1.controller中加参数
这种方法的实现最简单
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public void test(HttpServletRequest request) throws InterruptedException {
// 模拟程序执行了一段时间
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}Controller获取到request对象,如果需要在service中也使用这个对象,需要将request对象传递进去;这个方法是线程安全的;但是缺点比较明显:
1>如果在controller中多个方法都需要添加request对象,那么在每个方法的参数中都需要添加一遍;
2>request对象的获取只能从controller开始,如果使用request对象的地方在函数中调用的层次比较深,那么整个调用链上都需要传入该参数,相当不方便;
2.自动注入的方式
@Controller
public class TestController{
@Autowired
private HttpServletRequest request; //自动注入request
@RequestMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException{
//模拟程序执行了一段时间
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}这种方式同样是线程安全的;实现分析:Spring 中的controller默认是单例模式,但是在其中注入的httpServletReqeust却是安全安全的,是因为初始化的时候,并不是注入了一个request对象,而是注入了一个代理(proxy),当bean中需要该对象的时候,通过代理再去获取;可以断点调试下看看
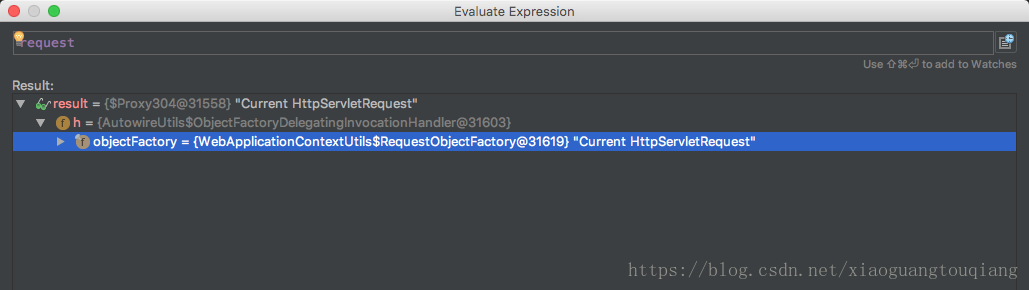
可以看到request实际是一个代理,代理具体的实现如下所示;之前的文章有提到动态代理的实现,如果调用request方法的时候,其实调用objectFactory对象的方法来执行
private static class ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private final ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory;
public ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler(ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) {
this.objectFactory = objectFactory;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
if (methodName.equals("equals")) {
// Only consider equal when proxies are identical.
return (proxy == args[0]);
}
else if (methodName.equals("hashCode")) {
// Use hashCode of proxy.
return System.identityHashCode(proxy);
}
else if (methodName.equals("toString")) {
return this.objectFactory.toString();
}
try {
return method.invoke(this.objectFactory.getObject(), args);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}下面跟踪下objectFactory对象,从上面可以看出是WebApplicationContextUtils类的RequestObjectFactory对象,具体代码如下
private static class RequestObjectFactory implements ObjectFactory<ServletRequest>, Serializable {
@Override
public ServletRequest getObject() {
return currentRequestAttributes().getRequest();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Current HttpServletRequest";
}
}private static ServletRequestAttributes currentRequestAttributes() {
RequestAttributes requestAttr = RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes();
if (!(requestAttr instanceof ServletRequestAttributes)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Current request is not a servlet request");
}
return (ServletRequestAttributes) requestAttr;
}public static RequestAttributes currentRequestAttributes() throws IllegalStateException {
RequestAttributes attributes = getRequestAttributes();
if (attributes == null) {public static RequestAttributes getRequestAttributes() {
RequestAttributes attributes = requestAttributesHolder.get();
if (attributes == null) {
attributes = inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.get();
}
return attributes;
}private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> requestAttributesHolder =
new NamedThreadLocal<RequestAttributes>("Request attributes");
private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> inheritableRequestAttributesHolder =
new NamedInheritableThreadLocal<RequestAttributes>("Request context");相关的代码片段如图,这里可以看出生成request对象是线程的局部变量ThreadLocal,因此这里的request也是局部变量;所有是线程安全的;
这种方法的优点:1>.注入不局限于controller中,可以是任何的bean,service,Repository及普通的Bean;
2>.除了注入request对象,该方法还可以注入其他scope为request或session的对象,如response对象、session对象等;并保证线程安全。
3>.大量减少代码的冗余,不用通过层层的参数传递的方式传递很深;
4>.注意一点,如果在另外的线程,比如new了一个线程或者在@Asyn标记的方法中,会创建一个新的线程,那么这种方式不行的;
3.手动注入
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) (RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes())).getRequest();
// 模拟程序执行了一段时间
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}最后
以上就是迷你鸵鸟最近收集整理的关于Spring获取HttpServletRequst 的几种方法的全部内容,更多相关Spring获取HttpServletRequst内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复