maxHttpHeaderSize带来的问题
前因
我们的服务是部署在docker容器中,使用SpringBoot框架搭建的微服务,jdk版本是open jdk 1.8_u201版,内存分配了4G,共部署了4个微服务,使用gateway作为网关负载均衡。有一天运营团队通知我,我们的服务不能访问,访问的页面都是没有数据的;我随即查看我们的系统运行状况,我是通过docker exec -it <容器ID> jstat -gcutil <pid> 1000来查看的;发现系统的年轻代占用50%,老年代占用97%,元空间占用93%,查看GC次数发现没有触发FullGC,只是触发了YGC 68次。
这下让我产生疑问,为什么内存几乎被占满了,jvm还不进行FullGC呢?
于是我通过命令docker exec -it <容器ID> jmap -dump:file=<filename> <pid>来生成dump快照文件,还有获取项目中的gc日志。而且通过MAT分析dump、使用gcviewer分析GC日志。
MAT分析工具 https://www.eclipse.org/mat/downloads.php
gcviewer https://github.com/chewiebug/GCViewer/releases
先来看看GC日志情况
java -jar ./gcviewer.jar service_gc.log
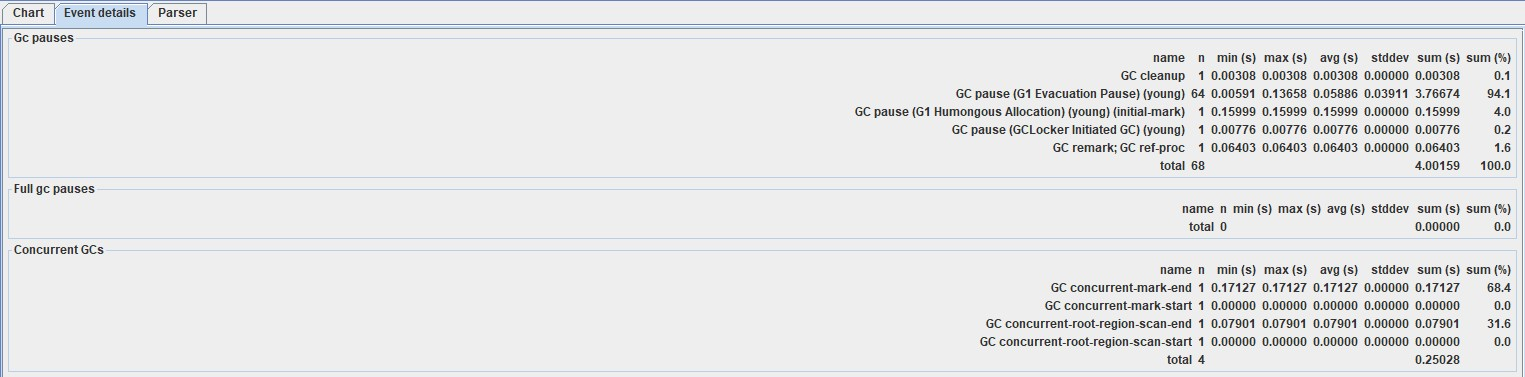
这里可以看到总的GC暂停次数和时间,和FullGC暂停次数和时间
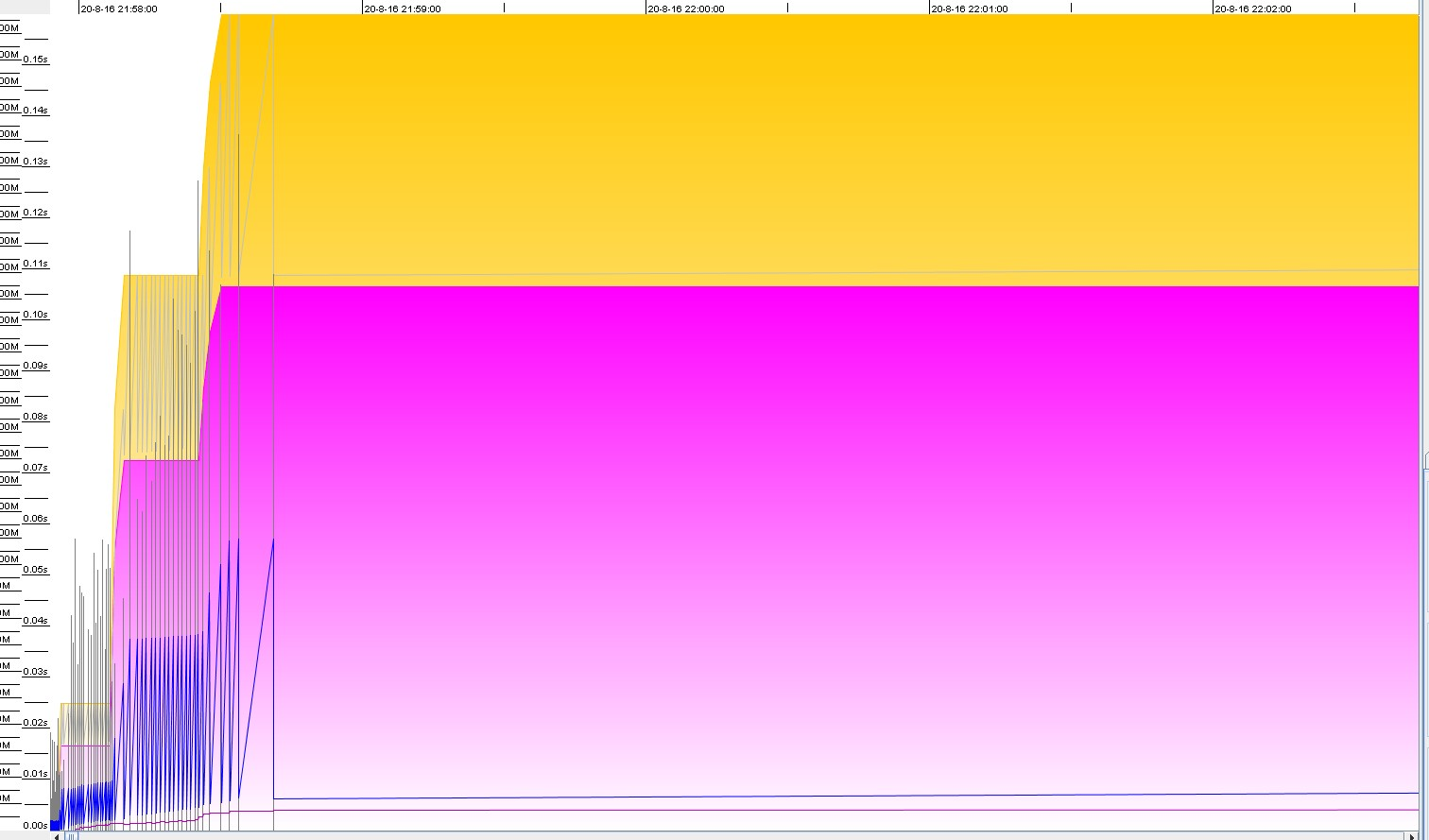

项目刚刚启动时,GC情况,jvm堆内存逐步变大,黄色代表年轻代,紫色代表老年代。
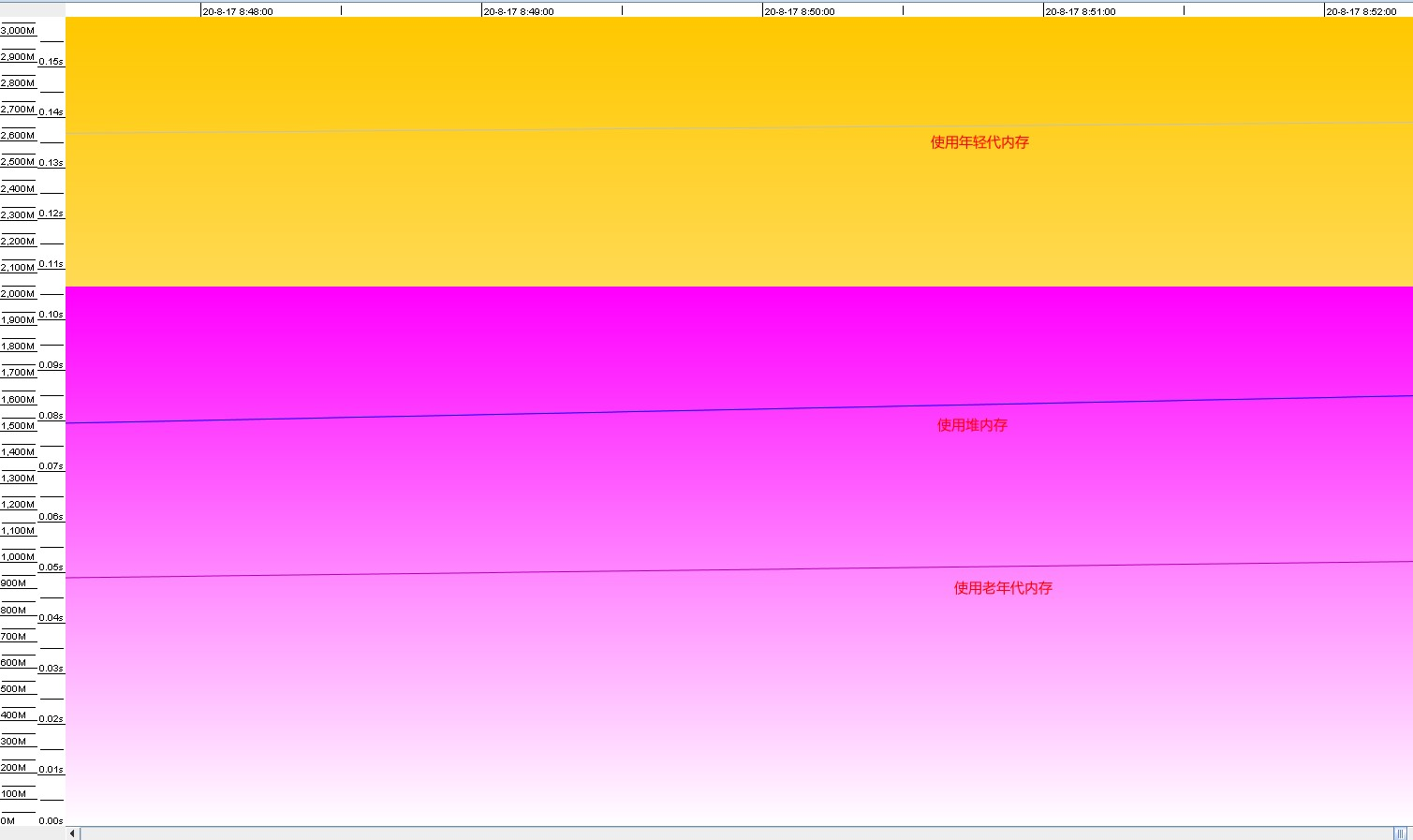
到最后的阶段
我们再来看看MAT分析情况是怎样:

出现两个可能发生内存溢出的问题
- byte[]占用堆内存比例约为46.24%
- 有61个实例Http11OutputBuffer被系统加载,总共耗费内存46.16%
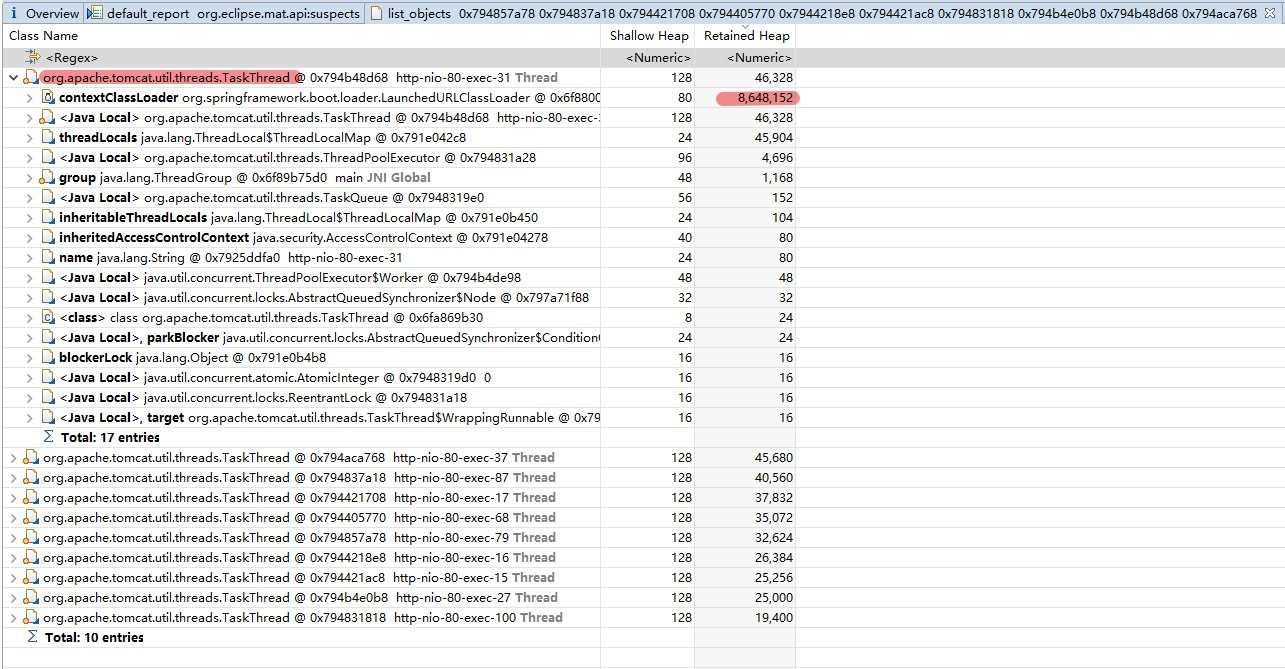
这里的指向的问题的线程是org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.TaskThread

继续往下看,发现跟我们项目有点接近的东西tk.mybatis.mapper.mapperhelper.EntityHelper,这个是实体类工具类 - 处理实体和数据库表以及字段关键的一个类。我们使用了这个插件,相信大家用过mybatis都会知道MyBatisPlus,其实tk.mapper做的功能也是和MyBatisPlus差不多。
那么这里为啥会装那么多的tk.mapper对象呢,主要来源是查数据库后转换实体类而创建的,我们再看看他的GC Roots最近节点

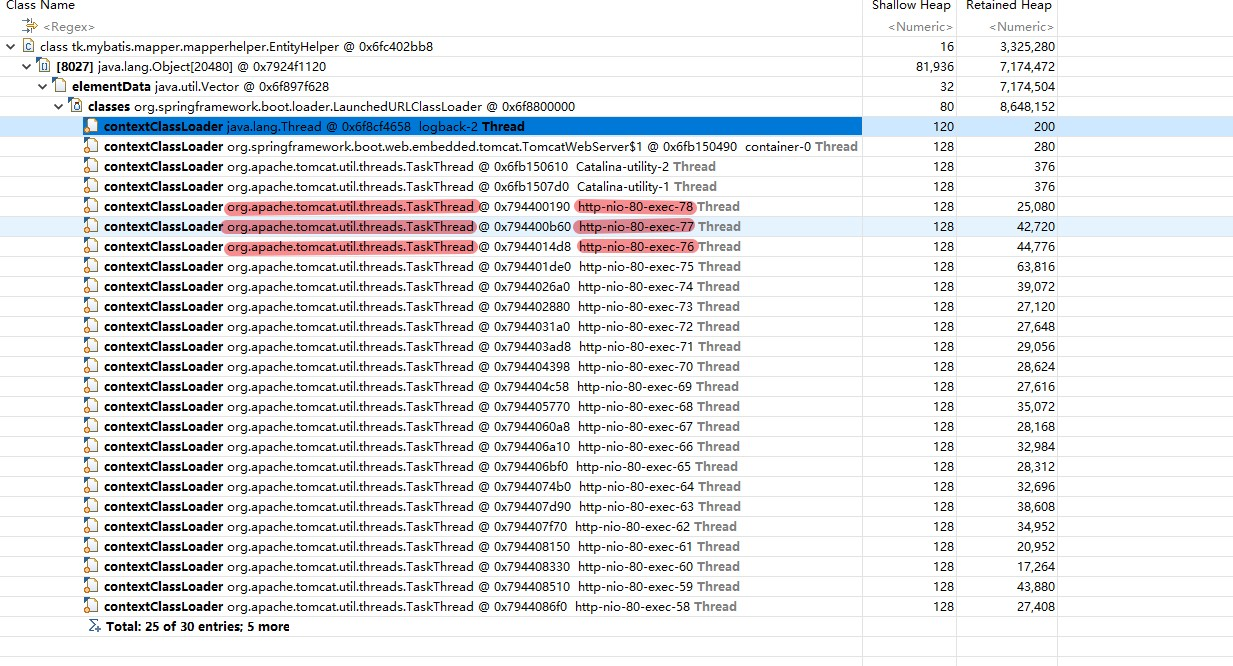
发现都是在org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.TaskThread类引用,我们打开这个类看看源码。
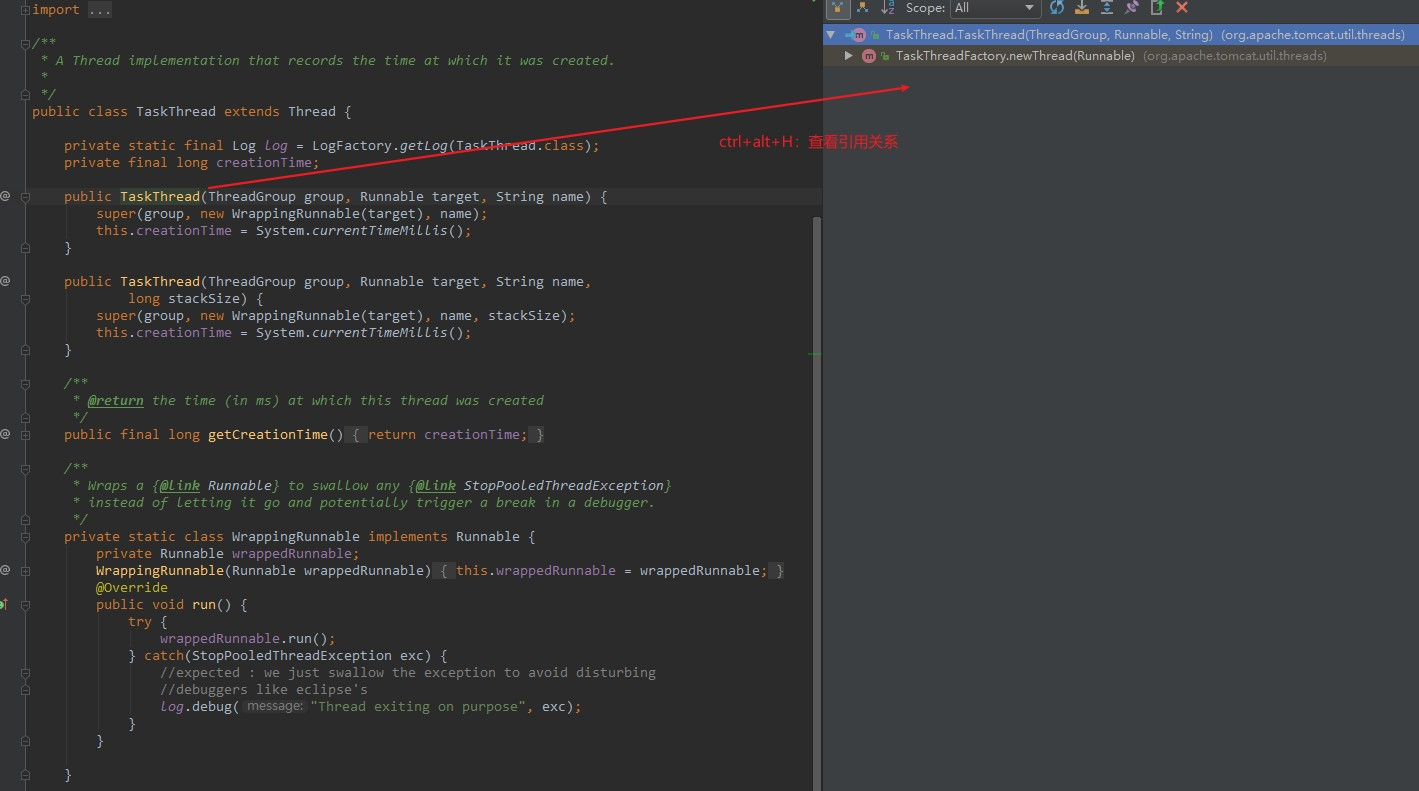
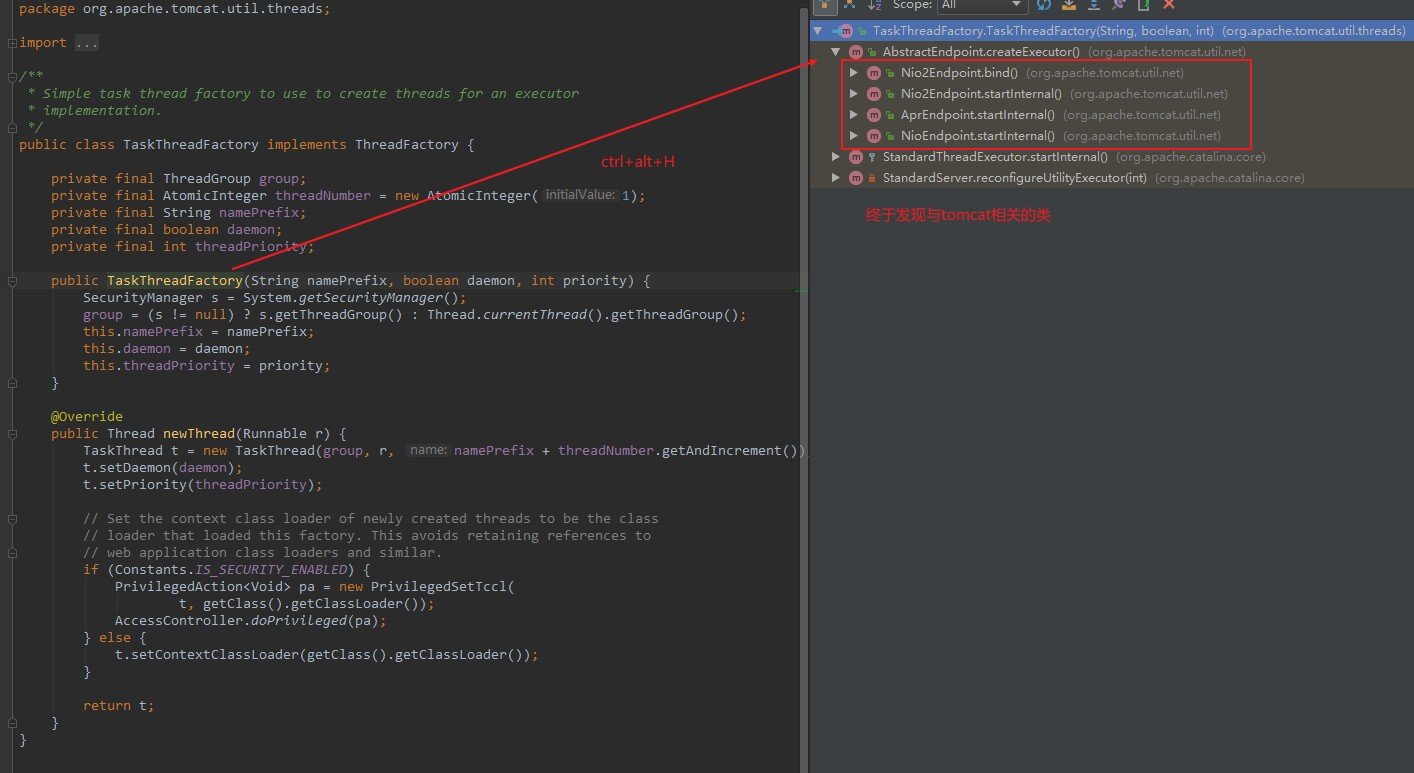
终于找到了与tomcat相关的类了,开心!!!!!
public class Nio2Endpoint extends AbstractJsseEndpoint<Nio2Channel,AsynchronousSocketChannel> {
...
@Override
public void bind() throws Exception {
// Create worker collection
if (getExecutor() == null) {
createExecutor(); // 统一在这个方法创建线程池
}
if (getExecutor() instanceof ExecutorService) {
threadGroup = AsynchronousChannelGroup.withThreadPool((ExecutorService) getExecutor());
}
// AsynchronousChannelGroup needs exclusive access to its executor service
if (!internalExecutor) {
log.warn(sm.getString("endpoint.nio2.exclusiveExecutor"));
}
serverSock = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(threadGroup);
socketProperties.setProperties(serverSock);
InetSocketAddress addr = new InetSocketAddress(getAddress(), getPortWithOffset());
serverSock.bind(addr, getAcceptCount());
// Initialize SSL if needed
initialiseSsl();
}
...
@Override
public void startInternal() throws Exception {
if (!running) {
allClosed = false;
running = true;
paused = false;
if (socketProperties.getProcessorCache() != 0) {
processorCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getProcessorCache());
}
if (socketProperties.getBufferPool() != 0) {
nioChannels = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getBufferPool());
}
// Create worker collection
if (getExecutor() == null) {
createExecutor(); // 统一在这个方法创建线程池
}
initializeConnectionLatch();
startAcceptorThread();
}
}
...
}
/**
* AprEndpoint使用JNI的接口来获得对Socket的访问
* NioEndpoint 同步
* Nio2Endpoint 异步
*/
// 调用 NioEndpoint、Nio2Endpoint、AprEndpoint的父类AbstractEndpoint#createExecutor()方法
public abstract class AbstractEndpoint<S,U> {
...
// 创建线程池
public void createExecutor() {
internalExecutor = true;
TaskQueue taskqueue = new TaskQueue();
// 找到了我们的类 TaskThreadFactory
TaskThreadFactory tf = new TaskThreadFactory(getName() + "-exec-", daemon, getThreadPriority());
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(getMinSpareThreads(), getMaxThreads(), 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,taskqueue, tf);
taskqueue.setParent( (ThreadPoolExecutor) executor);
}
...
}
上面涉及到Tomcat的网络NIO架构,大家更感兴趣的可以百度搜索相关文章。Nio2Endpoint的作用大致就是为Http请求分配线程执行,到这里大概明白byte[]数组就是分配在每一个tomact线程中,因为使用了Nio,就会有Buffer概念,那么这部分的内存是不能回收的,系统启动之后就一直不变。而且随着配置的tomcat线程server.tomcat.maxThreads越多占用的内存空间就越大。
随着配置的tomcat线程越多占用的内存空间就越大?
这个时候我联想到了配置文件,查看原来配置文件:application.yml
server:
port: 80
tomcat:
uri-encoding: UTF-8
maxHttpPostSize: 10240000
maxHttpHeaderSize: 10240000
maxThreads: 500
acceptCount: 500
maxConnections: 600
minSpareThreads: 100
可以看到我同时配置了maxHttpPostSize和maxHttpHeaderSize为10MB大小,而且我还配置了500个最大线程,满载时就单单Buffer就要耗费4G的内存。
后面我优化成:application.yml
server:
port: 80
servlet:
context-path: /
tomcat:
maxThreads: 400
minSpareThreads: 50
看了源码才发现maxHttpHeaderSize默认配置了8k,maxHttpPostSize默认配置2M,默认情况下是够用了,除非你再header上携带大量的信息。
maxHttpHeaderSize设置源码
SpringBoot是通过org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerProperties配置
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server", ignoreUnknownFields = true)
public class ServerProperties {
/**
* Server HTTP port.
*/
private Integer port;
/**
* Network address to which the server should bind.
*/
private InetAddress address;
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private final ErrorProperties error = new ErrorProperties();
/**
* Whether X-Forwarded-* headers should be applied to the HttpRequest.
*/
private Boolean useForwardHeaders;
/**
* Value to use for the Server response header (if empty, no header is sent).
*/
private String serverHeader;
/**
* Maximum size of the HTTP message header.
*/
private DataSize maxHttpHeaderSize = DataSize.ofKilobytes(8);
/**
* Time that connectors wait for another HTTP request before closing the connection.
* When not set, the connector's container-specific default is used. Use a value of -1
* to indicate no (that is, an infinite) timeout.
*/
private Duration connectionTimeout;
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private Ssl ssl;
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private final Compression compression = new Compression();
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private final Http2 http2 = new Http2();
private final Servlet servlet = new Servlet();
private final Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
private final Jetty jetty = new Jetty();
private final Undertow undertow = new Undertow();
...
public static class Tomcat {
...
/**
* Maximum size of the HTTP message header.
*/
private DataSize maxHttpHeaderSize = DataSize.ofBytes(0);
@Deprecated
@DeprecatedConfigurationProperty(replacement = "server.max-http-header-size")
public DataSize getMaxHttpHeaderSize() {
return this.maxHttpHeaderSize;
}
@Deprecated
public void setMaxHttpHeaderSize(DataSize maxHttpHeaderSize) {
this.maxHttpHeaderSize = maxHttpHeaderSize;
}
...
}
}
查看一下哪里调用getMaxHttpHeaderSize()方法
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer
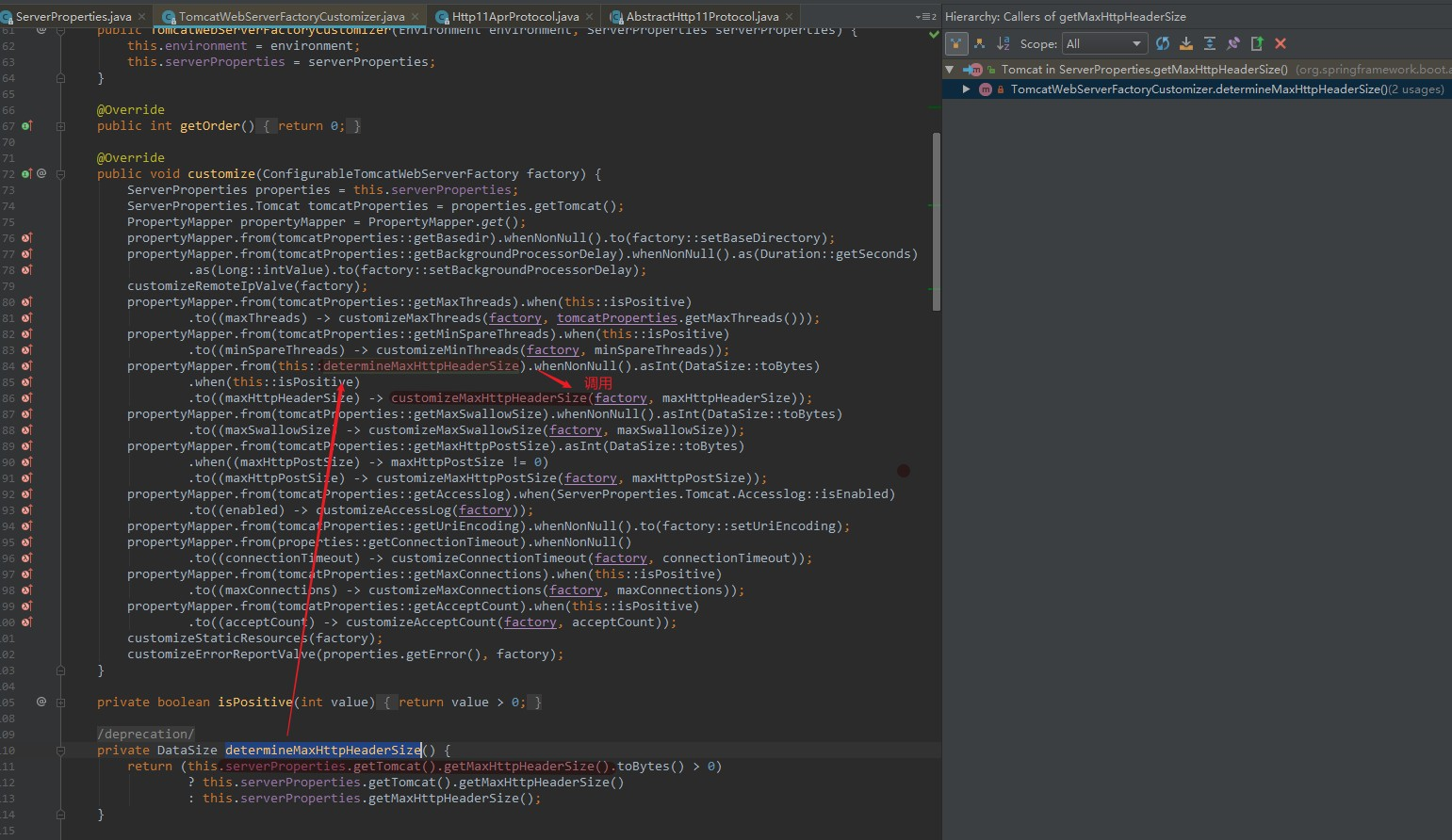
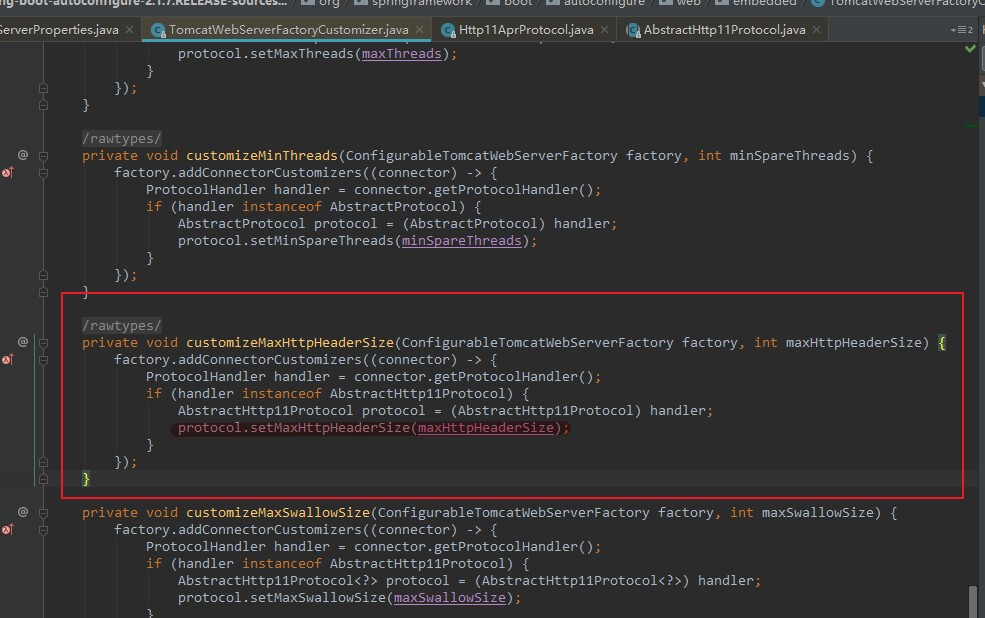
org.apache.coyote.http11.AbstractHttp11Protocol是一个抽象类,我们使用的是NIO,则它的子类是org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11AprProtocol
在org.apache.coyote.http11.AbstractHttp11Protocol中maxHttpHeaderSize是如何被调用
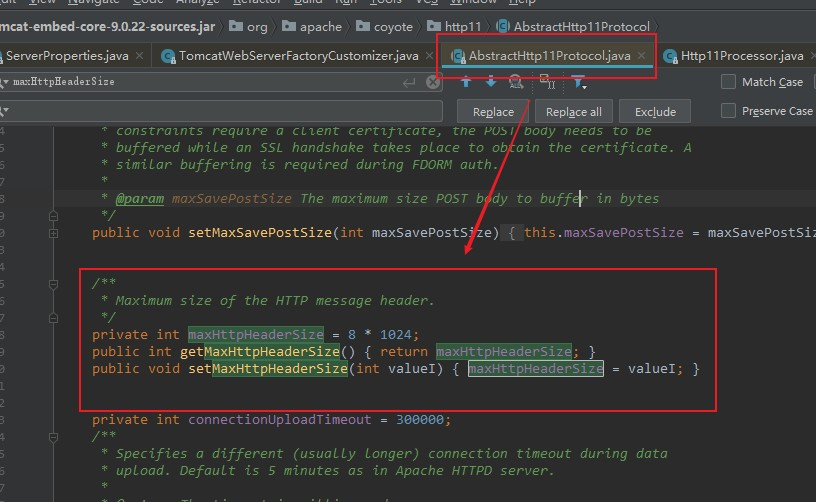
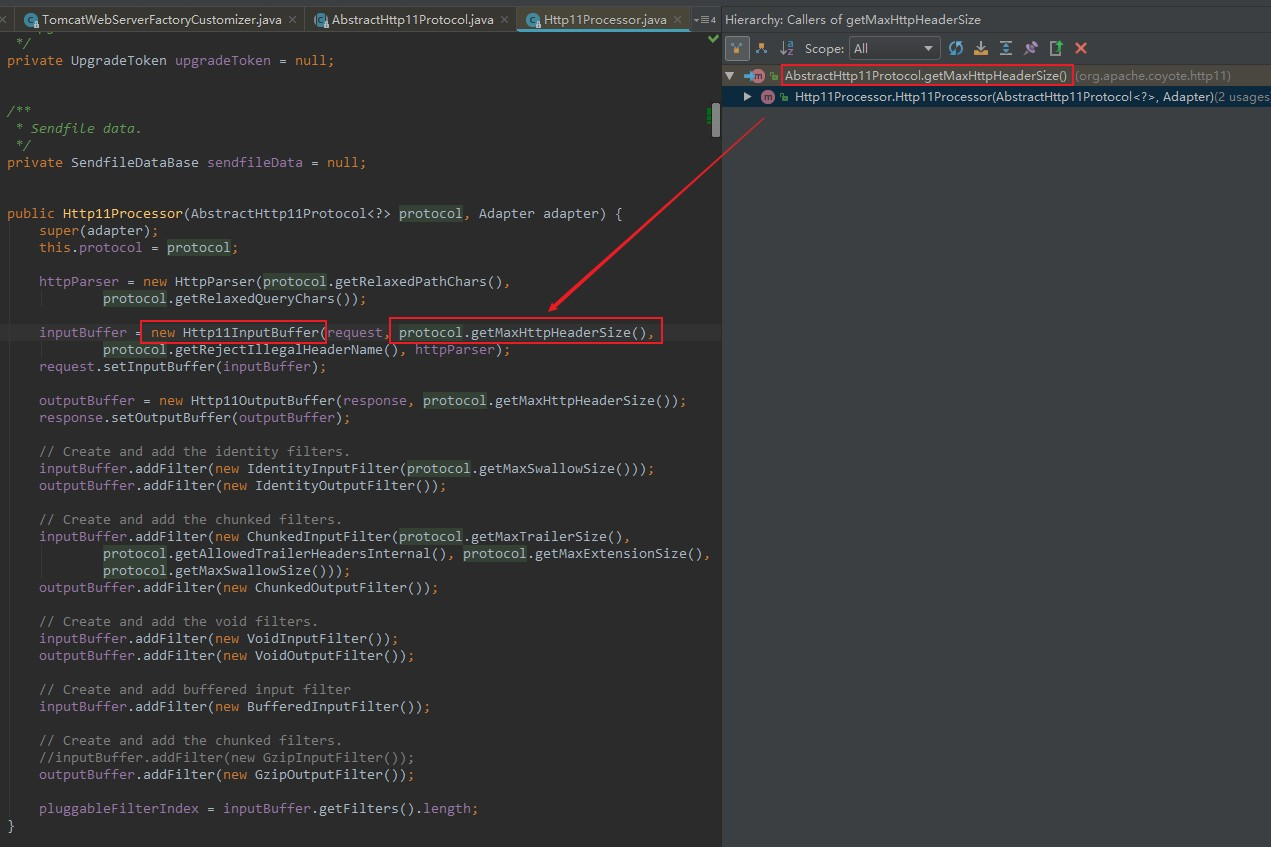
在Http11InputBuffer中我们可以查看到有一个init()方法
public class Http11InputBuffer implements InputBuffer, ApplicationBufferHandler {
...
public Http11InputBuffer(Request request, int headerBufferSize,
boolean rejectIllegalHeaderName, HttpParser httpParser) {
this.request = request;
headers = request.getMimeHeaders();
this.headerBufferSize = headerBufferSize;
this.rejectIllegalHeaderName = rejectIllegalHeaderName;
this.httpParser = httpParser;
filterLibrary = new InputFilter[0];
activeFilters = new InputFilter[0];
lastActiveFilter = -1;
parsingHeader = true;
parsingRequestLine = true;
parsingRequestLinePhase = 0;
parsingRequestLineEol = false;
parsingRequestLineStart = 0;
parsingRequestLineQPos = -1;
headerParsePos = HeaderParsePosition.HEADER_START;
swallowInput = true;
inputStreamInputBuffer = new SocketInputBuffer();
}
...
void init(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper) {
wrapper = socketWrapper;
wrapper.setAppReadBufHandler(this);
int bufLength = headerBufferSize +
wrapper.getSocketBufferHandler().getReadBuffer().capacity();
if (byteBuffer == null || byteBuffer.capacity() < bufLength) {
// 创建了一个ByteBuffer,而且它的长度是由headerBufferSize决定的
byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bufLength);
byteBuffer.position(0).limit(0);
}
}
...
}
我们现在可以继续往上追溯
byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bufLength); -> HeapByteBuffer
public abstract class ByteBuffer extends Buffer implements Comparable<ByteBuffer> {
...
public static ByteBuffer allocate(int capacity) {
if (capacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
return new HeapByteBuffer(capacity, capacity);
}
...
}
class HeapByteBuffer extends ByteBuffer {
// For speed these fields are actually declared in X-Buffer;
// these declarations are here as documentation
/*
protected final byte[] hb;
protected final int offset;
*/
HeapByteBuffer(int cap, int lim) { // package-private
super(-1, 0, lim, cap, new byte[cap], 0);
/*
hb = new byte[cap];
offset = 0;
*/
}
}
到这里,我们终于找到byte[]创建的地方。按照之前的计算这里创建的byte数组长度为10240000+,还真的挺大的。
最后,我们已经了解jvm占用byte[]数组过多的情况,且也了走了一遍tomcat的源码,对tomcat有更深入的了解。
最后
以上就是凶狠萝莉最近收集整理的关于一次线上JVM内存溢出分析,GC分析、MAT、gcviewermaxHttpHeaderSize带来的问题的全部内容,更多相关一次线上JVM内存溢出分析,GC分析、MAT、gcviewermaxHttpHeaderSize带来内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复