Zipkin : Golang 微服务全链路监控(二)
Golang 微服务全链路监控实现
- broker-service -> auth-service -> postgres db
- zipkin 监控:需代码入侵
一、auth-service
- 通过 context 传递 span
main.go
package main
import (
"broker-service/auth-service"
"broker-service/auth-service/data"
"database/sql"
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
"time"
"github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go"
zipkinot "github.com/openzipkin-contrib/zipkin-go-opentracing"
"github.com/openzipkin/zipkin-go"
zipkinhttp "github.com/openzipkin/zipkin-go/reporter/http"
_ "github.com/jackc/pgconn"
_ "github.com/jackc/pgx/v4"
_ "github.com/jackc/pgx/v4/stdlib"
)
const (
// Our service name.
serviceName = "auth"
// Host + port of our service.
hostPort = "localhost:8090"
// Endpoint to send Zipkin spans to.
zipkinHTTPEndpoint = "http://localhost:9411/api/v2/spans"
)
var counts int
//auth
func main() {
// set up a span reporter
reporter := zipkinhttp.NewReporter(zipkinHTTPEndpoint)
defer reporter.Close()
// create our local service endpoint
endpoint, err := zipkin.NewEndpoint(serviceName, hostPort)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("unable to create local endpoint: %+vn", err)
}
// initialize our tracer
nativeTracer, err := zipkin.NewTracer(reporter, zipkin.WithLocalEndpoint(endpoint))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("unable to create tracer: %+vn", err)
}
// use zipkin-go-opentracing to wrap our tracer
tracer := zipkinot.Wrap(nativeTracer)
// optionally set as Global OpenTracing tracer instance
opentracing.SetGlobalTracer(tracer)
//connect to DB
conn := connectToDB()
if conn == nil {
log.Panic("Can't connect to Postgres!")
}
// create the service implementation
service := auth.NewService(conn, data.New(conn))
// create the HTTP Server Handler for the service
handler := auth.NewHTTPHandler(tracer, service)
// start the service
fmt.Printf("Starting %s on %sn", serviceName, hostPort)
http.ListenAndServe(hostPort, handler)
}
func openDB(dsn string) (*sql.DB, error) {
db, err := sql.Open("pgx", dsn)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
err = db.Ping()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return db, nil
}
func connectToDB() *sql.DB {
dsn := "host=localhost port=5432 user=postgres password=password dbname=users sslmode=disable timezone=Asia/Shanghai connect_timeout=5"
}
for {
connection, err := openDB(dsn)
if err != nil {
log.Println(dsn)
log.Println("postgres is not ready...")
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
counts++
} else {
log.Println("connected to postgres")
return connection
}
if counts > 100 {
log.Panic(err)
}
}
}
- 定义 auth 服务
httpService.go
package auth
import (
"log"
"net/http"
opentracing "github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go"
"broker-service/middleware"
)
type httpService struct {
service Service
}
type RequestPayload struct {
Action string `json:"action"`
Auth AuthPayload `json:"auth,omitempty"`
Log loggerPayload `json:"log,omitempty"`
}
type AuthPayload struct {
Email string `json:"email"`
Password string `json:"password"`
}
type loggerPayload struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Data string `json:"data"`
}
// authHandler is our HTTP Handlerfunc for a Auth request.
func (s *httpService) authHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
var requestPayload AuthPayload
err := s.readJSON(w, req, &requestPayload)
if err != nil {
s.errorJSON(w, err)
return
}
log.Println("requestPayload:", requestPayload)
// call our Auth binding
result, err := s.service.Auth(req.Context(), requestPayload)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
// return the result
s.writeJSON(w, http.StatusAccepted, result)
}
// NewHTTPHandler returns a new HTTP handler our svc2.
func NewHTTPHandler(tracer opentracing.Tracer, service Service) http.Handler {
// Create our HTTP Service.
svc := &httpService{service: service}
// Create the mux.
mux := http.NewServeMux()
// Create the Auth handler.
var authHandler http.Handler
authHandler = http.HandlerFunc(svc.authHandler)
// Wrap the Auth handler with our tracing middleware.
authHandler = middleware.FromHTTPRequest(tracer, "Auth")(authHandler)
// Wire up the mux.
mux.Handle("/auth/", authHandler)
// Return the mux.
return mux
}
service.go
package auth
import (
"context"
"errors"
)
// Service interface to our svc2 service.
type Service interface {
Auth(ctx context.Context, a AuthPayload) (jsonResponse, error)
}
二、middleware.go
自定义 middleware.go,context 传递 Http 请求
// Package middleware provides some usable transport middleware to deal with
// propagating Zipkin traces across service boundaries.
package middleware
import (
"fmt"
"net"
"net/http"
"strconv"
opentracing "github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go"
"github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go/ext"
)
// RequestFunc is a middleware function for outgoing HTTP requests.
type RequestFunc func(req *http.Request) *http.Request
// ToHTTPRequest returns a RequestFunc that injects an OpenTracing Span found in
// context into the HTTP Headers. If no such Span can be found, the RequestFunc
// is a noop.
func ToHTTPRequest(tracer opentracing.Tracer) RequestFunc {
return func(req *http.Request) *http.Request {
// Retrieve the Span from context.
if span := opentracing.SpanFromContext(req.Context()); span != nil {
// We are going to use this span in a client request, so mark as such.
ext.SpanKindRPCClient.Set(span)
// Add some standard OpenTracing tags, useful in an HTTP request.
ext.HTTPMethod.Set(span, req.Method)
span.SetTag("http.host", req.URL.Host)
span.SetTag("http.path", req.URL.Path)
ext.HTTPUrl.Set(
span,
fmt.Sprintf("%s://%s%s", req.URL.Scheme, req.URL.Host, req.URL.Path),
)
// Add information on the peer service we're about to contact.
if host, portString, err := net.SplitHostPort(req.URL.Host); err == nil {
ext.PeerHostname.Set(span, host)
if port, err := strconv.Atoi(portString); err != nil {
ext.PeerPort.Set(span, uint16(port))
}
} else {
ext.PeerHostname.Set(span, req.URL.Host)
}
// Inject the Span context into the outgoing HTTP Request.
if err := tracer.Inject(
span.Context(),
opentracing.TextMap,
opentracing.HTTPHeadersCarrier(req.Header),
); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("error encountered while trying to inject span: %+vn", err)
}
}
return req
}
}
// HandlerFunc is a middleware function for incoming HTTP requests.
type HandlerFunc func(next http.Handler) http.Handler
// FromHTTPRequest returns a Middleware HandlerFunc that tries to join with an
// OpenTracing trace found in the HTTP request headers and starts a new Span
// called `operationName`. If no trace could be found in the HTTP request
// headers, the Span will be a trace root. The Span is incorporated in the
// HTTP Context object and can be retrieved with
// opentracing.SpanFromContext(ctx).
func FromHTTPRequest(tracer opentracing.Tracer, operationName string,
) HandlerFunc {
return func(next http.Handler) http.Handler {
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
// Try to join to a trace propagated in `req`.
wireContext, err := tracer.Extract(
opentracing.TextMap,
opentracing.HTTPHeadersCarrier(req.Header),
)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("error encountered while trying to extract span: %+vn", err)
}
// create span
span := tracer.StartSpan(operationName, ext.RPCServerOption(wireContext))
defer span.Finish()
// store span in context
ctx := opentracing.ContextWithSpan(req.Context(), span)
// update request context to include our new span
req = req.WithContext(ctx)
// next middleware or actual request handler
next.ServeHTTP(w, req)
})
}
}
三、implementation.go
处理实现验证服务
package auth
import (
"broker-service/auth-service/data"
"context"
"database/sql"
"fmt"
"log"
"github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go"
)
// Auth is our actual service implementation.
type auth struct {
DB *sql.DB
Models data.Models
}
// NewService returns a new implementation of our Service.
func NewService(db *sql.DB, models data.Models) Service {
return &auth{
DB: db,
Models: models,
}
}
// Auth implements our Service interface.
func (auth *auth) Auth(ctx context.Context, a AuthPayload) (jsonResponse, error) {
var jsonResp jsonResponse
jsonResp.Error = true
jsonResp.Message = "Auth fialed"
// Pull span from context.
span := opentracing.SpanFromContext(ctx)
// Example binary annotations.
span.SetTag("service", "auth")
span.SetTag("AuthPayload", a)
user, err := auth.Models.User.GetByEmail(span, a.Email)
if err != nil {
log.Println("get user failed from db: ", err)
span.SetTag("error", err.Error())
return jsonResp, err
}
log.Println("user:", user)
valid, err := user.PasswordMatches(a.Password)
if err != nil || !valid {
log.Println("invalid user: ", err)
span.SetTag("error", err.Error())
return jsonResp, err
}
jsonResp = jsonResponse{
Error: false,
Message: fmt.Sprintf("Logged in user %s", user.Email),
Data: user,
}
log.Println("auth response: ", jsonResp)
return jsonResp, nil
}
四、httpclinet.go
通过 client 向服务发送验证请求(由 broker-service 调用)
package auth
import (
"bytes"
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"broker-service/middleware"
opentracing "github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go"
)
// client is our actual client implementation
type client struct {
baseURL string
httpClient *http.Client
tracer opentracing.Tracer
traceRequest middleware.RequestFunc
}
// Auth implements our Service interface.
func (c *client) Auth(ctx context.Context, a AuthPayload) (data jsonResponse, err error) {
// create new span using span found in context as parent (if none is found,
// our span becomes the trace root).
span, ctx := opentracing.StartSpanFromContext(ctx, "Auth")
defer span.Finish()
log.Println("auth: ", a)
jsonData, _ := json.Marshal(a)
url := fmt.Sprintf("%s/auth/", c.baseURL)
var payload jsonResponse
payload.Error = true
payload.Message = "Authenticatioin failed!"
// create the HTTP request
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", url, bytes.NewBuffer(jsonData))
if err != nil {
span.SetTag("error", err.Error())
return payload, err
}
// use our middleware to propagate our trace
req = c.traceRequest(req.WithContext(ctx))
// execute the HTTP request
resp, err := c.httpClient.Do(req)
if err != nil {
// annotate our span with the error condition
span.SetTag("error", err.Error())
return
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
if resp.StatusCode == http.StatusAccepted {
err = json.NewDecoder(resp.Body).Decode(&data)
log.Println("result: ", data)
if err != nil {
span.SetTag("error", err.Error())
return
}
if data.Error {
span.SetTag("error", data.Error)
return
}
return data, nil
}
return
}
// NewHTTPClient returns a new client instance to our auth using the HTTP
// transport.
func NewHTTPClient(tracer opentracing.Tracer, baseURL string) Service {
return &client{
baseURL: baseURL,
httpClient: &http.Client{},
tracer: tracer,
traceRequest: middleware.ToHTTPRequest(tracer),
}
}
五、结果显示
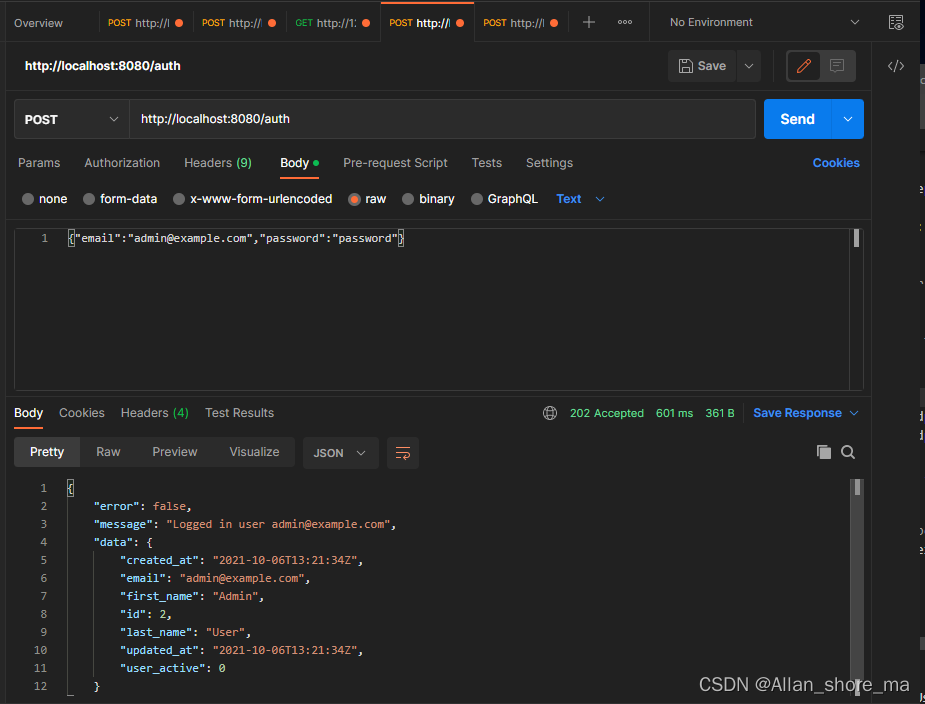
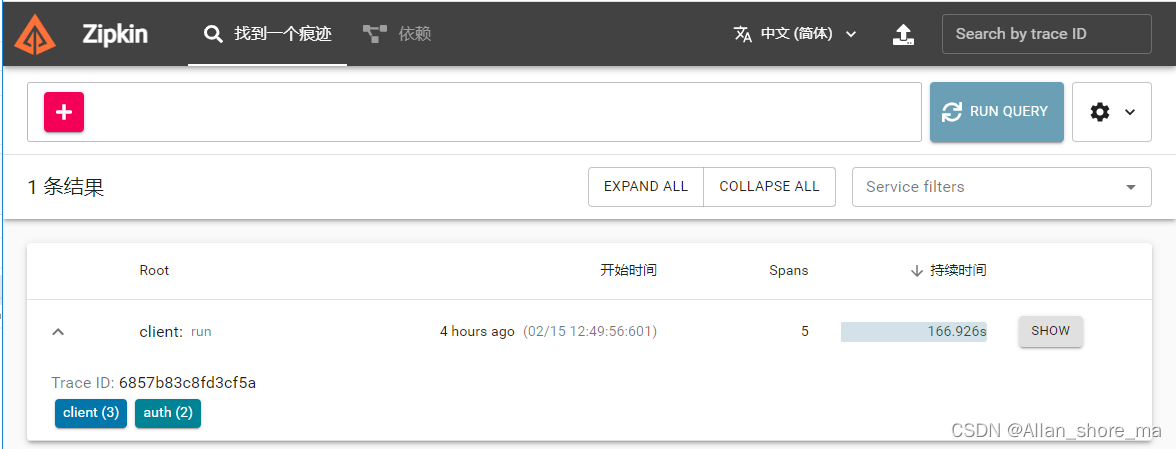
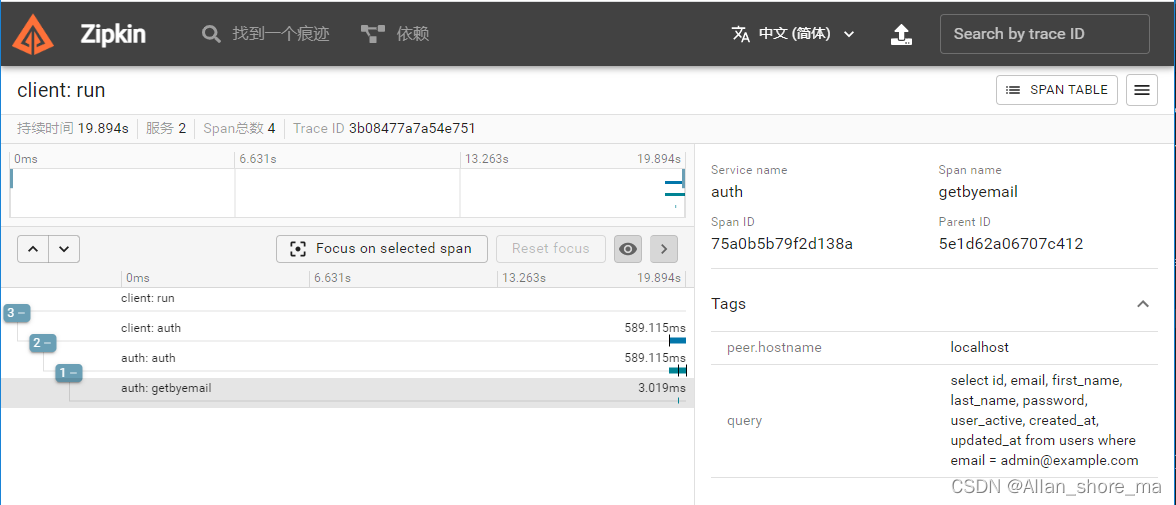
最后
以上就是爱听歌白云最近收集整理的关于Zipkin : Golang 微服务全链路监控(二)的全部内容,更多相关Zipkin内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复