这里介绍两种解决办法:1、利用LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder解码器 2、设置自定义编解码。
一般出现数据粘包问题很难复现,因为在开发中,我们都是模拟发数据,真正上线了,我们的数据发送就没有什么规律,可能很快,也可能慢,频率不同,难以捕捉问题,但是肯定会出现一些粘包问题。
所谓粘包,就是接收的数据,无法分开,一个包的数据可能是两个或者多个报文记录,我们需要严格按照报文格式将这些合在一起的包拆开。思路就是要么报文有严格的分隔符,要么定长,再就是自定义解码器或者利用netty自带的LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder解码器。
前面说过,粘包问题在实际中很难复现,这对于我们查找问题不是很方便,但是我这里通过自己编写的client发送报文,几乎可以100%的复现。
这个客户端,就是前面两篇博客中提到的c语言自定义tcp协议实现socket通信的客户端。
netty实现的tcp server代码如下所示:
package com.xxx.huali.hualitest.nettyio;
import java.nio.ByteOrder;
import com.xxx.huali.hualitest.nettyio.decode.MyDecoder;
import com.xxx.huali.hualitest.nettyio.decode.MyHandler;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
public class ServerApp {
private final static int port = 6666;
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup work = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(boss, work)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//ch.pipeline().addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN, 65535, 8 , 4, 1, 0, true));
//ch.pipeline().addLast("decoder",new MyDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
//ch.pipeline().addLast("handler", new MyHandler());
}
})
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
work.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
class ServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>{
int count = 1;
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// flag version type reserved length payload checksum
// 2 2 2 2 4 length 1
byte dst[] = new byte[8];
msg.readBytes(dst,0,2);
System.out.println("flag->"+(dst[0]&0xff)+","+(dst[1]&0xff));
msg.readBytes(dst, 0, 2);
System.out.println("version->"+(dst[0]&0xff)+","+(dst[1]&0xff));
msg.readBytes(dst, 0, 2);
System.out.println("type->"+(dst[0]&0xff)+","+(dst[1]&0xff));
msg.readBytes(dst, 0, 2);
System.out.println("reserved->"+(dst[0]&0xff)+","+(dst[1]&0xff));
msg.readBytes(dst, 0, 4);
System.out.println("length->"+(dst[0]&0xff)+","+(dst[1]&0xff)+","+(dst[2]&0xff)+","+(dst[3]&0xff));
byte[] dst2 = new byte[4];
System.arraycopy(dst, 0, dst2, 0, 4);
int len = bytes2Int(dst2);
byte[] payload = new byte[len];
msg.readBytes(payload,0,len);
System.out.println("payload->"+new String(payload));
msg.readBytes(dst,0,1);
System.out.println("checksum->"+(dst[0]&0xff));
System.out.println("***********************************"+(count++));
//ctx.fireChannelRead(payload);
System.out.println(msg.readableBytes());
}
private int bytes2Int(byte[] data) {
int res = 0;
if(4!=data.length)
throw new RuntimeException("invalid bytes,please check data");
for(int i=3;i>=0;i--) {
res <<= 8;
res |= (data[i]&0xff);
}
return res;
}
}
默认情况下,我启动这个服务,然后启动client发送10条报文数据。服务端第一次打印的记录总是少于10条,一般是8条或者9条。
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->27,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx6799","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************1
41
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->27,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx4068","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************2
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->27,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx9232","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************3
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->28,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx20097","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************4
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->28,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx10497","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************5
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->27,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx8182","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************6
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->28,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx11246","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************7
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->28,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx26867","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************8
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->28,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx13514","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************9
0我刚开始以为是网络传输丢掉了,最后加了一个打印,发现每次在第一包数据里面解析完成,会多余一些数据,后续的解析就都是正常的,即使多次运行client发送数据,也都是正常的,所以说这个粘包的问题很难复现。
我首先在childHandler这里通过pipeline增加了一个解码器:
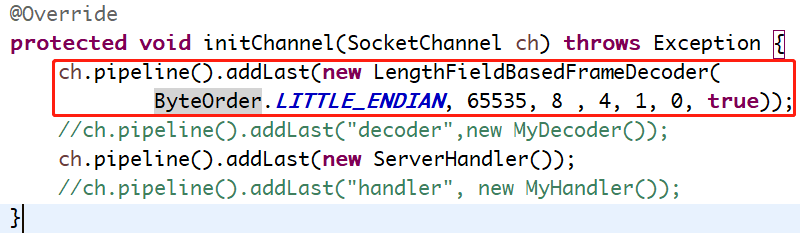
再次运行这个server,然后client第一次发送数据,第一包解析不会出现多余一些报文数据,服务端会打印10条报文记录:
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->27,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx8418","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************1
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->28,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx20121","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************2
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->28,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx17337","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************3
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->28,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx17083","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************4
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->28,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx24318","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************5
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->28,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx24843","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************6
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->28,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx11861","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************7
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->27,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx1109","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************8
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->28,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx24616","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************9
0
flag->165,90
version->1,0
type->1,0
reserved->255,255
length->28,0,0,0
payload->{"name":"xxx11497","age":18}
checksum->0
***********************************10
0这个解码器LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,需要设置几个参数:
1、byteOrder端序,这个必须要注意,netty其实支持小端序,所以这里就直接选择小端序ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN。
2、lengthFieldOffset 表示报文中length这个字段的起始位置,这个根据协议来指定。
3、lengthFieldLength表示length字段的长度,这个会用来计算报文体也就是payload的长度,他跟小端序大端序也有很大的关系。
4、lengthAdjustment,这个是length字段可以调整的位数,一般是1-2位,其实也就是校验位的长度。
从这些参数可以看出,有了这些东西其实就能根据协议各个字段的类型,以及长度来分割一包数据了。
还有一种办法,就是前面提到的,自定义解码器:
自定义解码,解码之后就不再是原始的byte数组了,就是我们的报文实体类,所以也需要新的handler来处理解析之后的数据。
这里会新增三个类:协议类,协议解码器,消息处理器。
协议类:
package com.xxx.huali.hualitest.nettyio.decode;
public class MyProtocol {
private String flag;
private short version;
private short type;
private short reserved;
private int length;
private byte[] payload;
private byte checksum;
public MyProtocol() {
}
public MyProtocol(String flag,short version,short type,short reserved,int length,
byte[] payload,byte checksum) {
this.flag = flag;
this.version = version;
this.type = type;
this.reserved = reserved;
this.length = length;
this.payload = payload;
this.checksum = checksum;
}
public String getFlag() {
return flag;
}
public void setFlag(String flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
public short getVersion() {
return version;
}
public void setVersion(short version) {
this.version = version;
}
public short getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(short type) {
this.type = type;
}
public short getReserved() {
return reserved;
}
public void setReserved(short reserved) {
this.reserved = reserved;
}
public int getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(int length) {
this.length = length;
}
public byte[] getPayload() {
return payload;
}
public void setPayload(byte[] payload) {
this.payload = payload;
}
public byte getChecksum() {
return checksum;
}
public void setChecksum(byte checksum) {
this.checksum = checksum;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.flag+":"+this.version+":"+this.type+":"+this.reserved+":"+this.length+":"+new String(this.payload)+":"+this.checksum;
}
}
协议解码器:
package com.xxx.huali.hualitest.nettyio.decode;
import java.util.List;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.ByteToMessageDecoder;
public class MyDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder{
private final String PACKET_FLAG = "A55A";
private final int BASE_LENGTH = 2+2+2+2+4+1;
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("decode bytes length -> "+in.readableBytes());
if(in.readableBytes()>=BASE_LENGTH) {
//skip
if(in.readableBytes()>2048) {
in.skipBytes(in.readableBytes());
}
int index;
String flag;
while(true) {
index = in.readerIndex();
in.markReaderIndex();
byte[] dst = new byte[2];
in.readBytes(dst, 0, 2);
flag = Utils.byte2Hex(dst);
if(PACKET_FLAG.equals(flag))
break;
in.resetReaderIndex();
in.readByte();
if(in.readableBytes()<BASE_LENGTH)
return;
}
System.out.println("start to resolve.");
short version = in.readShortLE();
short type = in.readShortLE();
short reserved = in.readShortLE();
int length = in.readIntLE();
if(in.readableBytes()<length) {
in.readerIndex(index);
return;
}
byte[] payload = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(payload);
byte checksum = in.readByte();
MyProtocol protocol = new MyProtocol(flag,version,type,reserved,length,payload,checksum);
out.add(protocol);
}
}
}
消息处理器:
package com.xxx.huali.hualitest.nettyio.decode;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
public class MyHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<MyProtocol>{
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MyProtocol msg) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
因为有了解码器,我们的handler就不再需要解析原始的ByteBuf了。
childHandler中的配置如下所示:
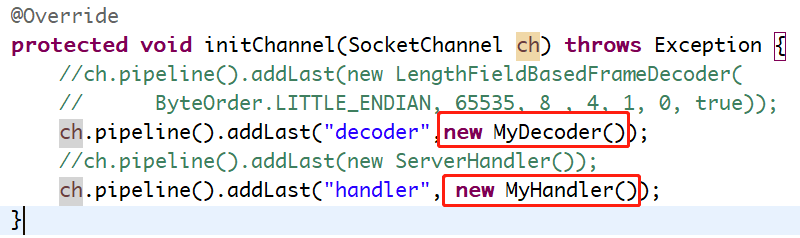
同样的,启动server,然后利用client发送10条报文,服务端也会打印10次消息,不会出现粘包问题。这里严格来说,还需要增加一个编码器,因为服务端会向客户端回复消息也需要编码,这里没有编写,主要服务端这里只做数据接收,不涉及向client发送数据。
服务端打印信息:
decode bytes length -> 41
start to resolve.
A55A:1:1:-1:28:{"name":"xxx12964","age":18}:0
decode bytes length -> 40
start to resolve.
A55A:1:1:-1:27:{"name":"xxx6927","age":18}:0
decode bytes length -> 41
start to resolve.
A55A:1:1:-1:28:{"name":"xxx13352","age":18}:0
decode bytes length -> 41
start to resolve.
A55A:1:1:-1:28:{"name":"xxx24320","age":18}:0
decode bytes length -> 41
start to resolve.
A55A:1:1:-1:28:{"name":"xxx29822","age":18}:0
decode bytes length -> 41
start to resolve.
A55A:1:1:-1:28:{"name":"xxx18595","age":18}:0
decode bytes length -> 41
start to resolve.
A55A:1:1:-1:28:{"name":"xxx19017","age":18}:0
decode bytes length -> 41
start to resolve.
A55A:1:1:-1:28:{"name":"xxx22343","age":18}:0
decode bytes length -> 40
start to resolve.
A55A:1:1:-1:27:{"name":"xxx5613","age":18}:0
decode bytes length -> 40
start to resolve.
A55A:1:1:-1:27:{"name":"xxx5834","age":18}:0正确打印了10条报文,说明利用自定义解码器解决了粘包问题。
个人推荐使用自定义编解码器,使用netty自带的LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,之后,还需要解码,而且如果需要向客户端传输数据,还需要编码器,不如编解码一起做了。
最后
以上就是奋斗路人最近收集整理的关于netty实现tcp通信服务端出现数据粘包问题解决办法的全部内容,更多相关netty实现tcp通信服务端出现数据粘包问题解决办法内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复