对二阶Markov信源编码译码
题目概述
设信源可能输出的符号是a, b, c 三个字母,构成一个二阶Markov信源,且各阶条件概率如下,试编写程序可以对任意字母序列(如abbcabcb)进行基于上下文的自适应算术编码,并进行相应的译码。
零阶条件概率:
p(a)=1/3; p(b)=1/3; p©=1/3;
一阶条件概率:
p(a/a)=1/2; p(b/a )=1/4; p(c/a)=1/4;
p(a/b)=1/4; p(b/b)=1/2; p(c/b)=1/4;
p(a/c)=1/4; p(b/c)=1/4; p(c/c)=1/2;
二阶条件概率:
p(a/aa)=3/5; p(b/aa)=1/5; p(c/aa)=1/5;
p(a/ab)=1/4; p(b/ab)=1/4; p(c/ab)=1/2;
p(a/ac)=1/4; p(b/ac)=1/4; p(c/a2)=1/2;
p(a/ba)=1/2; p(b/ba)=1/4; p(c/ba)=1/4;
p(a/bb)=1/5; p(b/bb)=3/5; p(c/bb)=1/5;
p(a/bc)=1/4; p(b/bc)=1/4; p(c/bc)=1/2;
p(a/ca)=1/2; p(b/ca)=1/4; p(c/ca)=1/4;
p(a/cb)=1/2; p(b/cb)=1/4; p(c/cb)=1/4;
p(a/cc)=1/5; p(b/cc)=1/5; p(c/cc)=3/5;
题目分析
该题目是对二阶的Markov信源进行编码,译码。所以每次的概率与之前的概率都有关系,所以可以初步设想采用迭代的方法。
输入
可以创建一个一维数组(可以选择大小确定的数组,也可以使用指针创建动态数组,为了减小难度,选择大小确定的数组),通过cin输入字符。
循环数组,当为0时(注意不同于‘0’),结束循环,得到数组长度。
保证程序的健壮性,要对输入进行合法性判断,通过if语句依次判断是否在a~c, A-C之间。
编码
判断每次的字符是什么,然后每次该字符的概率依次叠加,得到该字符串最后的概率pp。
通过公式求得最低位数digit。
并通过一个for循环,每次划分新的区间,得到最后的范围。
选取上界值然后减去pp的0.01,得到近似概率。
不断*2,得到二进制编码,直到达到最低位数digit。
译码
先将二进制编码转为十进制。
依次从0倒1选取区间,判断是否在相应区间内,如果在就输出相应字符。
知道字符数与输入相同。
问题分析
1.精度问题,当输入过长,long double的精度以及不够用了,所以我选择使用二维数组存储字符,编译译码也对每一组进行编译译码,理论上可以达到无穷精度。
2.方法复杂度是n2,待改进。
3.耦合度过高,所以可以考虑将运算封装到函数中,来降低耦合度。
运行图片
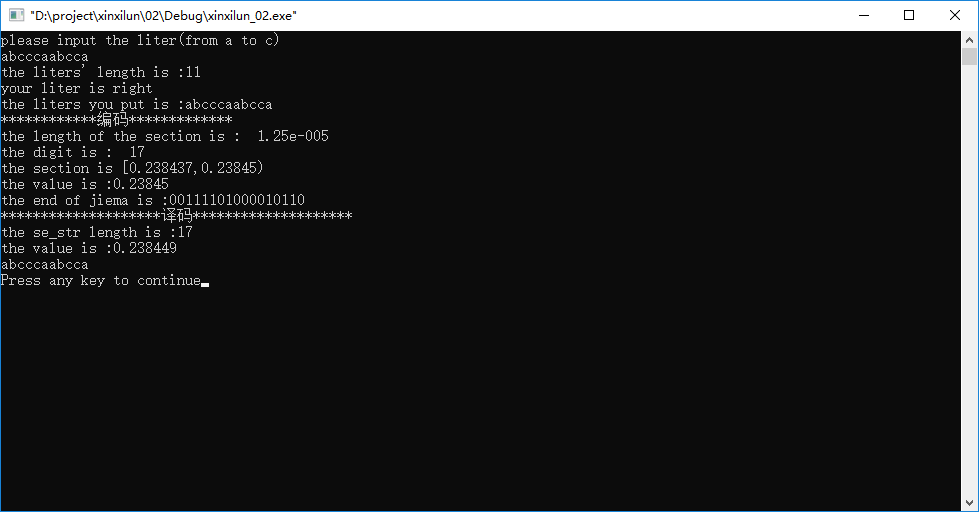
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
/*
2019.04.28.21.47
create by Yu Zhao
spend three hours
the methods is not good and the logic has a little defect
defectss:
1.Dynamic array
2.ergodic
3.Determination of Bits in Decoding**
*/
char str[1000]; //初始输入数组
char se_str[1000]; //二进制数组
char str_end[200][5]; //待定
char letter[3] = {'a','b','c'}; //字母表
int len,flag,flag_deno,flag_deno_sec,digit,se_len;
long double bottom,top,pp,value,start;
long double pro_one = 0.333333; //近似1/3
long double pro_two[3][3] = {0.5,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.5,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.5}; //pro_two[分母][分子]
long double pro_two_scale[3][4]={0.0,0.5,0.75,1.0,0.0,0.25,0.75,1.0,0.0,0.25,0.5,1.0}; //同上
long double pro_three[3][3][3] ={0.6,0.2,0.2,0.25,0.25,0.5,0.25,0.25,0.5,0.5,0.25,0.25,0.2,0.6,0.2,0.25,0.25,0.5,0.5,0.25,0.25,0.5,0.25,0.25,0.2,0.2,0.6}; //pro_three【一级】【二级】【分子】 //pro_three[一级][二级][分子]
long double pro_three_scale[3][3][4] ={0.0,0.6,0.8,1.0,0.0,0.25,0.5,1.0,0.0,0.25,0.5,1.0,0.0,0.5,0.75,1.0,0.0,0.2,0.8,1.0,0.0,0.25,0.5,1.0,0.0,0.5,0.75,1.0,0.0,0.5,0.75,1.0,0.0,0.2,0.4,1.0}; //同上 //pro_three[一级][二级][分子]
void ensure_flag(int a){ //映射函数——确定标志位
if(str[a] == 'a'||str[a] == 'A'){
flag = 0;
}
if(str[a] == 'b'||str[a]=='B'){
flag = 1;
}
if(str[a] == 'c'||str[a]=='C'){
flag = 2;
}
}
void ensure_flag_deno(int a){ //同上
if(a != 0){
a = a-1;
if(str[a] == 'a'||str[a] == 'A'){
flag_deno = 0;
}
if(str[a] == 'b'||str[a]=='B'){
flag_deno = 1;
}
if(str[a] == 'c'||str[a]=='C'){
flag_deno = 2;
}
}
}
void ensure_flag_deno_sec(int a){ //同上上
if(a != 0&&a != 1){
a = a-2;
if(str[a] == 'a'||str[a] == 'A'){
flag_deno_sec = 0;
}
if(str[a] == 'b'||str[a]=='B'){
flag_deno_sec = 1;
}
if(str[a] == 'c'||str[a]=='C'){
flag_deno_sec = 2;
}
}
}
bool input(){ //输入
int i = 0;
cout <<"please input the liter(from a to c)n";
cin >> str; //输入目标字符串
while(str[i]!=0 ){ //读取长度——有一个问题
len++;
i++;
}
cout <<"the liters' length is :"<< len<<endl;
for(i=0;i<len;i++){ //判断输入是否合理
if(str[i]>='a'&&str[i]<='c'||str[i]>='A'&&str[i]<='C'){
}
else {
cout << "your liter is wrong"<<endl;
exit(1);
return false;
}
}
cout<<"your liter is right"<<endl;
i = 0;
cout <<"the liters you put is :";
for(int j = 0;j<((len/5)+1);j++){ //改进——转为二维数组——未完成
for(int k = 0;k<5;k++){
if(j<len/5){
str_end[j][k] = str[i];
i++;
cout<<str_end[j][k];
}else{
str_end[j][k] = str[i];
i++;
cout<<str_end[j][k];
if(i ==len%5 )
break;
}
}
}
cout<<endl;
return true;
}
void bianma(){
cout<<"************编码*************"<<endl;
pp = 1;
for(int i = 0;i<len;i++){ //按顺序确定区间——算法过于多余——待改进
// cout<<"i ="<<i<<endl;
ensure_flag(i);
ensure_flag_deno(i);
ensure_flag_deno_sec(i);
if(i == 0){
bottom = bottom + flag*pro_one;
pp=pp*pro_one;
top = bottom + pp;
}else if (i == 1){
bottom = bottom + pp*pro_two_scale[flag_deno][flag];
pp = pp*pro_two[flag_deno][flag];
top = bottom + pp;
}else {
bottom = bottom + pp*pro_three_scale[flag_deno_sec][flag_deno][flag];
pp = pp*pro_three[flag_deno_sec][flag_deno][flag];
top = bottom + pp;
}
}
digit = ceil((log10(1/pp))/0.301); //确定最低位数
cout<<"the length of the section is :"<<" "<<pp<<endl;
cout<<"the digit is :"<<" "<<digit<<endl;
cout<<"the section is "<<"["<<bottom<<","<<top<<")"<<endl; //待确定
value = top-0.001*pp; //取值
cout<<"the value is :"<<value<<endl;
cout<<"the end of jiema is :";
for(i = 0;i<digit;i++){ //转为二进制
value = value*2;
se_str[i] = (char)((int)value+48); //转为字符数组
if(value>=1)
value = value-(int)value;
}
cout<<se_str<<endl;
}
void yima(){
cout<<"********************译码********************"<<endl;
int i = 0;
start = 0;
int j = 0;
value = 0;
se_len = 0;
pp = 1;
bottom = 0;
top = 0;
// top = bottom+scale[j+1]*pp;
// bottom = bottom+pp*scale[j];
while(se_str[i]!=0 ){ //读取二进制的长度
se_len++;
i++;
}
cout <<"the se_str length is :"<<se_len<<endl;
for(i=0;i<se_len;i++){ //转为十进制
value = value+((int)(se_str[i])-48)*pow(2,(-(i+1)));
}
cout<<"the value is :"<<value<<endl;
for(i = 0;i<len;i++){ //对应区间并输出——感觉方法不好——待改进
if(i==0){
// cout<<"number01"<<endl;
if(value>=0&&value<pro_one){
cout<<letter[0];
bottom = 0;
top = pro_one;
pp = top-bottom;
flag = 0;
}
else if(value>=pro_one&&value<pro_one*2){
cout<<letter[1]<<endl;
bottom = pro_one;
top = pro_one*2;
pp = top-bottom;
flag = 1;
}
else{
cout<<letter[2];
bottom = pro_one*2;
top = 1;
pp = top-bottom;
flag = 2;
}
start = bottom;
}else if(i == 1){
// cout<<"number02"<<endl;
for(int j = 0;j<3;j++){
top = start+pro_two_scale[flag][j+1]*pp;
bottom = start+pp*pro_two_scale[flag][j];
if(value>=bottom&&value<top){
cout<<letter[j];
// cout<<bottom<<","<<top<<endl;
pp = top-bottom;
start = bottom;
flag_deno = j;
break;
}
}
}else{
// cout<<"number03"<<endl;
for(int j = 0;j<3;j++){
top = start+pro_three_scale[flag][flag_deno][j+1]*pp;
bottom = start+pp*pro_three_scale[flag][flag_deno][j];
if(value>=bottom&&value<top){
cout<<letter[j];
pp = top-bottom;
start = bottom;
flag = flag_deno;
flag_deno =j;
break;
}
}
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main(){
input();
bianma();
yima();
return 0;
}
其他
最后
以上就是自觉寒风最近收集整理的关于二阶Markov信源编码译码题目概述运行图片代码其他的全部内容,更多相关二阶Markov信源编码译码题目概述运行图片代码其他内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复