任何成熟的MVC框架都应该提供成熟的异常处理机制,当然也可以在execute方法中手动捕捉异常,当捕捉到特定异常时返回特定的逻辑视图名。这种处理方式完全是手动处理异常,非常烦琐且维护性不好。如果我们要改变异常处理方式,就必须修改Action代码。最好的方式是可以通过声明式的方式管理异常处理。
手动捕捉异常示例:
public String execute() throws Exception {
try{
...
}catch(异常1 e){
return 结果1;
}catch(异常2 e){
return 结果2;
}
}
Struts2提供了一种声明式的异常处理方式。Struts2允许通过struts.xml文件来配置异常的处理。
处理用户请求的execute方法抛出所有异常,我们在重写该方法时,完全无需进行任何异常处理,而是把异常直接抛给Struts2框架处理,Struts2框架接收到Action抛出的异常后,根据struts.xml文件配置的异常映射,转入指定的视图资源。
为了使用Struts2的异常处理机制,我们必须打开Struts2的异常映射功能,开启异常映射功能需要一个拦截器。在struts-default.xml配置文件中已经开启了Struts2的异常映射功能。
<interceptors>
...
<!--执行异常处理的映射器 -->
<interceptor name="exception" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ExceptionMappingInterceptor"/>
...
</interceptors>
<!--Struts2默认的拦截器 -->
<interceptor-stack name="defaultStack">
...
<!-- 引用异常映射拦截器-->
<interceptor-ref name="exception"/>
...
</interceptor-stack>
声明式异常捕捉
Struts2的异常处理机制是通过在struts.xml文件中配置<exception-mapping .../>元素完成的,配置该元素时,需要制定两个属性。
1、exception:此属性指定该异常映射所设置的异常类型。
2、result:此属性指定Action出现该异常时,系统转入result属性所指向的结果
根据<exception-mapping .../>元素出现的位置不同,异常映射又可分为两种:
1、局部异常映射:将<exception-mapping .../>元素作为<action .../>元素的子元素配置。
2、全局异常映射:将<exception-mapping .../>元素作为<global-exception-mappings>元素的子元素配置。
全局异常映射对所有的Action都有效,但局部异常映射仅对该异常映射所在的Action内有效。如果局部异常映射和全局异常映射配置了同一个异常类型,在该Action内,局部异常映射会覆盖全局异常映射。
package com.test.action;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.Action;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ModelDriven;
import com.test.dao.User;
import com.test.exception.MyException;
//采用模型驱动的Action必须实现ModelDriven接口
public class LoginAction implements Action,ModelDriven<User>{
//定义用于封装请求参数和处理结果的模型
private User model=new User();
//处理用户请求的execute方法
public String execute() throws Exception {
//手动抛出异常
if(getModel().getName().equalsIgnoreCase("user")){
throw new MyException("自定义异常");
}
//手动抛出异常
if(getModel().getName().equalsIgnoreCase("sql")){
throw new java.sql.SQLException("用户名不能为SQL");
}
//当用户请求参数的name等于admin,密码请求参数为123456时
//返回success字符串,否则返回error
if(getModel().getName().equals("admin")&&
getModel().getPassword().equals("123456")){
return SUCCESS;
}else{
return ERROR;
}
}
//实现ModelDriven接口必须实现的方法
//该方法用于把Action和与之对应的Model实例关联起来
@Override
public User getModel() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return model;
}
}
package com.test.exception;
public class MyException extends Exception{
private String message;
public MyException(String message){
super(message);
this.message=message;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="GBK"?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<!-- 配置struts2的配置文件的根元素 -->
<struts>
<!-- Struts2的Action必须放在指定的包空间下定义 -->
<package name="test" extends="struts-default">
<!-- 此处定义所有的全局结果 -->
<global-results>
<!-- 名为sql的结果,映射到exception.jsp页面 -->
<result name="sql">exception.jsp</result>
<!-- 名为root的结果,映射到exception.jsp页面 -->
<result name="root">exception.jsp</result>
</global-results>
<!-- 此处定义所有的全局异常映射 -->
<global-exception-mappings>
<!-- 当Action抛出SQLException异常时,转入名为sql的结果 -->
<exception-mapping result="sql" exception="java.sql.SQLException"/>
<!-- 当Action抛出Exception异常时,转入名为root的结果 -->
<exception-mapping result="root" exception="java.lang.Exception"/>
</global-exception-mappings>
<!-- 定义login的Action -->
<action name="login" class="com.test.action.LoginAction">
<!-- 当Action抛出MyException异常时,转入名为my的结果 -->
<exception-mapping result="my" exception="com.test.exception.MyException"/>
<!-- 定义处理结果和视图资源之间的映射关系 -->
<result name="my">exception.jsp</result>
<result>error.jsp</result>
<result>welcome.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=GBK"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>登录页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="login" method="post">
<table>
<caption>
<h3>用户登录</h3>
</caption>
<tr>
<td>用户名:<input type="text" name="name" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>密码:<input type="password" name="password" /></td>
</tr>
<tr align="center">
<td colspan="2"><input type="submit" value="登录" /> <input
type="reset" value="重填" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=GBK"
pageEncoding="GBK"%>
<%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=GBK">
<title>成功页面</title>
</head>
<body>
欢迎,<s:property value="model.name"/>,您已经登录!
</body>
</html>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=GBK"
pageEncoding="GBK"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=GBK">
<title>失败页面</title>
</head>
<body>
请重新登录!
</body>
</html>
为了在异常处理页面中显示异常信息,我们可以使用Struts2的标签来输出异常信息。
<s:property value="exception"/>:输出异常对象本身。
<s:property value="exceptionStack"/>:输出异常堆栈信息
对于第一种直接输出异常对象本身的方式,完全可以使用表达式。
本应用的异常处理页面exception.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=GBK"
pageEncoding="GBK"%>
<%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=GBK">
<title>异常处理页面</title>
</head>
<body>
异常信息:<s:property value="exception.message"/>
</body>
</html>
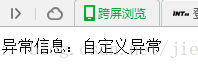
我们将输出异常信息的代码改为:
<!-- 使用struts2标签输出异常堆栈信息 -->
异常信息:<s:property value="exceptionStack"/>

最后
以上就是粗心河马最近收集整理的关于Struts2的异常处理机制的全部内容,更多相关Struts2内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复