一、HAL 层Sensor 流程
Hal 就是对Linux内核驱动程序的封装,向上提供接口,屏蔽低层的实现细节。也就是说,把对硬件的支持分成了两层,一层放在用户空间(User Space),一层放在内核空间(Kernel Space),其中,硬件抽象层运行在用户空间,而Linux内核驱动程序运行在内核空间。
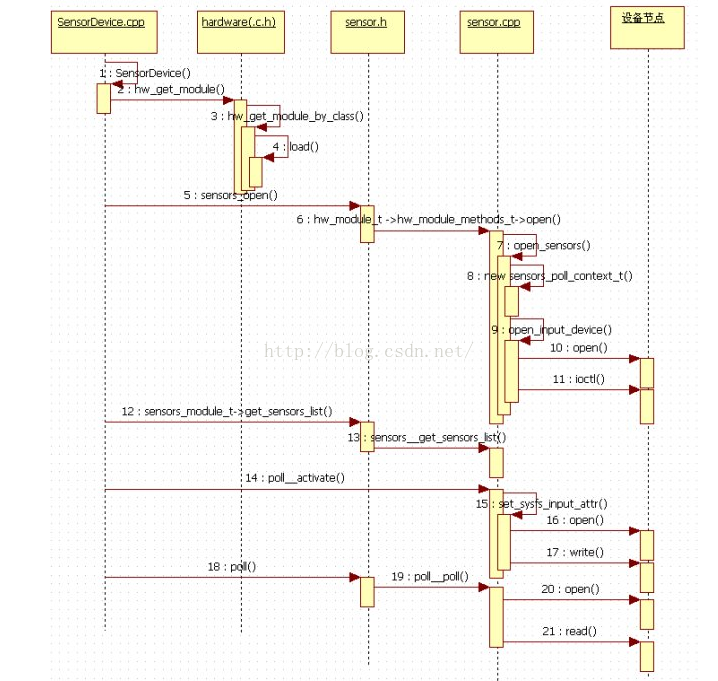
其中SensorDevice属于JNI层,与HAL进行通信的接口;在JNI层调用了HAL层的open_sensors()方法打开设备模块,再调用poll__activate()对设备使能,然后调用poll__poll读取数据。
二、HAL 层Sensor 框架实现
路径:frameworks/native/services/sensorservice/SensorDevice.cpp
1. Sensor设备对象
SensorDevice::SensorDevice()
: mSensorDevice(0),
mSensorModule(0)
{
status_t err = hw_get_module(SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
(hw_module_t const**)&mSensorModule);
.....
if (mSensorModule) {
err = sensors_open_1(&mSensorModule->common, &mSensorDevice);
sensor_t const* list;
ssize_t count = mSensorModule->get_sensors_list(mSensorModule, &list);
mActivationCount.setCapacity(count);
Info model;
for (size_t i=0 ; i<size_t(count) ; i++) {
mActivationCount.add(list[i].handle, model);
mSensorDevice->activate(
reinterpret_cast<struct sensors_poll_device_t *>(mSensorDevice),
list[i].handle, 0);
}
}
}
.....
}路径:hardware/libhardware/hardware.c
int hw_get_module(const char *id, const struct hw_module_t **module)
{
return hw_get_module_by_class(id, NULL, module);
}
3. 通过class 获取module
int hw_get_module_by_class(const char *class_id, const char *inst,
const struct hw_module_t **module)
{
.....
* Here we rely on the fact that calling dlopen multiple times on
* the same .so will simply increment a refcount (and not load
* a new copy of the library).
* We also assume that dlopen() is thread-safe.
*/
/* First try a property specific to the class and possibly instance */
snprintf(prop_name, sizeof(prop_name), "ro.hardware.%s", name);
if (property_get(prop_name, prop, NULL) > 0) {
if (hw_module_exists(path, sizeof(path), name, prop) == 0) {
goto found;
}
}
/* Loop through the configuration variants looking for a module */
for (i=0 ; i<HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT; i++) {
if (property_get(variant_keys[i], prop, NULL) == 0) {
continue;
}
if (hw_module_exists(path, sizeof(path), name, prop) == 0) {
goto found;
}
}
.....
found:
/* load the module, if this fails, we're doomed, and we should not try
* to load a different variant. */
return load(class_id, path, module);
}/**
* Load the file defined by the variant and if successful
* return the dlopen handle and the hmi.
* @return 0 = success, !0 = failure.
*/
static int load(const char *id,
const char *path,
const struct hw_module_t **pHmi)
{
/*
* load the symbols resolving undefined symbols before
* dlopen returns. Since RTLD_GLOBAL is not or'd in with
* RTLD_NOW the external symbols will not be global
*/
handle = dlopen(path, RTLD_NOW);
/* Get the address of the struct hal_module_info. */
const char *sym = HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM_AS_STR;
hmi = (struct hw_module_t *)dlsym(handle, sym);
return status;
}路径:hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/sensors.h
static inline int sensors_open_1(const struct hw_module_t* module,
sensors_poll_device_1_t** device) {
return module->methods->open(module,
SENSORS_HARDWARE_POLL, (struct hw_device_t**)device);
}
typedef struct hw_module_t {
.....
/** Modules methods */
struct hw_module_methods_t* methods;
.....
} hw_module_t;
typedef struct hw_module_methods_t {
/** Open a specific device */
int (*open)(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* id,
struct hw_device_t** device);
} hw_module_methods_t;
static int open_sensors(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* name,
struct hw_device_t** device);
static struct hw_module_methods_t sensors_module_methods = {
.open = open_sensors
};
struct sensors_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.version_major = 1,
.version_minor = 0,
.id = SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "MTK SENSORS Module",
.author = "Mediatek",
.methods = &sensors_module_methods,
},
.get_sensors_list = sensors__get_sensors_list,
};
static int open_sensors(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* name,
struct hw_device_t** device)
{
ALOGD("%s: name: %s! fwq debugrn", __func__, name);
return init_nusensors(module, device);
}int init_nusensors(hw_module_t const* module, hw_device_t** device)
{
int status = -EINVAL;
dev = new sensors_poll_context_t();
memset(&dev->device, 0, sizeof(sensors_poll_device_1));
dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
#if defined(SENSOR_BATCH_SUPPORT) || defined(CUSTOM_KERNEL_SENSORHUB)
dev->device.common.version = SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_1;
#else
dev->device.common.version = SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_0;
#endif
dev->device.common.module = const_cast<hw_module_t*>(module);
dev->device.common.close = poll__close;
dev->device.activate = poll__activate;
dev->device.setDelay = poll__setDelay;
dev->device.poll = poll__poll;
dev->device.batch = poll__batch;
dev->device.flush = poll__flush;
*device = &dev->device.common;
status = 0;
return status;
}sensors_poll_context_t::sensors_poll_context_t()
{
memset(&device, 0, sizeof(device));
mSensors[accel] = new AccelerationSensor();
mPollFds[accel].fd = ((AccelerationSensor*)mSensors[accel])->mdata_fd;
mPollFds[accel].events = POLLIN;
mPollFds[accel].revents = 0;
mSensors[proximity] = new ProximitySensor();
mPollFds[proximity].fd = ((ProximitySensor*)mSensors[proximity])->mdata_fd;
mPollFds[proximity].events = POLLIN;
mPollFds[proximity].revents = 0;
int wakeFds[2];
int result = pipe(wakeFds);
if (result < 0) {
ALOGE_IF(result < 0, "error creating wake pipe (%s)", strerror(errno));
mWritePipeFd = -1;
} else {
result = fcntl(wakeFds[0], F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
ALOGE_IF(result < 0, "fcntl(wakeFds[0] fail (%s)", strerror(errno));
result = fcntl(wakeFds[1], F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
ALOGE_IF(result < 0, "fcntl(wakeFds[1] fail (%s)", strerror(errno));
mWritePipeFd = wakeFds[1];
}
mPollFds[wake].fd = wakeFds[0];
mPollFds[wake].events = POLLIN;
mPollFds[wake].revents = 0;
}路径:vendor/mediatek/proprietary/hardware/sensor/Proximity.cpp
ProximitySensor::ProximitySensor()
: SensorBase(NULL, "m_alsps_input"),//PRO_INPUTDEV_NAME
mEnabled(0),
mInputReader(32)
{
char datapath[64]={"/sys/class/misc/m_alsps_misc/psactive"};
int fd = -1;
char buf[64]={0};
int len;
mdata_fd = FindDataFd();
if (mdata_fd >= 0) {
strcpy(input_sysfs_path, "/sys/class/misc/m_alsps_misc/");
input_sysfs_path_len = strlen(input_sysfs_path);
}
else
{
ALOGE("couldn't find input device ");
return;
}
ALOGD("prox misc path =%s", input_sysfs_path);
fd = open(datapath, O_RDWR);
if (fd >= 0)
{
len = read(fd,buf,sizeof(buf)-1);
if (len <= 0)
{
ALOGD("read div err, len = %d", len);
}
else
{
buf[len] = '�';
sscanf(buf, "%d", &mDataDiv);
ALOGD("read div buf(%s), mdiv %d", datapath,mDataDiv);
}
close(fd);
}
else
{
ALOGE("open acc misc path %s fail ", datapath);
}
}int ProximitySensor::FindDataFd() {
...
devnum_dir = "/sys/class/misc/m_alsps_misc/psdevnum";
fd = open(devnum_dir, O_RDONLY);
if (fd >= 0)
{
len = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf)-1);
close(fd);
if (len <= 0)
{
ALOGD("read devnum err, len = %d", len);
return -1;
}
else
{
buf[len] = '�';
sscanf(buf, "%dn", &num);
}
}
sprintf(buf_s, "/dev/input/event%d", num);
fd = open(buf_s, O_RDONLY);
ALOGE_IF(fd<0, "couldn't find input device");
return fd;
}//poll 函数对应framework中poll操作,这里只需了解它的功能实现,调用逻辑需要查看framework层代码
//poll 是一个非常重要的接口,它的实现基于linux 内核中IO多路复用策略(一种效率非常高的机制)
static int poll__poll(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
sensors_event_t* data, int count) {
sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev;
return ctx->pollEvents(data, count);
}//*** 这是一个构造方法,该对象创建,会启动轮询机制,监听sensorlist[]中文件描述符,等待事件上报 (使用IO多路复用策略)
int sensors_poll_context_t::pollEvents(sensors_event_t* data, int count)
{
.....
do {
for (int i=0 ; count && i<numSensorDrivers ; i++) {
SensorBase* const sensor(mSensors[i]);
if ((mPollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) || (sensor->hasPendingEvents())) {
int nb = sensor->readEvents(data, count);
.....
}
if (count) {
// we still have some room, so try to see if we can get
// some events immediately or just wait if we don't have
// anything to return
n = poll(mPollFds, numFds, nbEvents ? 0 : -1);
if (n<0) {
int err;
err = errno;
ALOGE("poll() failed (%s)", strerror(errno));
return -err;
}
if (mPollFds[wake].revents & POLLIN) {
char msg;
int result = read(mPollFds[wake].fd, &msg, 1);
ALOGE_IF(result<0, "error reading from wake pipe (%s)", strerror(errno));
ALOGE_IF(msg != WAKE_MESSAGE, "unknown message on wake queue (0x%02x)", int(msg));
mPollFds[wake].revents = 0;
}
}
// if we have events and space, go read them
} while (n && count);
return nbEvents;
}int ProximitySensor::readEvents(sensors_event_t* data, int count)
{
....
ssize_t n = mInputReader.fill(mdata_fd);
if (n < 0)
return n;
int numEventReceived = 0;
input_event const* event;
while (count && mInputReader.readEvent(&event)) {
int type = event->type;
//ALOGE("fwq1....rn");
if (type == EV_REL)
{
processEvent(event->code, event->value);
//ALOGE("fwq2....rn");
}
.....
mInputReader.next();
}
//ALOGE("fwq read Event 2rn");
return numEventReceived;
}void ProximitySensor::processEvent(int code, int value)
{
ALOGD("processEvent code=%d,value=%drn",code, value);
switch (code) {
case EVENT_TYPE_PS_VALUE:
mPendingEvent.distance= value-1;
break;
}
}static int poll__activate(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
int handle, int enabled) {
sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev;
return ctx->activate(handle-ID_OFFSET, enabled);
}
int sensors_poll_context_t::activate(int handle, int enabled)
{
....
int index = handleToDriver(handle);
.....
if(NULL != mSensors[index])
{
ALOGD( "use new sensor index=%d, mSensors[index](%x)", index, mSensors[index]);
if(this->device.common.version >= SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_1)
{
ALOGD("support batch active n" );
mSensors[batchsensor]->enable(handle, enabled);
}
err = mSensors[index]->enable(handle, enabled);
}
return err;
} int handleToDriver(int handle) const {
ALOGE("handleToDriver handle(%d)n",handle);
switch (handle) {
case ID_ACCELEROMETER:
return accel;
case ID_MAGNETIC:
case ID_ORIENTATION:
return magnetic;
case ID_PROXIMITY:
return proximity;
......
default:
break;
//return pressure;
}
return -EINVAL;
}
static const size_t wake = numFds - 1;
static const char WAKE_MESSAGE = 'W';
struct pollfd mPollFds[numFds]; //描述符表,存放各个sensor 对应的fd
int mWritePipeFd;
SensorBase* mSensors[numSensorDrivers];
};int ProximitySensor::enable(int32_t handle, int en)
{
ALOGD("PS enable: handle:%d, en:%d rn",handle,en);
strcpy(&input_sysfs_path[input_sysfs_path_len], "psactive");
ALOGD("path:%s rn",input_sysfs_path);
fd = open(input_sysfs_path, O_RDWR);
if(fd<0)
{
ALOGD("no PS enable control attrrn" );
return -1;
}
char buf[2]={0};
buf[1] = 0;
if (flags)
{
buf[0] = '1';
mEnabledTime = getTimestamp() + IGNORE_EVENT_TIME;
mPendingEvent.distance = -1; //reset p sensor value to invalid.
}
else
{
buf[0] = '0';
}
mEnabled = flags; //assign enable after reset p sensor value.
write(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
close(fd);
ALOGD("PS enable(%d) done", mEnabled );
return 0;
}路径:vendor/mediatek/proprietary/hardware/sensor/sensors.c
//这一步非常重要,HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM 映射了hal 层XXX.so 库的入口,上层hw_get_module 将获得该入口,使得上层可以和底层.so库进行交互
struct sensors_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.version_major = 1,
.version_minor = 0,
.id = SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "MTK SENSORS Module",
.author = "Mediatek",
.methods = &sensors_module_methods,
},
.get_sensors_list = sensors__get_sensors_list,
};
static int sensors__get_sensors_list(struct sensors_module_t* module,
struct sensor_t const** list)
{
ALOGD(" sSensorList addr =%p, module addr =%prn",sSensorList,module);
ALOGD(" ARRAY_SIZE(sSensorList) =%d SENSORS_NUM=%d MAX_NUM_SENSOR=%d rn",ARRAY_SIZE(sSensorList), SENSORS_NUM, MAX_NUM_SENSOR);
*list = sSensorList;
return ARRAY_SIZE(sSensorList);
}
struct sensor_t sSensorList[] =
{
#ifdef CUSTOM_KERNEL_ACCELEROMETER
{
.name = ACCELEROMETER,
.vendor = ACCELEROMETER_VENDER,
.version = 3,
.handle = ID_ACCELEROMETER+ID_OFFSET,
.type = SENSOR_TYPE_ACCELEROMETER,
.maxRange = ACCELEROMETER_RANGE,//32.0f,
.resolution = ACCELEROMETER_RESOLUTION,//4.0f/1024.0f,
.power = ACCELEROMETER_POWER,//130.0f/1000.0f,
.minDelay = 10000,
.maxDelay = 1000000,
.reserved = {}
},
#endif
#if defined(CUSTOM_KERNEL_ALSPS) || defined(CUSTOM_KERNEL_ALS)
{
.name = LIGHT,
.vendor = LIGHT_VENDER,
.version = 1,
.handle = ID_LIGHT+ID_OFFSET,
.type = SENSOR_TYPE_LIGHT,
.maxRange = LIGHT_RANGE,//10240.0f,
.resolution = LIGHT_RESOLUTION,//1.0f,
.power = LIGHT_POWER,//0.13f,
.reserved = {}
},
#endif
};
三、Psensor HAL 层log分析
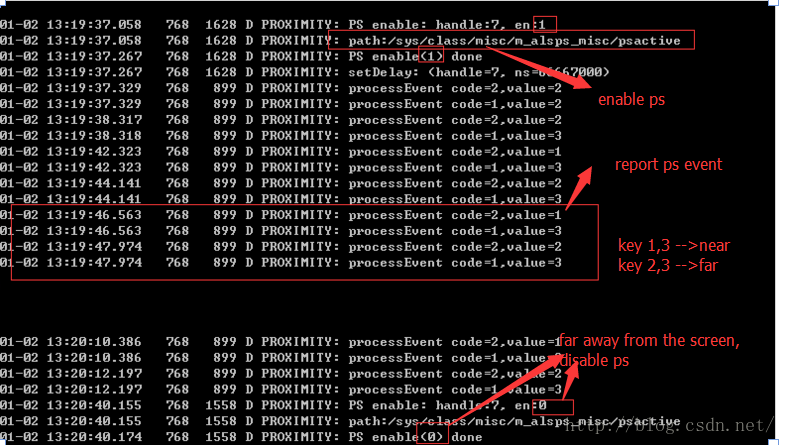
psensor 手机中常见的使用就是拨号时贴脸灭屏,拨号后遮挡psensor,使用Adb抓取android log ,过滤的的psensor log部分如下:
四、总结
Sensor HAL层相对来说比较简单,它的意图就是为framework层提供接口API的实现,如open_sensors,poll等,一旦实现完毕,framewoerk 里面的SensorManager,SensorService 里面的native(本地)方法可以直接被调用,关于framework层的学习,下一节继续更新!
ps:欢迎转载,交流学习!
最后
以上就是重要御姐最近收集整理的关于MTK6580-Psensor hal层驱动分析一、HAL 层Sensor 流程的全部内容,更多相关MTK6580-Psensor内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复