
ShowMeAI日报系列全新升级!覆盖AI人工智能 工具&框架 | 项目&代码 | 博文&分享 | 数据&资源 | 研究&论文 等方向。点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
1.工具&框架

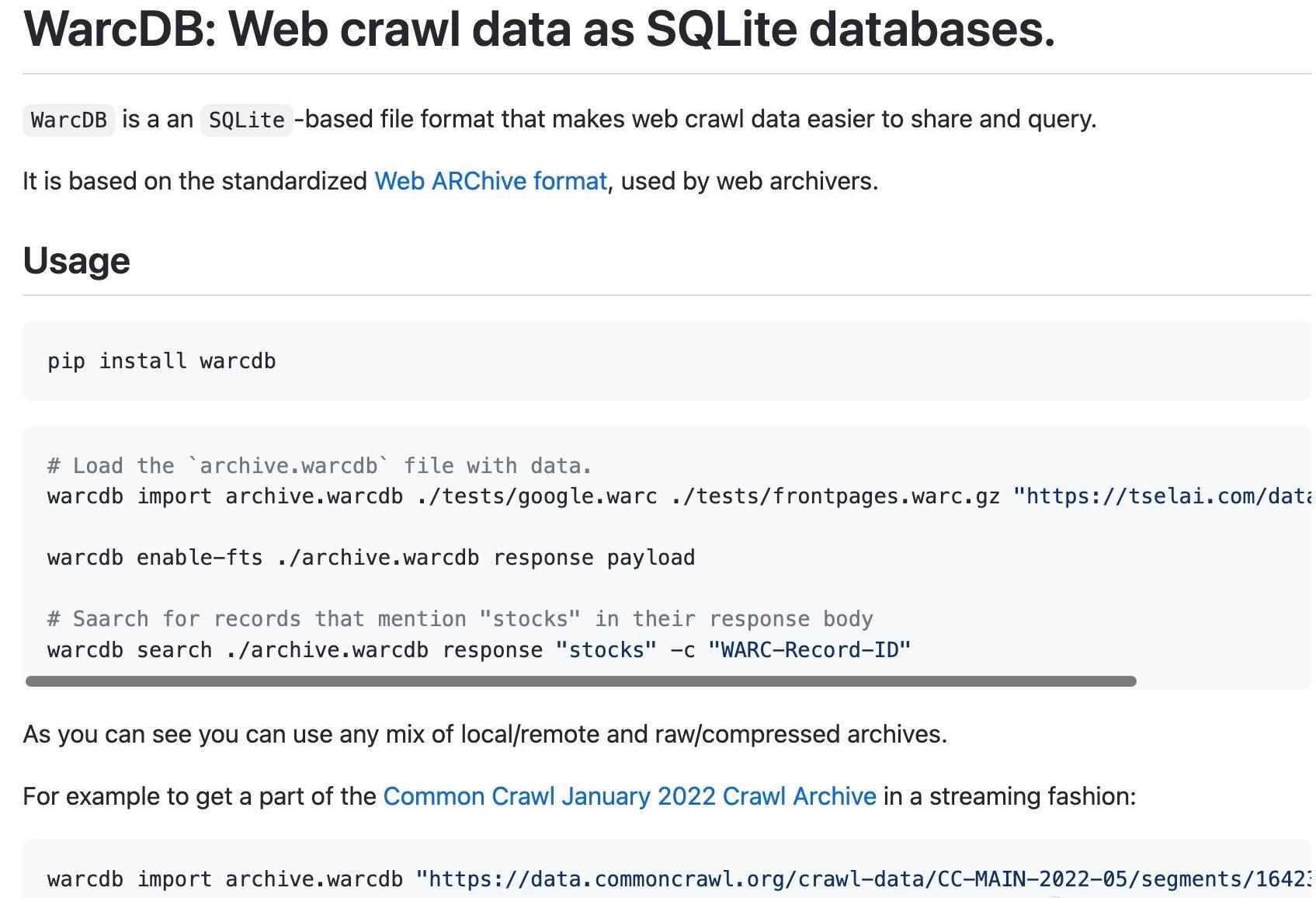
工具:WarcDB - 爬虫用SQLite数据库格式,方便分享与查询
tags: [数据库,爬虫]
‘WarcDB: Web crawl data as SQLite databases. - WarcDB: Web crawl data as SQLite databases.’ by Florents Tselai
GitHub: https://github.com/Florents-Tselai/WarcDB
工具:rspleeter - Rust写的人声与音乐分离工具
tags: [人声分离,音乐分离,声音分离]
‘rspleeter - Rust implementation of Spleeter’ by Donough Liu
GitHub: https://github.com/ldm0/rspleeter
工具:Dooit - 字符界面的待办事项(TODO)管理工具
tags: [ToDo,待办,工具]
‘Dooit - A TUI todo manager’ by Murli Tawari
GitHub: https://github.com/kraanzu/dooit
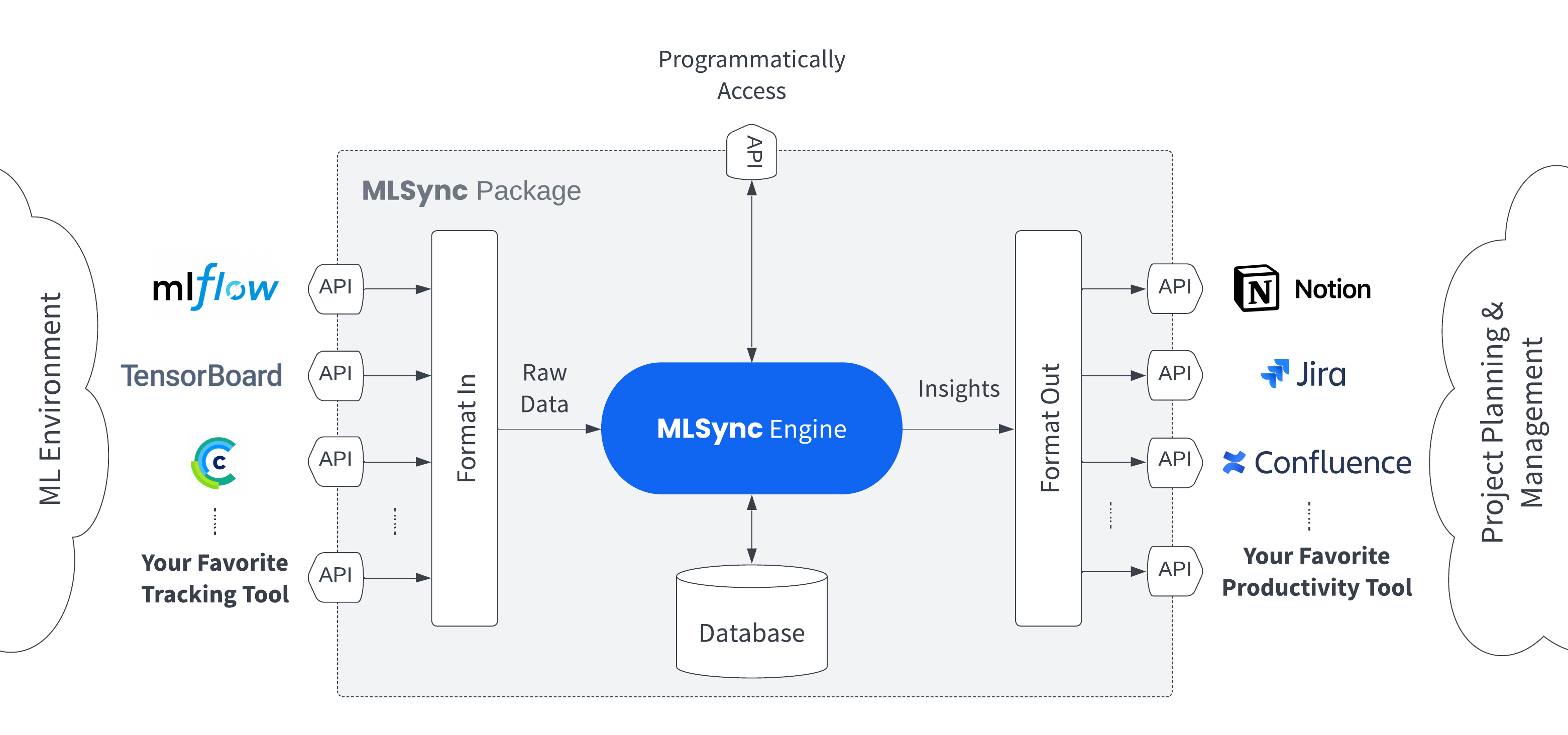
工具:mlsync - 机器学习数据同步工具
tags: [机器学习,数据同步]
‘mlsync - Sync your ML data with your favorite productivity tools!’ by PaletteML
GitHub: https://github.com/paletteml/mlsync


工具:Copy Translator - Rust写的简单、轻量、好用的划词翻译软件
tags: [DeepL,机器翻译,rust]
Copy Translator利用DeepL翻译,无需注册
GitHub: https://github.com/zu1k/copy-translator

2.博文&分享

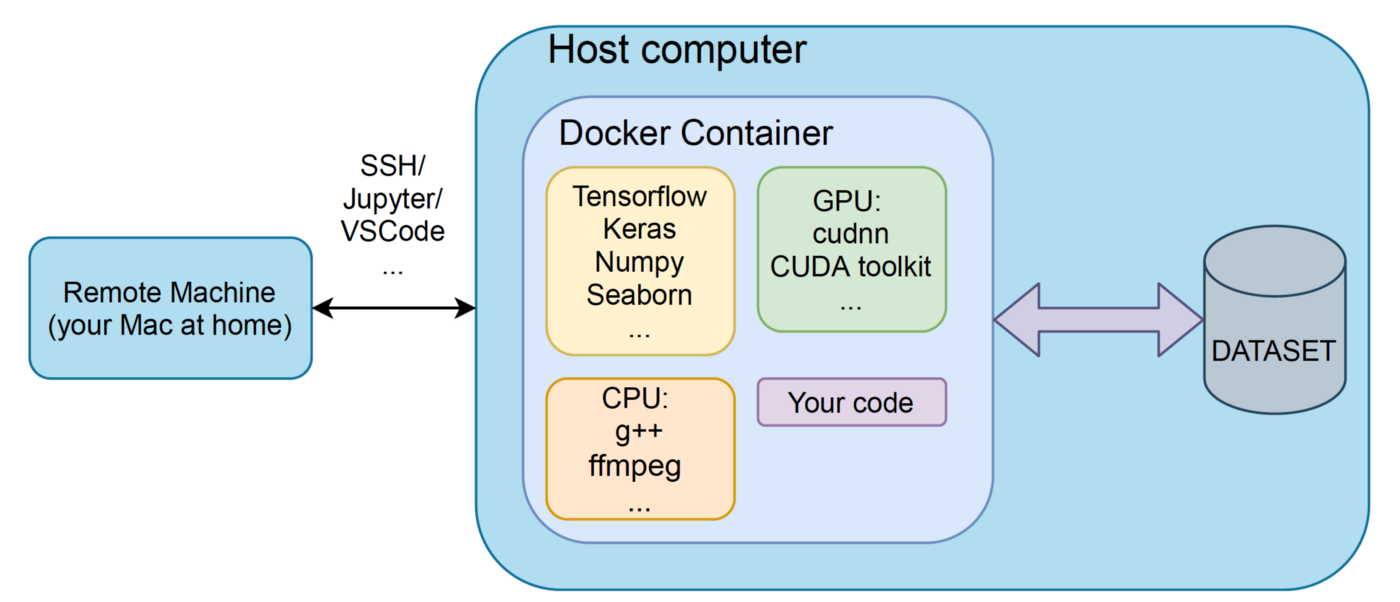
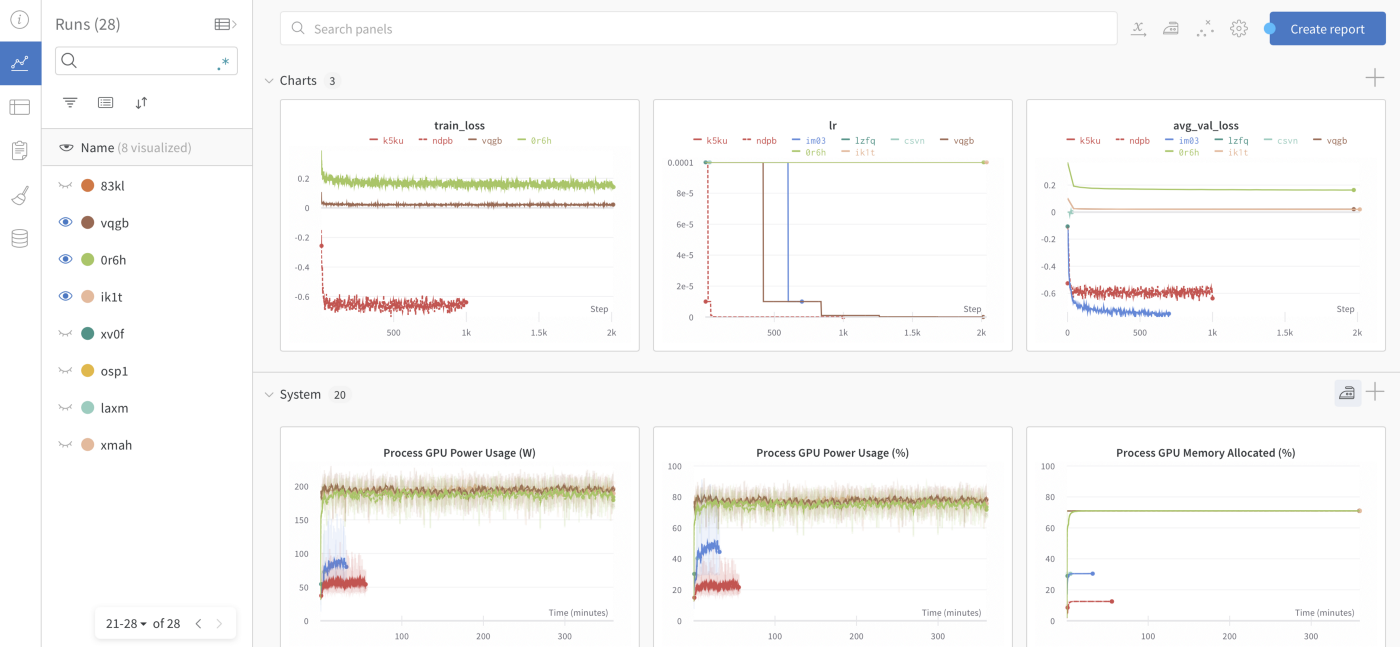
博文:机器学习博士“早知道就好了”的九种好工具
tags: [科研,机器学习,工具]
Docker、Conda、Weights and biases、MLflow、Screen、GitHub、Lucidchart、Inkscape、Streamlit
《Nine Tools I Wish I Mastered before My PhD in Machine Learning》by Aliaksei Mikhailiuk
Link: https://towardsdatascience.com/nine-tools-i-wish-i-mastered-before-my-phd-in-machine-learning-708c6dcb2fb0

3.数据&资源

资源列表:EyeGazeSurvey - 深度学习注视分析相关文献列表
tags: [深度学习,注视分析,资源列表]
‘EyeGazeSurvey - Automatic Gaze Analysis ‘in-the-wild’: A Survey’ by Shreya Ghosh
GitHub: https://github.com/i-am-shreya/Eye-Gaze-Survey
资源列表:Fake News Detection - 虚假新闻检测
tags: [虚假新闻,检测,资源列表]
This repo is a collection of AWESOME things about fake news detection, including papers, code, etc.’ by ICTMCG
GitHub: https://github.com/ICTMCG/fake-news-detection
4.研究&论文

可以点击 这里 回复关键字 日报,免费获取整理好的6月论文合辑。
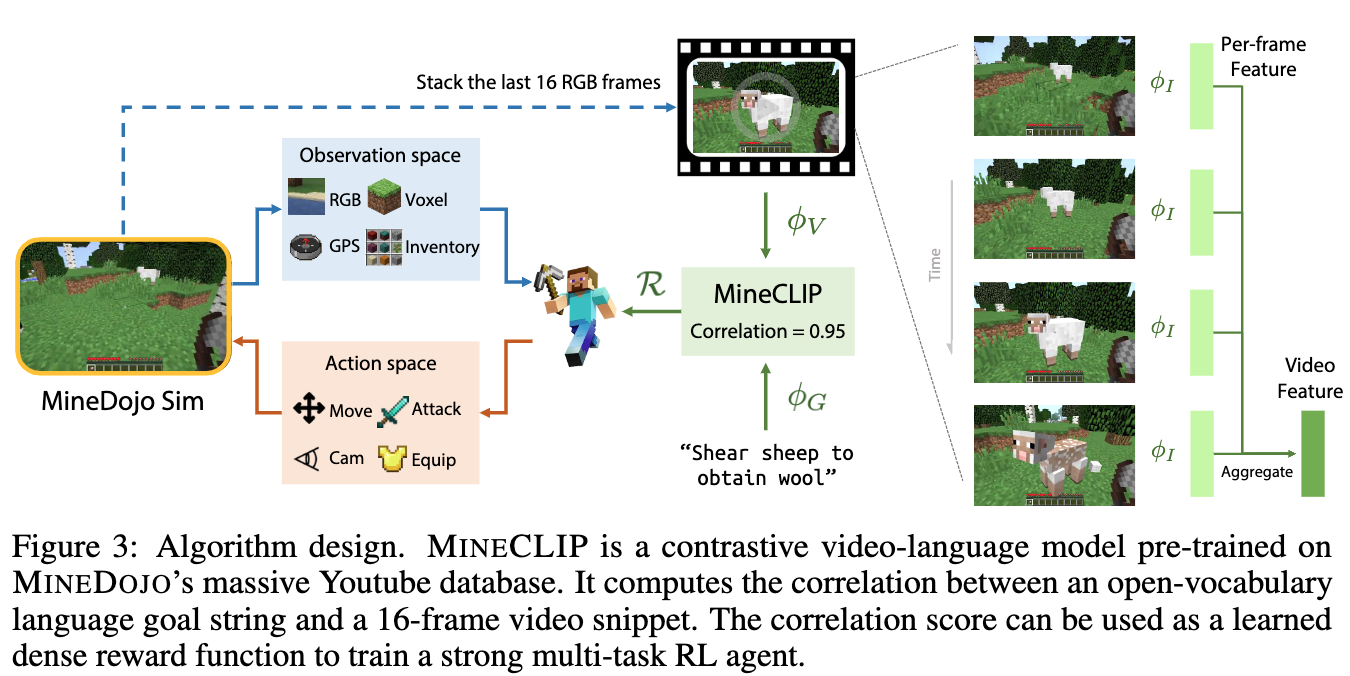
论文:MineDojo: Building Open-Ended Embodied Agents with Internet-Scale Knowledge
论文标题:MineDojo: Building Open-Ended Embodied Agents with Internet-Scale Knowledge
论文时间:17 Jun 2022
所属领域:游戏
对应任务:强化学习游戏
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08853
代码实现:https://github.com/MineDojo/MineDojo
论文作者:Linxi Fan, Guanzhi Wang, Yunfan Jiang, Ajay Mandlekar, Yuncong Yang, Haoyi Zhu, Andrew Tang, De-An Huang, Yuke Zhu, Anima Anandkumar
论文简介:Autonomous agents have made great strides in specialist domains like Atari games and Go./自主代理在Atari游戏和围棋等专业领域取得了长足的进步。
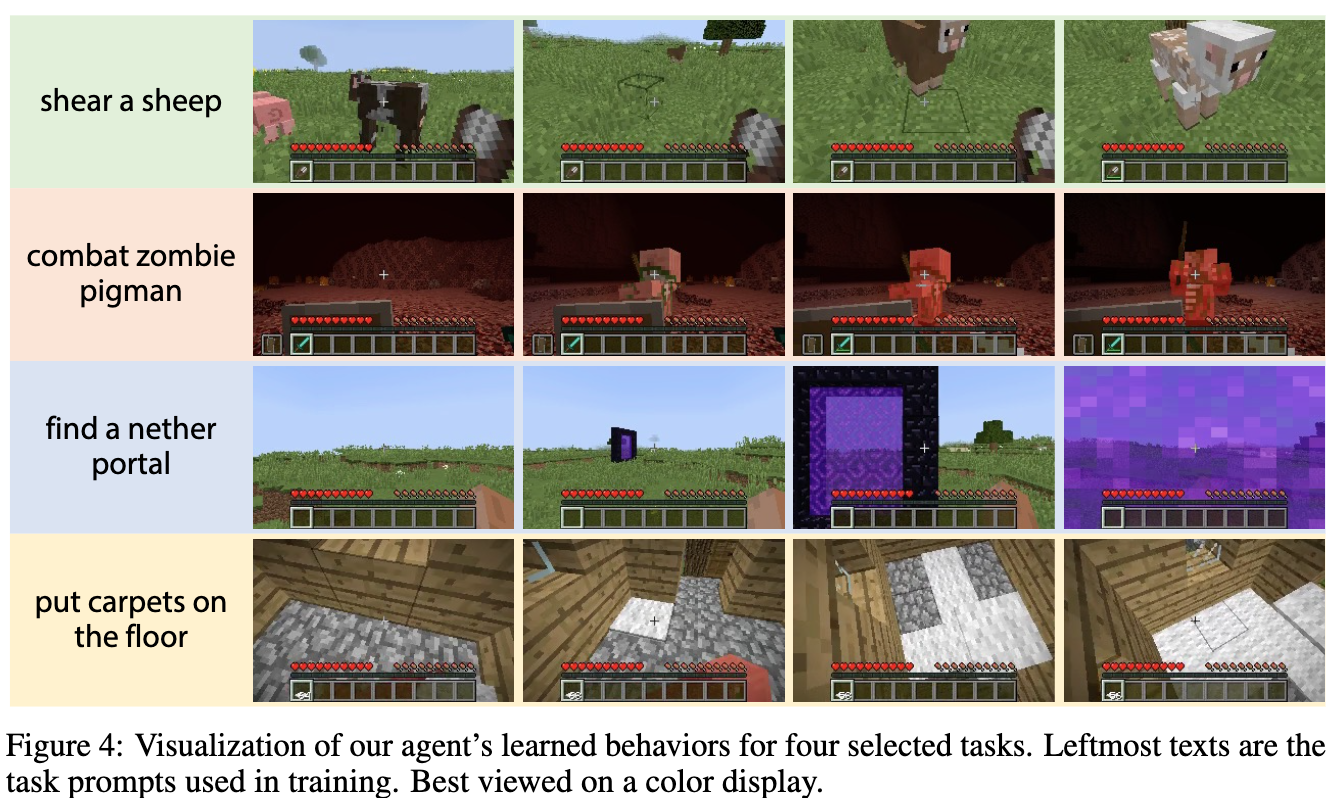
论文摘要:Autonomous agents have made great strides in specialist domains like Atari games and Go. However, they typically learn tabula rasa in isolated environments with limited and manually conceived objectives, thus failing to generalize across a wide spectrum of tasks and capabilities. Inspired by how humans continually learn and adapt in the open world, we advocate a trinity of ingredients for building generalist agents: 1) an environment that supports a multitude of tasks and goals, 2) a large-scale database of multimodal knowledge, and 3) a flexible and scalable agent architecture. We introduce MineDojo, a new framework built on the popular Minecraft game that features a simulation suite with thousands of diverse open-ended tasks and an internet-scale knowledge base with Minecraft videos, tutorials, wiki pages, and forum discussions. Using MineDojo’s data, we propose a novel agent learning algorithm that leverages large pre-trained video-language models as a learned reward function. Our agent is able to solve a variety of open-ended tasks specified in free-form language without any manually designed dense shaping reward. We open-source the simulation suite and knowledge bases (https://minedojo.org) to promote research towards the goal of generally capable embodied agents.
自主代理在像雅达利游戏和围棋这样的专业领域中取得了巨大的进步。然而,它们通常是在孤立的环境中以有限的、人工设想的目标进行学习,因此无法在广泛的任务和能力范围内进行推广。受到人类在开放世界中不断学习和适应的启发,我们主张建立三位一体的通用代理。1)一个支持多种任务和目标的环境,2)一个大规模的多模态知识数据库,以及3)一个灵活和可扩展的代理架构。我们推出MineDojo,这是一个建立在流行的Minecraft游戏基础上的新框架,它的特点是具有数千个不同的开放式任务的模拟套件和一个具有Minecraft视频、教程、维基页面和论坛讨论的互联网规模的知识库。利用MineDojo的数据,我们提出了一种新颖的代理学习算法,利用大型预训练的视频语言模型作为学习奖励函数。我们的代理能够解决各种用自由形式的语言指定的开放式任务,而不需要任何人工设计的密集型奖励。我们开源了模拟套件和知识库(https://minedojo.org),以促进对普遍具有能力的具身代理目标的研究。



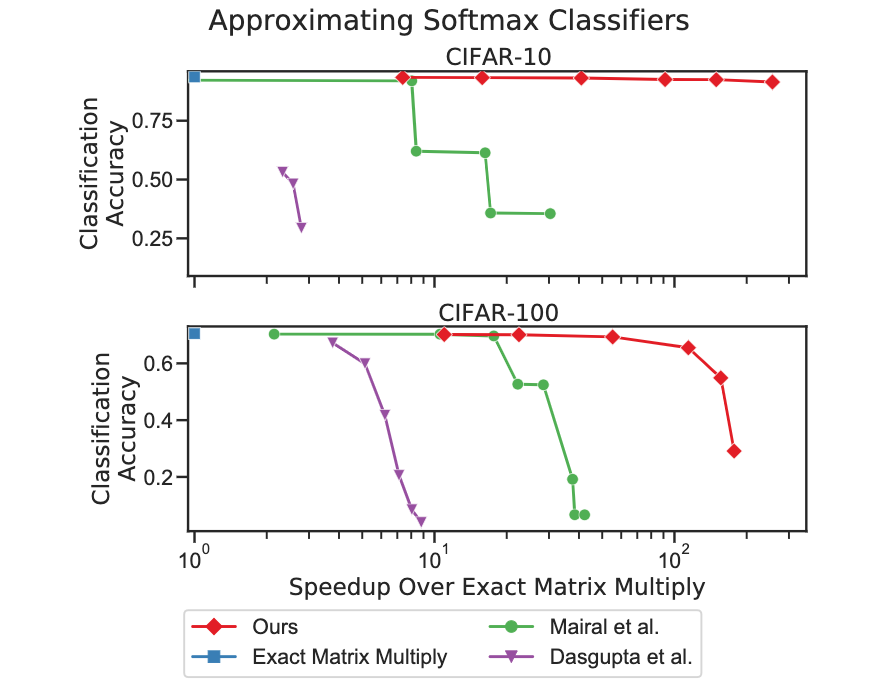
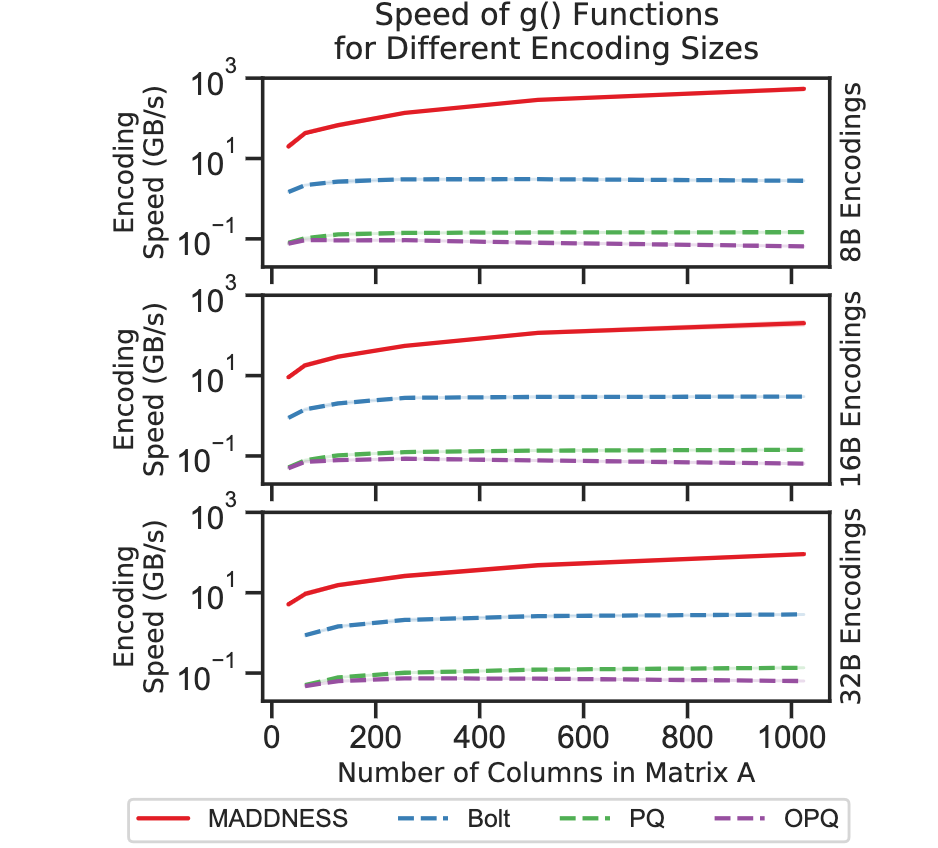
论文:Multiplying Matrices Without Multiplying
论文标题:Multiplying Matrices Without Multiplying
论文时间:21 Jun 2021
所属领域:科学计算
对应任务:矩阵计算
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.10860
代码实现:https://github.com/dblalock/bolt , https://github.com/joennlae/halutmatmul , https://github.com/nlpodyssey/gomaddness
论文作者:Davis Blalock, John Guttag
论文简介:Multiplying matrices is among the most fundamental and compute-intensive operations in machine learning./矩阵相乘是机器学习中最基本和最密集的操作之一。
论文摘要:Multiplying matrices is among the most fundamental and compute-intensive operations in machine learning. Consequently, there has been significant work on efficiently approximating matrix multiplies. We introduce a learning-based algorithm for this task that greatly outperforms existing methods. Experiments using hundreds of matrices from diverse domains show that it often runs 100× faster than exact matrix products and 10× faster than current approximate methods. In the common case that one matrix is known ahead of time, our method also has the interesting property that it requires zero multiply-adds. These results suggest that a mixture of hashing, averaging, and byte shuffling−the core operations of our method−could be a more promising building block for machine learning than the sparsified, factorized, and/or scalar quantized matrix products that have recently been the focus of substantial research and hardware investment.
矩阵相乘是机器学习中最基本的计算密集型操作之一。因此,在有效逼近矩阵乘法方面已经有了大量的工作。我们为这一任务引入了一种基于学习的算法,其性能大大超过了现有的方法。使用来自不同领域的数百个矩阵进行的实验表明,它的运行速度往往比精确的矩阵乘法快100倍,比目前的近似方法快10倍。在一个矩阵提前知道的常见情况下,我们的方法也有一个有趣的特性,即它无需乘法加法。这些结果表明,与最近成为大量研究和硬件投资焦点的稀疏化、因子化和/或标量化矩阵产品相比,混合散列、平均化和字节混序–我们方法的核心操作–可能是一个更有前途的机器学习构建块。
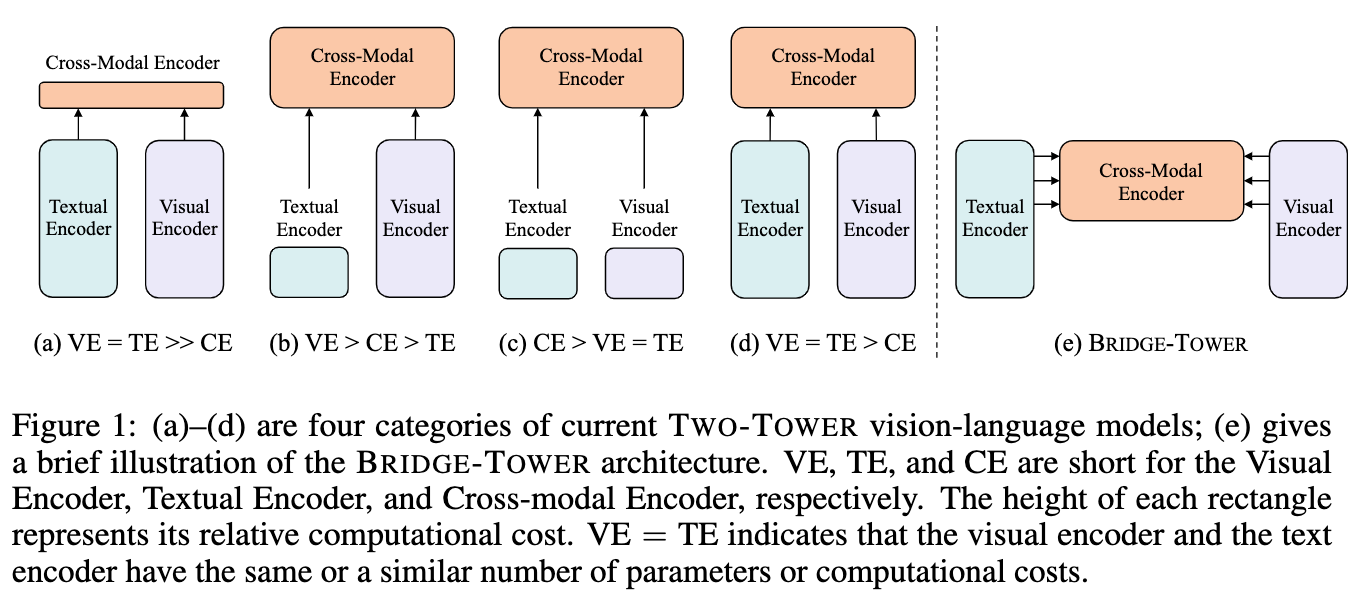
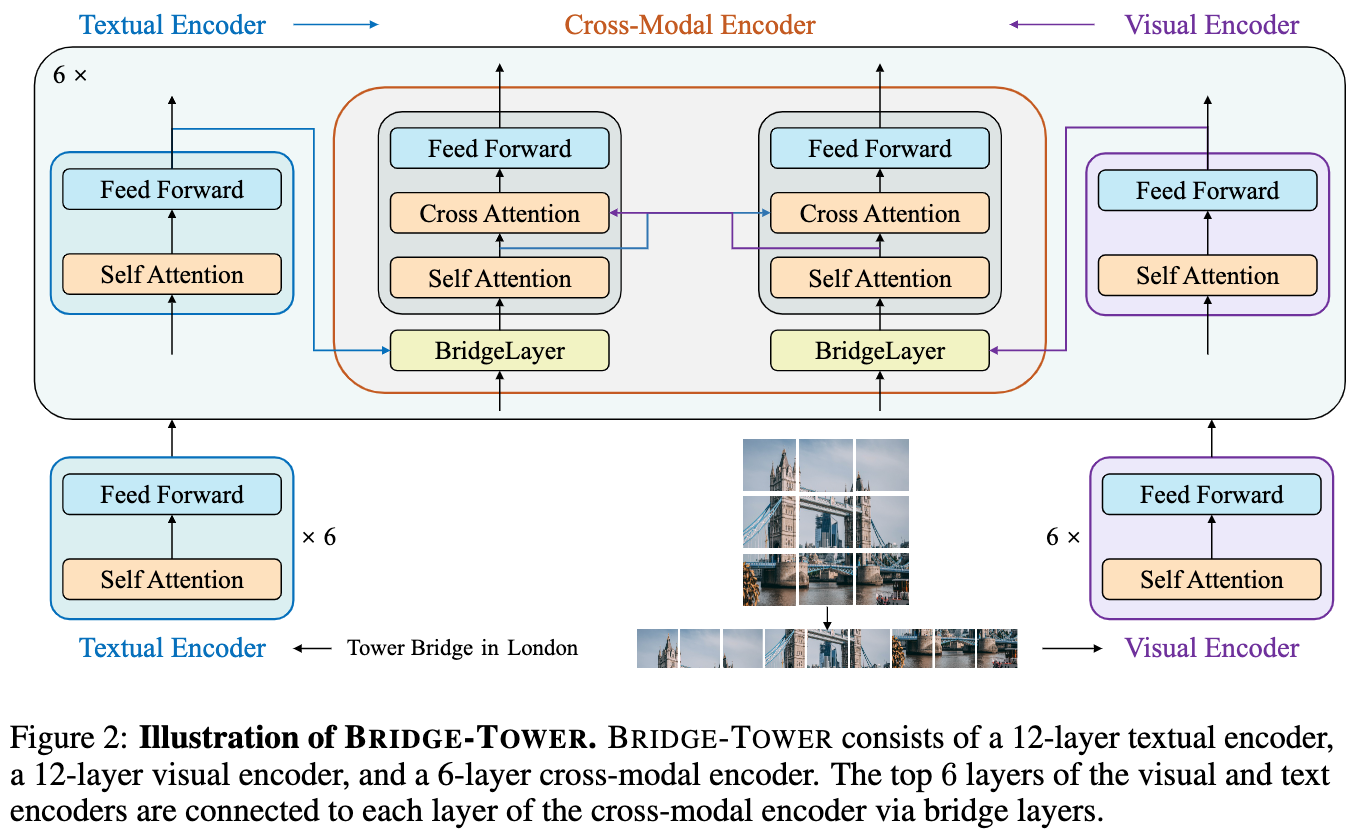
论文:Bridge-Tower: Building Bridges Between Encoders in Vision-Language Representation Learning
论文标题:Bridge-Tower: Building Bridges Between Encoders in Vision-Language Representation Learning
论文时间:17 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉,自然语言处理
对应任务:表征学习
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08657
代码实现:https://github.com/microsoft/BridgeTower
论文作者:Xiao Xu, Chenfei Wu, Shachar Rosenman, Vasudev Lal, Nan Duan
论文简介:Current VL models either use lightweight uni-modal encoders and learn to extract, align and fuse both modalities simultaneously in a cross-modal encoder, or feed the last-layer uni-modal features directly into the top cross-modal encoder, ignoring the semantic information at the different levels in the deep uni-modal encoders./目前的VL模型要么使用轻量级的单模态编码器,并学习在跨模态编码器中同时提取、对齐和融合两种模态,要么将最后一层的单模态特征直接送入顶部的跨模态编码器,忽略了深度单模态编码器中不同层面的语义信息。
论文摘要:Vision-Language (VL) models with the Two-Tower architecture have dominated visual-language representation learning in recent years. Current VL models either use lightweight uni-modal encoders and learn to extract, align and fuse both modalities simultaneously in a cross-modal encoder, or feed the last-layer uni-modal features directly into the top cross-modal encoder, ignoring the semantic information at the different levels in the deep uni-modal encoders. Both approaches possibly restrict vision-language representation learning and limit model performance. In this paper, we introduce multiple bridge layers that build a connection between the top layers of uni-modal encoders and each layer of the cross-modal encoder. This enables comprehensive bottom-up interactions between visual and textual representations at different semantic levels, resulting in more effective cross-modal alignment and fusion. Our proposed Bridge-Tower, pre-trained with only 4M images, achieves state-of-the-art performance on various downstream vision-language tasks. On the VQAv2 test-std set, Bridge-Tower achieves an accuracy of 78.73%, outperforming the previous state-of-the-art METER model by 1.09% with the same pre-training data and almost no additional parameters and computational cost. Notably, when further scaling the model, Bridge-Tower achieves an accuracy of 81.15%, surpassing models that are pre-trained on orders-of-magnitude larger datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/microsoft/BridgeTower
近年来,具有双塔结构的视觉语言(VL)模型在视觉语言表征学习中占主导地位。目前的视觉语言模型要么使用轻量级的单模态编码器,并学习在跨模态编码器中同时提取、调整和融合两种模态,要么将最后一层的单模态特征直接送入顶部的跨模态编码器中,忽略了深度单模态编码器中不同层次的语义信息。这两种方法都可能限制了视觉-语言表征的学习,并限制了模型的性能。在本文中,我们引入了多个桥梁层,在单模态编码器的顶层和跨模态编码器的每一层之间建立联系。这使得不同语义层面的视觉和文本表征之间能够进行全面的自下而上的互动,从而实现更有效的跨模态对齐和融合。我们提出的Bridge-Tower仅用400万张图像进行了预训练,在各种下游的视觉-语言任务中取得了最先进的性能。在VQAv2测试数据集上,Bridge-Tower达到了78.73%的准确率,在相同的预训练数据和几乎没有额外参数和计算成本的情况下,比之前最先进的METER模型高出1.09%。值得注意的是,当进一步扩展该模型时,Bridge-Tower达到了81.15%的准确率,超过了在更大数量级的数据集上预训练的模型。代码可在 https://github.com/microsoft/BridgeTower 获取。
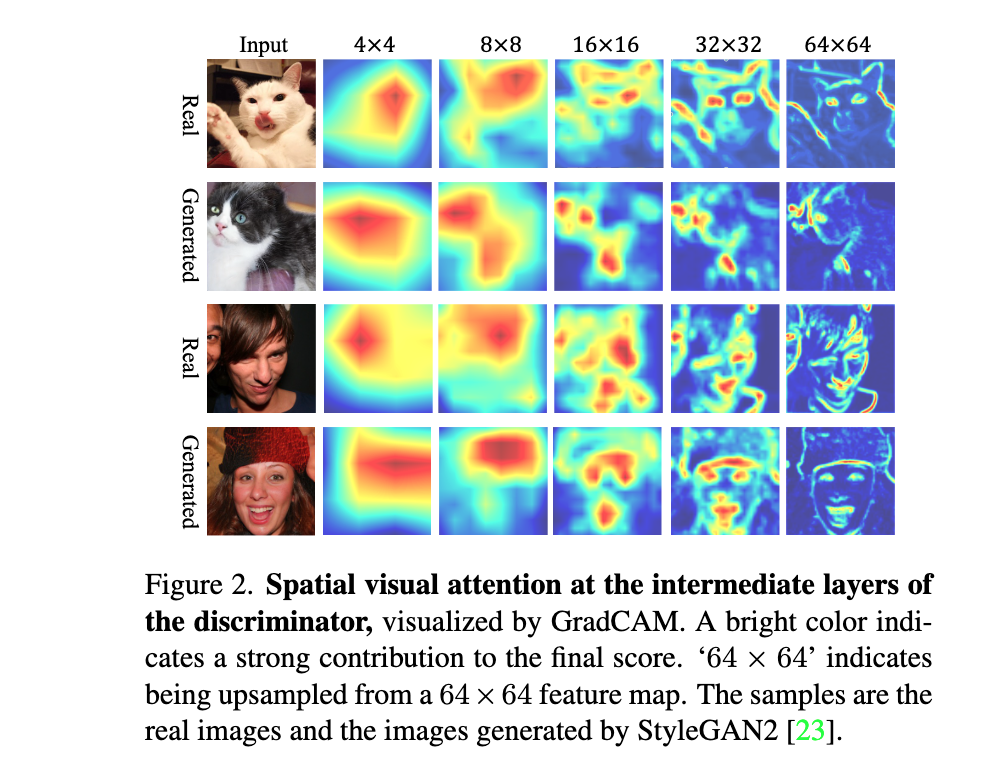
论文:Improving GAN Equilibrium by Raising Spatial Awareness
论文标题:Improving GAN Equilibrium by Raising Spatial Awareness
论文时间:CVPR 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:生成对抗网络
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.00718
代码实现:https://github.com/genforce/eqgan
论文作者:Jianyuan Wang, Ceyuan Yang, Yinghao Xu, Yujun Shen, Hongdong Li, Bolei Zhou
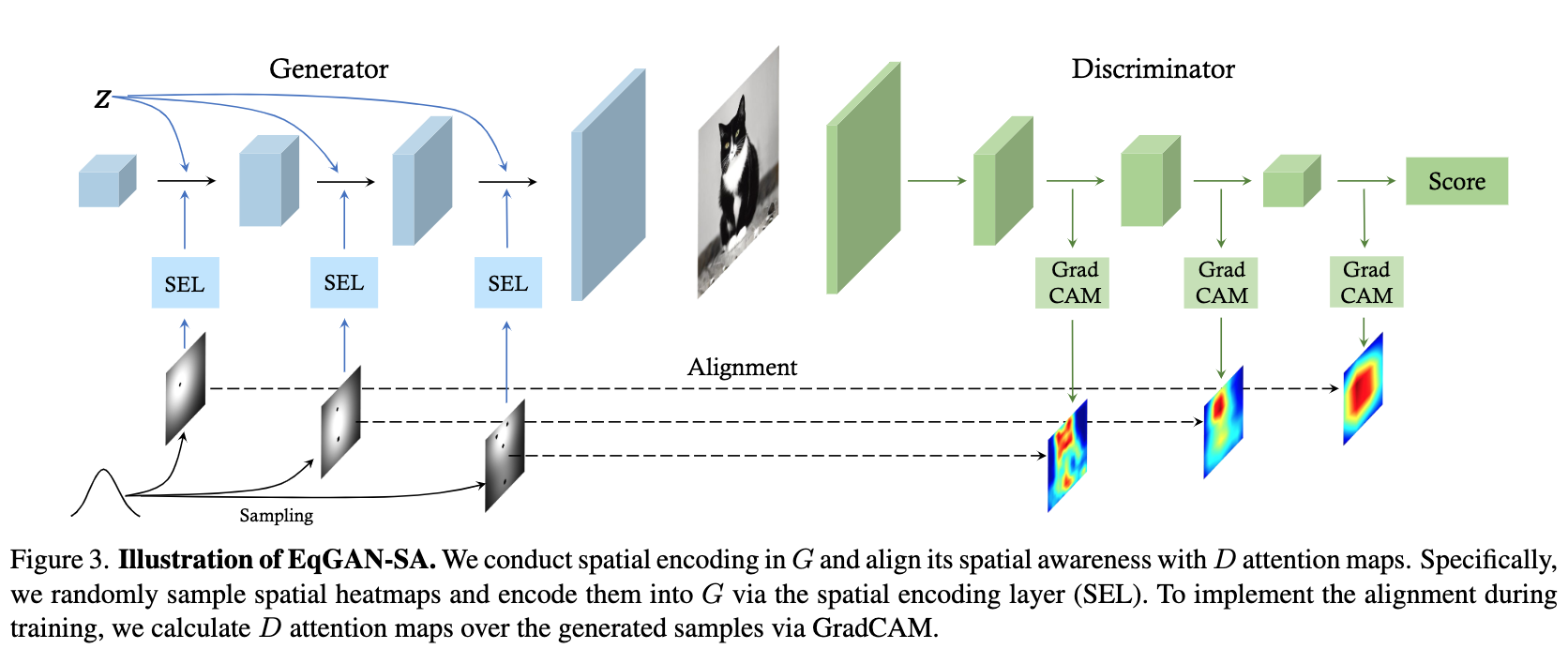
论文简介:We further propose to align the spatial awareness of G with the attention map induced from D. Through this way we effectively lessen the information gap between D and G. Extensive results show that our method pushes the two-player game in GANs closer to the equilibrium, leading to a better synthesis performance./我们进一步建议将G的空间意识与从D诱导出的注意图相一致。通过这种方式,我们有效地减少了D和G之间的信息差距。广泛的结果表明,我们的方法使GANs中的双人游戏更接近平衡,从而导致更好的合成性能。
论文摘要:The success of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) is largely built upon the adversarial training between a generator (G) and a discriminator (D). They are expected to reach a certain equilibrium where D cannot distinguish the generated images from the real ones. However, such an equilibrium is rarely achieved in practical GAN training, instead, D almost always surpasses G. We attribute one of its sources to the information asymmetry between D and G. We observe that D learns its own visual attention when determining whether an image is real or fake, but G has no explicit clue on which regions to focus on for a particular synthesis. To alleviate the issue of D dominating the competition in GANs, we aim to raise the spatial awareness of G. Randomly sampled multi-level heatmaps are encoded into the intermediate layers of G as an inductive bias. Thus G can purposefully improve the synthesis of certain image regions. We further propose to align the spatial awareness of G with the attention map induced from D. Through this way we effectively lessen the information gap between D and G. Extensive results show that our method pushes the two-player game in GANs closer to the equilibrium, leading to a better synthesis performance. As a byproduct, the introduced spatial awareness facilitates interactive editing over the output synthesis. Demo video and code are available at https://genforce.github.io/eqgan-sa/
生成对抗网络(GANs)的成功主要是建立在生成器(G)和判别器(D)之间的对抗性训练上。它们被期望达到某种平衡,即D不能区分生成的图像和真实的图像。然而,这样的平衡在实际的GAN训练中很少实现,相反,D几乎总是超过G。我们将其来源之一归结为D和G之间的信息不对称。我们观察到,在确定图像是真的还是假的时候,D会学习自己的视觉注意力,但G没有明确的线索来关注特定合成的区域。为了缓解D在GANs中主导竞争的问题,我们旨在提高G的空间意识。随机采样的多级热图被编码到G的中间层,作为一种归纳的偏向。因此,G可以有目的地改善某些图像区域的合成。我们进一步建议将G的空间意识与从D诱导出来的注意图相一致。通过这种方式,我们有效地减少了D和G之间的信息差距。广泛的结果表明,我们的方法使GANs中的双人游戏更接近平衡,导致更好的合成性能。作为一个副产品,引入的空间意识促进了对输出合成的交互式编辑。演示视频和代码可在 https://genforce.github.io/eqgan-sa/

论文:Powershap: A Power-full Shapley Feature Selection Method
论文标题:Powershap: A Power-full Shapley Feature Selection Method
论文时间:16 Jun 2022
所属领域:机器学习
对应任务:特征选择
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08394
代码实现:https://github.com/predict-idlab/powershap
论文作者:Jarne Verhaeghe, Jeroen Van Der Donckt, Femke Ongenae, Sofie Van Hoecke
论文简介:Benchmarks and simulations show that powershap outperforms other filter methods with predictive performances on par with wrapper methods while being significantly faster, often even reaching half or a third of the execution time./基准测试和模拟表明,powershap的预测性能优于其他filter方法,与包装方法相当,同时速度明显加快,甚至经常达到执行时间的一半或三分之一。
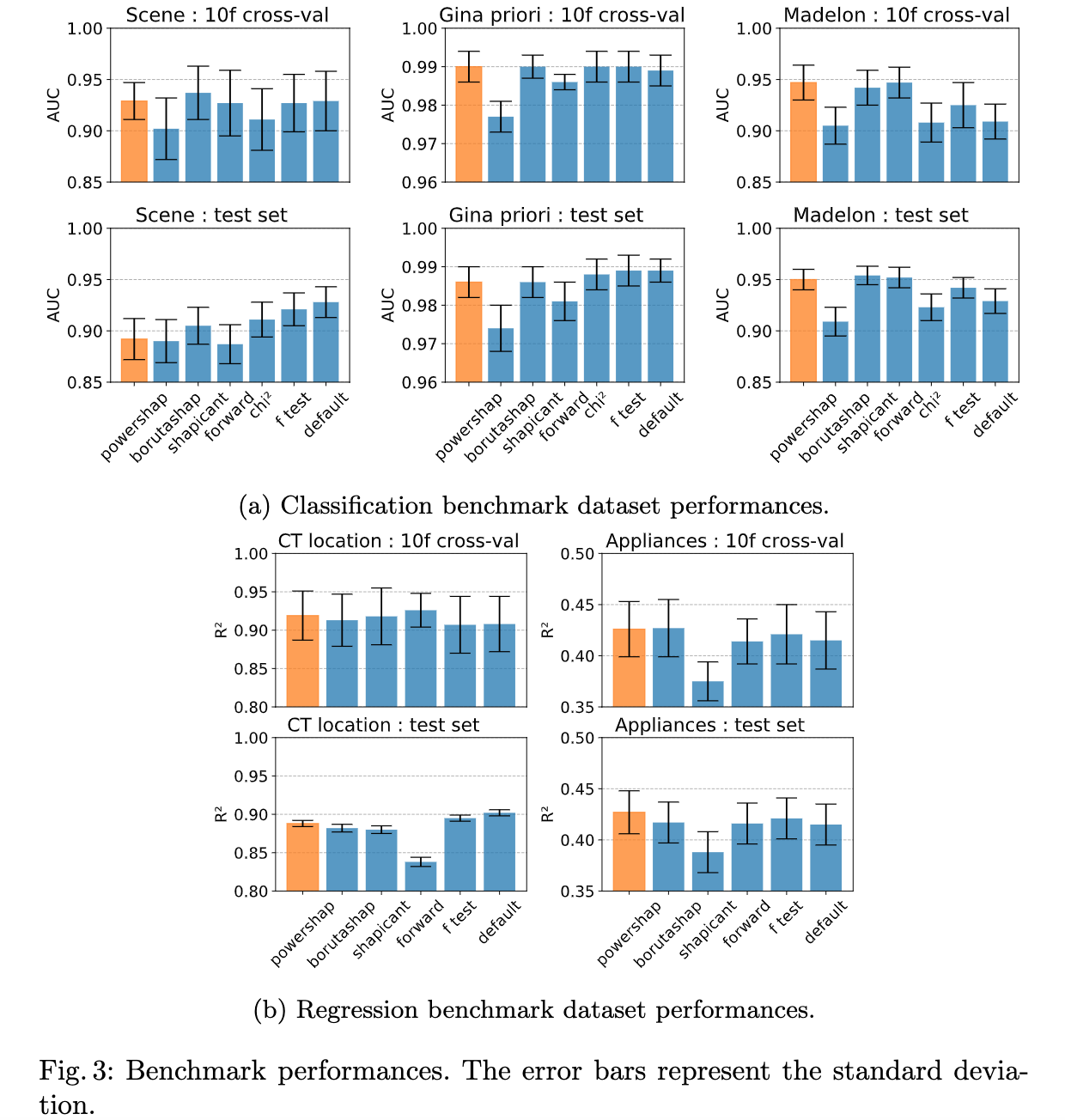
论文摘要:Feature selection is a crucial step in developing robust and powerful machine learning models. Feature selection techniques can be divided into two categories: filter and wrapper methods. While wrapper methods commonly result in strong predictive performances, they suffer from a large computational complexity and therefore take a significant amount of time to complete, especially when dealing with high-dimensional feature sets. Alternatively, filter methods are considerably faster, but suffer from several other disadvantages, such as (i) requiring a threshold value, (ii) not taking into account intercorrelation between features, and (iii) ignoring feature interactions with the model. To this end, we present powershap, a novel wrapper feature selection method, which leverages statistical hypothesis testing and power calculations in combination with Shapley values for quick and intuitive feature selection. Powershap is built on the core assumption that an informative feature will have a larger impact on the prediction compared to a known random feature. Benchmarks and simulations show that powershap outperforms other filter methods with predictive performances on par with wrapper methods while being significantly faster, often even reaching half or a third of the execution time. As such, powershap provides a competitive and quick algorithm that can be used by various models in different domains. Furthermore, powershap is implemented as a plug-and-play and open-source sklearn component, enabling easy integration in conventional data science pipelines. User experience is even further enhanced by also providing an automatic mode that automatically tunes the hyper-parameters of the powershap algorithm, allowing to use the algorithm without any configuration needed.
特征选择是开发稳健和强大的机器学习模型的一个关键步骤。特征选择技术可以分为两类:过滤式和包裹式方法。虽然包裹式方法通常会产生强大的预测性能,但它们有很大的计算复杂性,因此需要大量的时间来完成,特别是在处理高维特征集时。另外,过滤式方法的速度要快得多,但也有其他一些缺点,如(i)需要一个阈值,(ii)没有考虑到特征之间的相互关系,以及(iii)忽略了特征与模型的相互作用。为此,我们提出了powershap,一种新颖的包裹式特征选择方法,它利用统计假设检验和功率计算与Shapley值相结合,实现快速和直观的特征选择。Powershap建立在这样一个核心假设上:与已知的随机特征相比,信息量大的特征对预测的影响更大。基准测试和模拟表明,powershap的预测性能优于其他过滤式方法,与包裹式方法相当,同时速度明显加快,甚至经常达到执行时间的一半或三分之一。因此,powershap提供了一种有竞争力的快速算法,可以被不同领域的各种模型所使用。此外,powershap是作为一个即插即用的开源sklearn组件实现的,可以轻松地集成到传统的数据科学管道中。通过提供自动模式,自动调整powershap算法的超参数,允许使用该算法而不需要任何配置,用户体验得到进一步增强。
论文:MCUNetV2: Memory-Efficient Patch-based Inference for Tiny Deep Learning
论文标题:MCUNetV2: Memory-Efficient Patch-based Inference for Tiny Deep Learning
论文时间:28 Oct 2021
所属领域:自然语言处理
对应任务:Image Classification,Neural Architecture Search,object-detection,Object Detection,图像分类,神经结构搜索,物体检测,目标检测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.15352
代码实现:https://github.com/mit-han-lab/mcunet
论文作者:Ji Lin, Wei-Ming Chen, Han Cai, Chuang Gan, Song Han
论文简介:We further propose network redistribution to shift the receptive field and FLOPs to the later stage and reduce the computation overhead./我们进一步提出了网络重新分配,将接受场和FLOPs转移到后期,并减少计算开销。
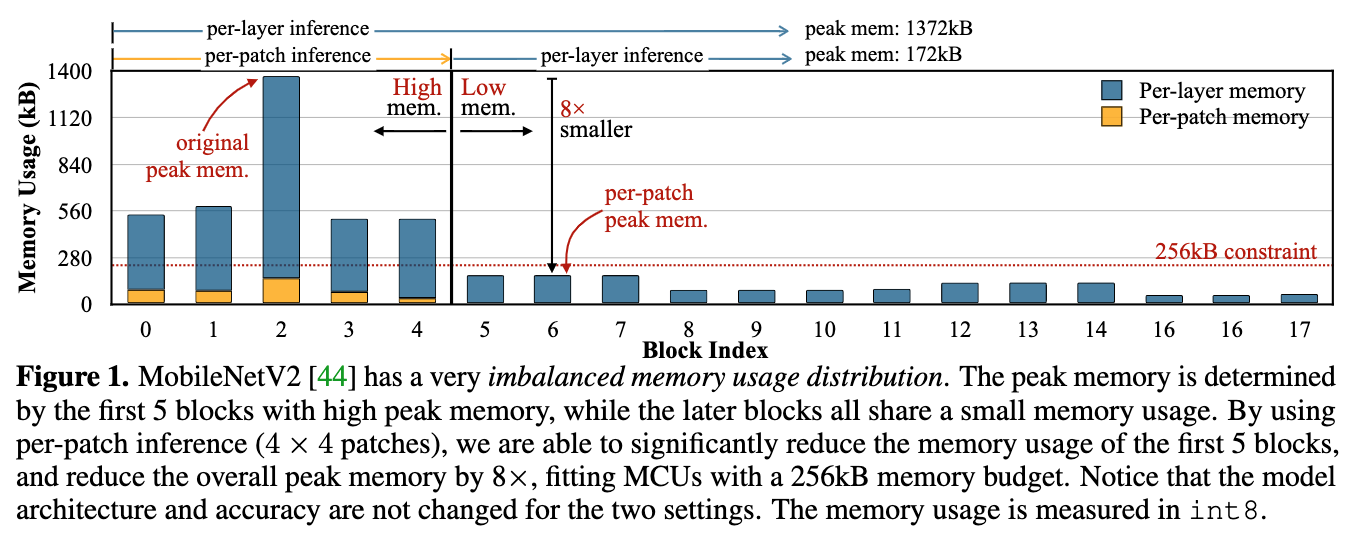
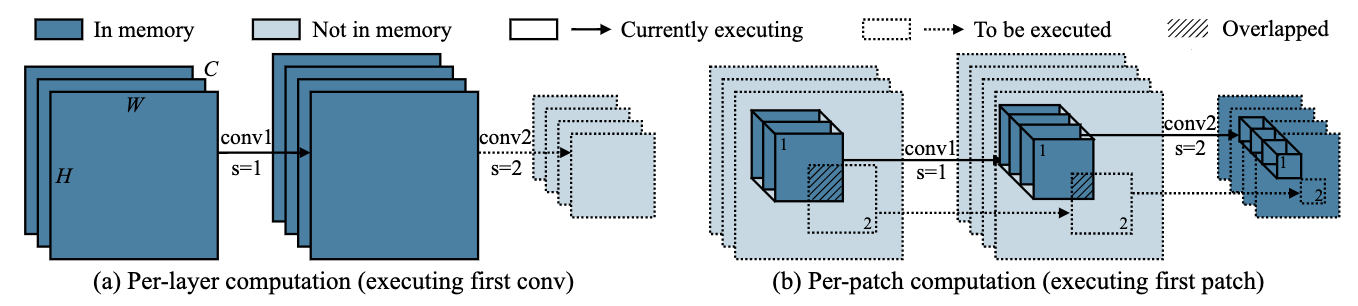
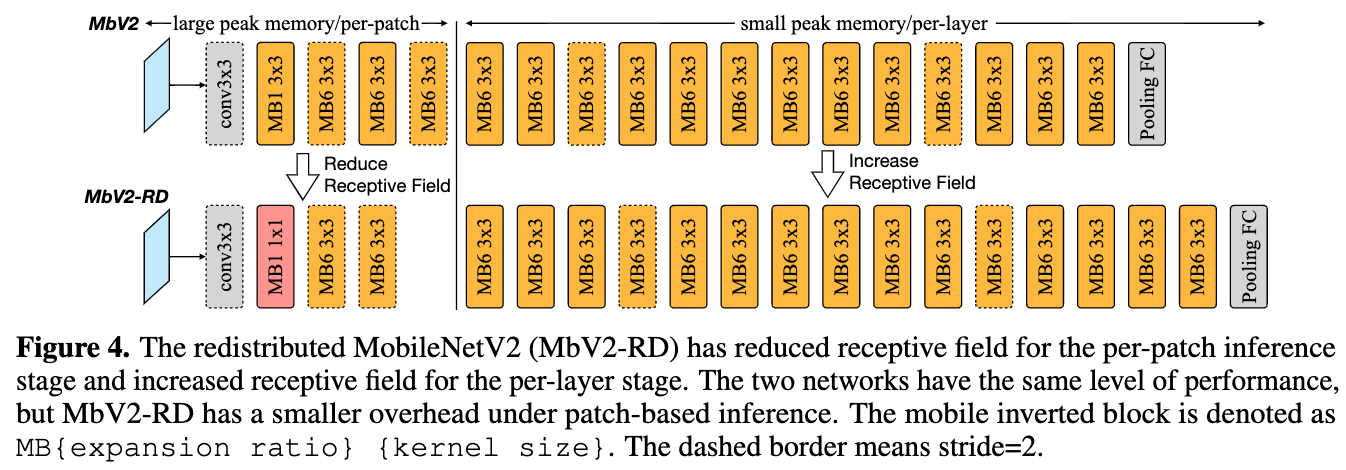
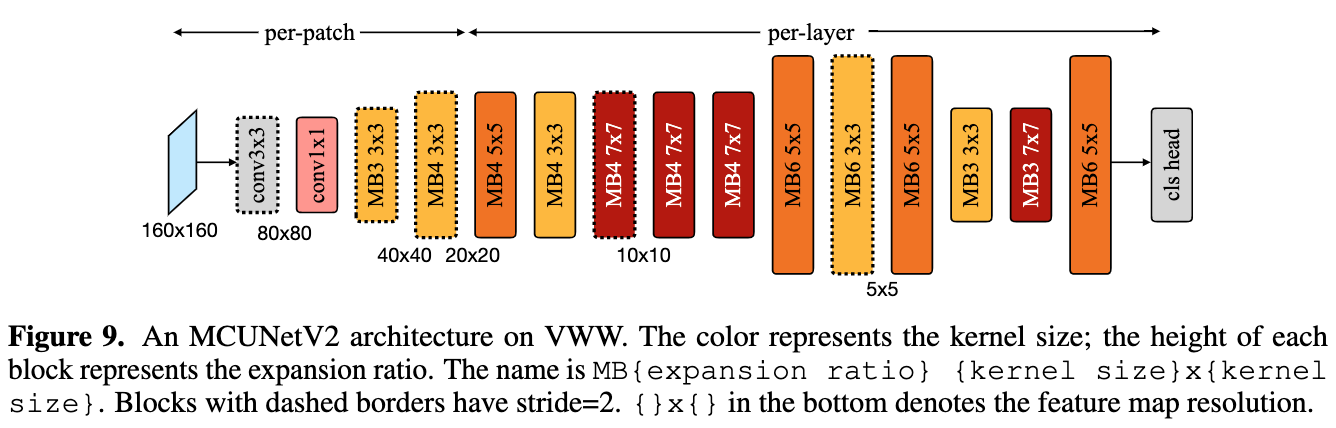
论文摘要:Tiny deep learning on microcontroller units (MCUs) is challenging due to the limited memory size. We find that the memory bottleneck is due to the imbalanced memory distribution in convolutional neural network (CNN) designs: the first several blocks have an order of magnitude larger memory usage than the rest of the network. To alleviate this issue, we propose a generic patch-by-patch inference scheduling, which operates only on a small spatial region of the feature map and significantly cuts down the peak memory. However, naive implementation brings overlapping patches and computation overhead. We further propose network redistribution to shift the receptive field and FLOPs to the later stage and reduce the computation overhead. Manually redistributing the receptive field is difficult. We automate the process with neural architecture search to jointly optimize the neural architecture and inference scheduling, leading to MCUNetV2. Patch-based inference effectively reduces the peak memory usage of existing networks by 4-8x. Co-designed with neural networks, MCUNetV2 sets a record ImageNet accuracy on MCU (71.8%), and achieves >90% accuracy on the visual wake words dataset under only 32kB SRAM. MCUNetV2 also unblocks object detection on tiny devices, achieving 16.9% higher mAP on Pascal VOC compared to the state-of-the-art result. Our study largely addressed the memory bottleneck in tinyML and paved the way for various vision applications beyond image classification.
由于内存大小有限,在微控制器单元(MCU)上进行微小的深度学习具有挑战性。我们发现,内存瓶颈是由于卷积神经网络(CNN)设计中不平衡的内存分布造成的:前几个块的内存用量比网络的其他部分大一个数量级。为了缓解这个问题,我们提出了一个通用的逐块推理调度,它只对特征图的一个小空间区域进行操作,并大大减少了峰值内存。然而,天真的实施带来了重叠的补丁和计算的开销。我们进一步提出了网络再分配,将接受区和FLOPs转移到后期,减少计算开销。手动重新分配接受区是很困难的。我们用神经结构搜索将这一过程自动化,以共同优化神经结构和推理调度,从而形成MCUNetV2。基于补丁的推理有效地将现有网络的峰值内存使用率降低了4-8倍。与神经网络共同设计的MCUNetV2在MCU上创造了ImageNet准确率的记录(71.8%),并在仅32kB的SRAM下对视觉唤醒词数据集实现了大于90%的准确率。MCUNetV2还解除了微小设备上的物体检测,与最先进的结果相比,在Pascal VOC上实现了16.9%的mAP。我们的研究在很大程度上解决了tinyML的内存瓶颈问题,并为图像分类以外的各种视觉应用铺平了道路。
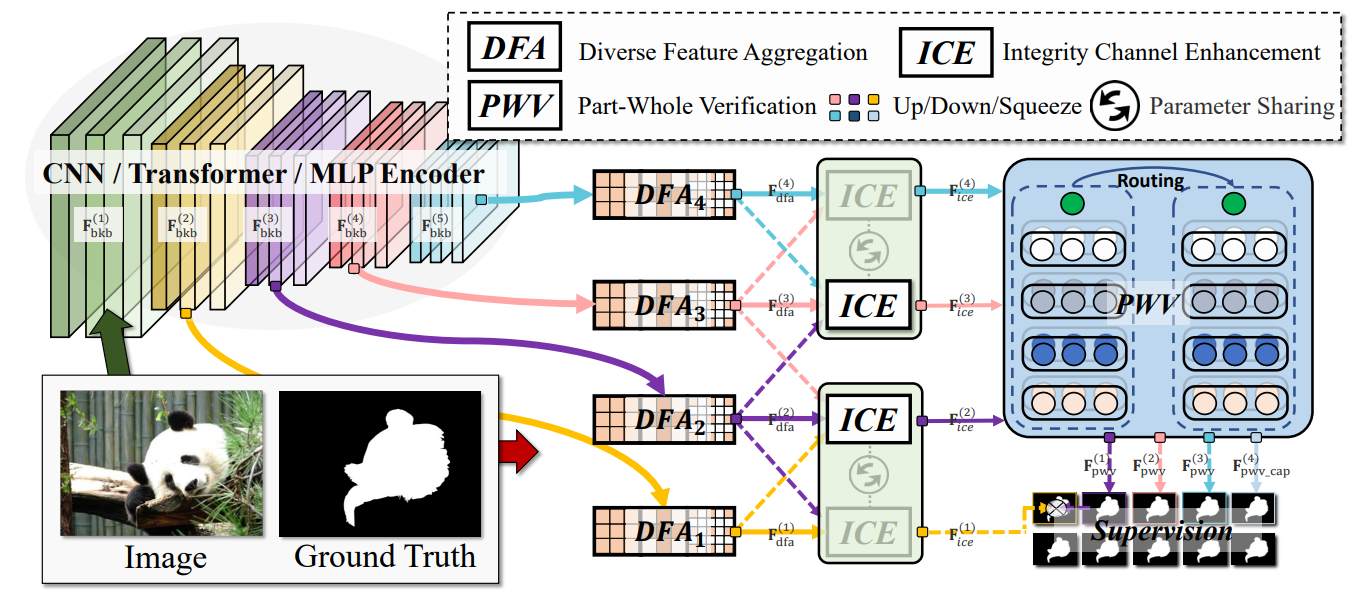
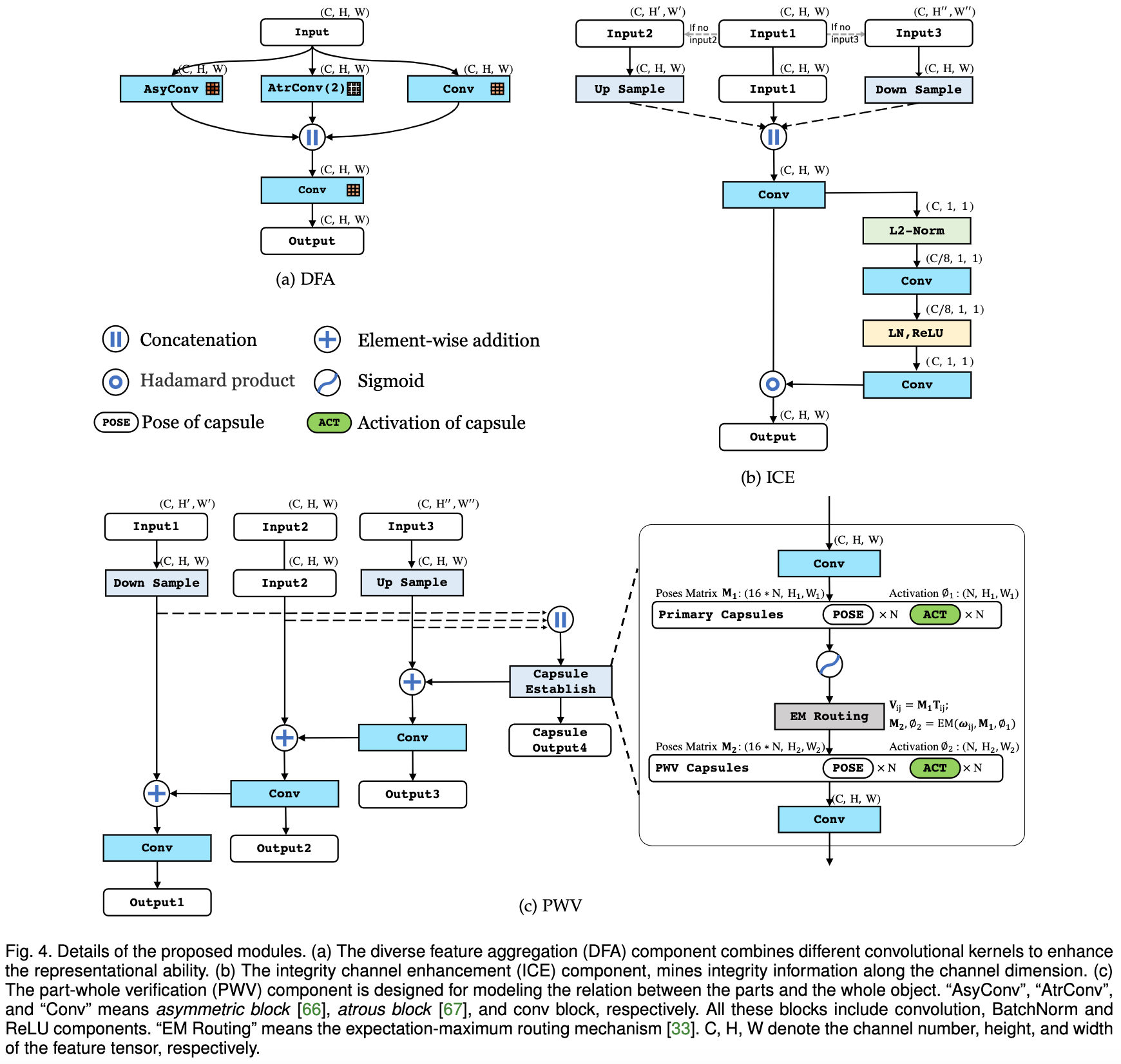
论文:Salient Object Detection via Integrity Learning
论文标题:Salient Object Detection via Integrity Learning
论文时间:19 Jan 2021
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:object-detection,Object Detection,Salient Object Detection,物体检测,倾斜物体检测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.07663
代码实现:https://github.com/mczhuge/ICON , https://github.com/mczhuge/Kaleido-BERT , https://github.com/mczhuge/SOCToolbox
论文作者:Mingchen Zhuge, Deng-Ping Fan, Nian Liu, Dingwen Zhang, Dong Xu, Ling Shao
论文简介:We define the concept of integrity at both a micro and macro level./我们在微观和宏观层面上定义了完整性的概念。
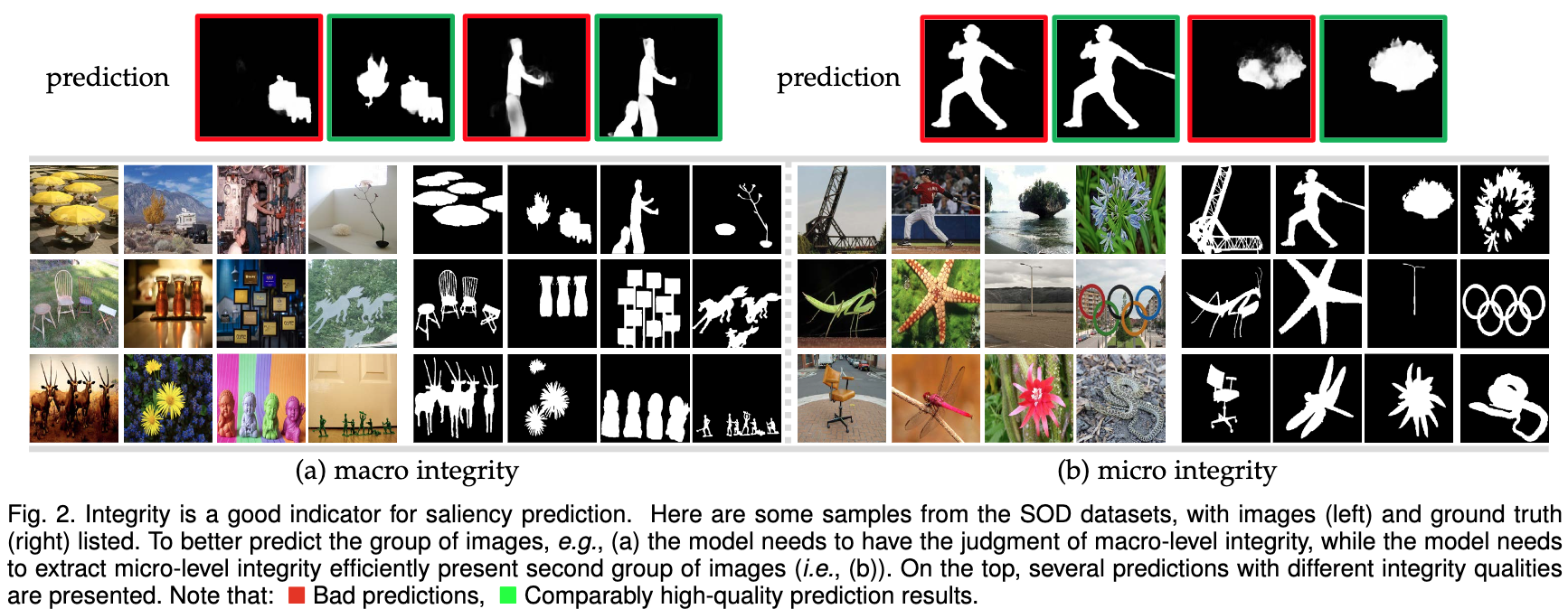
论文摘要:Although current salient object detection (SOD) works have achieved significant progress, they are limited when it comes to the integrity of the predicted salient regions. We define the concept of integrity at both a micro and macro level. Specifically, at the micro level, the model should highlight all parts that belong to a certain salient object. Meanwhile, at the macro level, the model needs to discover all salient objects in a given image. To facilitate integrity learning for SOD, we design a novel Integrity Cognition Network (ICON), which explores three important components for learning strong integrity features. 1) Unlike existing models, which focus more on feature discriminability, we introduce a diverse feature aggregation (DFA) component to aggregate features with various receptive fields (i.e., kernel shape and context) and increase feature diversity. Such diversity is the foundation for mining the integral salient objects. 2) Based on the DFA features, we introduce an integrity channel enhancement (ICE) component with the goal of enhancing feature channels that highlight the integral salient objects, while suppressing the other distracting ones. 3) After extracting the enhanced features, the part-whole verification (PWV) method is employed to determine whether the part and whole object features have strong agreement. Such part-whole agreements can further improve the micro-level integrity for each salient object. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our ICON, comprehensive experiments are conducted on seven challenging benchmarks. Our ICON outperforms the baseline methods in terms of a wide range of metrics. Notably, our ICON achieves about 10% relative improvement over the previous best model in terms of average false negative ratio (FNR), on six datasets. Codes and results are available at: https://github.com/mczhuge/ICON
尽管目前的突出物体检测(SOD)工作已经取得了重大进展,但当涉及到预测突出区域的完整性时,它们是有限的。我们在微观和宏观层面上都定义了完整性的概念。具体来说,在微观层面上,模型应该突出属于某个突出对象的所有部分。同时,在宏观层面上,模型需要发现给定图像中的所有突出对象。为了促进SOD的完整性学习,我们设计了一个新颖的完整性认知网络(ICON),它为学习强大的完整性特征探索了三个重要组成部分。1)与现有的模型不同,它更注重特征的可辨别性,我们引入了多样化的特征聚合(DFA)组件,以聚合具有不同感受野(即内核形状和背景)的特征,增加特征的多样性。这种多样性是挖掘整体突出对象的基础。2)在DFA特征的基础上,我们引入了完整性通道增强(ICE)组件,目的是增强突出整体突出对象的特征通道,同时抑制其他分散注意力的特征。3)在提取了增强的特征后,采用部分-整体验证(PWV)方法来确定部分和整体对象的特征是否有强烈的一致性。这种部分-整体的一致可以进一步提高每个突出对象的微观层面的完整性。为了证明我们的ICON的有效性,我们在七个具有挑战性的基准上进行了综合实验。我们的ICON在广泛的指标方面超过了基线方法。值得注意的是,在六个数据集上,我们的ICON在平均假阴性率(FNR)方面比以前的最佳模型取得了大约10%的相对改进。代码和结果见:https://github.com/mczhuge/ICON
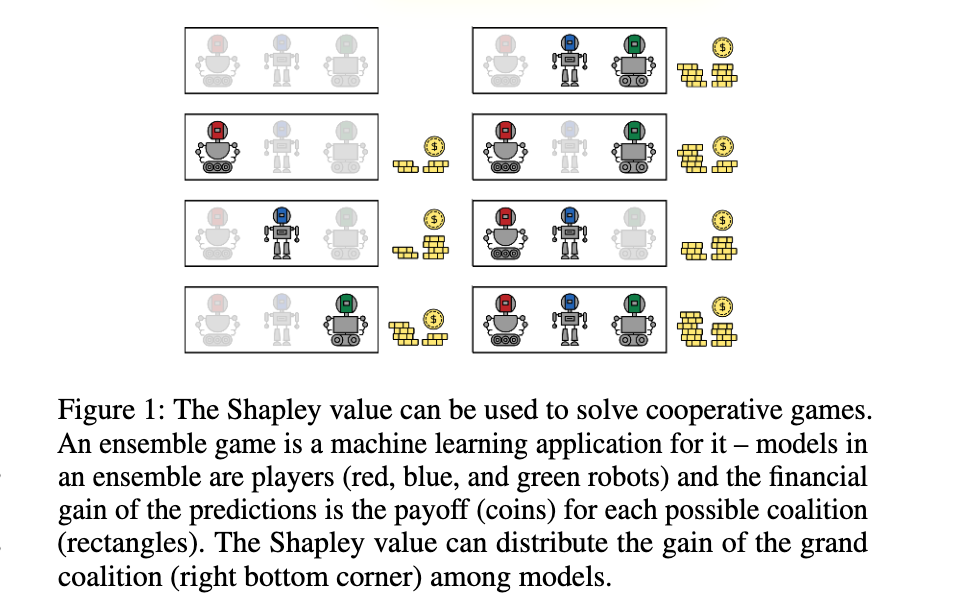
论文:The Shapley Value in Machine Learning
论文标题:The Shapley Value in Machine Learning
论文时间:11 Feb 2022
所属领域:机器学习
对应任务:Ensemble Pruning,feature selection,Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning,reinforcement-learning,集成剪枝,特征选择,多代理强化学习,强化学习
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.05594
代码实现:https://github.com/benedekrozemberczki/shapley , https://github.com/AstraZeneca/awesome-shapley-value
论文作者:Benedek Rozemberczki, Lauren Watson, Péter Bayer, Hao-Tsung Yang, Olivér Kiss, Sebastian Nilsson, Rik Sarkar
论文简介:Over the last few years, the Shapley value, a solution concept from cooperative game theory, has found numerous applications in machine learning./在过去的几年里,Shapley值,一个来自合作博弈理论的解决概念,已经在机器学习中找到了许多应用。
论文摘要:Over the last few years, the Shapley value, a solution concept from cooperative game theory, has found numerous applications in machine learning. In this paper, we first discuss fundamental concepts of cooperative game theory and axiomatic properties of the Shapley value. Then we give an overview of the most important applications of the Shapley value in machine learning: feature selection, explainability, multi-agent reinforcement learning, ensemble pruning, and data valuation. We examine the most crucial limitations of the Shapley value and point out directions for future research.
在过去的几年里,Shapley值,一个来自合作博弈理论的解决方案的概念,在机器学习中发现了许多应用。在本文中,我们首先讨论了合作博弈论的基本概念和Shapley值的公理特性。然后,我们概述了Shapley值在机器学习中最重要的应用:特征选择、可解释性、多代理强化学习、集成剪枝和数据评估。我们研究了Shapley值的最关键的局限性,并指出了未来的研究方向。
我们是 ShowMeAI,致力于传播AI优质内容,分享行业解决方案,用知识加速每一次技术成长!点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。

- 作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI
- 历史文章列表
- 专题合辑&电子月刊
- 声明:版权所有,转载请联系平台与作者并注明出处
- 欢迎回复,拜托点赞,留言推荐中有价值的文章、工具或建议,我们都会尽快回复哒~
最后
以上就是自然缘分最近收集整理的关于人工智能 | ShowMeAI资讯日报 #2022.06.251.工具&框架2.博文&分享3.数据&资源4.研究&论文的全部内容,更多相关人工智能内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复