一、项目简介:
最近在做netty 通信项目简介、 整个项目中服务器负责对底层硬件的数据进行收集、然后通过客户端与服务器建立起通信通道、实现客户端接收到服务器端发送的消息、
二、问题描述:
最近在测试过程中发现一个问题、当客户端断开连接时、netty服务器端并没有发现客户端已经断开连接、仍有线程持续进行写操作、多次连接会导致服务器端资源形成浪费、导致服务端性能下降、
三、解决方案:
使用netty 自带的 心跳检测、保持服务端和客户端的时心跳检测、当客户机因为人工或者非人工原因导致的断开连接、服务器端能及时对线程资源进行回收、从而对服务器资源实现充分利用
四、代码实现部分:
0、相关jar 包依赖如图所示:
1、远程过程调用 RpcDecoder.java 解码器:
package com.upsoft;
import java.util.List;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.ByteToMessageDecoder;
public class RpcDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
private Class<?> genericClass;
public RpcDecoder(Class<?> genericClass) {
this.genericClass = genericClass;
}
@Override
public final void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out)
throws Exception {
if (in.readableBytes() < 4) {
return;
}
in.markReaderIndex();
int dataLength = in.readInt();
if (dataLength < 0) {
ctx.close();
}
if (in.readableBytes() < dataLength) {
in.resetReaderIndex();
}
byte[] data = new byte[dataLength];
in.readBytes(data);
Object obj = SerializationUtil.deserializer(data, genericClass);
System.out.println("接收到的消息是:" + obj);
out.add(obj);
}
}2、远程过程调用 RpcEncoder.java 译码器:
package com.upsoft;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToByteEncoder;
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public class RpcEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder {
private Class<?> genericClass;
public RpcEncoder(Class<?> genericClass) {
this.genericClass = genericClass;
}
@Override
public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object in, ByteBuf out)
throws Exception {
if (genericClass.isInstance(in)) {
System.out.println("发送的请求是:" + in);
byte[] data = SerializationUtil.serializer(in);
out.writeInt(data.length);
out.writeBytes(data);
}
}
}3、SerializationUtil.java 序列化工具类:
package com.upsoft;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import org.objenesis.Objenesis;
import org.objenesis.ObjenesisStd;
import io.protostuff.LinkedBuffer;
import io.protostuff.ProtostuffIOUtil;
import io.protostuff.Schema;
import io.protostuff.runtime.RuntimeSchema;
public class SerializationUtil {
private static Map<Class<?>, Schema<?>> cachedSchema = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class<?>, Schema<?>>();
private static Objenesis objenesis = new ObjenesisStd(true);
private static <T> Schema<T> getSchema(Class<T> clazz) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Schema<T> schema = (Schema<T>)cachedSchema.get(clazz);
if (schema == null) {
schema = RuntimeSchema.getSchema(clazz);
if (schema != null) {
cachedSchema.put(clazz, schema);
}
}
return schema;
}
/**
* 序列化
*
* @param obj
* @return
*/
public static <T> byte[] serializer(T obj) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class<T> clazz = (Class<T>)obj.getClass();
LinkedBuffer buffer = LinkedBuffer.allocate(LinkedBuffer.DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
try {
Schema<T> schema = getSchema(clazz);
byte result[] = ProtostuffIOUtil.toByteArray(obj, schema, buffer);
return result;
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
finally {
buffer.clear();
}
}
/**
* 反序列化
*
* @param data
* @param clazz
* @return
*/
public static <T> T deserializer(byte[] data, Class<T> clazz) {
try {
T obj = objenesis.newInstance(clazz);
Schema<T> schema = getSchema(clazz);
ProtostuffIOUtil.mergeFrom(data, obj, schema);
return obj;
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}4、HeartBeatReqHandler.java心跳检测请求 :
package com.upsoft;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelDuplexHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleState;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateEvent;
public class HeartBeatReqHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
/**
* @see io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter#userEventTriggered(io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext,
* java.lang.Object)
*/
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt)
throws Exception {
if (IdleStateEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(evt.getClass())) {
IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent)evt;
if (event.state() == IdleState.READER_IDLE) {
System.out.println("Read 空闲");
ctx.disconnect();
}
else if (event.state() == IdleState.WRITER_IDLE) {
System.out.println("Write 空闲");
ctx.writeAndFlush(buildHeartBeat(MessageType.HEARTBEAT_REQ.getType()));
}
}
}
/**
*
* @return
* @author upsoft
*/
private NettyMessage buildHeartBeat(byte type) {
NettyMessage msg = new NettyMessage();
Header header = new Header();
header.setType(type);
msg.setHeader(header);
return msg;
}
}5、HeartBeatRespHandler.java心跳检测响应 :
package com.upsoft;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleState;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateEvent;
public class HeartBeatRespHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<NettyMessage> {
/**
* @see io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler#channelRead0(io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext,
* java.lang.Object)
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, NettyMessage msg)
throws Exception {
if (msg.getHeader() != null && msg.getHeader().getType() == MessageType.HEARTBEAT_REQ.getType()) {
NettyMessage heartBeat = buildHeartBeat(MessageType.HEARTBEAT_RESP.getType());
ctx.writeAndFlush(heartBeat);
}
else {
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}
/**
* @see io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter#userEventTriggered(io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext,
* java.lang.Object)
*/
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt)
throws Exception {
if (IdleStateEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(evt.getClass())) {
IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent)evt;
if (event.state() == IdleState.READER_IDLE) {
System.out.println("read 空闲 关闭链接");
ctx.disconnect();
}
}
}
// /**
// *
// * @return
// * @author upsoft
// */
private NettyMessage buildHeartBeat(byte type) {
NettyMessage msg = new NettyMessage();
Header header = new Header();
header.setType(type);
msg.setHeader(header);
return msg;
}
}6、MessageType.java 消息类型枚举 :
package com.upsoft;
public enum MessageType {
LOGIN_REQ((byte)1),
LOGIN_RESP((byte)2),
HEARTBEAT_REQ((byte)3),
HEARTBEAT_RESP((byte)4);
/**
* @param type
*/
private byte type;
private MessageType(byte type) {
this.type = type;
}
public byte getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(byte type) {
this.type = type;
}
public static MessageType getMessageType(byte type) {
for (MessageType b : MessageType.values()) {
if (b.getType() == type) {
return b;
}
}
return null;
}
}7、Headerj.java netty 心跳头 :
package com.upsoft;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Header implements Serializable {
/** */
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private int crcCode = 0xabef0101;
private int length;
private long sessionId;
private byte type;
private byte priority;
private Map<String, Object> attachment = new HashMap<>();
public int getCrcCode() {
return crcCode;
}
public void setCrcCode(int crcCode) {
this.crcCode = crcCode;
}
public int getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(int length) {
this.length = length;
}
public long getSessionId() {
return sessionId;
}
public void setSessionId(long sessionId) {
this.sessionId = sessionId;
}
public byte getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(byte type) {
this.type = type;
}
public byte getPriority() {
return priority;
}
public void setPriority(byte priority) {
this.priority = priority;
}
public Map<String, Object> getAttachment() {
return attachment;
}
public void setAttachment(Map<String, Object> attachment) {
this.attachment = attachment;
}
/**
* @see java.lang.Object#toString()
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Header [crcCode=" + crcCode + ", length=" + length + ", sessionId=" + sessionId + ", type=" + type
+ ", priority=" + priority + ", attachment=" + attachment + "]";
}
}8、 NettyMessage.java netty消息实体:
package com.upsoft;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class NettyMessage implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Header header;
private Object body;
public Header getHeader() {
return header;
}
public void setHeader(Header header) {
this.header = header;
}
public Object getBody() {
return body;
}
public void setBody(Object body) {
this.body = body;
}
/**
* @see java.lang.Object#toString()
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "NettyMessage [header=" + header + ", body=" + body + "]";
}
}9、NettyClient.java 客户端代码:
package com.upsoft;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateHandler;
public class NettyClient {
public void connect(String remoteServer, int port)
throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(workerGroup).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).remoteAddress(remoteServer, port).handler(
new ChildChannelHandler());
ChannelFuture f = b.connect();
System.out.println("Netty time Client connected at port " + port);
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
// netty重新连接、线程睡眠自动连接
// finally {
// try {
// TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
// try {
// System.out.println("重新链接。。。");
// connect(remoteServer, port);
// }
// catch (Exception e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// }
// catch (Exception e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// }
}
public static class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(final SocketChannel ch)
throws Exception {
// -8表示lengthAdjustment,让解码器从0开始截取字节,并且包含消息头
ch.pipeline().addLast(new RpcEncoder(NettyMessage.class)).addLast(
new RpcDecoder(NettyMessage.class)).addLast(new IdleStateHandler(120, 10, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS)).addLast(
new HeartBeatReqHandler());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
new NettyClient().connect("127.0.0.1", 12000);
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}10、NettyServer.java 服务器代码:
package com.upsoft;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateHandler;
public class NettyServer {
public void bind(int port)
throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,
1024).childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler());
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
System.out.println("Netty time Server connected at port" + port);
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}
finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(final SocketChannel ch)
throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new RpcDecoder(NettyMessage.class)).addLast(
new RpcEncoder(NettyMessage.class)).addLast(new IdleStateHandler(120, 0, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS)).addLast(
new HeartBeatRespHandler());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
new NettyServer().bind(12000);
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}11、首先启动服务器、然后启动客户端程序运行效果如下:
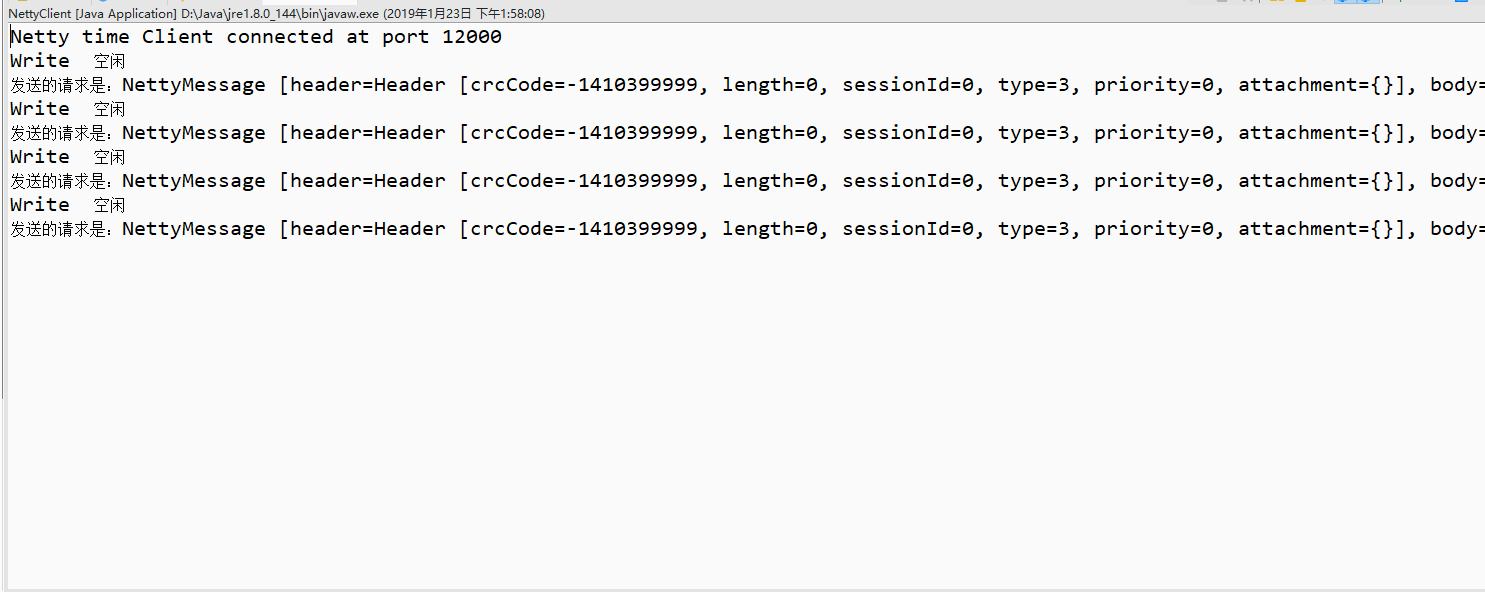
五、总结:
到此我们使用了netty实现了心跳检测 当客户端断开连接后、服务器将不会收到客户端的心跳回应、服务器将会把服务器端的对应的线程从内存中移除、从而节约了服务器资源、喝杯咖啡哈哈哈哈
本文参考博客感谢博主:https://wujiu.iteye.com/blog/2283669
最后
以上就是谦让砖头最近收集整理的关于(DEMO可用)Netty 实现保持长连接、 心跳检测、 断开自动重新连接、保持连接转态的全部内容,更多相关(DEMO可用)Netty内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复