前言:
从宏观环境来看互联网用户正在飞速发展,在我国互联网的普及率已接近了60%;
互联网用户的上涨势必会对网站的规模和性能带来更大的要求,所以就需要1个庞大的系统 支撑起海量用户的并发访问;
对于运维人员来说我们需要 以一种更加自动化的方式 加速运维效率应对突发流量,以及更加可靠的技术手段保障系统稳定运行;
2大核心功能:
资产自动化扫描、发现 (CMDB)
Ansible自动化任务执行 (批量执行任务)
一、整体功能设计
资产自动化扫描发现
使用Python程序扫描、发现企业内部的所有资产(实体机+虚拟机【KVM+ESX+Docker】+网络设备+其他),当资产信息变更(设备升级、资产下线)自动发现并完成数据库资产变更记录;

Ansible自动化任务执行
基于Ansible的ad-hoc和playbook方式实现批量主机任务执行;

二、扫描出网络中存活的主机
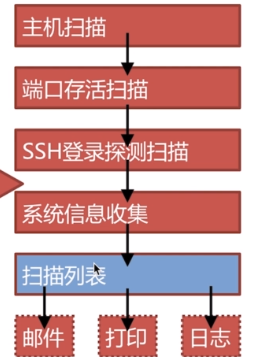
想要做CMDB就需要知道您所在公司到底有多少资产?都有那些统计方式呢?
0.人工录入
服务器变更人工干涉维护;
1.程序自动发现
使用nmap网络扫描工具,扫描公司内网每个网络中存活的主机列表。
三、硬件/系统信息获取
通过paramiko登录主机列中服务器,调用shell命令,通过awk、send截取指定内容;
1.获取主机名
hostname
2.获取mac地址
Linux系统:
cat /sys/class/net/[^vtlsb]*/address
EXSI:
esxcfg-vmknic -l|awk '{print $8}' | grep ':'
通用型
cat /sys/class/net/[^vtlsb]*/address || esxcfg-vmknic -l|awk '{print $8}' | grep ':'
3.系统版本
cat /etc/issue || cat /etc/reahat-release
4.服务机型
dmidecode -s system-product-name PS:安装 yum -y install dmidecode
5.SN(服务器唯一标识)
dmidecode -s system-serial-number
以上信息都可以基于paramiko远程执行命令返回信息结果(不包含 docker和网络设备);
6.获取网络设备、docker容器的信息
6.1 获取网络设备的硬件信息
对于网络设备管理人员我们除了使用ssh协议(TCP/22)之外还要使用Telnet协议(TCP/23)
如果想要获取网络设备的信息可以通过 snmap(简单网络管理协议)
使用python snmap模块作为客户端去连接网络设备 并获取网络设备信息;
pip install pysnmp
from pysnmp.entity.rfc3413.oneliner import cmdgen cg=cmdgen.CommandGenerator() ret=cg.getCmd(cmdgen.CommunityData('snmpt','public',0), #,安全my-agent、社区名public、snmp协议版本,之间用逗号隔开, snmp协议版本:0代表 2C 1 cmdgen.UdpTransportTarget(('172.17.10.112',161 )),'.1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0') #ip 端口 OID,一个OID对应一种设备(比如网卡、磁盘等,在不同机器上同种设备的OID是一样的) # print(ret) ''' (None, 0, 0, 错误信息 [执行结果] ''' print( ret[-1]) for i in ret[-1]: print(i)
注意:
OID:1个OID对应 1种服务器硬件信息(比如网卡、磁盘等,在不同机器上同种设备的OID是一样的),不同厂商网络设备 的OID可见官网;
6.2获取docker容器的信息

安装docker容器
shell获取docker容器(端口、容器ID、镜像ID)。
[root@localhost zhanggen]# docker ps | awk -F '->' '{print $1}' | grep -v 'CONTAINER' |awk 'BEGIN{FS~/s+/;}{print $NF " "$1" "$2;}' |sed s/0.0.0.0:// 5166 43958ff0fbaa 78a959232453 [root@localhost zhanggen]#


import paramiko,time ssh = paramiko.SSHClient() ssh._policy = paramiko.AutoAddPolicy() ssh.connect(hostname='192.168.226.139',port=22, username='root',password='123.com') docker_list_cmd="""docker ps | awk -F '->' '{print $1}' | grep -v 'CONTAINER' |awk 'BEGIN{FS~/s+/;}{print $NF " "$1" "$2;}' |sed s/0.0.0.0://""" stdin,stdout,stderr=ssh.exec_command(docker_list_cmd) docker_info=stdout.read().decode('utf-8').split('n')[:-1] for row in docker_info: docker_info_dict = {} docker_info_dict['dcoker_port']=row.split(' ')[0] docker_info_dict['docker_container_id'] = row.split(' ')[1] docker_info_dict['dcoker_image_id'] = row.split(' ')[2] print(docker_info_dict) # {'dcoker_port': '5188', 'docker_container_id': 'd69a0f80a4d2', 'dcoker_image_id': '78a959232'} # {'dcoker_port': '5166', 'docker_container_id': '43958ff0fbaa', 'dcoker_image_id': '78a959232453'}
6.2 登录宿主机 获取宿主机kvm虚拟机信息
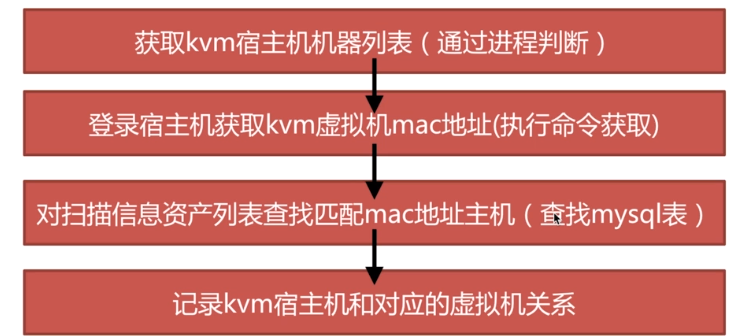
cat /sys/class/net/vnet*/address #查看到所有虚拟机的网卡mac地址
6.3.ESXI物理机的扫描
pyVmomi模块
三、Ansible模块执行自动化任务
自动化任务可以提升运维效率、避免人为操作错误;
Ansible是Python中一套模块、可以基于Unix平台做系统管理、自动化批量命令、定时任务执行等功能,注意本文基于ansible 2.6.3;
那么Ansible有什么优势呢?我可以通过paramiko+线程做自动化、批量执行任务啊!
Ansible是python中一套比较完整现成的模块并且兼容不同系统例如 EXSI、docker多进程并发;
Ansible包含众多子模块 包含shell、定时任务、用户管理、MySQL直接连接管理;
pip intstall ansible #安装Ansible
[root@cmdb ansible]# ansible --version ansible 2.6.3 config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg configured module search path = ['/usr/share/my_modules'] ansible python module location = /usr/local/python3/lib/python3.6/site-packages/ansible executable location = /usr/bin/ansible python version = 3.6.1 (default, Mar 15 2018, 14:09:21) [GCC 4.4.7 20120313 (Red Hat 4.4.7-18)] [root@cmdb ansible]#
1.Ansible的配置文件


/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
执行全局性、默认的配置文件例如:设置连接服务器的默认端口、用户、并发数据量


/etc/ansible/hosts
配置Ansible 连接主机、端口、用户、密码


[root@cmdb tmp]# export ANSIBLE_CONFIG=/tmp/ansible.cfg [root@cmdb tmp]# ansible --version ansible 2.6.3 config file = /tmp/ansible.cfg configured module search path = ['/usr/share/my_modules'] ansible python module location = /usr/local/python3/lib/python3.6/site-packages/ansible executable location = /usr/bin/ansible python version = 3.6.1 (default, Mar 15 2018, 14:09:21) [GCC 4.4.7 20120313 (Red Hat 4.4.7-18)] [root@cmdb tmp]# export ANSIBLE_CONFIG=/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg [root@cmdb tmp]# ansible --version ansible 2.6.3 config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
PS:Ansible读取主配置文件的优先级
export ANSIBLE_CONFIG=声明的路径 ./ansible.cfg:当前执行ansible命令所在路径 ~/ansible.cfg:用户家目录下寻找 /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
1.3:ansible.cfg文件详解
inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts #资源清单文件的路径
library = /usr/share/my_modules/ #ansible执行时加载的其他子模块
forks = 10 #并发进程最大支持数量
sudo_user =root #设置命令执行的用户
remote_port = 22 #执行命令时 默认连接端口
host_key_checking = True #设置第一次连接远程主机的时候是否检查主机的秘钥
timeout = 30 #连接超时的时间
log_path = /var/log/ansible.log #ansible日志的路径
private_key_file=/path/to/file.pem #在使用ssh公钥私钥登录系统时候,使用的密钥路径。
更多
1.4:hosts文件配置
hosts配置文件主要记录 远程主机IP、ansible_sudo_user、ansible_sudo_pass
[Hytest] #主机组 10.150.29.163 ansible_sudo_pass='Best@123' #使用ansible.cfg中默认的用户、密码 10.150.29.155 ansible_sudo_pass='Best@123' 10.150.29.154 ansible_sudo_pass='Best@123' 10.150.29.162 ansible_sudo_pass='Best@123' 10.150.29.157 ansible_sudo_pass='Best@123' 10.150.29.156 ansible_sudo_pass='Best@123' 10.150.29.160 ansible_sudo_pass='Best@123' 10.150.29.161 ansible_sudo_pass='Best@123' 10.150.29.164 ansible_sudo_pass='Best@123' 10.150.29.158 ansible_sudo_pass='Best@123' 10.150.29.159 ansible_sudo_pass='Best@123' 10.150.29.165 ansible_sudo_pass='Best@123' 10.150.29.152 ansible_sudo_pass='Best@123'
2、Ansible常用命令
[root@cmdb ansible]# ansible --version #查看Ansible相关信息
ansible 2.6.3
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = ['/usr/share/my_modules']
ansible python module location = /usr/local/python3/lib/python3.6/site-packages/ansible
executable location = /usr/bin/ansible
python version = 3.6.1 (default, Mar 15 2018, 14:09:21) [GCC 4.4.7 20120313 (Red Hat 4.4.7-18)]
[root@cmdb ansible]# ansible all --list-hosts #列出所有可以远程登录的远程主机(不区分主机组)
[root@cmdb ansible]# ansible Hytest --list-hosts #列出某个主机组的主机
ansible all -a 'ls' #批量执行命令
3:Ansible的ad-hoc模式
在Ansible中一共有两种模式分别是:ad-hoc模式 、 paybook模式
ad-hoc模式: 适用于短、简、快的 任务执行场景(临时命令);
paybook模式: 适用于命令比较复杂的 任务执行场景,任务可以持久化保存成剧本;
ad-hoc模式的命令使用
ansible <host-pattern> [option] cmd
host-pattern:匹配IP地址或主机组支持正则表示式
[root@cmdb ~]# ansible Hytest -a 'ls' #匹配组
[root@cmdb ~]# ansible 10.150.29.* -a 'ls' #按IP做正则匹配
配置别名
[Hybris] zhanggen ansible_shh_ip=10.150.25.199 ansible_sudo_pass='Hybris$BS^_199'
执行
[root@cmdb ansible]# ansible zhangg* -a 'ls' #按别名匹配执行
4: ad-hoc模式常用的模块
查看 Ansible ad-hoc模式所支持的模块
[root@cmdb ansible]# ansible-doc -l
使用 -m 参数加载Ansible支持的模块
[root@cmdb /]# ansible 192.168.1.18 -m shell -a "echo $HOSTNAME" #加载 shell模块
[root@cmdb ~]# ansible test -m copy -a "src=/tmp/zhanggen.txt dest=/tmp/" -f 1 -l 192.168.1.18
-f 开启1个进程 -l 从test机组中筛选主机
192.168.1.18 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "checksum": "3ee88a74d3722b336a69c428d226f731435c71ba", "dest": "/tmp/zhanggen.txt", "gid": 0, "group": "root", "mode": "0644", "owner": "root", "path": "/tmp/zhanggen.txt", "size": 7, "state": "file", "uid": 0 } [root@cmdb ~]#
setup模块批量 获取系统信息
[root@cmdb ~]# ansible test -m setup -f 1 -l 192.168.1.18
-a "filter=ansible_distribution" 添加过滤器
[root@cmdb ~]# ansible test -m setup -a "filter=ansible_distribution" -f 1 -l 192.168.1.18192.168.1.18 | SUCCESS => { "ansible_facts": { "ansible_distribution": "RedHat" }, "changed": false } [root@cmdb ~]#
yum模块批量安装应用
[root@cmdb ~]# ansible test -m yum -a "name=nginx state=present" -f 1 -l 192.168.1.18
#state=present 如果已经安装nginx则不会再进行安装更新
#state=latest 比对安装最新的版本
#state=removed yum remove
service模块批量启、停服务
[root@cmdb ~]# ansible test -m service -a "name=mysql state=restarted" -f 1 -l 192.168.1.18192.168.1.18 | SUCCESS => { "changed": true, "name": "mysql", "state": "started" }
git模块批量下载代码
如果你开发了CMDB汇报客户端,如何让1000台主机安装上它呢?This is a way.
[root@cmdb ~]# ansible test -m git -a "repo=https://github.com/zhanggen3714/zhanggen_audit.git dest=/zhanggen/ version=First" -f 1 -l 192.168.1.18
5:playbook模式
什么是Ansible的playbook模式?
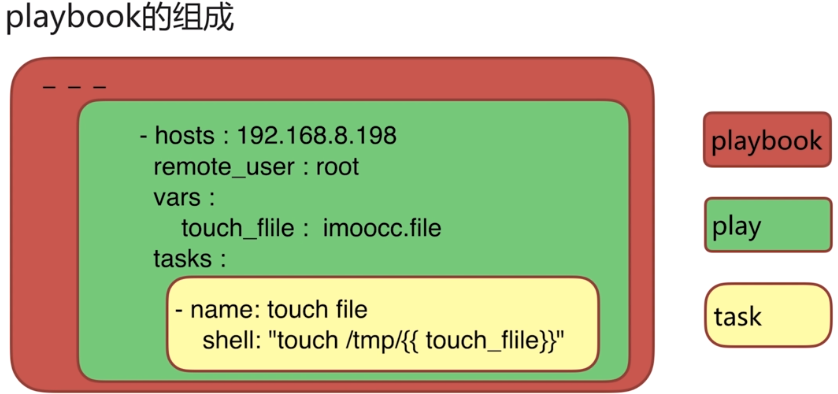
playbook就是剧本的意思
play:定义主机的角色
task:定义的是具体执行的任务
playbook:1个playbook可以包含N个play,1个play包含N个task。
相比 ad-hoc, playbook的优势?
a.功能比adhoc模式更全面; The Playbook mode is more powerfull than the Ad-hoc mode.
b.控制依赖
c.展示直观
d.持久使用
playbook的配置语法
A.基本使用
ansible-playbook playbook.yml [options]
生成剧本.yml配置文件
---
- hosts : 192.168.1.18
remote_user : root
vars :
touch_file : zhanggen.txt
tasks:
- name : touch file
shell : "touch /tmp/{{touch_file}}"
查看该剧本中可执行的主机
[root@cmdb ansible]# ansible-playbook -i hosts --list-hosts f1.yml playbook: f1.yml play #1 (192.168.1.18): 192.168.1.18 TAGS: [] pattern: ['192.168.1.18'] hosts (1): 192.168.1.18
执行剧本
[root@cmdb ansible]# ansible-playbook -i hosts f1.yml #-i 指定主机清单的路径 剧本配置文件.yml PLAY [192.168.1.18] *************************************************************************************** TASK [Gathering Facts] ************************************************************************************ ok: [192.168.1.18] TASK [touch file] ***************************************************************************************** [WARNING]: Consider using the file module with state=touch rather than running touch. If you need to use command because file is insufficient you can add warn=False to this command task or set command_warnings=False in ansible.cfg to get rid of this message. changed: [192.168.1.18] PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************************************ 192.168.1.18 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
6、playbook的使用
语法
yaml文件以 “---”作为文档的开始的标志;
区分大小写;
使用空白符缩进表示层级关系(只能使用 空格 不能是table键),可以是 空格个数不限可以是4个空格可以是1个;
yaml支持的数据类型
字典: {name:zhanggen }
列表:-Apple -Orange -Strawberry -Mango
数字、布尔、字符串
yaml格式转成json格式
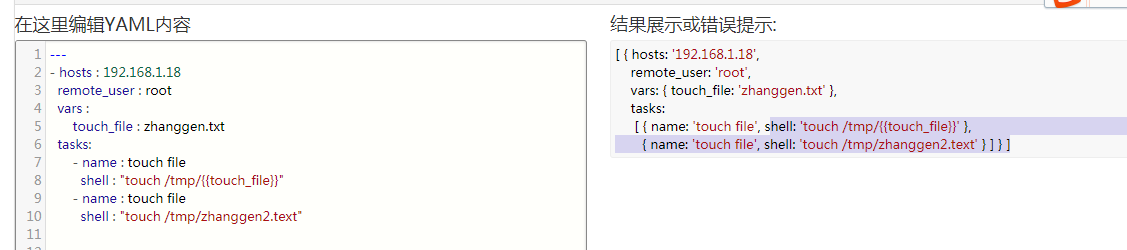
点我嘛~
Playbook剧本中变量的 定义方式
A.在剧本中引用
myname:zhanggen name:"{{ myname }}"
B.extra-vars执行参数 赋值给剧中 指定变量
每次都把变量定义在文件里面这也太费劲了,于是--extra参数出现了;
[root@cmdb ansible]# ansible-playbook -i hosts f1.yml --extra-vars "touch_file=aaa"
C.通过在资产清单文件(hosts)中定义变量


[test] 192.168.1.18 10.150.22.211 [test:vars] touch_file=whatdidIsay
D.regist关机键字 获取1个指定命令的 输出结果到 1个自定义变量中
--- - hosts : 192.168.1.18 remote_user : root vars : touch_file : zhanggen.txt tasks: - name : get_current_time command : date register: current_time #把 date命令的输出结果 声明为变量current_time - name : touch file shell: "echo {{current_time.stdout}}>/tmp/{{touch_file}}" #把current_time 输出到 文件中!
playbook中的条件判断、循环语句
playbook不仅支持变量的声明、还支持条件判断和循环语句
when条件判断
---
- hosts : 192.168.1.18
remote_user : root
tasks:
- name : "touch_file"
command : "touch /tmp/this_is_{{ansible_distribution}}_system"
when : (ansible_distribution == "RedHat" and 1 == 1) or (ansible_distribution == "CentOS" and 1 == 1)
循环语句
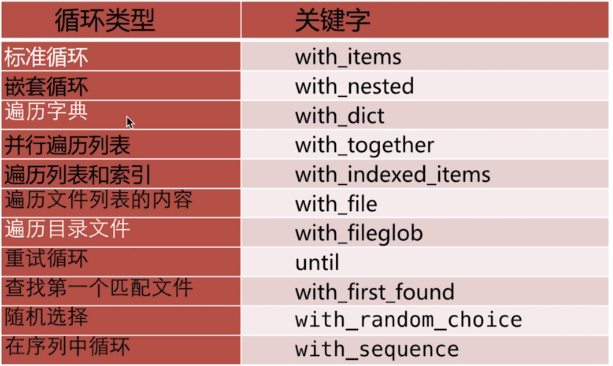
with_items循环列表
--- - hosts : 192.168.1.18 remote_user : root tasks: - name : add_server_user user : name={{ item.name }} state=present groups={{ item.groups }} #加载user模块添加2个用户:test_user01--->whee组 test_user02--->root组 with_items: - { name: 'test_user01', groups: 'wheel'} #循环列表 - { name: 'test_user02', groups: 'root'}
with_dict 循环字典
--- - hosts : 192.168.1.18 remote_user : root tasks: - name : add_server_user user : name={{ item.key }} state=present groups={{ item.value }} #key value with_dict: {'test_user01':'wheel','test_user02':'root'}
with_fileglob 循环目录下的文件
---
- hosts : 192.168.1.18
remote_user : root
tasks:
- file : dest=/tmp/ state=directory #加载文件模块
- copy : src={{item}} dest=/tmp/ owner=root mode=600 #设置源文件路径 目标主机文件路径 属组 权限
with_fileglob: #设置循环的路径
- /tmp/*


[root@cmdb ansible]# ansible-playbook f1.yml
[DEPRECATION WARNING]: DEFAULT_SUDO_USER option, In favor of Ansible Become, which is a generic framework. See become_user. , use
become instead. This feature will be removed in version 2.8. Deprecation warnings can be disabled by setting
deprecation_warnings=False in ansible.cfg.
PLAY [192.168.1.18] ***************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ************************************************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.18]
TASK [file] ***********************************************************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.18]
TASK [copy] ***********************************************************************************************************************
changed: [192.168.1.18] => (item=/tmp/zhanggen)
changed: [192.168.1.18] => (item=/tmp/yum_save_tx-2018-12-19-15-24PpuYlP.yumtx)
changed: [192.168.1.18] => (item=/tmp/yum_save_tx-2018-12-19-15-27baIMAT.yumtx)
changed: [192.168.1.18] => (item=/tmp/ansible.cfg)
changed: [192.168.1.18] => (item=/tmp/yum_save_tx-2018-12-19-16-179EqSv3.yumtx)
changed: [192.168.1.18] => (item=/tmp/yum_save_tx-2018-12-19-15-16eArxQ9.yumtx)
changed: [192.168.1.18] => (item=/tmp/yum_save_tx-2018-12-19-16-000PcZKT.yumtx)
changed: [192.168.1.18] => (item=/tmp/zhanggen.txt)
changed: [192.168.1.18] => (item=/tmp/yum_save_tx-2018-12-19-16-16zpp5v3.yumtx)
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************************************************************
192.168.1.18 : ok=3 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
循环+判断混合
---
- hosts : 192.168.1.18
remote_user : root
tasks:
- debug: msg="{{item.key}}" #debug模式打印
with_dict: { "zhanggen":{'math':25,'chinese':27},'Martin':{'englist':80,'chinese':90} }
when : item.value.chinese >=60 #判断


[root@cmdb ansible]# ansible-playbook f1.yml
PLAY [192.168.1.18] ***************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ************************************************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.18]
TASK [debug] **********************************************************************************************************************
skipping: [192.168.1.18] => (item={'key': 'zhanggen', 'value': {'math': 25, 'chinese': 27}})
ok: [192.168.1.18] => (item={'key': 'Martin', 'value': {'englist': 80, 'chinese': 90}}) => {
"msg": "Martin"
}
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************************************************************
192.168.1.18 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0
[root@cmdb ansible]#
ignore_errors异常处理
---
- hosts : 192.168.1.18
remote_user : root
tasks:
- name: ignore false
command: /bin/false
ignore_errors : yes #处理异常错误
- name: touch a file
file: path=/tmp/test06 state=touch mode=0700 owner=root group=root
执行结果
[root@cmdb ansible]# ansible-playbook f1.yml PLAY [192.168.1.18] ******************************************************************************************************* TASK [Gathering Facts] **************************************************************************************************** ok: [192.168.1.18] TASK [ignore false] ******************************************************************************************************* fatal: [192.168.1.18]: FAILED! => {"changed": true, "cmd": ["/bin/false"], "delta": "0:00:00.003266", "end": "2018-12-29 08:17:25.302094", "msg": "non-zero return code", "rc": 1, "start": "2018-12-29 08:17:25.298828", "stderr": "", "stderr_lines": [], "stdout": "", "stdout_lines": []} ...ignoring 处理掉错误 TASK [touch a file] ******************************************************************************************************* changed: [192.168.1.18] PLAY RECAP **************************************************************************************************************** 192.168.1.18 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0
failed_when 根据条件判断主动抛出异常
---
- hosts: 192.168.1.18
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: get_process
shell: ps -ef|wc -l
register: process_count
#- debug: msg="{{process_count.stdout}}"
failed_when: process_count.stdout|int > 3 #进程数据量大于 3 抛出异常,小于三 往下进行
- name: touch_a_file
file: path=/tmp/test06 state=touch mode=0700 owner=root group=root
changed_when: false 隐藏前端输出的changed信息
---
- hosts: 192.168.1.18
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: get_process
shell: touch /tmp/change_test
changed_when: false


[root@cmdb ansible]# ansible-playbook f1.yml [DEPRECATION WARNING]: DEFAULT_SUDO_USER option, In favor of Ansible Become, which is a generic framework. See become_user. , use become instead. This feature will be removed in version 2.8. Deprecation warnings can be disabled by setting deprecation_warnings=False in ansible.cfg. PLAY [192.168.1.18] ******************************************************************************************************* TASK [Gathering Facts] **************************************************************************************************** ok: [192.168.1.18] TASK [get_process] ******************************************************************************************************** [WARNING]: Consider using the file module with state=touch rather than running touch. If you need to use command because file is insufficient you can add warn=False to this command task or set command_warnings=False in ansible.cfg to get rid of this message. ok: [192.168.1.18] PLAY RECAP **************************************************************************************************************** 192.168.1.18 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0
7.playbooks标签的使用
playbook中的tasks是由1个个子任务(name)组成的,我们可以通过对这些子任务打标签的方式控制 执行哪些子任务,不执行哪些子任务!
7.0:给playbooks中的name子任务打好标签
---
- hosts: 192.168.1.18
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: create_file1 0 1
shell: touch /tmp/file1.txt
tags:
- cfile0
- cfile1
- name: create_file2 2
shell: touch /tmp/file2.txt
tags:
- cfile2
7.1: -t 指定执行那些cfile2子任务
root@cmdb ansible]# ansible-playbook f1.yml -t cfile2
7.2:--skip-tags指定跳过那些子任务
[root@cmdb ansible]# ansible-playbook f1.yml --skip-tags cfile2
8.playbook中的include语法
include方法可以把playbook分布式存放,提高灵活性,功能类似 C中include python中 import 语法
---
- hosts: 192.168.1.18
remote_user: root
tasks:
- include_tasks: /tmp/touchf1.yml
- include_tasks: /tmp/touchf2.yml


---
- name: createfile1
shell: touch /tmp/file1.txt


---
- name: createfile1
shell: touch /tmp/file2.txt
四、Python调用Ansible的API
0.Ansible python API的6个类
from ansible.parsing.dataloader import DataLoader # 用于读取yaml、json格式的文件 from ansible.vars.manager import VariableManager # 读取host中变量信息 from ansible.inventory.manager import InventoryManager # 导入资产文件 from ansible.playbook.play import Play #存储hosts的角色信息 from ansible.executor.task_queue_manager import TaskQueueManager #ansibile 底层调用到得任务队列 from ansible.plugins.callback import CallbackBase #状回调态
1.资源资产配置清单操作
from ansible.parsing.dataloader import DataLoader # 用于读取yaml、json格式的文件 from ansible.vars.manager import VariableManager # 读取host中变量信息 from ansible.inventory.manager import InventoryManager # 导入资产文件 from ansible.playbook.play import Play #存储hosts的角色信息 from ansible.executor.task_queue_manager import TaskQueueManager #ansibile 底层调用到得任务队列 from ansible.plugins.callback import CallbackBase #状回调态 #InventoryManager:操作host主机清单中的主机信息 loader=DataLoader() inventory=InventoryManager(loader=loader,sources=['/etc/ansible/hosts']) # print(inventory.get_groups_dict()) #查看host信息 (主机组---对应的机器) # print(inventory.get_hosts()) #查看所有主机IP # print(inventory.get_host('192.168.1.18')) #筛选查看单个主机 # inventory.add_host(host='8.8.8.8',port=22,group='test') #在现有主机中添加主机 # VariableManager:操作host主机清单中的变量信息 VM= VariableManager(loader=loader,inventory=inventory) host=inventory.get_host('192.168.1.18') VM.get_vars() #查看变量 VM.set_host_variable(host=host,varname='ansible_ssh_pass',value='xxxxxx1234') #设置单个主机的变量信息,host对象必须为对象 VM.extra_vars={'extra_variable01':1,'extra_variable02':2,} #设置扩展全局变量
2.ad-hoc模式调用
python3.6.1 ---> ansible 2.6.3
from collections import namedtuple from ansible.executor.task_queue_manager import TaskQueueManager #通过调用 from ansible.inventory.manager import InventoryManager # 导入资产文件 from ansible.parsing.dataloader import DataLoader # 用于读取yaml、json格式的文件 from ansible.playbook.play import Play # 存储hosts的角色信息 from ansible.vars.manager import VariableManager # 读取host中变量信息 loader = DataLoader() inventory = InventoryManager(loader=loader, sources=['/etc/ansible/hosts']) variable_manager = VariableManager(loader=loader, inventory=inventory) # Options 执行选项 Options = namedtuple('Options', ['connection', 'remote_user', 'ask_sudo_pass','verbosity','ack_pass','module_path','forks', 'become', 'become_method', 'become_user', 'check', 'listhosts', 'listtags', 'sudo', 'syntax', 'sudouser', 'diff']) options = Options(connection='smart', remote_user=None, ask_sudo_pass=False,ack_pass=None,sudo=None,sudouser=None, module_path=None, forks=100, become=None, become_method=None, become_user=None, check=False, diff=False, syntax=None, listtags=None, listhosts=None, verbosity=5) # play执行对象和模块 play_source = dict( name="Ansible Play ad-hoc test", hosts='192.168.1.18,', #执行任务的主机 多个以,隔开 gather_facts='no', # 执行任务之前去获取基本信息 tasks=[ # 加载模块 dict(action=dict(module='shell', args='ls'), register='shell_out'), #1个任务1个字典 dict(action=dict(module='debug', args=dict(msg='{{shell_out.stdout}}'))) #2个任务2个字典 ] ) play = Play().load(play_source, variable_manager=variable_manager, loader=loader) passwords = dict()#密码 tqm = TaskQueueManager( #运行 inventory=inventory, variable_manager=variable_manager, loader=loader, options=options, passwords=passwords, # stdout_callback=results_callback, # Use our custom callback instead of the ``default`` callback plugin ) rest = tqm.run(play=play)
3.playbook模式调用
from collections import namedtuple from ansible.executor.playbook_executor import PlaybookExecutor # PlaybookExecutor 调用执行ansible的playbook 模式 from ansible.inventory.manager import InventoryManager # 导入资产文件 from ansible.parsing.dataloader import DataLoader # 用于读取yaml、json格式的文件 from ansible.vars.manager import VariableManager # 读取host中变量信息 loader = DataLoader() inventory = InventoryManager(loader=loader, sources=['/etc/ansible/hosts']) variable_manager = VariableManager(loader=loader, inventory=inventory) # Options 执行选项 Options = namedtuple('Options', ['connection', 'remote_user', 'ask_sudo_pass', 'verbosity', 'ack_pass', 'module_path', 'forks', 'become', 'become_method', 'become_user', 'check', 'listhosts','listtasks','listtags', 'sudo', 'syntax', 'sudouser', 'diff']) options = Options(connection='smart', remote_user=None, ask_sudo_pass=False, ack_pass=None, sudo=None, sudouser=None, module_path=None, forks=100, become=None, become_method=None, become_user=None, check=False, diff=False, syntax=None, listtags=None,listtasks=None,listhosts=None, verbosity=5) # listtasks passwords = dict() # 密码 # 执行 ansible的 playbook模式就需要 使用 play_book = PlaybookExecutor(playbooks=['/etc/ansible/f1.yml'],inventory=inventory, variable_manager=variable_manager, loader=loader, options=options, passwords=passwords) play_book.run()
4. 重写 CallbackBase自定制ansible输出json格式数据
from collections import namedtuple from ansible.executor.task_queue_manager import TaskQueueManager #通过TaskQueueManager调用ansible的ad-hoc模式 from ansible.inventory.manager import InventoryManager # 导入资产文件 from ansible.parsing.dataloader import DataLoader # 用于读取yaml、json格式的文件 from ansible.playbook.play import Play # 存储hosts的角色信息 from ansible.vars.manager import VariableManager # 读取host中变量信息 loader = DataLoader() inventory = InventoryManager(loader=loader, sources=['/etc/ansible/hosts']) variable_manager = VariableManager(loader=loader, inventory=inventory) # Options 执行选项 Options = namedtuple('Options', ['connection', 'remote_user', 'ask_sudo_pass','verbosity','ack_pass','module_path','forks', 'become', 'become_method', 'become_user', 'check', 'listhosts', 'listtags', 'sudo', 'syntax', 'sudouser', 'diff']) options = Options(connection='smart', remote_user=None, ask_sudo_pass=False,ack_pass=None,sudo=None,sudouser=None, module_path=None, forks=100, become=None, become_method=None, become_user=None, check=False, diff=False, syntax=None, listtags=None, listhosts=None, verbosity=5) # play执行对象和模块 play_source = dict( name="Ansible Play ad-hoc test", hosts='192.168.1.18,', #执行任务的主机 多个以,隔开 gather_facts='no', # 执行任务之前去获取基本信息 tasks=[ # 加载模块 dict(action=dict(module='shell', args='ls'), register='shell_out'), #1个任务1个字典 dict(action=dict(module='debug', args=dict(msg='{{shell_out.stdout}}'))) #2个任务2个字典 ] ) play = Play().load(play_source, variable_manager=variable_manager, loader=loader) passwords = dict()#密码 from ansible.plugins.callback import CallbackBase # 重写CallbackBas类定制 ansible 输出格式 class MyCallback(CallbackBase): def __init__(self,*args,**kwargs): super(CallbackBase,self).__init__(*args,**kwargs) self.host_ok={} self.host_uncreachable={} self.host_failed={} def v2_runner_on_unreachable(self, result): self.host_uncreachable[result._host.get_name()]=result def v2_runner_on_ok(self, result): self.host_ok[result._host.get_name()] = result def v2_runner_on_failed(self, result, ignore_errors=False): self.host_failed[result._host.get_name()] = result my_callback=MyCallback() tqm = TaskQueueManager( #运行 inventory=inventory, variable_manager=variable_manager, loader=loader, options=options, passwords=passwords, stdout_callback=my_callback, # Use our custom callback instead of the ``default`` callback plugin ) tqm.run(play=play) #从 mycallback对象中 获取执行结果 resault={'success':{},'failed':{},'uncreachable':{}} for h,r in my_callback.host_ok.items(): print(h,r) resault['success'][h]=r._result for h,r in my_callback.host_failed.items(): resault['failed'][h]=r._result for h,r in my_callback.host_uncreachable.items(): resault['uncreachable'][h]=r._result print(resault)
GitHub地址
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/sss4/p/10131953.html
最后
以上就是高高柚子最近收集整理的关于自动化运维开发项目的全部内容,更多相关自动化运维开发项目内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复