在android开发中,我们可以用flow来为Fragment和Activity采集数据,然后显示出来。当Fragment和Activity不可见时,就应该停止采集。在ViewModel的实践中,LiveData是典型的代表。这些组件都能够感知Fragment和Activity的生命周期的变化。Flow也可以做到这一点。
Demo下载链接
首先,app的依赖不能少了下面的配置:
// Coroutines(includes kotlin flow)
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:1.5.0"
// test Coroutines flow
testImplementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-test:1.6.4"
// lifecycle components
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-extensions:2.2.0"
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx:2.3.1"
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-runtime-ktx:2.3.1"
使用Flow来实现MVVM是相当方便,我们大概来描述一下:
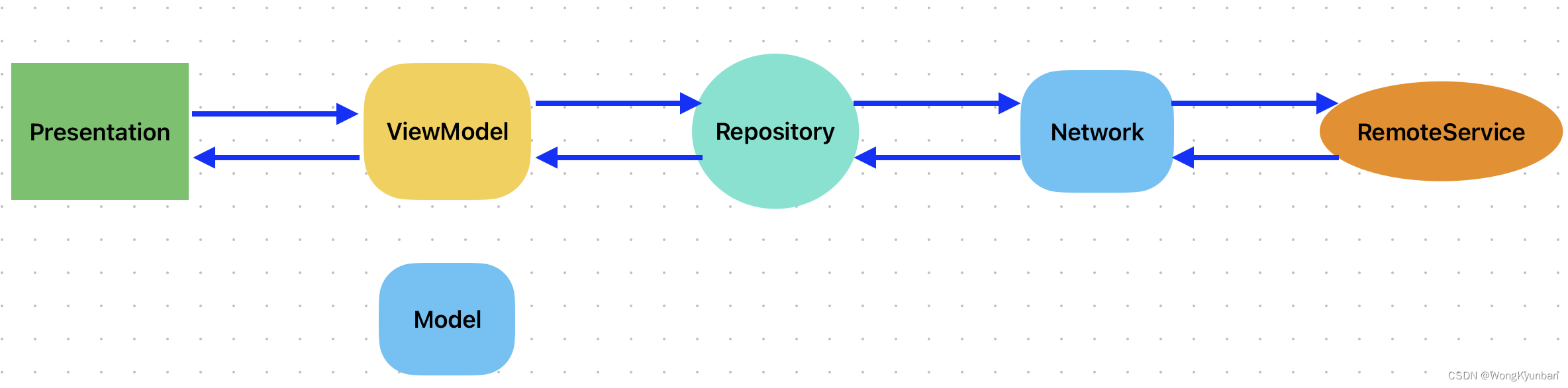
这是我们的数据流。
创建项目的目录结构
首先,亮出我们的目录先。这个目录结构对应着我们上面的数据流的每个环节。
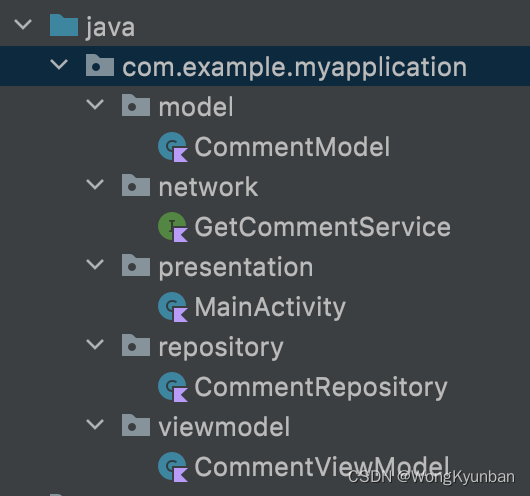
接下来我们一层一层地说它们的实现。
模型层
我们将要从网络获取到的数据格式是这样的:
{
"postId": 1,
"id": 5,
"name": "vero eaque aliquid doloribus et culpa",
"email": "Hayden@althea.biz",
"body": "harum non quasi et rationentempore iure ex voluptates in rationenharum architecto fugit inventore cupiditatenvoluptates magni quo et"
}
因此,我们定义这样一个数据模型:
@Keep
data class CommentModel(
val body: String,
val email: String,
val id: Int,
val name: String,
val postId: Int
)
网络层的数据服务
因为我们用的是Retrofit,所以服务接口这样先这么定,通过此服务返回我们的数据模型。
interface GetCommentService {
@GET("comments/{id}")
suspend fun getCommentWithId(@Path("id") id: Int): CommentModel
}
数据仓库
接下来定义数据仓库,它主要用于获取多种数据源,目前我们只有一种,因此这个可以这么来定:
class CommentRepository(private val apiService: GetCommentService) {
suspend fun getCommentWithId(id: Int): Flow<CommentModel> {
return flow {
val data = apiService.getCommentWithId(id)
emit(data)
}.flowOn(Dispatchers.IO)
}
}
这里是我们应用Flow的关键点之一。首先flow操作符,创建一个Flow,这是一个冷流,也就是只要一用末端操作符collect之类,就可以触发它调用网络层的接口。因为Flow是在coroutine之上建立的技术,而且我们的网络层服务也是suspend的,也就是说可以挂起的,那么,就是说,一对这个flow对象调collect操符进行网络请求,在网络请求没有结束之前,都会被挂起,网络回来后就继续后面emit(data)的操作。flowOn则只是将flow的执行上下切换到IO。
ViewModel
这一层要负责调用数据仓库的数据源,并将数据暴露给展现层。
class CommentViewModel : ViewModel() {
private val BASE_URL = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/"
private val apiService = Retrofit.Builder().baseUrl(BASE_URL)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create(GsonBuilder().create()))
.build()
.create(GetCommentService::class.java)
private val repository = CommentRepository(apiService)
private val commentMutableStateFlow = MutableStateFlow<CommentModel?>(null)
val commentStateFlow: StateFlow<CommentModel?> = commentMutableStateFlow
init {
getACommentWithId(1)
}
fun getACommentWithId(id: Int) {
val job = viewModelScope.launch {
repository.getCommentWithId(id).catch {
commentMutableStateFlow.value = null
}.collect {
commentMutableStateFlow.value = it
}
}
}
}
这一层里负责调用数据仓库的源的代码也必须在coroutine的上下文中调用:
val job = viewModelScope.launch {
repository.getCommentWithId(id).catch {
commentMutableStateFlow.value = null
}.collect {
commentMutableStateFlow.value = it
}
}
ViewModel提供了这样一个协程上下文viewModelScope,实际上是提供了一个协程的执行范围,这个范围里就有对应的Context。
说完了调用,那么ViewModel向展现层暴露数据也是用了Flow,而且这里有个技巧介绍给大家:
private val commentMutableStateFlow = MutableStateFlow<CommentModel?>(null)
val commentStateFlow: StateFlow<CommentModel?> = commentMutableStateFlow
我们用这个commentMutableStateFlow更新数据,它是私有的,因此展示层不能改变它的值,我们也不想它改变,所以我们会提供一个不可改变,只可读取的变量给展示层:commentStateFlow。
展现层
private lateinit var commentViewModel: CommentViewModel
private var currentId = 1;
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val button = findViewById<Button>(R.id.button)
val textView = findViewById<TextView>(R.id.textView)
button.setOnClickListener {
currentId += 1
commentViewModel.getACommentWithId(currentId)
}
commentViewModel = ViewModelProvider(this).get(CommentViewModel::class.java)
lifecycleScope.launchWhenStarted {
commentViewModel.commentStateFlow.collect {
it?.let { comment ->
textView.text = "${comment.id} nn ${comment.email} nn ${comment.body}"
}
}
}
}
展现层读取数据的地方,也必须在一个协程范围里。
Flow的简单使用就是这样啦。
最后
以上就是伶俐钢笔最近收集整理的关于如何在android开发中使用Kotlin Flow(二)的全部内容,更多相关如何在android开发中使用Kotlin内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复