上节课我们成功的连接了数据库,这节课我们试试来用java操作数据库
想要操作数据库,必定要借助sql,java.sql包里提供了一些类和接口来方便我们执行sql语句
Demo 01:
package jdbc; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; //jdbc 操作 mysql 教学 public class JdbcOperateMysqlTeach { public static void main(String[] args) { /** * jdbc 操作 mysql步骤: * 1. 连接数据库,获得Connection对象 * 2. 使用Connection对象创建Statement对象 * 3. 写好sql * 4. 使用Statement对象执行sql * 5. 关闭连接 */ try { //1 连接数据库,获得Connection对象 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/teach"; String user = "root"; String password = "root"; Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password); //2. 使用Connection对象创建Statement对象 //调用Connection对象的createStatement()方法即可创建一个Statement对象 //注意,只有使用这种方式创建的Statement对象在能操作connection对象连接的数据库 Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); //3. 写好sql String sql = "insert into t_user(name,age) values ('zhangsan',null);"; //4. 使用Statement对象执行sql //注意: //4.1 当sql语句是 insert、update、delete语句时使用executeUpdate()方法 //4.2 当sql语句时 select语句时使用executeQuery()方法 statement.executeUpdate(sql); //5. 关闭连接 connection.close(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
运行前:
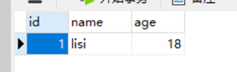
运行后:
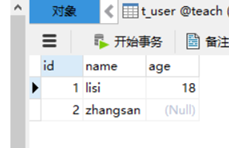
插入成功
Demo 02:
删除zhangsan
package jdbc; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; //jdbc 操作 mysql 教学 public class JdbcOperateMysqlTeach { public static void main(String[] args) { /** * jdbc 操作 mysql步骤: * 1. 连接数据库,获得Connection对象 * 2. 使用Connection对象创建Statement对象 * 3. 写好sql * 4. 使用Statement对象执行sql * 5. 关闭连接 */ try { //1 连接数据库,获得Connection对象 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/teach"; String user = "root"; String password = "root"; Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password); //2. 使用Connection对象创建Statement对象 //调用Connection对象的createStatement()方法即可创建一个Statement对象 //注意,只有使用这种方式创建的Statement对象在能操作connection对象连接的数据库 Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); //3. 写好sql String sql = "delete from t_user where id = 2;"; //4. 使用Statement对象执行sql //注意: //4.1 当sql语句是 insert、update、delete语句时使用executeUpdate()方法 //4.2 当sql语句时 select语句时使用executeQuery()方法 statement.executeUpdate(sql); //5. 关闭连接 connection.close(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
执行前:
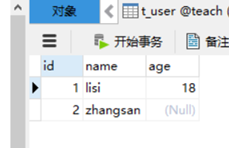
执行后:
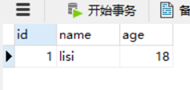
下节课讲查询。
最后
以上就是昏睡绿茶最近收集整理的关于jdbc篇第2课:使用jdbc操作数据库的全部内容,更多相关jdbc篇第2课内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复