AppStart和AppUpdate是MS介绍其智能客户端时所涉及的两个通用的库。
AppStart,相当于一个shell,根据配置文件拉起要管理的进程。如果进程退出,而且查询退出码为2时,会重启进程。
AppUpdate,自定义控件,根据其属性来读取配置文件,当配置文件发生更新时,根据配置文件自动下载待管理的dll,更新完毕后提示用户是否重启,如果重启则退出进程,且设置退出码为2。
代码剪辑:
AppStart,其是根据配置文件来确定进程是从应用程序域启动还是进程启动
启动应用程序域和根据退出码判断是否需要重启
 private
static
void
StartAndWait_Domain()
private
static
void
StartAndWait_Domain() {
{ bool flag1 = true;
bool flag1 = true; int num1 = 0;
int num1 = 0; while (flag1)
while (flag1) {
{ try
try {
{ num1 = AppStart.StartApp_Domain(false);
num1 = AppStart.StartApp_Domain(false); }
} catch (Exception exception1)
catch (Exception exception1) {
{ AppStart.HandleTerminalError(exception1);
AppStart.HandleTerminalError(exception1); }
} if (num1 == 2) //根据退出码判断是否需要重启
if (num1 == 2) //根据退出码判断是否需要重启 {
{ flag1 = true;
flag1 = true;  }
} else
else {
{ flag1 = false;
flag1 = false; }
} }
} }
}
 public
static
int
StartApp_Domain(
bool
restartApp)
public
static
int
StartApp_Domain(
bool
restartApp) {
{ AppStartConfig config1 = AppStart.LoadConfig();
AppStartConfig config1 = AppStart.LoadConfig(); AppStart.AppExePath = config1.AppExePath;
AppStart.AppExePath = config1.AppExePath; int num1 = 0;
int num1 = 0; try
try {
{ string[] textArray1;
string[] textArray1; AppDomain domain1 = AppDomain.CreateDomain("New App Domain", AppDomain.CurrentDomain.Evidence, Path.GetDirectoryName(AppStart.AppExePath) + @"", "", false);
AppDomain domain1 = AppDomain.CreateDomain("New App Domain", AppDomain.CurrentDomain.Evidence, Path.GetDirectoryName(AppStart.AppExePath) + @"", "", false); if (restartApp)
if (restartApp) {
{ textArray1 = AppStart.RestartCommandLineArgs;
textArray1 = AppStart.RestartCommandLineArgs; }
} else
else {
{ textArray1 = AppStart.CommandLineArgs;
textArray1 = AppStart.CommandLineArgs; }
} num1 = domain1.ExecuteAssembly(AppStart.AppExePath, AppDomain.CurrentDomain.Evidence, textArray1);
num1 = domain1.ExecuteAssembly(AppStart.AppExePath, AppDomain.CurrentDomain.Evidence, textArray1); AppDomain.Unload(domain1); //应用程序执行完了,关闭应用程序域
AppDomain.Unload(domain1); //应用程序执行完了,关闭应用程序域 }
} catch (Exception exception1)
catch (Exception exception1) {
{ AppStart.HandleTerminalError(exception1);
AppStart.HandleTerminalError(exception1); }
} return num1;
return num1; }
}
private static Process AppProcess; //子进程定义
 private
static
void
StartAndWait_Process()
private
static
void
StartAndWait_Process() {
{ bool flag1 = true;
bool flag1 = true; AppStart.StartApp_Process(false);
AppStart.StartApp_Process(false); while (flag1)
while (flag1) {
{ try
try {
{ AppStart.AppProcess.WaitForExit(); //等待退出
AppStart.AppProcess.WaitForExit(); //等待退出 }
} catch (Exception)
catch (Exception) {
{ return;
return; }
} if (AppStart.AppProcess.ExitCode == 2)//根据退出码判断是否需要重启
if (AppStart.AppProcess.ExitCode == 2)//根据退出码判断是否需要重启 {
{ flag1 = true;
flag1 = true; AppStart.AppProcess = null;
AppStart.AppProcess = null; AppStart.StartApp_Process(true);
AppStart.StartApp_Process(true); }
} else
else {
{ flag1 = false;
flag1 = false; }
} }
} }
}

 public
static
void
StartApp_Process(
bool
restartApp)
public
static
void
StartApp_Process(
bool
restartApp) {
{ AppStartConfig config1 = AppStart.LoadConfig();
AppStartConfig config1 = AppStart.LoadConfig(); AppStart.AppExePath = config1.AppExePath;
AppStart.AppExePath = config1.AppExePath; if ((AppStart.AppProcess == null) || AppStart.AppProcess.HasExited)
if ((AppStart.AppProcess == null) || AppStart.AppProcess.HasExited) {
{ try
try {
{ ProcessStartInfo info1 = new ProcessStartInfo(AppStart.AppExePath);
ProcessStartInfo info1 = new ProcessStartInfo(AppStart.AppExePath); info1.WorkingDirectory = Path.GetDirectoryName(AppStart.AppExePath);
info1.WorkingDirectory = Path.GetDirectoryName(AppStart.AppExePath); if (restartApp)
if (restartApp) {
{ info1.Arguments = AppStart.RestartCommandLineString;
info1.Arguments = AppStart.RestartCommandLineString; }
} else
else {
{ info1.Arguments = AppStart.CommandLineString;
info1.Arguments = AppStart.CommandLineString; }
} AppStart.AppProcess = Process.Start(info1);
AppStart.AppProcess = Process.Start(info1); }
} catch (Exception exception1)
catch (Exception exception1) {
{ AppStart.HandleTerminalError(exception1);
AppStart.HandleTerminalError(exception1); }
} }
} }
}
附:
应用程序域的另外一个例子
 ApplicationHost.CreateApplicationHost
ApplicationHost.CreateApplicationHost 参数
参数 hostType
hostType  要在新应用程序域中创建的由用户提供的类的名称。
要在新应用程序域中创建的由用户提供的类的名称。  virtualDir
virtualDir  应用程序域的虚拟目录;例如
/
myapp。
应用程序域的虚拟目录;例如
/
myapp。  physicalDir
physicalDir  ASP.NET 页所在的应用程序域的物理目录;例如 c:mypages。
ASP.NET 页所在的应用程序域的物理目录;例如 c:mypages。  返回值
返回值 由用户提供的用于将调用封送到新创建的应用程序域中的类的实例。
由用户提供的用于将调用封送到新创建的应用程序域中的类的实例。
 {
{ _myhost = (MyHost)ApplicationHost.CreateApplicationHost(typeof(MyHost), _virtualPath, _physicalPath);
_myhost = (MyHost)ApplicationHost.CreateApplicationHost(typeof(MyHost), _virtualPath, _physicalPath); _myhost.Configure(this, _port, _virtualPath, _physicalPath, _installPath);
_myhost.Configure(this, _port, _virtualPath, _physicalPath, _installPath); {
{ _onAppDomainUnload = new EventHandler(OnAppDomainUnload);
_onAppDomainUnload = new EventHandler(OnAppDomainUnload); Thread.GetDomain().DomainUnload += _onAppDomainUnload;
Thread.GetDomain().DomainUnload += _onAppDomainUnload; }
} }
}
AppUpdate
涉及点,
文件是否更新:
1. 本地文件日期设置到HTTP头中发送过去,可以避免重复下载相同文件;更新文件后用HTTP头日期设置更新文件日期。
2. 用当前用户信息设置HTTP头的身份验证信息。
 public
static
void
UpdateFile(
string
url,
string
filePath)
public
static
void
UpdateFile(
string
url,
string
filePath) {
{ HttpWebResponse response1;
HttpWebResponse response1; HttpWebRequest request1 = (HttpWebRequest) WebRequest.Create(url);
HttpWebRequest request1 = (HttpWebRequest) WebRequest.Create(url); request1.Headers.Add("Translate: f");
request1.Headers.Add("Translate: f"); request1.Credentials = CredentialCache.DefaultCredentials; //获取应用程序的系统凭据,设置身份验证信息
request1.Credentials = CredentialCache.DefaultCredentials; //获取应用程序的系统凭据,设置身份验证信息 if (File.Exists(filePath))
if (File.Exists(filePath)) {
{ request1.IfModifiedSince = WebFileLoader.LastModFromDisk(filePath){FileInfo info1 = new FileInfo(filePath);
request1.IfModifiedSince = WebFileLoader.LastModFromDisk(filePath){FileInfo info1 = new FileInfo(filePath); return info1.LastWriteTime;};
return info1.LastWriteTime;}; }
} try
try {
{ response1 = (HttpWebResponse) request1.GetResponse();
response1 = (HttpWebResponse) request1.GetResponse(); }
} catch (WebException exception1)
catch (WebException exception1) {
{ if (exception1.Response == null)
if (exception1.Response == null) {
{ throw;
throw; }
} HttpWebResponse response2 = (HttpWebResponse) exception1.Response;
HttpWebResponse response2 = (HttpWebResponse) exception1.Response; if (response2.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.NotModified) //文件没有修改就不会下载且发生此异常
if (response2.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.NotModified) //文件没有修改就不会下载且发生此异常 {
{ exception1.Response.Close();
exception1.Response.Close(); return;
return; }
} exception1.Response.Close();
exception1.Response.Close(); throw;
throw; }
} Stream stream1 = null;
Stream stream1 = null; try
try {
{ stream1 = response1.GetResponseStream();
stream1 = response1.GetResponseStream(); WebFileLoader.CopyStreamToDisk(stream1, filePath);
WebFileLoader.CopyStreamToDisk(stream1, filePath); DateTime time1 = Convert.ToDateTime(response1.GetResponseHeader("Last-Modified"));
DateTime time1 = Convert.ToDateTime(response1.GetResponseHeader("Last-Modified")); File.SetLastWriteTime(filePath, time1); //根据目标文件时间设置更新文件修改时间
File.SetLastWriteTime(filePath, time1); //根据目标文件时间设置更新文件修改时间 }
} catch (Exception)
catch (Exception) {
{ throw;
throw; }
} finally
finally {
{ if (stream1 != null)
if (stream1 != null) {
{ stream1.Close();
stream1.Close(); }
} if (response1 != null)
if (response1 != null) {
{ response1.Close();
response1.Close(); }
} }
} }
}
 private
static
void
CopyStreamToDisk(Stream responseStream,
string
filePath)
private
static
void
CopyStreamToDisk(Stream responseStream,
string
filePath) {
{ byte[] buffer1 = new byte[0x1000];
byte[] buffer1 = new byte[0x1000]; Random random1 = new Random();
Random random1 = new Random(); string text1 = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("temp") + @"";
string text1 = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("temp") + @""; text1 = text1 + filePath.Remove(0, filePath.LastIndexOf(@"") + 1);
text1 = text1 + filePath.Remove(0, filePath.LastIndexOf(@"") + 1); text1 = text1 + random1.Next(0x2710).ToString() + ".tmp";
text1 = text1 + random1.Next(0x2710).ToString() + ".tmp"; FileStream stream1 = File.Open(text1, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.ReadWrite);
FileStream stream1 = File.Open(text1, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.ReadWrite); for (int num1 = responseStream.Read(buffer1, 0, 0x1000); num1 > 0; num1 = responseStream.Read(buffer1, 0, 0x1000))
for (int num1 = responseStream.Read(buffer1, 0, 0x1000); num1 > 0; num1 = responseStream.Read(buffer1, 0, 0x1000)) {
{ stream1.Write(buffer1, 0, num1);
stream1.Write(buffer1, 0, num1); }
} stream1.Close();
stream1.Close(); if (File.Exists(filePath))
if (File.Exists(filePath)) {
{ File.Delete(filePath);
File.Delete(filePath); }
} File.Move(text1, filePath);
File.Move(text1, filePath); }
}
远程到本地的目录拷贝:
先获取远程目录信息,然后根据目录信息更新文件,更新文件操作就是上面那些
 public
static
SortedList GetDirectoryContents(
string
url,
bool
deep)
public
static
SortedList GetDirectoryContents(
string
url,
bool
deep) {
{ StreamReader reader1;
StreamReader reader1; HttpWebRequest request1 = (HttpWebRequest) WebRequest.Create(url);
HttpWebRequest request1 = (HttpWebRequest) WebRequest.Create(url); request1.Headers.Add("Translate: f");
request1.Headers.Add("Translate: f"); request1.Credentials = CredentialCache.DefaultCredentials;
request1.Credentials = CredentialCache.DefaultCredentials; string text1 = "<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?><a:propfind xmlns:a="DAV:"><a:prop><a:displayname/><a:iscollection/><a:getlastmodified/></a:prop></a:propfind>";
string text1 = "<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?><a:propfind xmlns:a="DAV:"><a:prop><a:displayname/><a:iscollection/><a:getlastmodified/></a:prop></a:propfind>"; request1.Method = "PROPFIND";
request1.Method = "PROPFIND"; if (deep)
if (deep) {
{ request1.Headers.Add("Depth: infinity");
request1.Headers.Add("Depth: infinity"); }
} else
else {
{ request1.Headers.Add("Depth: 1");
request1.Headers.Add("Depth: 1"); }
} request1.ContentLength = text1.Length;
request1.ContentLength = text1.Length; request1.ContentType "text/xml";
request1.ContentType "text/xml"; Stream stream1 = request1.GetRequestStream();
Stream stream1 = request1.GetRequestStream(); stream1.Write(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(text1), 0, Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(text1).Length);
stream1.Write(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(text1), 0, Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(text1).Length); stream1.Close();
stream1.Close(); try
try {
{ HttpWebResponse response1 = (HttpWebResponse) request1.GetResponse();
HttpWebResponse response1 = (HttpWebResponse) request1.GetResponse(); reader1 = new StreamReader(response1.GetResponseStream());
reader1 = new StreamReader(response1.GetResponseStream()); }
} catch (WebException exception1)
catch (WebException exception1) {
{ throw exception1;
throw exception1; }
} StringBuilder builder1 = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder builder1 = new StringBuilder(); char[] chArray1 = new char[0x400];
char[] chArray1 = new char[0x400]; int num1 = 0;
int num1 = 0; for (num1 = reader1.Read(chArray1, 0, 0x400); num1 > 0; num1 = reader1.Read(chArray1, 0, 0x400))
for (num1 = reader1.Read(chArray1, 0, 0x400); num1 > 0; num1 = reader1.Read(chArray1, 0, 0x400)) {
{ builder1.Append(chArray1, 0, num1);
builder1.Append(chArray1, 0, num1); }
} reader1.Close();
reader1.Close(); XmlDocument document1 = new XmlDocument();
XmlDocument document1 = new XmlDocument(); document1.LoadXml(builder1.ToString());
document1.LoadXml(builder1.ToString()); XmlNamespaceManager manager1 = new XmlNamespaceManager(document1.NameTable);
XmlNamespaceManager manager1 = new XmlNamespaceManager(document1.NameTable); manager1.AddNamespace("a", "DAV:");
manager1.AddNamespace("a", "DAV:"); XmlNodeList list1 = document1.SelectNodes("//a:prop/a:displayname", manager1);
XmlNodeList list1 = document1.SelectNodes("//a:prop/a:displayname", manager1); XmlNodeList list2 = document1.SelectNodes("//a:prop/a:iscollection", manager1);
XmlNodeList list2 = document1.SelectNodes("//a:prop/a:iscollection", manager1); XmlNodeList list3 = document1.SelectNodes("//a:prop/a:getlastmodified", manager1);
XmlNodeList list3 = document1.SelectNodes("//a:prop/a:getlastmodified", manager1); XmlNodeList list4 = document1.SelectNodes("//a:href", manager1);
XmlNodeList list4 = document1.SelectNodes("//a:href", manager1); SortedList list5 = new SortedList();
SortedList list5 = new SortedList(); for (int num2 = 0; num2 < list1.Count; num2++)
for (int num2 = 0; num2 < list1.Count; num2++) {
{ if (list4[num2].InnerText.ToLower(new CultureInfo("en-US")).TrimEnd(new char[] { '/' }) != url.ToLower(new CultureInfo("en-US")).TrimEnd(new char[] { '/' }))
if (list4[num2].InnerText.ToLower(new CultureInfo("en-US")).TrimEnd(new char[] { '/' }) != url.ToLower(new CultureInfo("en-US")).TrimEnd(new char[] { '/' })) {
{ Resource resource1 = new Resource();
Resource resource1 = new Resource(); resource1.Name = list1[num2].InnerText;
resource1.Name = list1[num2].InnerText; resource1.IsFolder = Convert.ToBoolean(Convert.ToInt32(list2[num2].InnerText));
resource1.IsFolder = Convert.ToBoolean(Convert.ToInt32(list2[num2].InnerText)); resource1.Url = list4[num2].InnerText;
resource1.Url = list4[num2].InnerText; resource1.LastModified = Convert.ToDateTime(list3[num2].InnerText);
resource1.LastModified = Convert.ToDateTime(list3[num2].InnerText); list5.Add(resource1.Url, resource1);
list5.Add(resource1.Url, resource1); }
} }
} return list5;
return list5; }=
}=
 public
static
int
CopyDirectory(
string
url,
string
filePath)
public
static
int
CopyDirectory(
string
url,
string
filePath) {
{ int num1 = 0;
int num1 = 0; SortedList list1 = WebFileLoader.GetDirectoryContents(url, false);
SortedList list1 = WebFileLoader.GetDirectoryContents(url, false); foreach (object obj1 in list1)
foreach (object obj1 in list1) {
{ string text1;
string text1; DictionaryEntry entry1 = (DictionaryEntry) obj1;
DictionaryEntry entry1 = (DictionaryEntry) obj1; Resource resource1 = (Resource) entry1.Value;
Resource resource1 = (Resource) entry1.Value; if (!Directory.Exists(filePath))
if (!Directory.Exists(filePath)) {
{ Directory.CreateDirectory(filePath);
Directory.CreateDirectory(filePath); }
} if (!resource1.IsFolder)
if (!resource1.IsFolder) {
{ num1++;
num1++; text1 = filePath + resource1.Name;
text1 = filePath + resource1.Name; if (!File.Exists(text1))
if (!File.Exists(text1)) {
{ WebFileLoader.UpdateFile(resource1.Url, text1);
WebFileLoader.UpdateFile(resource1.Url, text1); continue;
continue; }
} if (resource1.LastModified > WebFileLoader.LastModFromDisk(text1))
if (resource1.LastModified > WebFileLoader.LastModFromDisk(text1)) {
{ WebFileLoader.UpdateFile(resource1.Url, text1);
WebFileLoader.UpdateFile(resource1.Url, text1); }
} }
} else
else {
{ text1 = filePath + resource1.Name + @"";
text1 = filePath + resource1.Name + @""; num1 += WebFileLoader.CopyDirectory(resource1.Url, text1); //递归
num1 += WebFileLoader.CopyDirectory(resource1.Url, text1); //递归 }
} }
} return num1;
return num1; }
}

重启程序
 public
void
RestartApp()
public
void
RestartApp() {
{ Environment.ExitCode = 2;
Environment.ExitCode = 2; Application.Exit();
Application.Exit(); this.Poller.Stop();
this.Poller.Stop(); this.Downloader.Stop();
this.Downloader.Stop(); }
}
另外一个涉及点,如果实现自定义控件
 public
class
AppUpdater : Component, ISupportInitialize
public
class
AppUpdater : Component, ISupportInitialize {
{ public AppUpdater()
public AppUpdater() {
{ this.components = null;
this.components = null; this._UpdateUrl = "http://localhost/";
this._UpdateUrl = "http://localhost/"; this._ChangeDetectionMode = ChangeDetectionModes.DirectFileCheck;
this._ChangeDetectionMode = ChangeDetectionModes.DirectFileCheck; this._ShowDefaultUI = false;
this._ShowDefaultUI = false; this._AutoFileLoad = false;
this._AutoFileLoad = false; this.Poller = new ServerPoller(this);
this.Poller = new ServerPoller(this); this.Downloader = new AppDownloader(this);
this.Downloader = new AppDownloader(this); }
}
 public AppUpdater(IContainer container)
public AppUpdater(IContainer container) {
{ this.components = null;
this.components = null; this._UpdateUrl = "http://localhost/";
this._UpdateUrl = "http://localhost/"; this._ChangeDetectionMode = ChangeDetectionModes.DirectFileCheck;
this._ChangeDetectionMode = ChangeDetectionModes.DirectFileCheck; this._ShowDefaultUI = false;
this._ShowDefaultUI = false; this._AutoFileLoad = false;
this._AutoFileLoad = false; this.Poller = new ServerPoller(this);
this.Poller = new ServerPoller(this); this.Downloader = new AppDownloader(this);
this.Downloader = new AppDownloader(this); container.Add(this);
container.Add(this); this.InitializeComponent();
this.InitializeComponent(); }
} 类可被设置的属性
类可被设置的属性 [DefaultValue(2), Description("Number of times times to retry the app update.")]
[DefaultValue(2), Description("Number of times times to retry the app update.")] public int UpdateRetryAttempts
public int UpdateRetryAttempts {
{ get
get {
{ return this._UpdateRetryAttempts;
return this._UpdateRetryAttempts; }
} set
set {
{ this._UpdateRetryAttempts = value;
this._UpdateRetryAttempts = value; }
} }
}
 内嵌另外一个成员,其也支持设置属性
内嵌另外一个成员,其也支持设置属性 [Category("AppUpdate Configuration"), Description("The object that periodically polls for new updates."), DesignerSerializationVisibility(DesignerSerializationVisibility.Content), TypeConverter(typeof(ExpandableObjectConverter))]
[Category("AppUpdate Configuration"), Description("The object that periodically polls for new updates."), DesignerSerializationVisibility(DesignerSerializationVisibility.Content), TypeConverter(typeof(ExpandableObjectConverter))] public ServerPoller Poller
public ServerPoller Poller {
{ get
get {
{ return this._Poller;
return this._Poller; }
} set
set {
{ this._Poller = value;
this._Poller = value; }
} }
} 
 private void InitializeComponent()
private void InitializeComponent() {
{  this.components = new Container();
this.components = new Container(); }
}  }
}
附上相关转文一片
通过应用程序域AppDomain加载和卸载程序集
微 软装配车的大门似乎只为货物装载敞开大门,却将卸载工人拒之门外。车门的钥匙只有一把,若要获得还需要你费一些心思。我在学习Remoting的时候,就 遇到一个扰人的问题,就是Remoting为远程对象仅提供Register的方法,如果你要注销时,只有另辟蹊径。细心的开发员,会发现Visual Studio.Net中的反射机制,同样面临这个问题。你可以找遍MSDN的所有文档,在Assembly类中,你永远只能看到Load方法,却无法寻觅 到Unload的踪迹。难道我们装载了程序集后,就不能再将它卸载下来吗?
想一想这样一个场景。你通过反射动态加载了一个dll文件,如今你需要在未关闭程序的情况下,删除或覆盖该文件,那么结果会怎样?很遗憾,系统会提示你无法访问该文件。事实上该文件正处于被调用的状态,此时要对该文件进行修改,就会出现争用的情况。
显然,为程序集提供卸载功能是很有必要的,但为什么微软在其产品中不提供该功能呢?CLR 产品单元经理(Unit Manager) Jason Zander 在文章 Why isn't there an Assembly.Unload method? 中解释了没有实现该功能的原因。Flier_Lu在其博客里(Assembly.Unload)有详细的中文介绍。文中介绍了解决卸载程序集的折中方法。Eric Gunnerson在文章《AppDomain 和动态加载》中也提到:Assembly.Load() 通常运行良好,但程序集无法独立卸载(只有 AppDomain 可以卸载)。Enrico Sabbadin 在文章《Unload Assemblies From an Application Domain》也有相关VB.Net实现该功能的相关说明。
尤其是Flier_Lu的博客里已经有了很详细的代码。不过,这些代码没有详细地说明。我在我的项目中也需要这一项功能。这段代码给了我很大的提示。但在实际的实现中,还是遇到一些具体的问题。所以我还是想再谈谈我的体会。
通过AppDomain来实现程序集的卸载,这个思路是非常清晰的。由于在程序设计中,非特殊的需要,我们都是运行在同一个应用程序域中。由于程序 集的卸载存在上述的缺陷,我们必须要关闭应用程序域,方可卸载已经装载的程序集。然而主程序域是不能关闭的,因此唯一的办法就是在主程序域中建立一个子程 序域,通过它来专门实现程序集的装载。一旦要卸载这些程序集,就只需要卸载该子程序域就可以了,它并不影响主程序域的执行。
不过现在看来,最主要的问题不是子程序域如何创建,关键是我们必须实现一种机制,来达到两个程序域之间完成通讯的功能。如果大家熟悉 Remoting,就会想到这个问题不是和Remoting的机制有几分相似之处吗?那么答案就可以呼之欲出了,对了,就是使用代理的方法!不过与 Remoting不同的是两个程序域之间的关系。因为子程序域是在主程序域中建立的,因此对该域的控制显然就与Remoting不相同了。
我想先用一副图来表述实现的机制: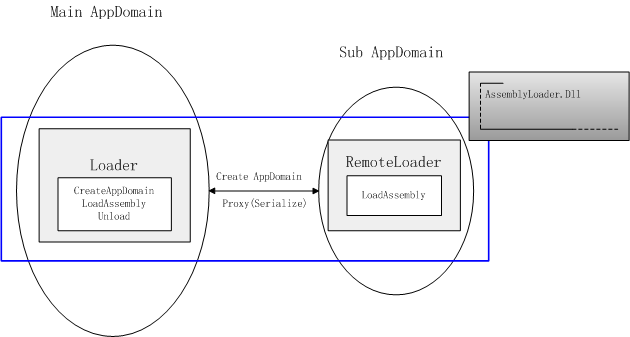
说明:
1、Loader类提供创建子程序域和卸载程序域的方法;
2、RemoteLoader类提供装载程序集方法;
3、Loader类获得RemoteLoader类的代理对象,并调用RemoteLoader类的方法;
4、RemoteLoader类的方法在子程序域中完成;
5、Loader类和RemoteLoader类均放在AssemblyLoader.dll程序集文件中;
我们再来看代码:
Loader类:
SetRemoteLoaderObject()方法:
private Hashtable domains = new Hashtable();
private RemoteLoader rl = null;
 public
RemoteLoader SetRemoteLoaderObject(
string
dllName)
public
RemoteLoader SetRemoteLoaderObject(
string
dllName) {
{ AppDomainSetup setup = new AppDomainSetup();
AppDomainSetup setup = new AppDomainSetup();  setup.ShadowCopyFiles = "true";
setup.ShadowCopyFiles = "true"; domain = AppDomain.CreateDomain(dllName,null,setup);
domain = AppDomain.CreateDomain(dllName,null,setup);
 domains.Add(dllName,domain);
domains.Add(dllName,domain);  try
try {
{
"AssemblyLoader.dll","AssemblyLoader.RemoteLoader");

 }
} catch
catch {
{ throw new Exception();
throw new Exception(); }
} }
}
代码中的变量rl为RemoteLoader类对象,在Loader类中是其私有成员。SetRemoteLoaderObject()方法实际上提供了两个功能,一是创建了子程序域,第二则是获得了RemoteLoader类对象。
请大家一定要注意语句:
rl = (AssemblyLoader.RemoteLoader)domain.CreateInstanceFromAndUnwrap("AssemblyLoader.dll","AssemblyLoader.RemoteLoader");
这 条语句就是实现两个程序域之间通讯的关键。因为Loader类是在主程序域中,RemoteLoader类则是在子程序域中。如果我们在Loader类即 主程序域中显示实例化RemoteLoader类对象rl,此时调用rl的方法,实际上是在主程序域中调用的。因此,我们必须使用代理的方式,来获得rl 对象,这就是CreateInstanceFromAndUnwrap方法的目的。其中参数一为要创建类对象的程序集文件名,参数二则是该类的类型名。
CreateCreateInstanceFromAndUnwrap方法有多个重载。代码中的调用方式是当RemoteLoader类为默认构造函数时的其中一种重载。如果RemoteLoader类的构造函数有参数,则方法应改为:
 object
[] parms
=
{dllName}
;
object
[] parms
=
{dllName}
; BindingFlags bindings
=
BindingFlags.CreateInstance
|
BindingFlags bindings
=
BindingFlags.CreateInstance
|
 BindingFlags.Instance
|
BindingFlags.Public;
BindingFlags.Instance
|
BindingFlags.Public; rl
=
(AssemblyLoader.RemoteLoader)domain.CreateInstanceFromAndUnwrap(
"
AssemblyLoader.dll
"
,
"
AssemblyLoader.RemoteLoader
"
,
true
,bindings,
rl
=
(AssemblyLoader.RemoteLoader)domain.CreateInstanceFromAndUnwrap(
"
AssemblyLoader.dll
"
,
"
AssemblyLoader.RemoteLoader
"
,
true
,bindings, null
,parms,
null
,
null
,
null
);
null
,parms,
null
,
null
,
null
);
详细的调用方式可以参考MSDN。
以下Loader类的Unload方法和LoadAssembly方法():
 public
Assembly LoadAssembly(
string
dllName)
public
Assembly LoadAssembly(
string
dllName) {
{ try
try {
{ SetRemoteLoaderObject(dllName);
SetRemoteLoaderObject(dllName); return rl.LoadAssembly(dllName);
return rl.LoadAssembly(dllName); }
} catch (Exception)
catch (Exception) {
{ throw new AssemblyLoadFailureException();
throw new AssemblyLoadFailureException(); }
} }
}
 public
void
Unload(
string
dllName)
public
void
Unload(
string
dllName) {
{ if (domains.ContainsKey(dllName))
if (domains.ContainsKey(dllName)) {
{ AppDomain appDomain = (AppDomain)domains[dllName];
AppDomain appDomain = (AppDomain)domains[dllName]; AppDomain.Unload(appDomain);
AppDomain.Unload(appDomain); domains.Remove(dllName);
domains.Remove(dllName); }
}  }
}
当我们调用Unload方法时,则程序域domain加载的程序集也将随着而被卸载。LoadAssembly方法中的异常AssemblyLoadFailureException为自定义异常:
 public
class
AssemblyLoadFailureException:Exception
public
class
AssemblyLoadFailureException:Exception {
{ public AssemblyLoadFailureException():base()
public AssemblyLoadFailureException():base() {
{  }
}
 public override string Message
public override string Message {
{ get
get {
{ return "Assembly Load Failure";
return "Assembly Load Failure"; }
} }
}
 }
}
既然在Loader类获得的RemoteLoader类实例必须通过代理的方式,因此该类对象必须支持被序列化。所以我们可以令该类派生MarshalByRefObject。RemoteLoader类的代码:
 public
class
RemoteLoader:MarshalByRefObject
public
class
RemoteLoader:MarshalByRefObject {
{ public RemoteLoader(string dllName)
public RemoteLoader(string dllName) {
{ if (assembly == null)
if (assembly == null) {
{ assembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(dllName);
assembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(dllName); }
} }
} 
 private Assembly assembly = null;
private Assembly assembly = null;
 public Assembly LoadAssembly(string dllName)
public Assembly LoadAssembly(string dllName) {
{ try
try {
{ assembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(dllName);
assembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(dllName);  return assembly;
return assembly; }
} catch (Exception)
catch (Exception) {
{ throw new AssemblyLoadFailureException();
throw new AssemblyLoadFailureException(); }
} }
} }
}
通过上述的两个类,我们就可以实现程序集的加载和卸载。另外,为了保证应用程序域的对象在内存中被清除,应该令这两个类都实现IDisposable接口,和实现Dispose()方法。
然而在实际的操作过程中,我发现在RemoteLoader类的LoadAssembly方法,是存在遗患的。在我的 LoadAssembly方法中,会返回一个Assembly对象。令我百思不得其解的是,虽然都是Assembly对象,但在加载某些程序集并返回 Assembly时,在Loader类中会抛出SerializationException异常,并报告反序列化的对象状态不足。这个异常是在序列化获 反序列化过程中发生的。我反复比较了两个程序集,一个可以正常加载并序列化,一个会抛出如上异常。会抛出异常的程序集并没有什么特殊之处,且我在程序中的 其他地方也没有重复加载该程序集。这是一个疑问!!
不过通常我们在RemoteLoader类中,要实现的方法并非返回一个Assembly对象,而是通过反射加载程序集后,创建该程序集的对象。由 于类对象都为object类型,此时序列化就不会出现问题。在我的项目中,因为要获得程序集的版本号,比较版本号在确定是否需要更新,因此我在 RemoteLoader类中,只需要在加载程序集后,返回程序集的版本号字符串类型就可以了。字符串类型是绝对支持序列化的。
AssemlbyLoader.Dll的源代码可以点击这里获得。在应用程序中,显示添加对该程序集的引用,然后实例化Loader类对象,来调用该方法即可。我还做了一个简单的测试程序,用的是LoadAssembly方法。大家可以测试一下,是否如我所说,对于某些程序集,可能会抛出序列化的异常!?
测试的代码请点击这里获得,测试界面如下: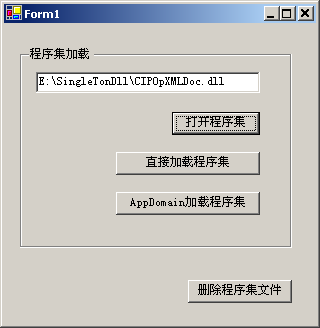
同时,大家也可以测试一下,直接加载和通过AppDomain加载,删除程序集文件时会有什么区别?
最后
以上就是单身月饼最近收集整理的关于AppStart和appupdate解读的全部内容,更多相关AppStart和appupdate解读内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复