tag文件的attribute指令和variable指令
文章目录
- tag文件的attribute指令和variable指令
- 一、attribute指令
- 1、attribute指令的作用与用法
- 2、运用实例
- 1 example3_3.jsp
- 2 Triangle.tag
- 3 效果图与总结
- 二、variable指令
- 1.variable指令的作用与用法
- 2、运用实例
- 1 uesone.jsp
- 2 giveroot.tag
- 3 效果图与总结
- 总结
一、attribute指令
1、attribute指令的作用与用法
attribute指令本质就是JSP页面向tag文件传输数据的一种应用
格式:在Tag中
<%@ attribute name=“对象名字” required=“true” type=“对象类型” %>
在引用Tag的JSP中
<前缀: Tag文件名字 对象名字=“对象的引用” />
或
<前缀: Tag文件名字 对象名字=“对象的引用” >
标记体
</前缀: Tag文件名字 >
如:tag中定义:<%@ attribute name=“length” required=“true” %>
JSP中代码: <beijing: AddSum length=“1000” />
2、运用实例
1 example3_3.jsp
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: ruochen
Date: 2020/10/29
Time: 8:20
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib tagdir="/WEB-INF/tags" prefix="computer"%>
<html>
<body>
<h3>以下是调用Tag文件的效果:</h3>
<computer:Triangle sideA="5" sideB="6" sideC="7"/>
</body>
</html>
2 Triangle.tag
<%@ tag pageEncoding="utf-8" %>
<h4>这是一个Tag文件,负责计算三角形的面积。
<%@ attribute name="sideA" required="true" %>
<%@ attribute name="sideB" required="true" %>
<%@ attribute name="sideC" required="true" %>
<%! public String getArea(double a,double b,double c) {
if(a+b>c&&a+c>b&&c+b>a) {
double p=(a+b+c)/2.0;
double area=Math.sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c)) ;
return "<BR>三角形的面积:"+area;
}
else
return("<BR>"+a+","+b+","+c+"不能构成一个三角形,无法计算面积");
}
%>
<% out.println("<BR>JSP页面传递过来的三条边:"+sideA+","+sideB+","+sideC);
double a=Double.parseDouble(sideA);
double b=Double.parseDouble(sideB);
double c=Double.parseDouble(sideC);
out.println(getArea(a,b,c));
%>
3 效果图与总结
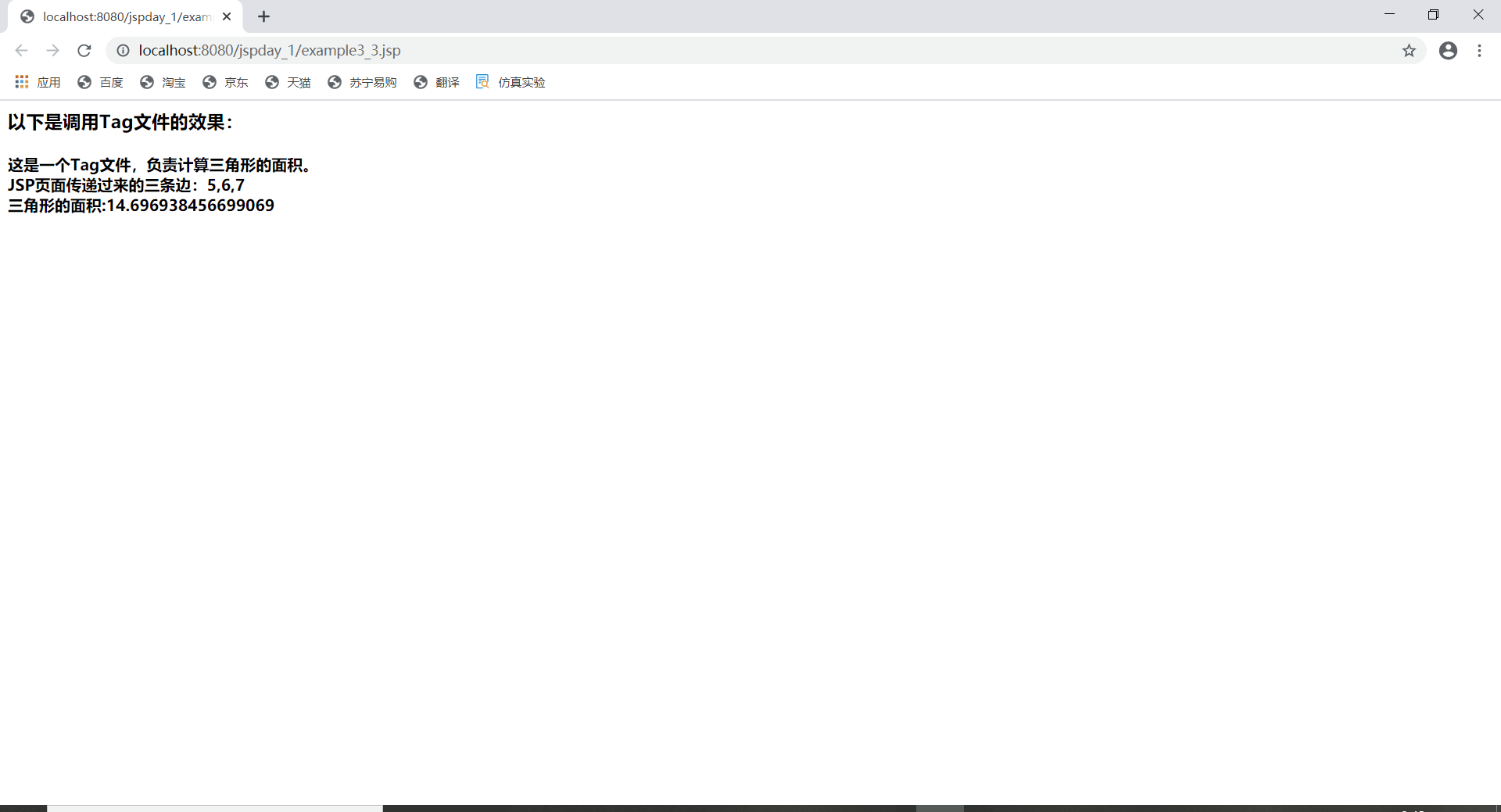
通过<computer:Triangle sideA=“5” sideB=“6” sideC=“7”/>
向Triangle.tag文件传输三个数据
再通过
<%@ attribute name=“sideA” required=“true” %>
<%@ attribute name=“sideB” required=“true” %>
<%@ attribute name=“sideC” required=“true” %>
接收三个数据,从而完成tag文件从jsp文件中获取数据的需求
二、variable指令
1.variable指令的作用与用法
variable指令本质就是实现Tag向JSP返回数据。
格式:
1.在Tag中首先声明:
<%@ variable name-given=“对象名字” variable-class=“对象类型” scope=“有效范围” %>
2.然后调用jspContext内置对象的setAttribute()将对象存储到jspContext中,以便JSP调用。如:
jspContext.setAttribute(“time”, new Date());
3.那么在JSP中,可以直接通过对象名来使用这个对象。如:
int year=time.getYear()+1900;
该代码使用Date的getYear()方法,将Tag传送的time对象中记录的时间年赋给year变量。
注意:
1. 返回的是一个对象。
2. JSP中不可再定义与name具有相同名字的变量,否则会出现编译错误。
3. scope定义了variable在JSP中的使用范围,可取值为AT_BEGIN、NESTED和AT_END。
AT_BEGIN: JSP页面一旦使用Tag,就可以使用variable给出的对象。
NESTED: JSP页面只可以在Tag标记的标记体中使用variable给出的对象。
AT_END: JSP页面在Tag标记结束后才可以使用variable给出的对象。
2、运用实例
1 uesone.jsp
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: ruochen
Date: 2020/10/29
Time: 9:21
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib tagdir="/WEB-INF/tags" prefix="computer"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<computer:giveroot coefficientA="3" coefficientB="6" coefficientC="-2"/>
<h4> 方程的根以及计算两个根的和:
<%
if(rootOne!=null&&rootTwo!=null){
double r1=rootOne.doubleValue(); //rootOne是giveroot.tag文件返回的Double型对象
double r2=rootTwo.doubleValue(); //rootTwo是giveroot.tag文件返回的Double型对象
out.println("<br>根1:"+r1);
out.println("<br>根2:"+r2);
double sum=r1+r2;
out.println("<br>根1与根2之和:"+sum);
}
else{
out.println("<br>方程没有实根");
}
%>
</body>
</html>
2 giveroot.tag
<%@ tag pageEncoding="UTF-8" %>
<%@ attribute name="coefficientA" required="true" %>
<%@ attribute name="coefficientB" required="true" %>
<%@ attribute name="coefficientC" required="true" %>
<%@ variable name-given="rootOne" variable-class="java.lang.Double" scope="AT_END" %>
<%@ variable name-given="rootTwo" variable-class="java.lang.Double" scope="AT_END" %>
<% double disk,root1,root2;
double a=Double.parseDouble(coefficientA);
double b=Double.parseDouble(coefficientB);
double c=Double.parseDouble(coefficientC);
disk=b*b-4*a*c;
if(disk>=0&&a!=0){
root1=(-b+Math.sqrt(disk))/(2*a);
root2=(-b-Math.sqrt(disk))/(2*a);
jspContext.setAttribute("rootOne",root1); //为JSP页面返回对象rootOne
jspContext.setAttribute("rootTwo",root2); //为JSP页面返回对象rootTwo
}
else{
jspContext.setAttribute("rootOne",null);
jspContext.setAttribute("rootTwo",null);
}
%>
3 效果图与总结
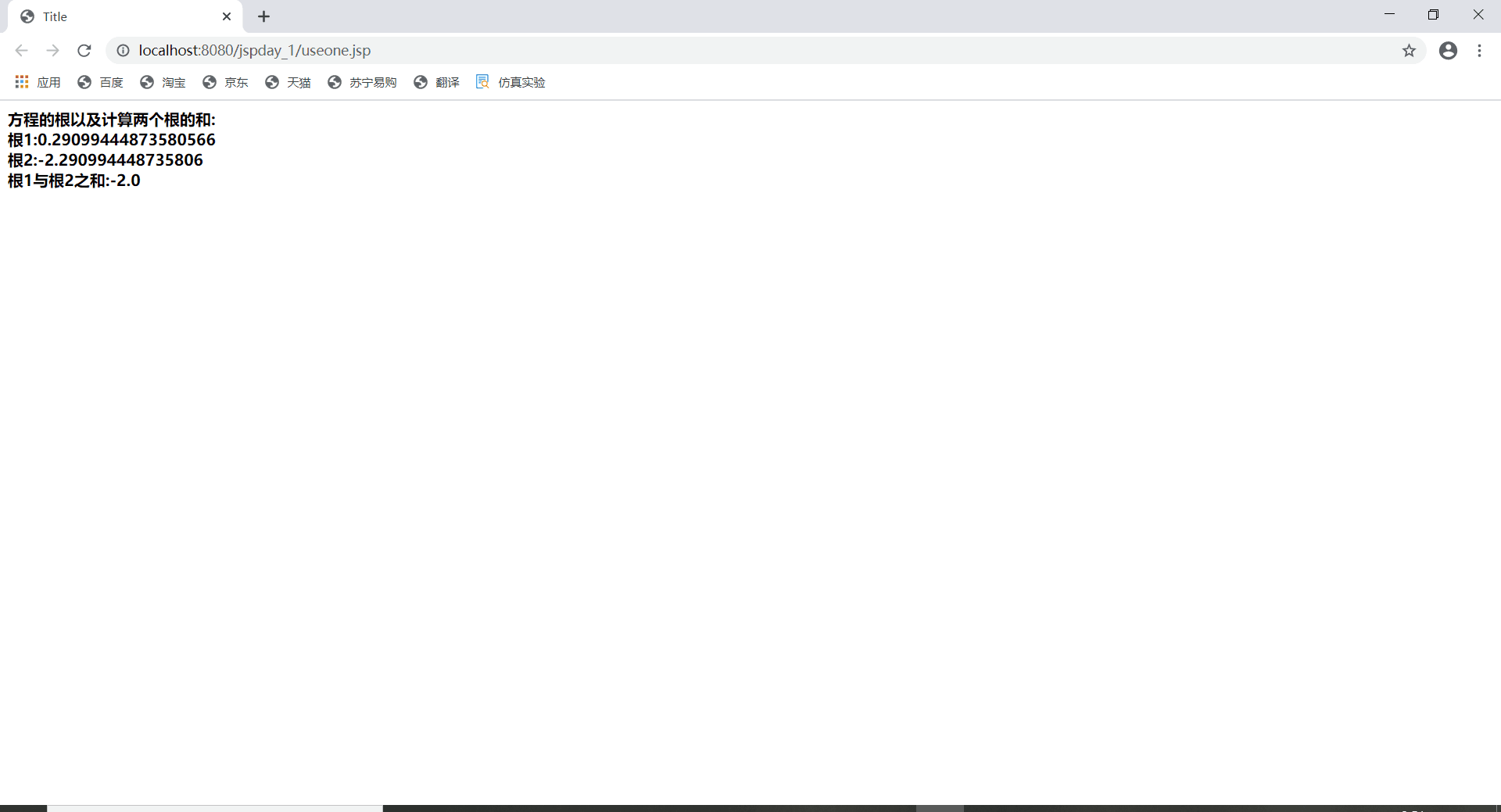
通过<computer:giveroot coefficientA=“3” coefficientB=“6” coefficientC="-2"/>
向giveroot.tag文件传输三个数据
再通过
<%@ attribute name=“sideA” required=“true” %>
<%@ attribute name=“sideB” required=“true” %>
<%@ attribute name=“sideC” required=“true” %>
接收数据
通过variable指令向jsp页面传输数据
<%@ variable name-given=“rootOne” variable-class=“java.lang.Double” scope=“AT_END” %>
<%@ variable name-given=“rootTwo” variable-class=“java.lang.Double” scope=“AT_END” %>
调用jspContext内置对象的setAttribute()将对象存储到jspContext中,以便JSP调用。
如 jspContext.setAttribute(“rootOne”,root1);
总结
提示:这里对文章进行总结:
attribute指令是jsp页面向tag文件传输数据
variable指令是从tag文件向jsp页面传输数据
最后
以上就是潇洒荷花最近收集整理的关于JSP tag文件的attribute指令和variable指令的使用tag文件的attribute指令和variable指令一、attribute指令二、variable指令总结的全部内容,更多相关JSP内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复