文章目录
- 5.2 卷积神经网络的基础算子
- 5.2.1 卷积算子
- 5.2.1.1 多通道卷积
- 5.2.1.2 多通道卷积层算子
- 5.2.1.3 卷积算子的参数量和计算量
- 5.2.2 汇聚层算子
- 选做题:使用pytorch实现Convolution Demo
5.2 卷积神经网络的基础算子
我们先实现卷积网络的两个基础算子:卷积层算子和汇聚层算子。
5.2.1 卷积算子
卷积层是指用卷积操作来实现神经网络中一层。
为了提取不同种类的特征,通常会使用多个卷积核一起进行特征提取。
5.2.1.1 多通道卷积
5.2.1.2 多通道卷积层算子
- 多通道卷积卷积层的代码实现
自定义多通道卷积层,基于numpy
为了与pytorch框架的卷积层进行对照,基本上实现了框架中的除反向传播之外的大部分功能。主要支持多通道卷积、边缘填充、边缘填充方式,自定义步长、自定义卷积核参数、是否使用偏置等。除此之外,还添加了是否不舍弃冗余值。
大体轮廓:
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
class myMultipassageConv():
def __init__(self,in_chanels,out_chanels,kernel_size,padding,stride=(1,1),padding_str='zeros',use_bias=True):
'''
:param in_chanels: 输入通道数
:param out_chanels: 输出通道数
:param kernel_size: 卷积核尺寸 tuple类型
:param padding: 边缘填充数
:param stride: 步长 tuple类型 (可选)默认为(1,1)
:param padding_str: 边缘填充方式 str类型(可选)
:param use_bias: 是否使用偏置 bool类型(可选)
'''
self.kernel_size=kernel_size
self.in_chanels=in_chanels
self.out_chanels=out_chanels
self.padding=padding
self.stride=stride
(self.kernel_hight,self.kernel_width)=kernel_size
self.weights,self.bias=self.__parameters()
self.padding_str=padding_str
self.use_bias=use_bias
def __parameters(self):
'''内部函数,默认标准正态分布初始化参数'''
'''权重尺寸为in_chanels*out_chanels*kernelsize'''
weights=np.random.randn(self.out_chanels,self.in_chanels,self.kernel_hight,self.kernel_width)
'''偏置尺寸为out_kernels'''
bias=np.random.randn(self.out_chanels,1)
return weights,bias
def forward(self,x):
'''前向计算'''
'''输入格式(batch_size,chanels,hight,width)'''
output =[]
(batch_size, chanels, hight, width)=x.shape
for batch_num in range(batch_size):
img=x[batch_num,:,:,:]
for chanel_num in range(chanels):
_img=img[chanel_num,:,:]
kernels=self.weights[:,chanel_num,:,:]
for kernel in kernels:
_img = self.__paddingzeros(_img)#边缘填充
out_img=self.__myConv(_img,kernel)
output.append(out_img.tolist())
'''计算输出图像的尺寸 '''
img=x[0,0,:,:]
k1 = int((self.kernel_size[0] - 1) / 2)
k2 = int((self.kernel_size[1] - 1) / 2)
out_shape=(img.shape[0] - 2 * k1+2*self.padding, img.shape[1] - 2 * k2+2*self.padding)
output=np.array(output).reshape(batch_size,self.out_chanels,out_shape[0],out_shape[1])
if self.use_bias:
return output+self.bias
else:
return output
def __paddingzeros(self,img):
'''内部函数,默认 边缘0填充'''
if self.padding_str=='zeros':
out=np.zeros(shape=(img.shape[0]+self.padding*2,img.shape[1]+self.padding*2))
out[self.padding:-self.padding,self.padding:-self.padding]=img
return out
elif self.padding_str=='ones':
out=np.oness(shape=(img.shape[0]+self.padding*2,img.shape[1]+self.padding*2))
out[self.padding:-self.padding,self.padding:-self.padding]=img
return out
else:
raise ValueError('Value error: unexcepted key value of 'padding'. excepted key values:zeros,ones')
def __myConv(self,img, kernel):#单层单核卷积
'''内部参数,用于计算单个单核卷积'''
k1 = int((kernel.shape[0] - 1) / 2)
k2 = int((kernel.shape[1] - 1) / 2)
out_img = []
for i in range(k1, img.shape[0] - k1):
for j in range(k2, img.shape[1] - k2):
sight = img[i - 1:i + 2, j - 1:j + 2]
out_img.append(np.sum(np.multiply(np.array(sight), np.array(kernel))))
return np.array(out_img).reshape((img.shape[0] - 2 * k1, img.shape[1] - 2 * k2))
def get_parameters(self):
return self.weights,self.bias
def set_parameters(self,weights,bias):
self.weights, self.bias=weights,bias
def show_img(img):
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.show()
if __name__=='__main__':
myconv=myMultipassageConv(1,1,kernel_size=(3,3),padding=1,stride=(1,1))
img=np.array([[
[
[1,1,1,1,1,1],
[0,1,0,1,0,1],
[1,0,1,0,1,0],
[0,1,0,1,0,1],
[1,1,1,1,1,1],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]
]]])
kernel_weights=np.array([[
[
[1,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[0,0,1]
]
]])
bias=np.array([
[0]
])
show_img(np.squeeze(img))
show_img(np.squeeze(kernel_weights))
myconv.set_parameters(kernel_weights,bias)
out_img=myconv.forward(img)
show_img(np.squeeze(out_img))
上面是过程记录,只能完成双方向步长均为1,卷积核尺寸为3*3的卷积。下面对代码卷积累进行完善后,可以支持卷积核尺寸为任意奇数axa,双方向上任意步长的卷积。同时可以设置是否舍弃边界冗余值,参数为use_adundancy,默认为不舍弃。
细节完善后:
#coding:utf-8
import math
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
class myMultipassageConv():
def __init__(self,in_chanels,out_chanels,kernel_size,padding,stride=(1,1),padding_str='zeros',use_bias=True,use_redundancy=True):
'''
:param in_chanels: 输入通道数
:param out_chanels: 输出通道数
:param kernel_size: 卷积核尺寸 tuple类型
:param padding: 边缘填充数
:param stride: 步长 tuple类型 (可选)默认为(1,1)
:param padding_str: 边缘填充方式 str类型(可选)
:param use_bias: 是否使用偏置 bool类型(可选)
use_redundancy:是否使用冗余值 bool 默认不舍弃
'''
self.kernel_size=kernel_size
self.in_chanels=in_chanels
self.out_chanels=out_chanels
self.padding=padding
self.stride=stride
(self.kernel_hight,self.kernel_width)=kernel_size
self.weights,self.bias=self.__parameters()
self.padding_str=padding_str
self.use_bias=use_bias
self.use_redundancy=use_redundancy
def __parameters(self):
'''内部函数,默认标准正态分布初始化参数'''
'''权重尺寸为in_chanels*out_chanels*kernelsize'''
weights=np.random.randn(self.out_chanels,self.in_chanels,self.kernel_hight,self.kernel_width)
'''偏置尺寸为out_kernels'''
bias=np.random.randn(self.out_chanels,1)
return weights,bias
def forward(self,x):
'''前向计算'''
'''输入格式(batch_size,chanels,hight,width)'''
output =[]
(batch_size, chanels, hight, width)=x.shape
for batch_num in range(batch_size):
img=x[batch_num,:,:,:]
for chanel_num in range(chanels):
_img=img[chanel_num,:,:]
kernels=self.weights[:,chanel_num,:,:]
for kernel in kernels:
if self.padding>0:
_img = self.__paddingzeros(_img)#边缘填充
out_img,_=self.__myConv(_img,kernel)
output.append(out_img.tolist())
'''计算输出图像的尺寸 '''
img=x[0,0,:,:]
if self.padding>0:
img = self.__paddingzeros(img) # 边缘填充
kernel=self.weights[0,0,:,:]
_,out_shape=self.__myConv(img,kernel)
output=np.array(output).reshape(batch_size,self.out_chanels,out_shape[0],out_shape[1])
'''是否使用偏置b'''
if self.use_bias:
return output+self.bias
else:
return output
def __paddingzeros(self,img):
'''内部函数,默认 边缘0填充'''
if self.padding_str=='zeros':
out=np.zeros(shape=(img.shape[0]+self.padding*2,img.shape[1]+self.padding*2))
out[self.padding:-self.padding,self.padding:-self.padding]=img
return out
elif self.padding_str=='ones':
out=np.ones(shape=(img.shape[0]+self.padding*2,img.shape[1]+self.padding*2))
out[self.padding:-self.padding,self.padding:-self.padding]=img
return out
else:
raise ValueError('Value error: unexcepted key value of 'padding'. excepted key values:zeros,ones')
def __myConv(self,img, kernel):#单层单核卷积
'''内部参数,用于计算单图像单核卷积'''
if (self.stride==(1,1))&(self.kernel_size==(3,3)):
k1 = int((kernel.shape[0] - 1) / 2)
k2 = int((kernel.shape[1] - 1) / 2)
out_img = []
for i in range(k1, img.shape[0] - k1):
for j in range(k2, img.shape[1] - k2):
sight = img[i - 1:i + 2, j - 1:j + 2]
out_img.append(np.sum(np.multiply(np.array(sight), np.array(kernel))))
return np.array(out_img).reshape((img.shape[0] - 2 * k1, img.shape[1] - 2 * k2)),(img.shape[0] - 2 * k1, img.shape[1] - 2 * k2)
else:
k1 = int((kernel.shape[0] - 1) / 2)
k2 = int((kernel.shape[1] - 1) / 2)
print('k1,k2=',k1,k2)
print('stride:',self.stride)
out_img = []
right_line=[]
bottom_line=[]
botton_right=[]
print('img.shape:',img.shape)
for x_index,i in enumerate(range(k1, img.shape[0] - k1)):
if x_index%self.stride[1]==0:#纵向移动
for y_index,j in enumerate(range(k2, img.shape[1] - k2)):
if y_index%self.stride[0]==0:#横向移动
#print('current i j', i, j)
sight = img[i - k1:i + k2+1, j - k1:j + k2+1]
#print(sight)
#print(kernel)
out_img.append(np.sum(np.multiply(np.array(sight), np.array(kernel))))
#print('out img:',out_img)
''' 这里考虑到步长大于1时卷积到右侧边缘或下侧会有边缘不足的情况,因此尝试对边界的溢出进行检测与处理 '''
'''处理边界冗余值'''
if (j+self.stride[0]+k1)>(img.shape[1]-1):
#print('列索引',(j+self.stride[0]+k1),'>',(img.shape[1]-k1))
#print('检测到达右边界,向右移动并填充后几列')
_j=j+self.stride[0]
redundancy=img[i - k1:i + k2+1,_j - k1:]
split_kernel = kernel[:, :np.array(redundancy).shape[1]]
#print(redundancy)
#print(split_kernel)
right_line.append(np.sum(np.multiply(np.array(redundancy), np.array(split_kernel))))
#print( 'right line',right_line)
if (i+self.stride[1]+k2)>(img.shape[0]-1):
#print('行索引',(i+self.stride[1]),'>',(img.shape[0]-1))
#print('检测到达下边界,向下移动并填充下几行')
'''达下边界,向下移动并分别获取冗余值以及分割的卷积核,在对两者计算点积和,其他几种也是这种方法'''
_i=i+self.stride[1]
redundancy=img[_i - k2:, j - k1:j + k2+1]
split_kernel=kernel[:np.array(redundancy).shape[0], :]
#print(redundancy)
#print(split_kernel)
bottom_line.append(np.sum(np.multiply(np.array(redundancy), np.array(split_kernel))))
#print('bottopn line:',bottom_line)
if ((j+self.stride[0]+k1)>(img.shape[1]-1))&((i+self.stride[1]+k2)>(img.shape[0]-1)):
#print('达右下角,向右下移动并填充')
_i+=self.stride[0]
_j+=self.stride[1]
redundancy = img[_i - k2:, _j - k1:]
split_kernel = kernel[:np.array(redundancy).shape[0], :np.array(redundancy).shape[1]]
#print(redundancy)
#print(split_kernel)
botton_right.append(np.sum(np.multiply(np.array(redundancy),np.array(split_kernel))))
out_shape=[0,0]
for i in range( img.shape[0] - 2*k1):
if i%self.stride[1]==0:
out_shape[0]+=1
for i in range( img.shape[1] - 2*k2):
if i %self.stride[0]==0:
out_shape[1]+=1
print(out_shape)
if self.use_redundancy:
base_img=np.array(out_img).reshape(out_shape)
#print(base_img)
#print(right_line)
#print(bottom_line)
#print(botton_right)
return self.__Conbine(base_img,right_line,bottom_line,botton_right),self.__Conbine(base_img,right_line,bottom_line,botton_right).shape
else:
return np.array(out_img).reshape(out_shape), out_shape
def __Conbine(self,baseimg,rightline,bottomline,rightbottom):
'''内置函数,用于将冗余值信息与基本信息组合到一起'''
br=np.append(np.array(baseimg),np.array(rightline).reshape(len(rightline),1),axis=1)
#print(br)
bbr=np.append(np.array(bottomline),np.array(rightbottom))
bbrr=bbr.reshape(1,len(bbr))
#print(bbr)
#print(bbrr)
return np.append(br,bbrr,axis=0)
def get_parameters(self):
return self.weights,self.bias
def set_parameters(self,weights,bias):
self.weights, self.bias=weights,bias
def set_weights(self,weights):
self.weights=weights
def set_bias(self,bias):
self.bias=bias
def show_img(img):
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.show()
if __name__=='__main__':
img=np.array([[
[
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
]]])
kernel_weights=np.array([[
[
[1,0,0,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,0],
[0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,1]
]
]])
kernel_weights1=np.array([[
[
[1,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[0,0,1]
]
]])
bias=np.array([
[0]
])
for kernel_weight,k_size in [(kernel_weights1,(3,3)),(kernel_weights,(5,5))]:
myconv = myMultipassageConv(1, 1, kernel_size=k_size, padding=0, stride=(2,2), use_bias=False,
use_redundancy=False)
myconv.set_parameters(kernel_weight,bias)
out_img=myconv.forward(img)
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(1,3,1)
plt.imshow(np.squeeze(img),cmap='gray')
plt.title('original')
plt.subplot(1,3,2)
plt.imshow(np.squeeze(kernel_weight),cmap='gray')
plt.title('kernel')
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.imshow(np.squeeze(out_img),cmap='gray')
plt.title('output')
plt.show()
测试各个功能:
设置use_redundancy为False时:padding=0
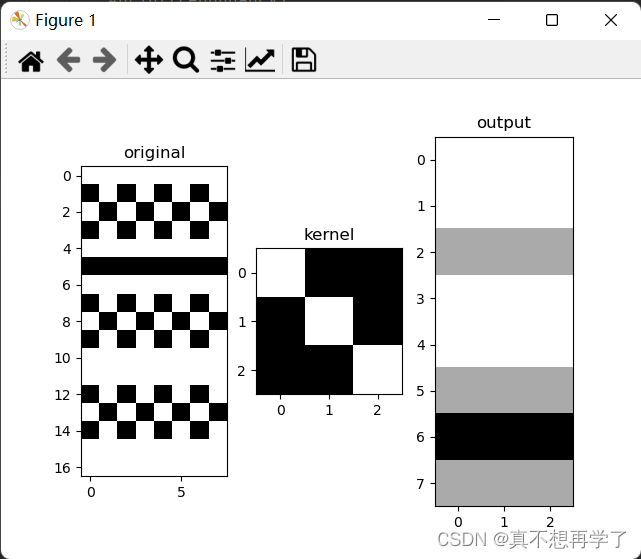
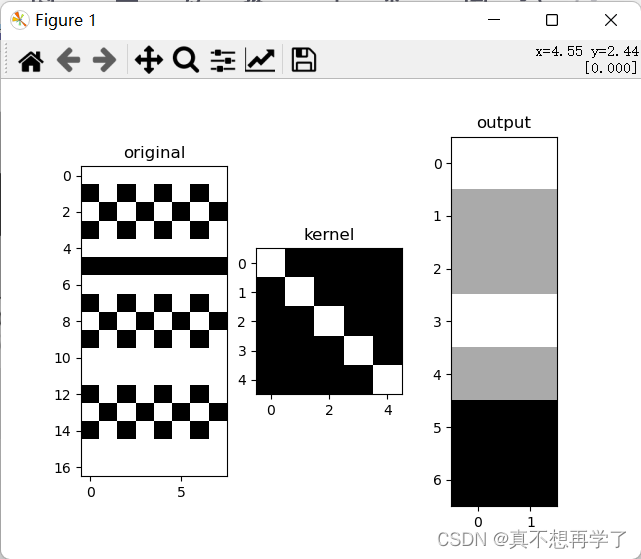
padding=1
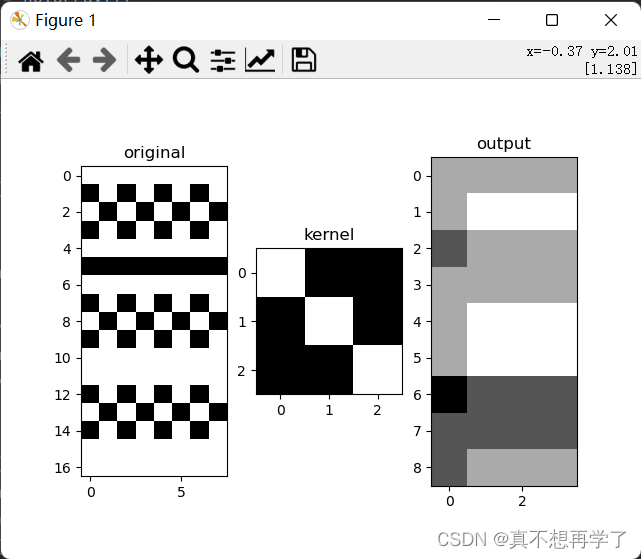
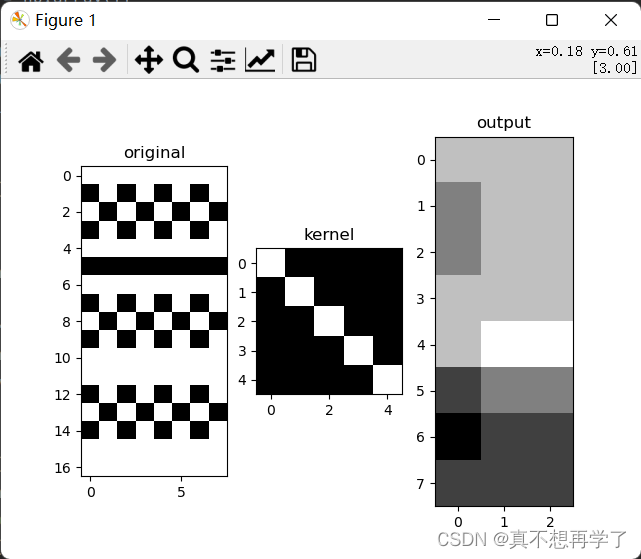
设置use_redundancy为True时:
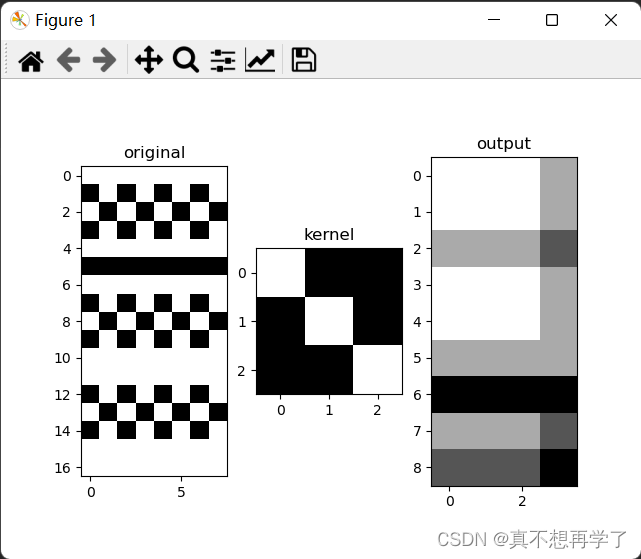
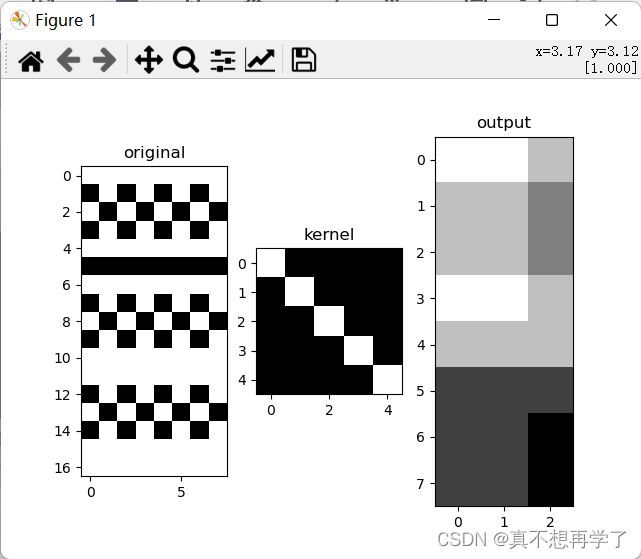
设置padding=1
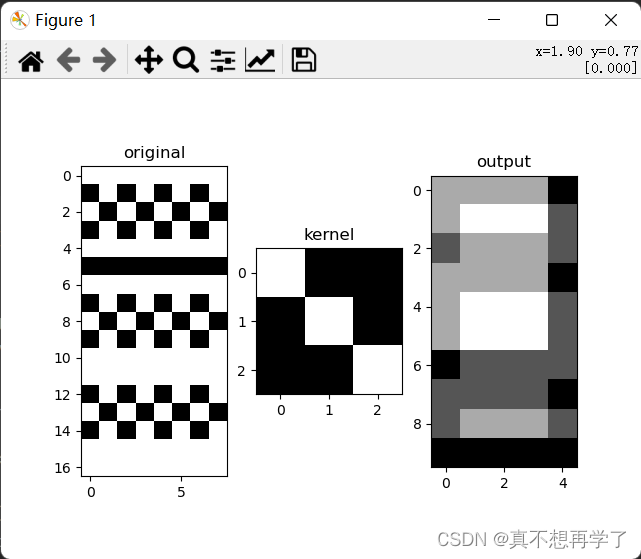
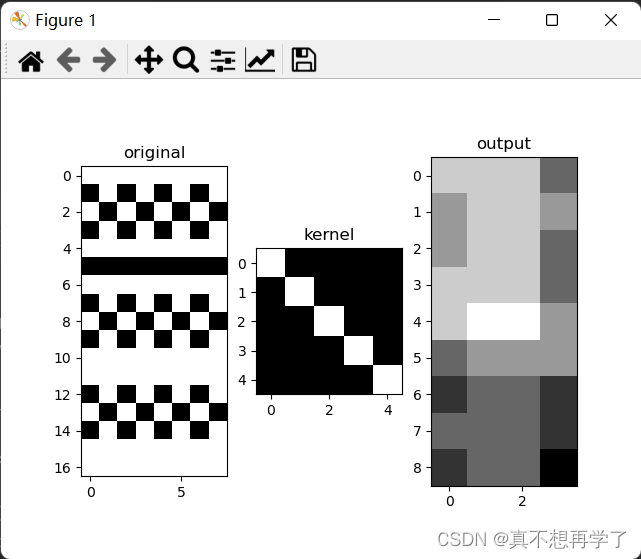
设置padding_str为‘ones’
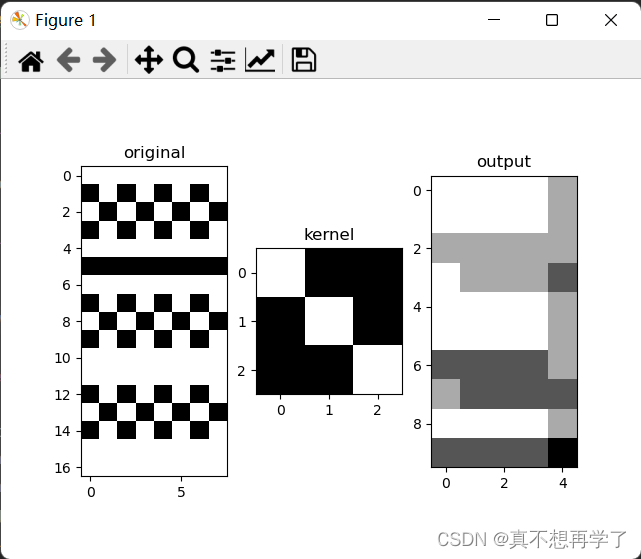
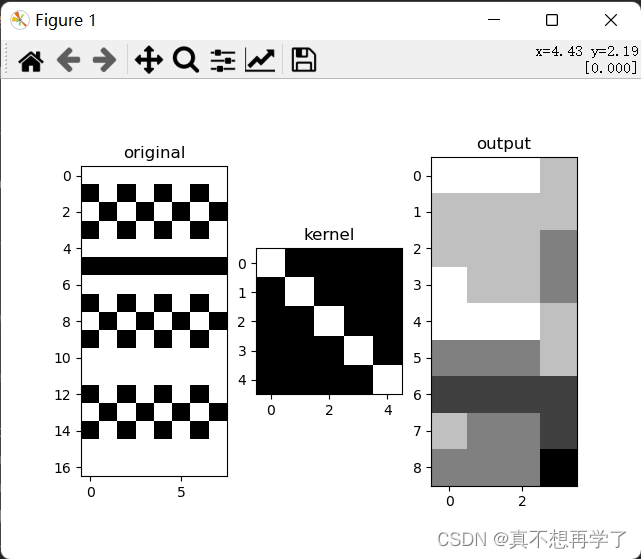
- Pytorch:torch.nn.Conv2d()代码实现
import numpy as np
import torch
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
if __name__=='__main__':
img = np.array([[
[
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
]]])
kernel_weights = np.array([[
[
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1]
]
]])
kernel_weights1 = np.array([[
[
[1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1]
]
]])
bias = np.array([
[0]
])
for kernel_weight,k_size in [(kernel_weights1,(3,3)),(kernel_weights,(5,5))]:
conv2d = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=1, kernel_size=kernel_weights.shape,stride=(2,2))
conv2d.weight.data = torch.Tensor(kernel_weight.astype(np.float32))
out_img=conv2d.forward(torch.Tensor(img.astype(np.float32)))
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(1,3,1)
plt.imshow(np.squeeze(img),cmap='gray')
plt.title('original')
plt.subplot(1,3,2)
plt.imshow(np.squeeze(kernel_weight),cmap='gray')
plt.title('kernel')
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.imshow(np.squeeze(out_img.detach().numpy()),cmap='gray')
plt.title('output')
plt.show()
测试各个功能:
padding=0


设置padding=1


- 比较自定义算子和框架中的算子
1)经过测试发现pytorch的算子是默认舍弃冗余值的,查看官方资料得知,他没有关于冗余的参数。(也可能我没看到)
2)自定义算子只能进行前向传播,因为numpy没有自动求导机制,如果把代码中的numpy数组转化为torch中的Tensor算子其实就可以实现自动求导了。
3)如果不看自定义卷积类的定义代码的话,实例化所用的代码量和pytorch框架相当,因此并没有显得很复杂,这体现出了类封装的优势。
5.2.1.3 卷积算子的参数量和计算量
参数量
权重尺寸为in_chanels
∗
*
∗out_chanels
∗
*
∗ kernel_size
偏置尺寸为out_kernels
计算量为in_chanels
∗
*
∗out_chanels次kernel_size尺度的卷积运算
5.2.2 汇聚层算子
汇聚层的作用是进行特征选择,降低特征数量,从而减少参数数量。
由于汇聚之后特征图会变得更小,如果后面连接的是全连接层,可以有效地减小神经元的个数,节省存储空间并提高计算效率。
常用的汇聚方法有两种,分别是:平均汇聚、最大汇聚。
- 代码实现一个简单的汇聚层。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class myPooling():
def __init__(self,size,pooling_mode,stride):
self.h,self.w=size
self.pool_mode=pooling_mode
self.stride=stride
def __mypool(self, img):
output=[]
for x_index, i in enumerate(range(img.shape[0] )):
if x_index % self.stride == 0: # 纵向移动
for y_index, j in enumerate(range(img.shape[1])):
if y_index % self.stride== 0: # 横向移动
_img=img[i:i+self.h,j:j+self.w]
print(_img)
if self.pool_mode == 'ave':
output.append(np.average(_img))
elif self.pool_mode == 'max':
output.append(np.max(_img))
elif self.pool_mode == 'min':
output.append(np.min(_img))
else:
raise ValueError('Value error: unexcepted key value of 'pooling_mode'. excepted key values:ave,max,min')
out_shape = [0, 0]
for i in range(img.shape[0]):
if i % self.stride == 0:
out_shape[0] += 1
for i in range(img.shape[1]):
if i % self.stride == 0:
out_shape[1] += 1
print(out_shape)
return np.array(output).reshape(out_shape), out_shape
def forward(self, x):
'''前向计算'''
'''输入格式(batch_size,chanels,hight,width)'''
output = []
(batch_size, chanels, hight, width) = x.shape
for batch_num in range(batch_size):
img = x[batch_num, :, :, :]
for chanel_num in range(chanels):
_img = img[chanel_num, :, :]
out_img,out_shape=self.__mypool(_img)
output.append(out_img)
return np.array(output).reshape(batch_size,chanels,out_shape[0],out_shape[1])
if __name__=='__main__':
img=np.array([[
[
[1,0,0,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,0],
[0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,1]
]
]])
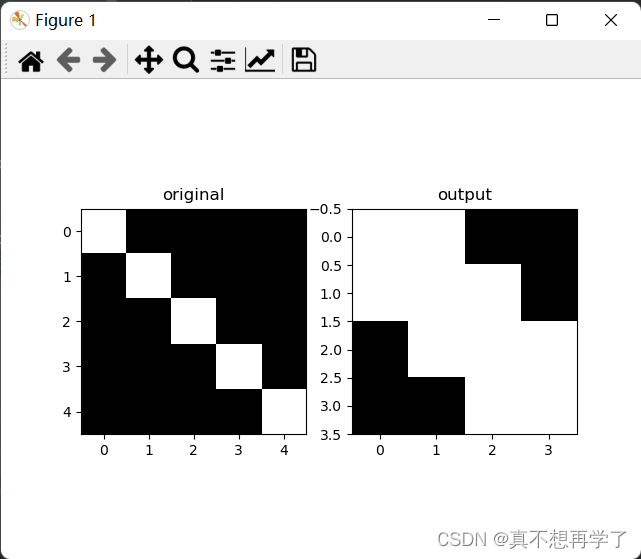
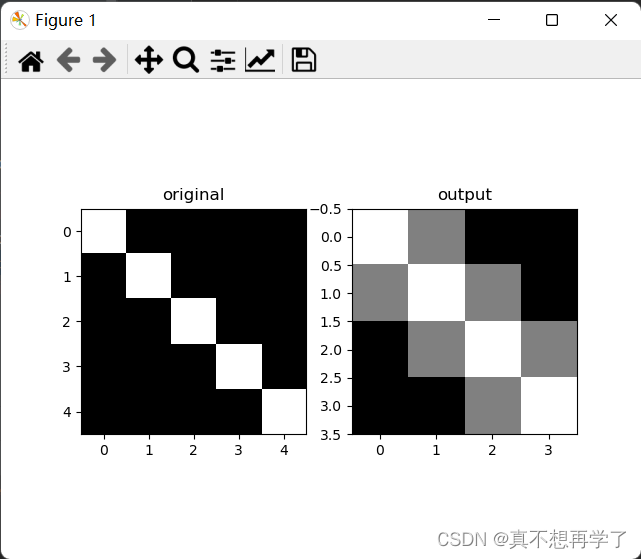
mypool=myPooling(size=(2,2),stride=1,pooling_mode='max')
out_img=mypool.forward(img)
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(np.squeeze(img), cmap='gray')
plt.title('original')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(np.squeeze(out_img), cmap='gray')
plt.title('output')
plt.show()
max:
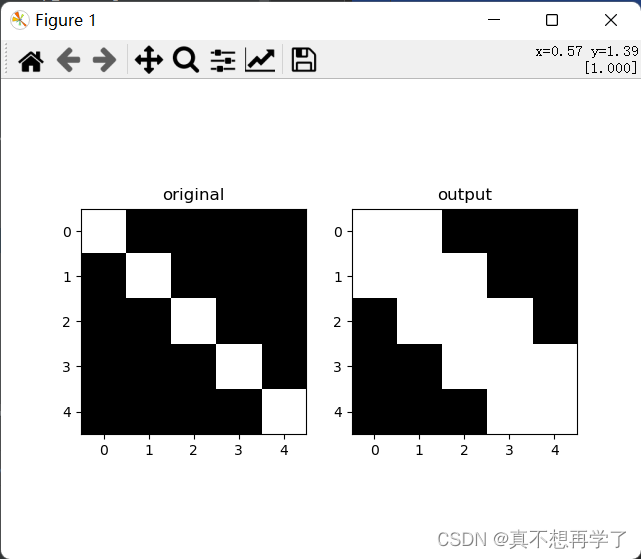
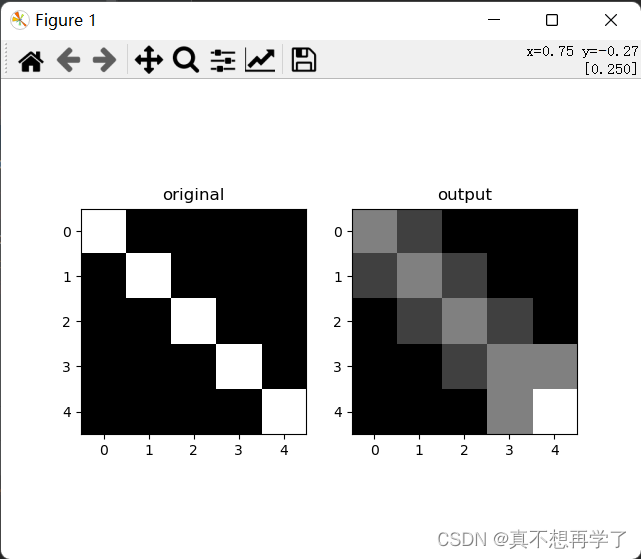
ave:
- torch.nn.MaxPool2d();torch.nn.avg_pool2d()代码实现
import numpy as np
import torch
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
if __name__=='__main__':
img=np.array([[
[
[1,0,0,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,0],
[0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,1]
]
]])
mypool=torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2,2),stride=1)
out_img=mypool.forward(torch.Tensor(img.astype(np.float32)))
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(np.squeeze(img), cmap='gray')
plt.title('original')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(np.squeeze(out_img), cmap='gray')
plt.title('output')
plt.show()
- 比较自定义算子和框架中的算子
汇聚层的参数量和计算量
由于汇聚层中没有参数,所以参数量为0;
最大汇聚中,没有乘加运算,所以计算量为0,
平均汇聚中,输出特征图上每个点都对应了一次求平均运算。
选做题:使用pytorch实现Convolution Demo
CS231n Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition
-
翻译以下内容
内容原图见文章末尾comefrom链接
卷积样例,如下是运行一个卷积层的样例,因为三维卷积很难表现,所有的输入层(蓝色)权重(红色),输出(绿色)都在一排中展示,输入的一卷w=5,h=5,d=3,卷积层的参数k=2,f=3,s=2,p=1,也就是说,我们有两层卷积核,他们的步长为2,除此之外,输出尺寸为(5-2+3)+1=3,此外,注意到填充p=1,给输入围上了一圈0,图示显示了输出活动(绿色),并且展现了每个元素都是由高亮的输入(蓝色)和对应的卷积核(红色)的点积,再加到一起,然后整体加上偏置b。 -
代码实现下图
图鉴文章末尾come from链接
#coding:utf-8
import math
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
class myMultipassageConv():
def __init__(self,in_chanels,out_chanels,kernel_size,padding,stride=(1,1),padding_str='zeros',use_bias=True,use_redundancy=True):
'''
:param in_chanels: 输入通道数
:param out_chanels: 输出通道数
:param kernel_size: 卷积核尺寸 tuple类型
:param padding: 边缘填充数
:param stride: 步长 tuple类型 (可选)默认为(1,1)
:param padding_str: 边缘填充方式 str类型(可选)
:param use_bias: 是否使用偏置 bool类型(可选)
use_redundancy:是否使用冗余值 bool 默认不舍弃
'''
self.kernel_size=kernel_size
self.in_chanels=in_chanels
self.out_chanels=out_chanels
self.padding=padding
self.stride=stride
(self.kernel_hight,self.kernel_width)=kernel_size
self.weights,self.bias=self.__parameters()
self.padding_str=padding_str
self.use_bias=use_bias
self.use_redundancy=use_redundancy
def __parameters(self):
'''内部函数,默认标准正态分布初始化参数'''
'''权重尺寸为in_chanels*out_chanels*kernelsize'''
weights=np.random.randn(self.out_chanels,self.in_chanels,self.kernel_hight,self.kernel_width)
'''偏置尺寸为out_kernels'''
bias=np.random.randn(self.out_chanels,1)
return weights,bias
def forward(self,x):
'''前向计算'''
'''输入格式(batch_size,chanels,hight,width)'''
output =[]
(batch_size, chanels, hight, width)=x.shape
for batch_num in range(batch_size):
img=x[batch_num,:,:,:]
for chanel_num in range(chanels):
_img=img[chanel_num,:,:]
print(_img)
kernels=self.weights[:,chanel_num,:,:]
to=[]
for kernel in kernels:
print('kernel:',kernel)
if self.padding>0:
t_img = self.__paddingzeros(_img)#边缘填充
print(t_img)
out_img,_=self.__myConv(t_img,kernel)
to.append(out_img.tolist())
print(out_img)
print(to)
'''计算输出图像的尺寸 '''
img=x[0,0,:,:]
if self.padding>0:
img = self.__paddingzeros(img) # 边缘填充
kernel=self.weights[0,0,:,:]
_,out_shape=self.__myConv(img,kernel)
output=np.array(output).reshape(batch_size,self.out_chanels,out_shape[0],out_shape[1])
'''是否使用偏置b'''
if self.use_bias:
return output+self.bias
else:
return output
def __paddingzeros(self,img):
'''内部函数,默认 边缘0填充'''
if self.padding_str=='zeros':
out=np.zeros(shape=(img.shape[0]+self.padding*2,img.shape[1]+self.padding*2))
out[self.padding:-self.padding,self.padding:-self.padding]=img
return out
elif self.padding_str=='ones':
out=np.ones(shape=(img.shape[0]+self.padding*2,img.shape[1]+self.padding*2))
out[self.padding:-self.padding,self.padding:-self.padding]=img
return out
else:
raise ValueError('Value error: unexcepted key value of 'padding'. excepted key values:zeros,ones')
def __myConv(self,img, kernel):#单层单核卷积
'''内部参数,用于计算单图像单核卷积'''
if (self.stride==(1,1))&(self.kernel_size==(3,3)):
k1 = int((kernel.shape[0] - 1) / 2)
k2 = int((kernel.shape[1] - 1) / 2)
out_img = []
for i in range(k1, img.shape[0] - k1):
for j in range(k2, img.shape[1] - k2):
sight = img[i - 1:i + 2, j - 1:j + 2]
out_img.append(np.sum(np.multiply(np.array(sight), np.array(kernel))))
return np.array(out_img).reshape((img.shape[0] - 2 * k1, img.shape[1] - 2 * k2)),(img.shape[0] - 2 * k1, img.shape[1] - 2 * k2)
else:
k1 = int((kernel.shape[0] - 1) / 2)
k2 = int((kernel.shape[1] - 1) / 2)
#print('k1,k2=',k1,k2)
#print('stride:',self.stride)
out_img = []
right_line=[]
bottom_line=[]
botton_right=[]
#print('img.shape:',img.shape)
for x_index,i in enumerate(range(k1, img.shape[0] - k1)):
if x_index%self.stride[1]==0:#纵向移动
for y_index,j in enumerate(range(k2, img.shape[1] - k2)):
if y_index%self.stride[0]==0:#横向移动
#print('current i j', i, j)
sight = img[i - k1:i + k2+1, j - k1:j + k2+1]
#print(sight)
#print(kernel)
out_img.append(np.sum(np.multiply(np.array(sight), np.array(kernel))))
#print('out img:',out_img)
''' 这里考虑到步长大于1时卷积到右侧边缘或下侧会有边缘不足的情况,因此尝试对边界的溢出进行检测与处理 '''
'''处理边界冗余值'''
if (j+self.stride[0]+k1)>(img.shape[1]-1):
#print('列索引',(j+self.stride[0]+k1),'>',(img.shape[1]-k1))
#print('检测到达右边界,向右移动并填充后几列')
_j=j+self.stride[0]
redundancy=img[i - k1:i + k2+1,_j - k1:]
split_kernel = kernel[:, :np.array(redundancy).shape[1]]
#print(redundancy)
#print(split_kernel)
right_line.append(np.sum(np.multiply(np.array(redundancy), np.array(split_kernel))))
#print( 'right line',right_line)
if (i+self.stride[1]+k2)>(img.shape[0]-1):
#print('行索引',(i+self.stride[1]),'>',(img.shape[0]-1))
#print('检测到达下边界,向下移动并填充下几行')
'''达下边界,向下移动并分别获取冗余值以及分割的卷积核,在对两者计算点积和,其他几种也是这种方法'''
_i=i+self.stride[1]
redundancy=img[_i - k2:, j - k1:j + k2+1]
split_kernel=kernel[:np.array(redundancy).shape[0], :]
#print(redundancy)
#print(split_kernel)
bottom_line.append(np.sum(np.multiply(np.array(redundancy), np.array(split_kernel))))
#print('bottopn line:',bottom_line)
if ((j+self.stride[0]+k1)>(img.shape[1]-1))&((i+self.stride[1]+k2)>(img.shape[0]-1)):
#print('达右下角,向右下移动并填充')
_i+=self.stride[0]
_j+=self.stride[1]
redundancy = img[_i - k2:, _j - k1:]
split_kernel = kernel[:np.array(redundancy).shape[0], :np.array(redundancy).shape[1]]
#print(redundancy)
#print(split_kernel)
botton_right.append(np.sum(np.multiply(np.array(redundancy),np.array(split_kernel))))
out_shape=[0,0]
for i in range( img.shape[0] - 2*k1):
if i%self.stride[1]==0:
out_shape[0]+=1
for i in range( img.shape[1] - 2*k2):
if i %self.stride[0]==0:
out_shape[1]+=1
#print(out_shape)
if self.use_redundancy:
base_img=np.array(out_img).reshape(out_shape)
#print(base_img)
#print(right_line)
#print(bottom_line)
#print(botton_right)
return self.__Conbine(base_img,right_line,bottom_line,botton_right),self.__Conbine(base_img,right_line,bottom_line,botton_right).shape
else:
return np.array(out_img).reshape(out_shape), out_shape
def __Conbine(self,baseimg,rightline,bottomline,rightbottom):
'''内置函数,用于将冗余值信息与基本信息组合到一起'''
br=np.append(np.array(baseimg),np.array(rightline).reshape(len(rightline),1),axis=1)
#print(br)
bbr=np.append(np.array(bottomline),np.array(rightbottom))
bbrr=bbr.reshape(1,len(bbr))
#print(bbr)
#print(bbrr)
return np.append(br,bbrr,axis=0)
def get_parameters(self):
return self.weights,self.bias
def set_parameters(self,weights,bias):
self.weights, self.bias=weights,bias
def set_weights(self,weights):
self.weights=weights
def set_bias(self,bias):
self.bias=bias
def show_img(img):
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.show()
if __name__=='__main__':
img = np.array([[
[
[0, 1, 1, 0, 2],
[2, 2, 2, 2, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 2, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 2, 0, 0, 2]
],
[
[1, 0, 2, 2, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 2, 0],
[1, 2, 1, 2, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 2, 1, 1, 1]
],
[
[2, 1, 2, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 2, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 2, 2, 2],
[2, 1, 0, 0, 1]
]]])
kernel_weights=np.array([[
[
[-1,1,0],
[0,1,0],
[0,1,1]
],
[
[-1,-1,0],
[0,0,0],
[0,-1,0]
],
[
[0,0,-1],
[0,1,0],
[1,-1,-1]
]
],
[
[
[1,1,-1],
[-1,-1,1],
[0,-1,1]
],
[
[0,1,0],
[-1,0,-1],
[-1,1,0]
],
[
[-1,0,0],
[-1,0,1],
[-1,0,0]
]
]])
myconv = myMultipassageConv(3, 2, kernel_size=(3,3), padding=1, stride=(2,2), use_bias=False,
use_redundancy=False,padding_str='zeros')
myconv.set_weights(kernel_weights)
out_img=myconv.forward(img)
#print(out_img)
总结:虽然代码就那么几行,却耗费了我大量的脑细胞,想了各种思路,试了又试,也踩了很多的坑,浪费了很多时间。尤其是自定义算子的冗余信息处理那里是绕来绕去,改了又改,终于改的差不多满意了,一看时间已经很晚了。为了便于下次查看,我没有把注释删掉,也为读者作为参考。
由于冗余信息的原因,自定义卷积层算子在这几个里面是最复杂的,相比较来说,池化层就显得很’小型‘了(其实也并不)。
comefrom:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38975453/article/details/127189403
ref:
NNDL 实验5(上) - HBU_DAVID - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
NNDL 实验5(下) - HBU_DAVID - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
6. 卷积神经网络 — 动手学深度学习 2.0.0-beta1 documentation (d2l.ai)
7. 现代卷积神经网络 — 动手学深度学习 2.0.0-beta1 documentation (d2l.ai)
最后
以上就是饱满眼神最近收集整理的关于NNDL 实验六 卷积神经网络(2)基础算子 基于numpy和基于pytorch的的多通道卷积类与池化层类5.2 卷积神经网络的基础算子的全部内容,更多相关NNDL内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复