap采用的是ConcurrentHashMap实现,保证了原子性的操作,所以不需要通过同步代码块进行控制。
Applications中代表的是Eureka Server中已注册的服务实例的集合信息,主要是对Application的封装,里面的操作大多也是的同步操作。
EurekaClient继承了LookupService接口,为DiscoveryClient提供了一个上层的接口,目的是试图方便从eureka 1.x 到eureka 2.x 的过渡,这说明EurekaClient这个接口属于比较稳定的接口,即使在下一大阶段也会被依旧保留。
EurekaCient在LookupService的基础上扩充了更多的接口,提供了更丰富的获取服务实例的功能,主要有:
- 提供了多种的方式获取
InstanceInfo,例如根据region,Eureka Server地址等获取; - 提供了本地客户端(位于的区域,可用区等)的数据,这部分与AWS密切相关;
- 提供了为客户端注册和获取健康检查处理器;
除去查询相关的接口,关注EurekaClient中的以下两个接口:
// 为Eureka Client注册健康检查处理器
// 一旦注册,客户端将通过调用新注册的健康检查处理器来对注册中instanceInfo
// 进行一个按需更新,随后按照eurekaclientconfig.getinstanceinforeplicationintervalseconds()
// 中配置的指定时间调用HealthCheckHandler
public void registerHealthCheck(HealthCheckHandler healthCheckHandler);
// 为eureka client注册一个EurekaEventListener(事件监听器)
// 一旦注册,当eureka client的内部状态发生改变的时候,将会调用EurekaEventListener.onEvent()
// 触发一定的事件。可以通过这种方式监听client的更新而非通过轮询的方式询问client
public void registerEventListener(EurekaEventListener eventListener);
Eureka Server一般通过心跳(heartbeats)来识别一个实例的状态。Eureka Client中存在一个定时任务定时通过HealthCheckHandler检测当前client的状态,如果client的状态发生改变,将会触发新的注册事件,同步Eureka Server的注册表中该服务实例的相关信息。
public interface HealthCheckHandler {
InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus getStatus(InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus currentStatus);
}
在spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-client中实现了这个的接口,EurekaHealthCheckHandler,主要的组合了spring-boot-actuator中的HealthAggregator和HealthIndicator实现了对spring-boot应用的状态检测。
主要有以下的状态:
public enum InstanceStatus {
UP, // 可以接受服务请求
DOWN, // 无法发送流量-健康检查失败
STARTING, // 正在启动,无法发送流量
OUT_OF_SERVICE, // 服务关闭,不接受流量
UNKNOWN; // 未知状态
}
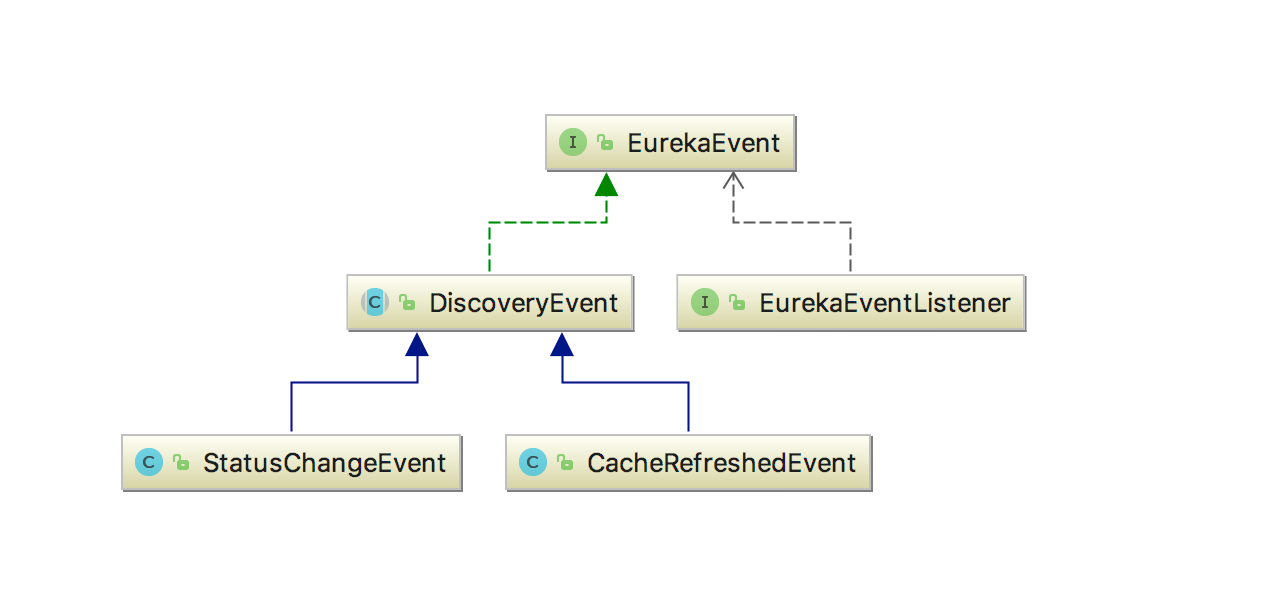
Eureka中的事件模式,这是一个很明显的观察者模式,以下为它的类图类图:
客户端的服务注册与发现
在DiscoveryClient的代码中,有实现服务注册与发现的功能的具体代码。在DiscoveryClient构造函数中,Eureka Client会执行从Eureka Server中拉取注册表信息,注册自身等操作。
DiscoveryClient的构造函数如下:
DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, EurekaClientConfig config,
AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args, Provider<BackupRegistry> backupRegistryProvider)
ApplicationInfoManager和EurekaClientConfig在前面的介绍中已经了解,一个是封装当前服务实例的配置信息的类,另一个是封装了client与server交互配置信息的类,
AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs和BackupRegistry是未介绍过的
BackupRegistry的接口代码如下:
@ImplementedBy(NotImplementedRegistryImpl.class)
public interface BackupRegistry {
Applications fetchRegistry();
Applications fetchRegistry(String[] includeRemoteRegions);
}
它充当了备份注册中心的职责,当Eureka Client无法从任何一个Eureka Server中获取注册表信息时,BackupRegistry将被调用以获取注册表信息,但是默认的实现是NotImplementedRegistryImpl,即没有实现。
public abstract class AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs<T> {
// 生成健康检查回调的工厂类,HealthCheckCallback已废弃
Provider<HealthCheckCallback> healthCheckCallbackProvider;
// 生成健康处理器的工厂类
Provider<HealthCheckHandler> healthCheckHandlerProvider;
// 向Eureka Server注册之前的预处理器
PreRegistrationHandler preRegistrationHandler;
// Jersey过滤器集合,Jersey1和Jersey2均可使用
Collection<T> additionalFilters;
// Jersey客户端,主要用于client与server之间的HTTP交互
EurekaJerseyClient eurekaJerseyClient;
// 生成Jersey客户端的工厂
TransportClientFactory transportClientFactory;
// 生成Jersey客户端的工厂的工厂
TransportClientFactories transportClientFactories;
// Eureka事件的监听器
private Set<EurekaEventListener> eventListeners;
....
}
AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs是用于注入一些可选参数的,以及一些jersey1和jersey2通用的过滤器,@Inject(optional = true)属性说明了该参数的可选性
在构造方法中,忽略掉大部分的赋值操作,逐步了解配置类中的属性会对DiscoveryClient的行为造成什么影响
if (config.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
this.registryStalenessMonitor = new ThresholdLevelsMetric(this, METRIC_REGISTRY_PREFIX + "lastUpdateSec_", new long[]{15L, 30L, 60L, 120L, 240L, 480L});
} else {
this.registryStalenessMonitor = ThresholdLevelsMetric.NO_OP_METRIC;
}
if (config.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {
this.heartbeatStalenessMonitor = new ThresholdLevelsMetric(this, METRIC_REGISTRATION_PREFIX + "lastHeartbeatSec_", new long[]{15L, 30L, 60L, 120L, 240L, 480L});
} else {
this.heartbeatStalenessMonitor = ThresholdLevelsMetric.NO_OP_METRIC;
}
config.shouldFetchRegistry()(对应配置为eureka.client.fetch-register),为true表示Eureka Client将从Eureka Server中拉取注册表的信息,config.shouldRegisterWithEureka(对应配置为eureka.client.register-with-eureka),为true表示Eureka Client将注册到Eureka Server中。
如果上述的两个配置均为false,那么Discovery的初始化就直接结束,表示该客户端既不进行服务注册也不进行服务发现
接着初始化一个基于线程池的定时器线程池ScheduledExecutorService,线程池大小为2,一个用于心跳,一个用于缓存刷新,同时初始化了心跳和缓存刷新线程池(ThreadPoolExecutor)。关于ScheduledExecutorService与ThreadPoolExecutor之间的关系在此不展开。
scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2,
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build());
heartbeatExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-HeartbeatExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
); // use direct handoff
cacheRefreshExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-CacheRefreshExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
); // use direct handoff
接着初始化了Eureka Client与Eureka Server进行HTTP交互的Jersy客户端,将AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs中的属性用来构建EurekaTransport。
eurekaTransport = new EurekaTransport();
scheduleServerEndpointTask(eurekaTransport, args);
EurekaTransport是DiscoveryClient中的一个内部类,其内封装了DiscoveryClient与Eureka Server进行HTTP调用的Jersy客户端:
private static final class EurekaTransport {
// Server endPoint解析器
private ClosableResolver bootstrapResolver;
// Jersy客户端生成工厂
private TransportClientFactory transportClientFactory;
// 注册客户端
private EurekaHttpClient registrationClient;
// 注册客户端生成工厂
private EurekaHttpClientFactory registrationClientFactory;
// 发现服务客户端
private EurekaHttpClient queryClient;
// 发现服务客户端生成工厂
private EurekaHttpClientFactory queryClientFactory;
....
}
关于AWSregion中的相关配置略过。
客户端的更多内容,将会在下篇文章介绍,敬请关注。
详细了解本书:地址
推荐阅读
微服务合集
订阅最新文章,欢迎关注我的公众号
最后
以上就是害怕钻石最近收集整理的关于服务注册与发现组件 Eureka 客户端实现原理解析的全部内容,更多相关服务注册与发现组件内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复