opencv教程(四)凸包检测c++
凸包(Convex Hull)是一个计算几何图形学中的概念,在二维欧几里得空间中,凸包可想象为一条刚好包住所有点的橡皮圈。
对于给定二维平面上的点集,凸包就是将最外层的点连接起来构成的凸多边形。物体的凸包检测常常应用在物体识别,手势识别及边界检测等领域。
C++: void convexHull(InputArray points, OutputArray hull, bool clockwise=false, bool returnPoints=true )
函数解析:
实现一个点集的凸包检测。参数points表示输入2维点集,可存储在向量或矩阵Mat中;参数hull为输出的凸包,这是一个整数索引的载体或点的矢量;参数clockwise为方向标志位;参数returnPoints为操作标准位。
承接上篇教程
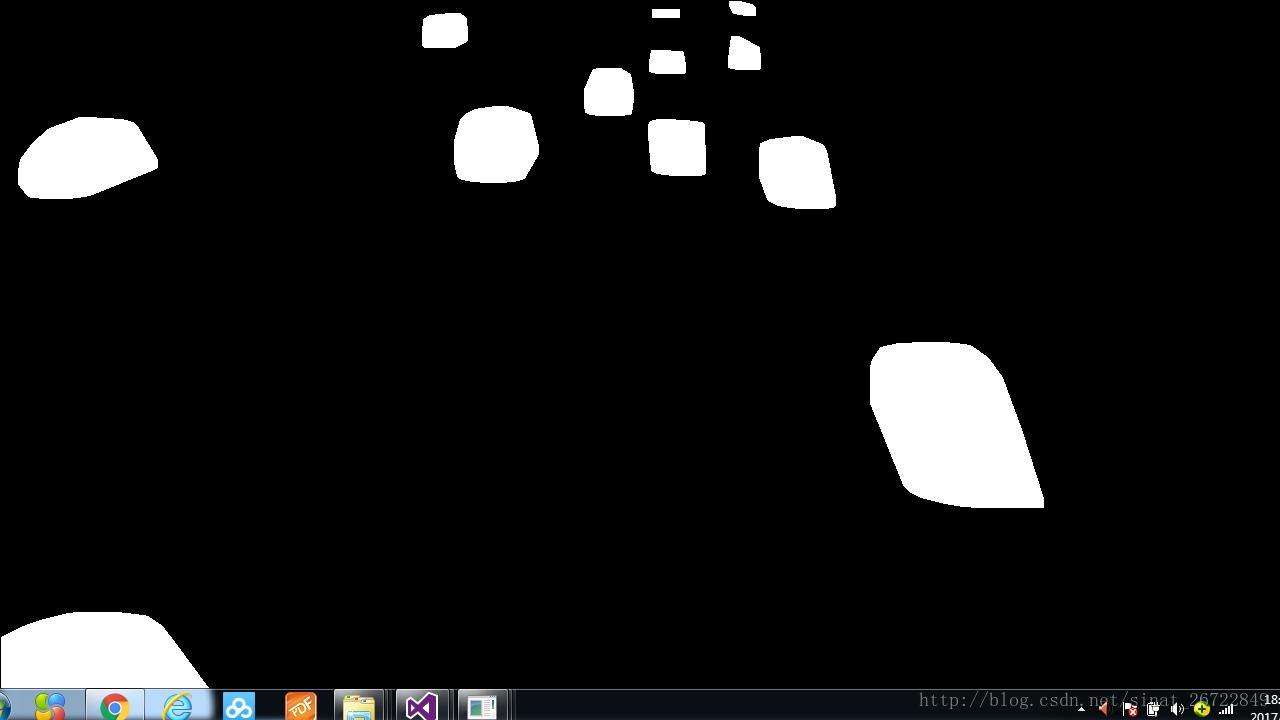
凸包检测(检测行驶的车辆)
#include<opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include<opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include<iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
const cv::Scalar SCALAR_BLACK = cv::Scalar(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
const cv::Scalar SCALAR_WHITE = cv::Scalar(255.0, 255.0, 255.0);
const cv::Scalar SCALAR_YELLOW = cv::Scalar(0.0, 255.0, 255.0);
const cv::Scalar SCALAR_GREEN = cv::Scalar(0.0, 200.0, 0.0);
const cv::Scalar SCALAR_RED = cv::Scalar(0.0, 0.0, 255.0);
void drawAndShowContours(cv::Size imageSize, std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point> > contours, std::string strImageName) {
cv::Mat image(imageSize, CV_8UC3, SCALAR_BLACK);
cv::drawContours(image, contours, -1, SCALAR_WHITE, -1);
cv::imshow(strImageName, image);
}
int main(){
VideoCapture capVideo;
Mat frame_1;
Mat frame_2;
Mat frame_difference;
Mat frame_threshold;
Point crossingLine[2];
capVideo.open("CarsDrivingUnderBridge.mp4");
if (!capVideo.isOpened()){
cout << "Failed to open the video" << endl;
return -1;
}
while (true){
capVideo.read(frame_1);
if (frame_1.empty()) break;
capVideo.read(frame_2);
cvtColor(frame_1, frame_1, CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(frame_2, frame_2, CV_BGR2GRAY);
//高斯滤波,输入像素点与高斯内核进行卷积,卷积和当作输出像素值。size(,,)用于定义内核大小
GaussianBlur(frame_1, frame_1, Size(5, 5), 0);
GaussianBlur(frame_2, frame_2, Size(5, 5), 0);
Calculates the per-element absolute difference between two arrays or between an array and a scalar.
absdiff(frame_1, frame_2, frame_difference);
threshold(frame_difference, frame_threshold, 30, 255.0, CV_THRESH_BINARY);
imshow("threshold", frame_threshold);
//Returns a structuring element of the specified size and shape for morphological operations.
cv::Mat structuringElement3x3 = cv::getStructuringElement(cv::MORPH_RECT, cv::Size(3, 3));
cv::Mat structuringElement5x5 = cv::getStructuringElement(cv::MORPH_RECT, cv::Size(5, 5));
cv::Mat structuringElement7x7 = cv::getStructuringElement(cv::MORPH_RECT, cv::Size(7, 7));
cv::Mat structuringElement15x15 = cv::getStructuringElement(cv::MORPH_RECT, cv::Size(15, 15));
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
//Dilates(扩展) an image by using a specific structuring element.
cv::dilate(frame_threshold, frame_threshold, structuringElement5x5);
cv::dilate(frame_threshold, frame_threshold, structuringElement5x5);
cv::erode(frame_threshold, frame_threshold, structuringElement5x5);
}
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point> > contours;
Mat frame_thresholdCopy = frame_threshold.clone();
cv::findContours(frame_thresholdCopy, contours, cv::RETR_EXTERNAL, cv::CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
drawAndShowContours(frame_threshold.size(), contours, "imgContours");
vector<vector<Point>> convexHulls(contours.size());
for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++){
convexHull(contours[i], convexHulls[i]);
}
drawAndShowContours(frame_threshold.size(), convexHulls, "imgConvexHulls");
if (char(waitKey(1)) == 'q'){
break;
}
}
capVideo.release();
return 0;
}
**一个同名变量不能在main()函数里声明两次,需要多次声明的话就把它转成方法。
最后
以上就是自觉口红最近收集整理的关于opencv教程(四)c++的全部内容,更多相关opencv教程(四)c++内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复