我是靠谱客的博主 懦弱黄蜂,这篇文章主要介绍Verilog学习脚印4-状态机(串口)bash命令串口协议简介(来自B站-北交李金城老师的PPT,侵删)实例1:串口数据接收实例2:串口数据发送实例3:串口指令处理器实例综合:顶层模块封装与验证,现在分享给大家,希望可以做个参考。
Verilog学习脚印4-状态机(串口)
附:verilog语法笔记(持续更新ing)
目录
- bash命令
- 串口协议简介(来自B站-北交李金城老师的PPT,侵删)
- 实例1:串口数据接收
- 电路原理(来自B站-北交李金城老师的PPT,侵删)
- 代码实现与验证
- 实例2:串口数据发送
- 电路原理(来自B站-北交李金城老师的PPT,侵删)
- 代码实现与验证
- 实例3:串口指令处理器
- 电路原理(来自B站-北交李金城老师的PPT,侵删)
- 代码实现
- 实例综合:顶层模块封装与验证
- 电路原理(来自B站-北交李金城老师的PPT,侵删)
- makefile
- 代码实现与验证
bash命令
bash调用dve和vcs的命令:
dve & // 启用VDE
vcs *.v -R -timescale=1ns/10ps +v2k +define+RTL_SAIF // 编译
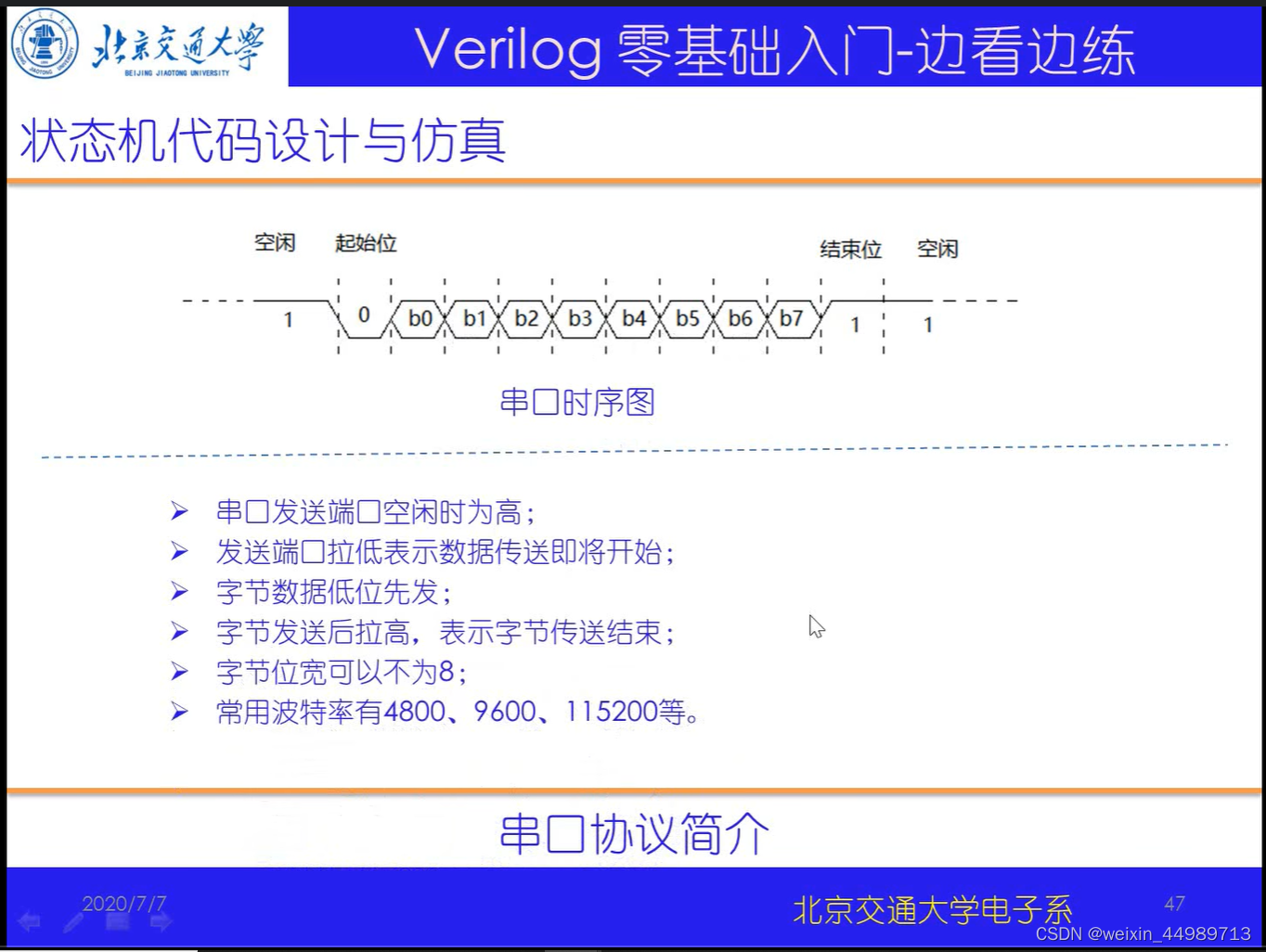
串口协议简介(来自B站-北交李金城老师的PPT,侵删)
实例1:串口数据接收
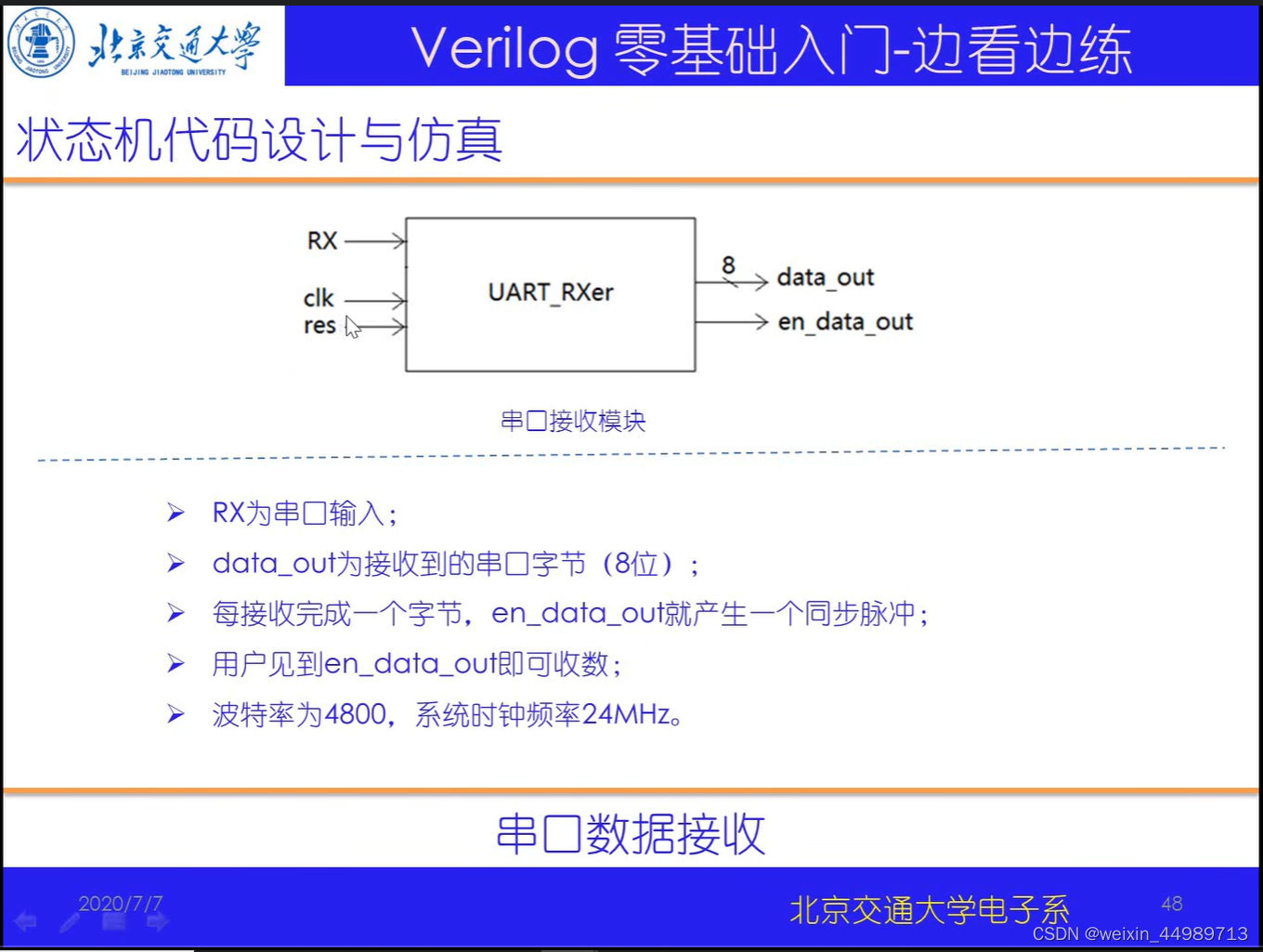
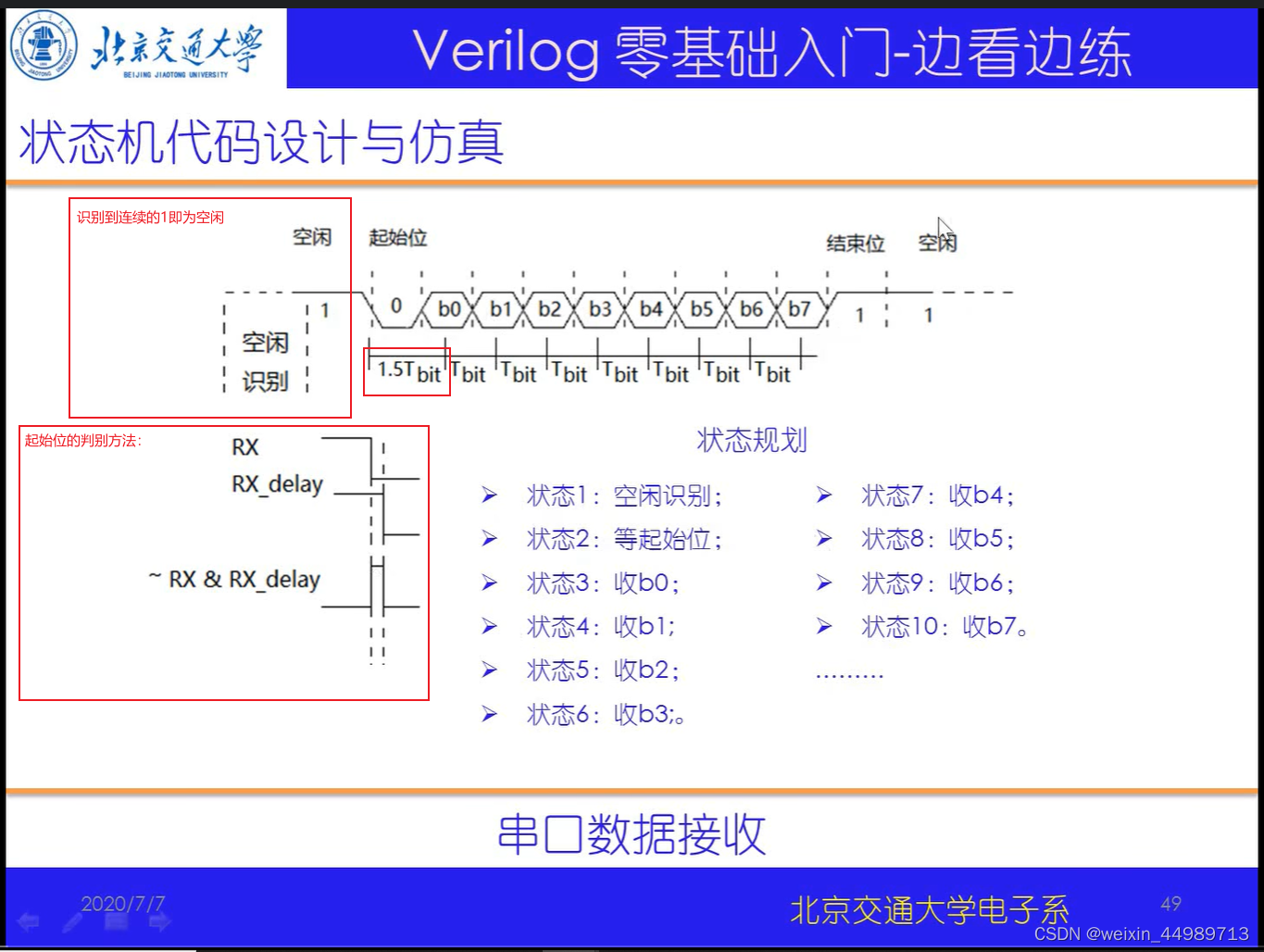
电路原理(来自B站-北交李金城老师的PPT,侵删)

代码实现与验证
完整代码:
// 串口数据接收
`timescale 1ns/10ps
// ----- 定义 -----
module serial_rec(
clk,
res,
RX,
data_out,
en_data_out
);
input clk;
input res;
input RX;
output[7:0] data_out; //接收字节输出
output en_data_out; //输出使能
reg[7:0] data_out;
reg en_data_out;
reg[3:0] state; //主状态机
reg[12:0] count; //用于计算bit宽度,24M/4800=5000,1.5bit_wide=7500
reg[3:0] count_bits;//用于bit数的计数
reg RX_delay; //RX的延时
always@(posedge clk or negedge res)
if(~res)begin
state<=0;count<=0;count_bits<=0;RX_delay<=0;
data_out<=0;en_data_out<=0;
end
else begin
RX_delay<=RX;
case(state)
0:begin //等空闲
if(count==5000-1)begin //5000-1 !!!
count<=0;
end
else begin
count<=count+1;
end
if(count==0)begin
if(RX) begin //处于空闲状态时,对bit计数
count_bits<=count_bits+1;
end
else begin
count_bits<=0;
end
end
if(count_bits===12)begin // 保证处于空闲状态
count_bits<=0;
state<=1; // 进入state 1 ,等起始位
end
end
1:begin //等起始位
en_data_out<=0; //接收使能清零!
if((~RX)&(RX_delay))begin //等到了脉冲尖!即RX开始拉低!
state<=2;
end
end
2:begin //经过1.5bit后开始接收数据,收最低位b0
if(count==7500-1)begin
count<=0;
data_out[0]<=RX;
state<=3;
end
else begin
count<=count+1;
end
end
3:begin //接收b1
if(count==5000-1)begin
count<=0;
data_out[1]<=RX;
state<=4;
end
else begin
count<=count+1;
end
end
4:begin //接收b2
if(count==5000-1)begin
count<=0;
data_out[2]<=RX;
state<=5;
end
else begin
count<=count+1;
end
end
5:begin //接收b3
if(count==5000-1)begin
count<=0;
data_out[3]<=RX;
state<=6;
end
else begin
count<=count+1;
end
end
6:begin //接收b4
if(count==5000-1)begin
count<=0;
data_out[4]<=RX;
state<=7;
end
else begin
count<=count+1;
end
end
7:begin //接收b5
if(count==5000-1)begin
count<=0;
data_out[5]<=RX;
state<=8;
end
else begin
count<=count+1;
end
end
8:begin //接收b6
if(count==5000-1)begin
count<=0;
data_out[6]<=RX;
state<=9;
end
else begin
count<=count+1;
end
end
9:begin //接收b7
if(count==5000-1)begin
count<=0;
data_out[7]<=RX;
state<=10;
end
else begin
count<=count+1;
end
end
10:begin //产生使能脉冲
en_data_out<=1;
state<=1;
end
default:begin
state<=0;
count<=0;
count_bits<=0;
data_out<=0;
end
endcase
end
endmodule
// ----- testbench -----
module serial_rec_tb;
reg clk,res;
wire RX;
wire[7:0] data_out;
wire en_data_out;
reg[25:0] RX_send; //!!!里面装有串口字节发送数据 16个1+起始位+数据+结束位,即16+1+8+1=26!!!
reg[12:0] count; //对系统时钟计数,以满足波特率
assign RX=RX_send; //连接RX!
serial_rec serial_rec(
.clk(clk),
.res(res),
.RX(RX),
.data_out(data_out),
.en_data_out(en_data_out)
);
initial begin
$dumpfile("serial_rec_tb.vcd"); // save wave file
$dumpvars(0,serial_rec);
end
initial begin
clk<=0;res<=0;RX_send<={1'b1,8'haa,1'b0,16'hffff};count<=0;
#17 res<=1;
#4000000 $stop;
end
always #5 clk<=~clk;
//注意!testbench中串口发送数据的写法!!!让RX_send以波特率节奏不断右移!
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(count==5000-1)begin
count<=0;
end
else begin
count<=count+1;
end
if(count==0)begin //循环右移!
RX_send[24:0]<=RX_send[25:1];
RX_send[25]<=RX_send[0];
end
end
endmodule
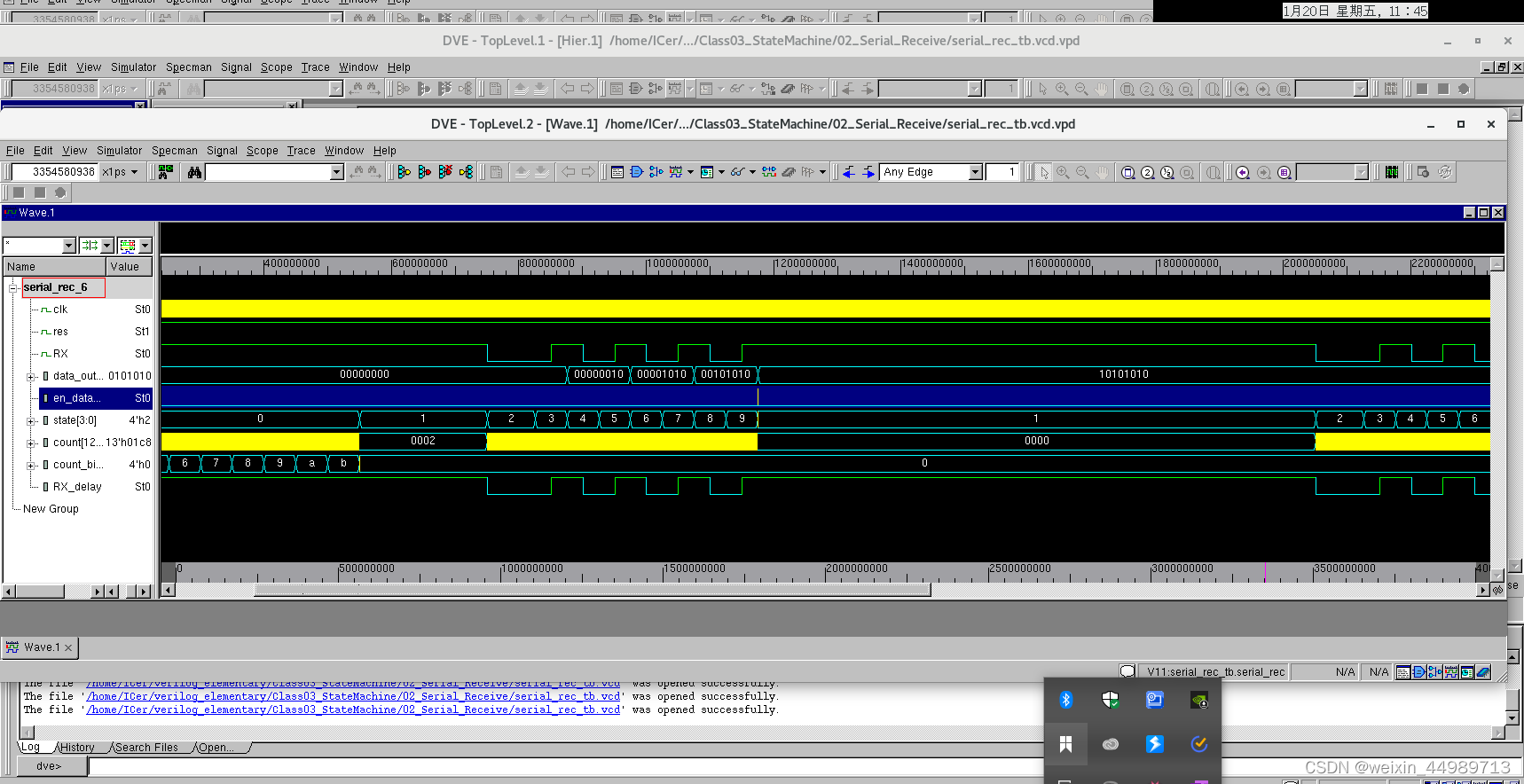
波形输出:
实例2:串口数据发送
电路原理(来自B站-北交李金城老师的PPT,侵删)
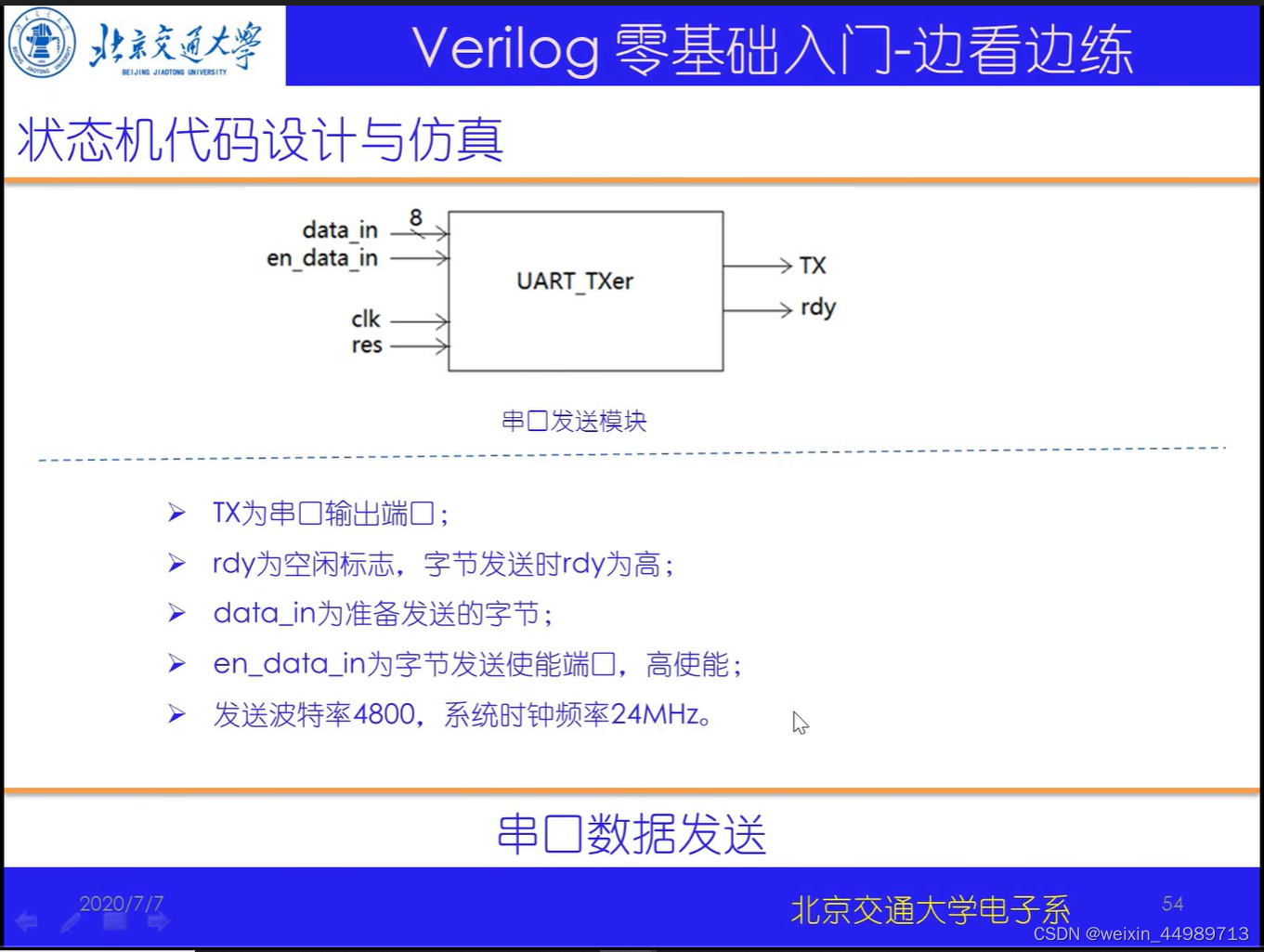
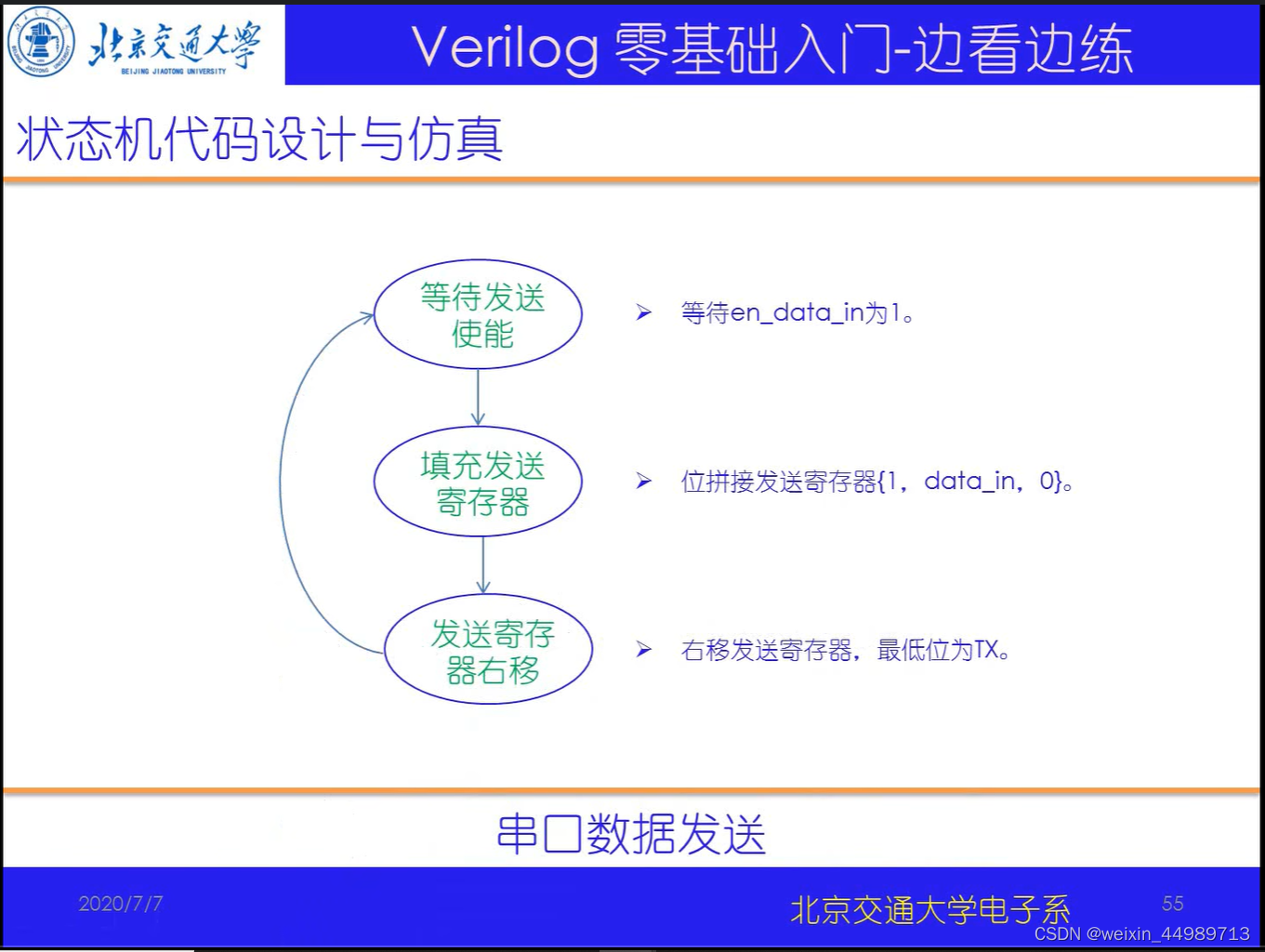
代码实现与验证
代码如下:
// 串口数据发送
`timescale 1ns/1ps
module serial_send(
clk,
res,
data_in,
en_data_in,
TX,
rdy
);
input clk;
input res;
input[7:0] data_in; //准备发送的数据
input en_data_in; //发送使能
output TX;
output rdy; //空闲标志,0表示空闲
reg[3:0] state; //主状态机
reg[9:0] send_buf; //发送寄存器,存储需要发送的数据
assign TX=send_buf[0]; //连接TX,使sned_buf不断右移,相当于TX发送
reg[9:0] send_flag; //用于判断右移结束!10'b10_0000_0000!!!
reg[12:0] count; //用于计数波特率
reg rdy; //表示空闲,防止数据发送冲突
always@(posedge clk or negedge res)
if(~res)begin
state<=0;send_buf<=1;count<=0;send_flag<=10'b10_0000_0000;rdy<=0;
end
else begin
case(state)
0:begin //等使能信号
if(en_data_in)begin
send_buf={1'b1,data_in,1'b0}; //结束位+数据+起始位
send_flag<=10'b10_0000_0000;
rdy<=1;
state<=1;
end
end
1:begin //串口发送,寄存器按照波特率右移
if(count==5000-1)begin
count<=0;
end
else begin
count<=count+1;
end
if(count==5000-1)begin
send_buf[8:0]<=send_buf[9:1];
send_flag[8:0]<=send_flag[9:1];
end
if(send_flag[0])begin
rdy<=0;
state<=0;
end
end
default:begin
state<=0;count<=0;rdy<=0;
end
endcase
end
endmodule
// ----- testbench -----
module serial_send_tb;
reg clk,res;
reg[7:0] data_in;
reg en_data_in;
wire TX;
wire rdy;
serial_send serial_send(
.clk(clk),
.res(res),
.data_in(data_in),
.en_data_in(en_data_in),
.TX(TX),
.rdy(rdy)
);
initial begin
$dumpfile("serial_send_tb.vcd"); // save wave file
$dumpvars(0,serial_send);
end
initial begin
clk<=0;res<=0;data_in<=8'h0a;en_data_in<=0;
#17 res<=1;
#30 en_data_in<=1;
#10 en_data_in<=0;
#9000000 $stop;
end
always #5 clk=~clk;
endmodule
验证结果如下:
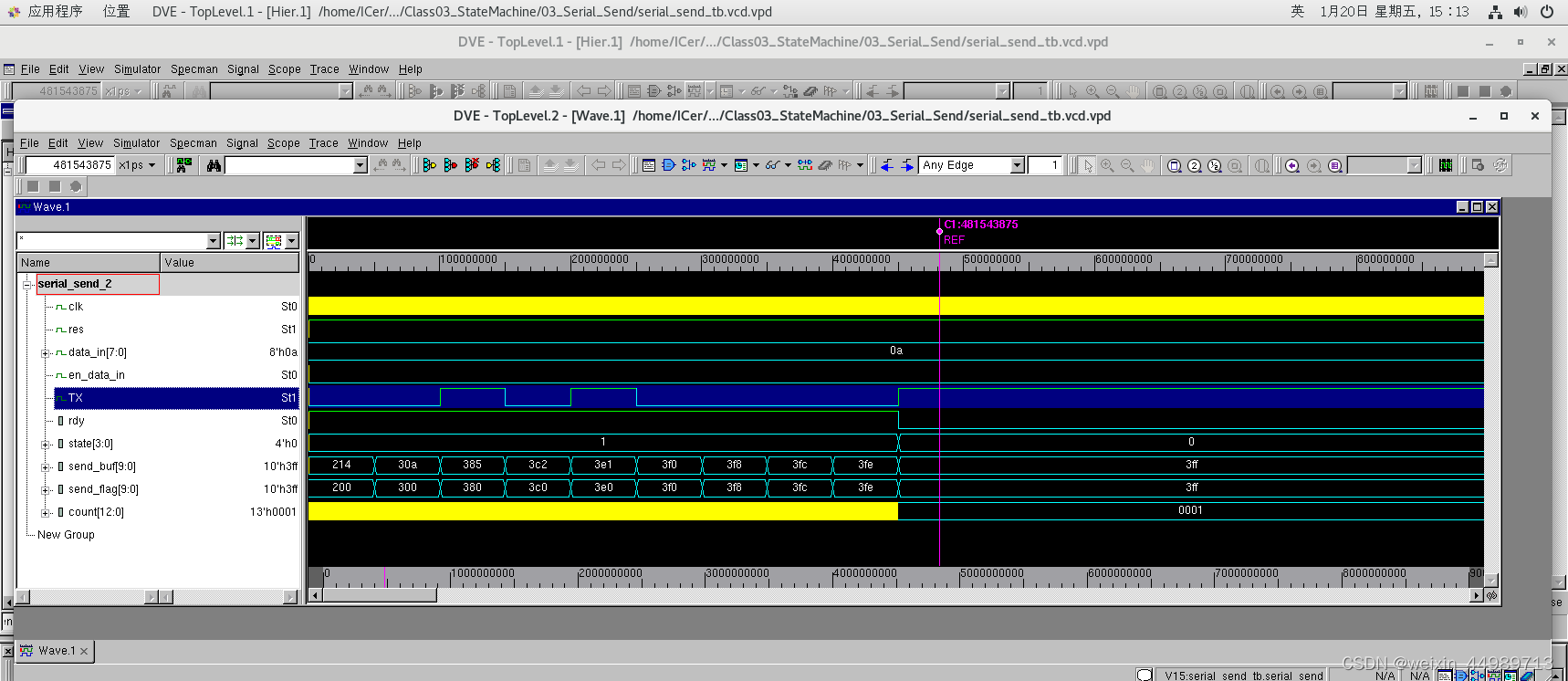
实例3:串口指令处理器
电路原理(来自B站-北交李金城老师的PPT,侵删)
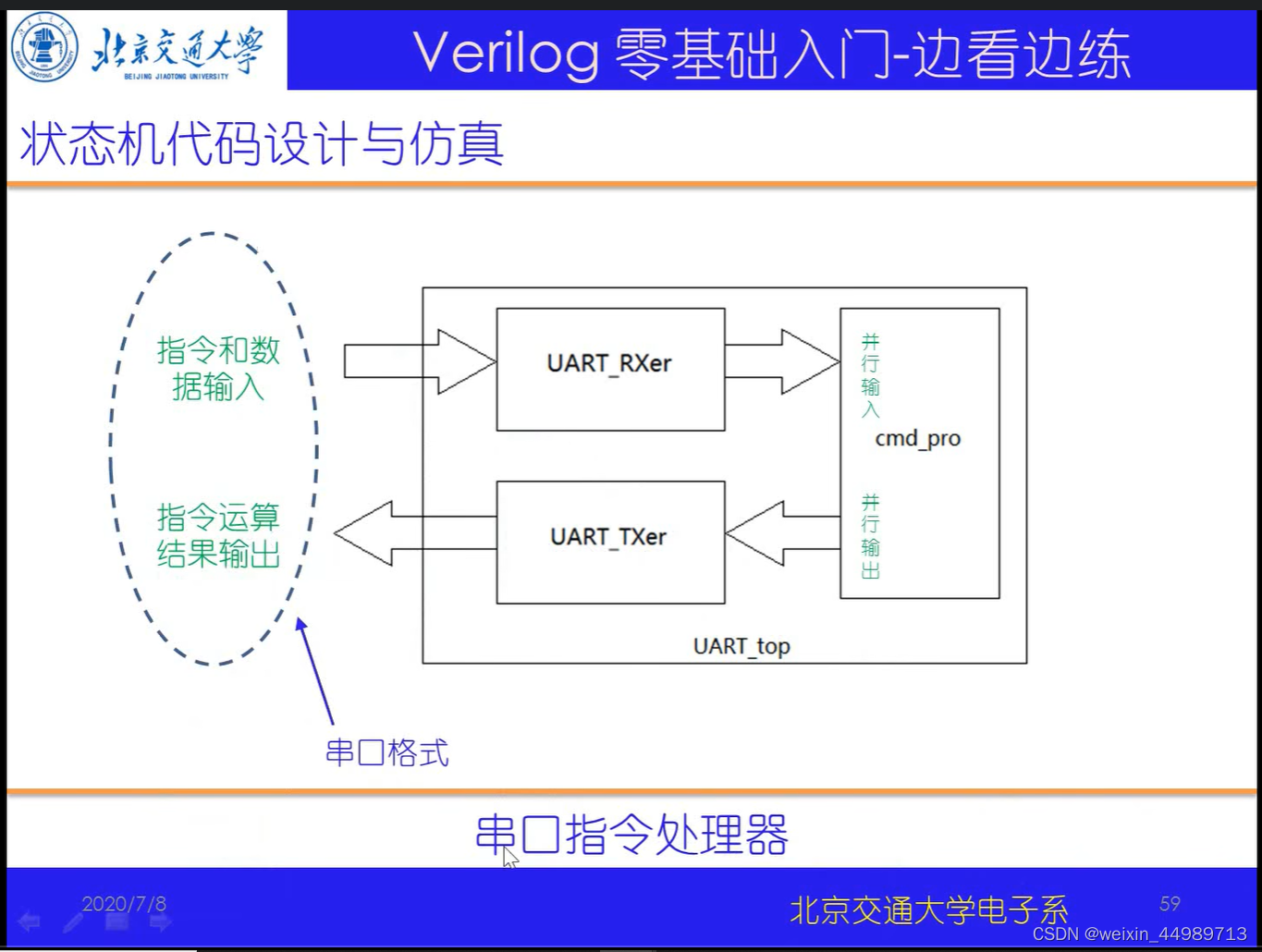
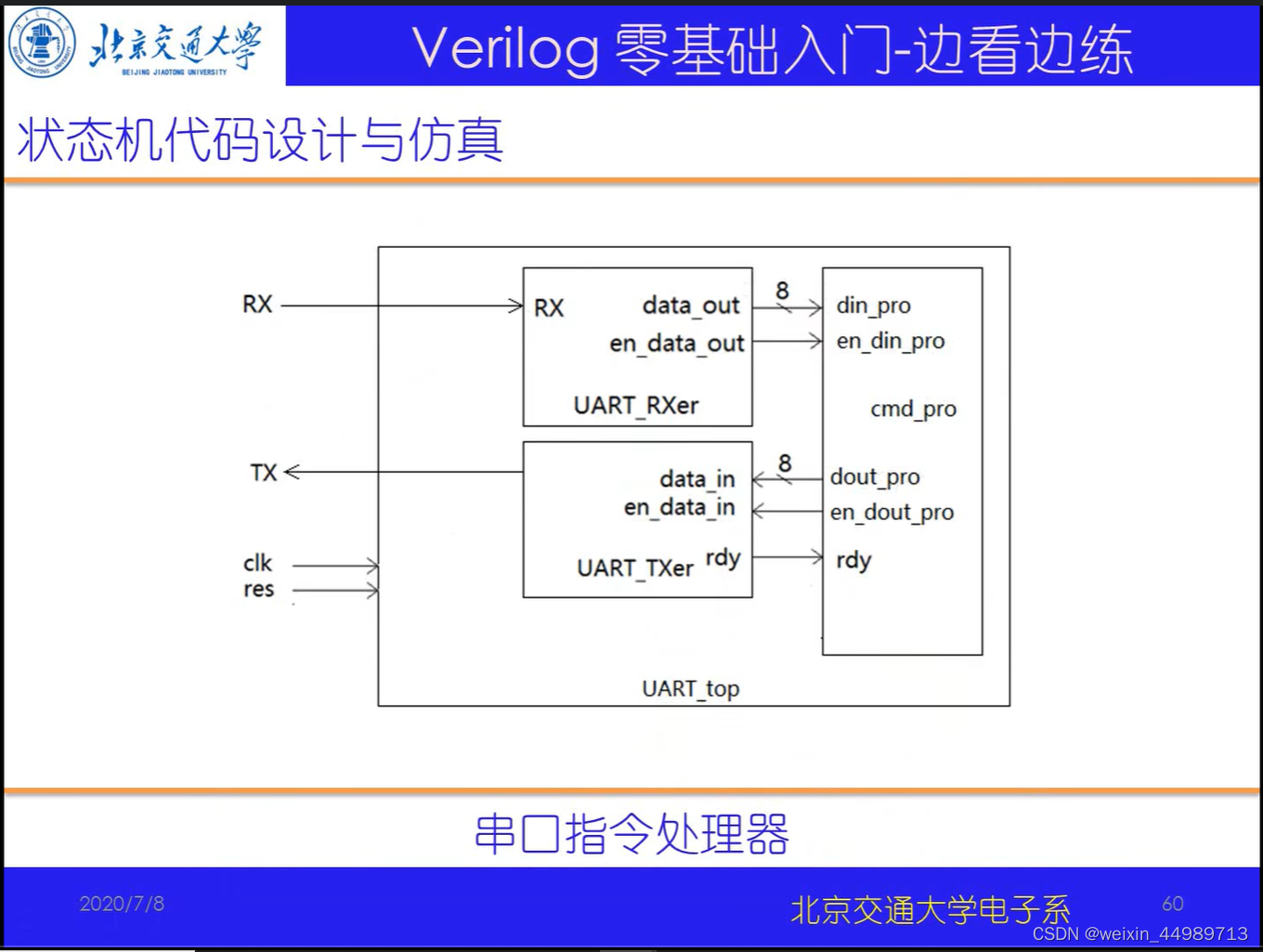
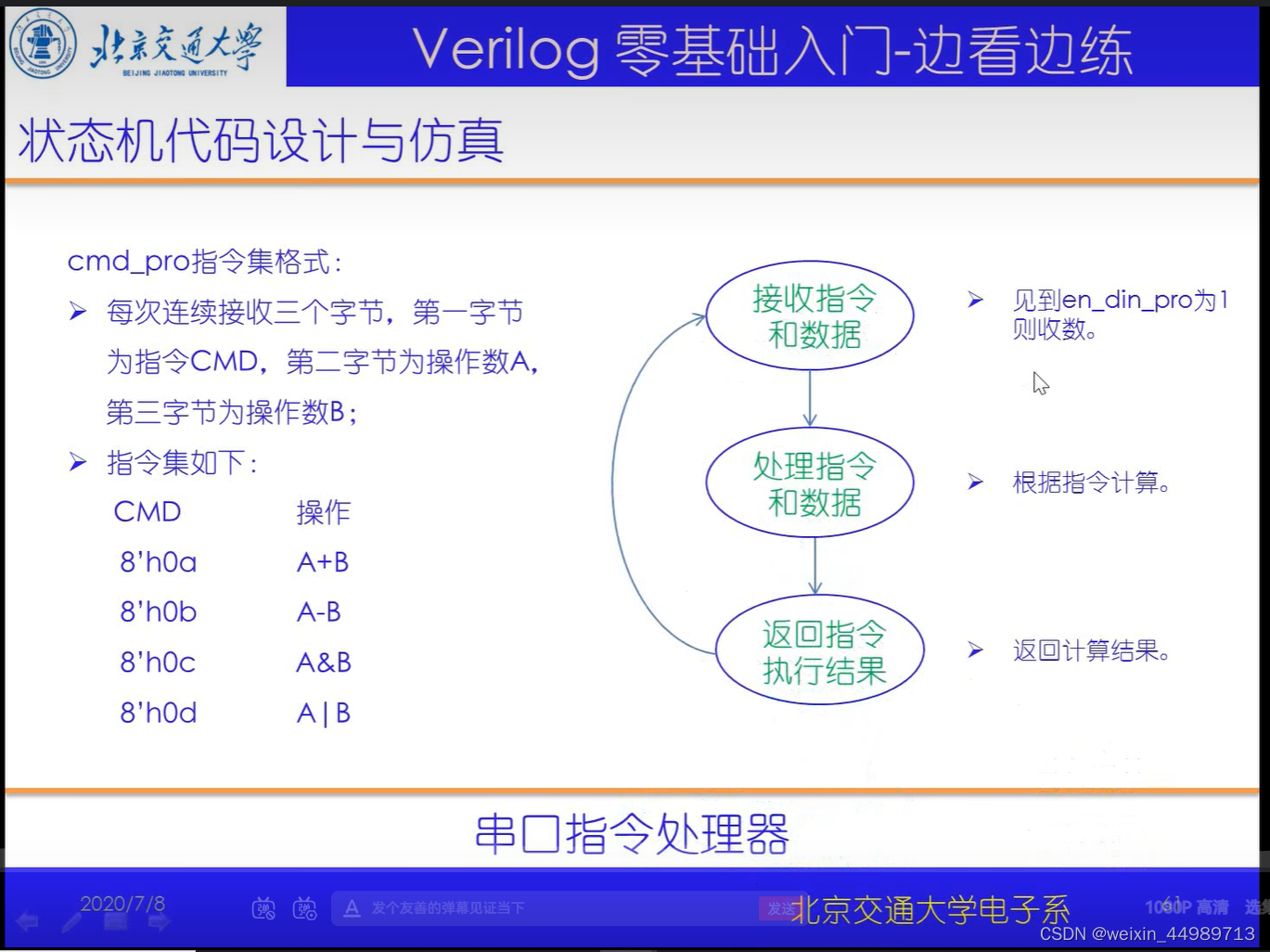
代码实现
完整代码:
serial_amd_pro.v
// 串口指令处理器
`timescale 1ns/10ps
// ----- 定义 -----
module cmd_pro(
clk,
res,
din_pro,
en_din_pro,
dout_pro,
en_dout_pro,
rdy
);
input clk;
input res;
input[7:0] din_pro; //指令和数据输入端口
input en_din_pro; //输入使能
output[7:0] dout_pro; //指令执行结果
output en_dout_pro; //指令输出使能
output rdy; //串口发送模块空闲标志,0表示空闲
parameter add_AB=8'h0a; //指令集!
parameter sub_AB=8'h0b;
parameter and_AB=8'h0c;
parameter or_AB=8'h0d;
reg[3:0] state; //主状态机
reg[7:0] cmd_reg,A_reg,B_reg; //存放指令、数据A、数据B
reg[7:0] dout_pro;
reg en_dout_pro;
always@(posedge clk or negedge res)
if(~res)begin
state<=0;cmd_reg<=0;A_reg<=0;B_reg<=0;dout_pro<=0;en_dout_pro<=0;
end
else begin
case(state)
0:begin //等指令
en_dout_pro<=0;
if(en_din_pro)begin
cmd_reg<=din_pro;
state<=1;
end
end
1:begin //收数据A
if(en_din_pro)begin
A_reg<=din_pro;
state<=2;
end
end
2:begin //收数据B
if(en_din_pro)begin
B_reg<=din_pro;
state<=3;
end
end
3:begin //根据指令进行处理,即指令译码和执行
state<=4;
case(cmd_reg)
add_AB:begin dout_pro<=A_reg+B_reg;end
sub_AB:begin dout_pro<=A_reg-B_reg;end
and_AB:begin dout_pro<=A_reg&B_reg;end
or_AB:begin dout_pro<=A_reg|B_reg;end
endcase
end
4:begin //发送指令执行结果
if(~rdy)begin
en_dout_pro<=1;
state<=0;
end
end
default:begin
state<=0;
end
endcase
end
endmodule
实例综合:顶层模块封装与验证
电路原理(来自B站-北交李金城老师的PPT,侵删)

makefile
makefile(在cmd中输入make compile即可执行命令)
compile:
vcs *.v ../04_Serial_Amd_Pro/*.v ../03_Serial_Send/*.v ../02_Serial_Receive/*.v -R -timescale=1ns/10ps +v2k +define+RTL_SAIF
代码实现与验证
完整代码:
UART_top.v
//串口指令处理器
module UART_top(
clk,
res,
RX,
TX
);
input clk;
input res;
input RX;
output TX;
wire[7:0] din_pro; // 定义5个中间信号以连接子模块(从顶层看,一定是wire)
wire en_din_pro;
wire[7:0] dout_pro;
wire en_dout_pro;
wire rdy;
serial_send serial_send( //实例化3个子模块,并进行连接,注意!top层只进行连接,不进行逻辑操作
.clk(clk),
.res(res),
.data_in(dout_pro),
.en_data_in(en_dout_pro),
.TX(TX),
.rdy(rdy)
);
serial_rec serial_rec(
.clk(clk),
.res(res),
.RX(RX),
.data_out(din_pro),
.en_data_out(en_din_pro)
);
cmd_pro cmd_pro(
.clk(clk),
.res(res),
.din_pro(din_pro),
.en_din_pro(en_din_pro),
.dout_pro(dout_pro),
.en_dout_pro(en_dout_pro),
.rdy(rdy)
);
endmodule
// ----- testbench -----
module UART_top_tb;
reg clk,res;
wire RX;
wire TX;
reg[45:0] RX_send; //!!!里面装有串口字节发送数据 16个1+起始位+数据+结束位,即16+1+8+1=26!!!当有3个字节数据时,为16+10+10+10=46bit位宽
assign RX=RX_send; //连接RX
reg[12:0] count; //对系统时钟计数,以满足波特率
UART_top UART_top( //同名例化
clk,
res,
RX,
TX
);
initial begin
$dumpfile("UART_top_tb.vcd"); // save wave file
$dumpvars(0,UART_top);
end
initial begin
clk<=0;res<=0;
RX_send<={1'b1,8'h09,1'b0,1'b1,8'h06,1'b0,1'b1,8'h0a,1'b0,16'hffff};
count<=0;
#17 res<=1;
#4000000 $stop;
end
always #5 clk<=~clk;
//注意!testbench中串口发送数据的写法!!!让RX_send以波特率节奏不断右移!
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(count==5000-1)begin
count<=0;
end
else begin
count<=count+1;
end
if(count==0)begin //循环右移!
RX_send[44:0]<=RX_send[45:1];
RX_send[45]<=RX_send[0];
end
end
endmodule
验证如下:
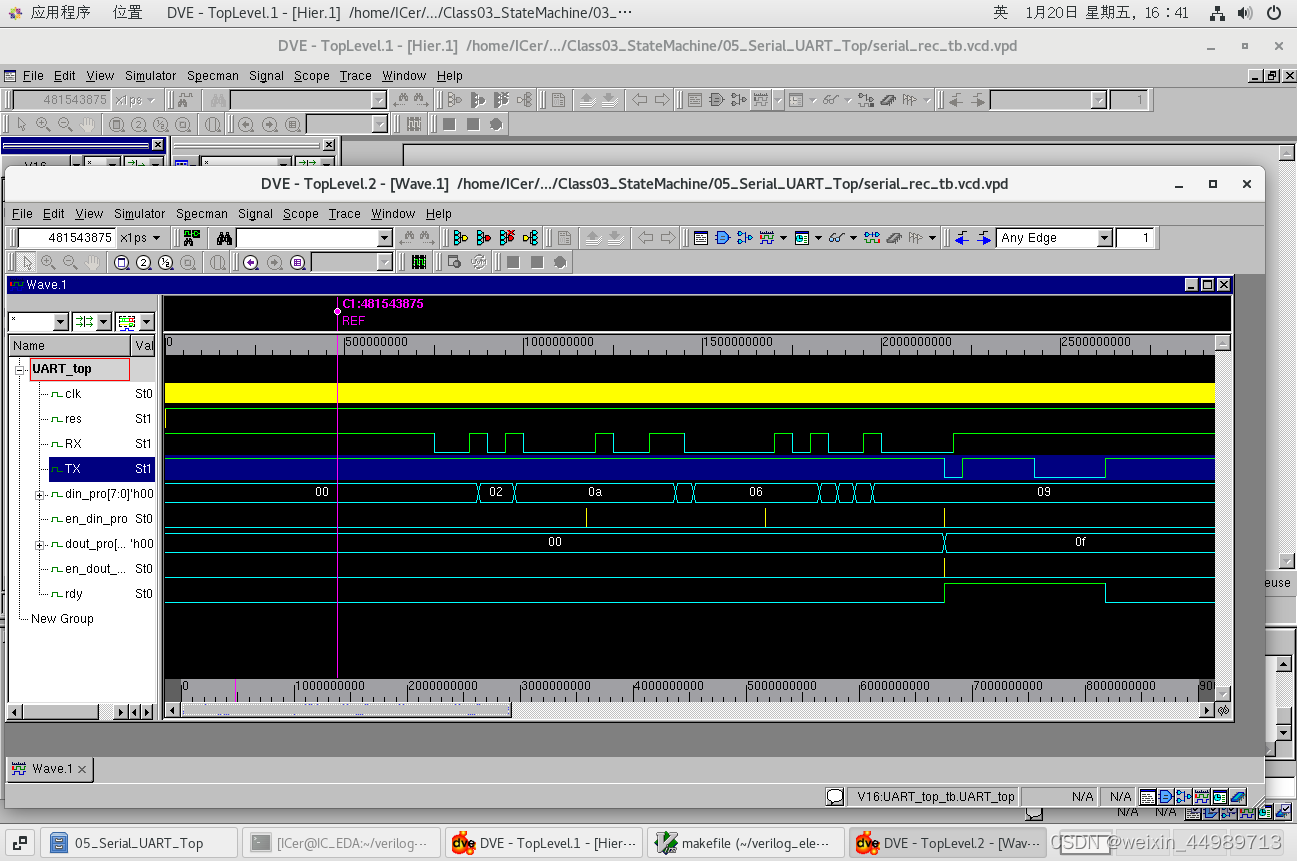
最后
以上就是懦弱黄蜂最近收集整理的关于Verilog学习脚印4-状态机(串口)bash命令串口协议简介(来自B站-北交李金城老师的PPT,侵删)实例1:串口数据接收实例2:串口数据发送实例3:串口指令处理器实例综合:顶层模块封装与验证的全部内容,更多相关Verilog学习脚印4-状态机(串口)bash命令串口协议简介(来自B站-北交李金城老师内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复