每日心得:
老师继上次的集合Collection又讲了链表,还有set,Map,虽说东西不多,但听得一脸懵逼,这两东西还是比较难的,特别是老师去重写linkedlist,还有讲Map类时,跳来跳去,有点缓不过来。。
Collection接口:
1、List:
ArrayList,有序的集合,与数组类似,所以也与数组一样(数组访问任意一个时间一样,但长度固定,需要数组复制进行扩容,会占用浪费内存,更新性能较慢)。(为什么不用ArrayLIst)List list = new ArrayList();父类的引用指向子类的实例,为了实现多态,为了有必要时将后方的ArrayList()进行替换(面向接口编程),只是这样没法使用ArrayList中特有的方法。一些方法:add(),直接传值可以在最后插值,size(),remove(){若传入的对象在集合里有多个,则只移除第一个},若要移除多个可使用removeIf(),不过里面得放匿名方法,老师写了一个:
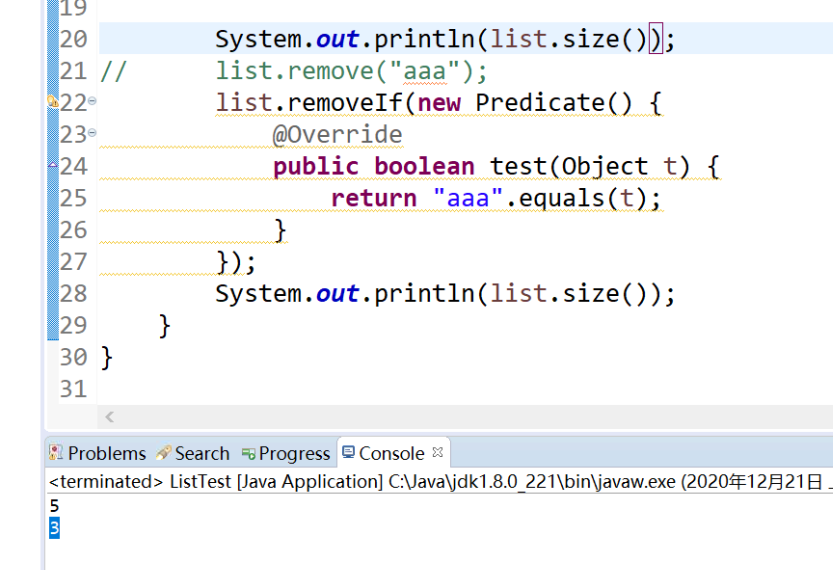
get()-->与数组中的[]类似,根据索引取值,contains()是否包含。此外,老师还讲了一种增强for循环,可以减少遍历元素的代码,我还从另一篇文章上查到了for循环与增强for循环的区别,“https://www.cnblogs.com/XiaojianGo/p/7471860.html”这文章中介绍的很清楚,增强for循环也称foreach循环,只能用来遍历,无法作添加修改等其他动作。foreach循环可以对多种类型进行遍历,但里面的实现该功能的代码会不同。
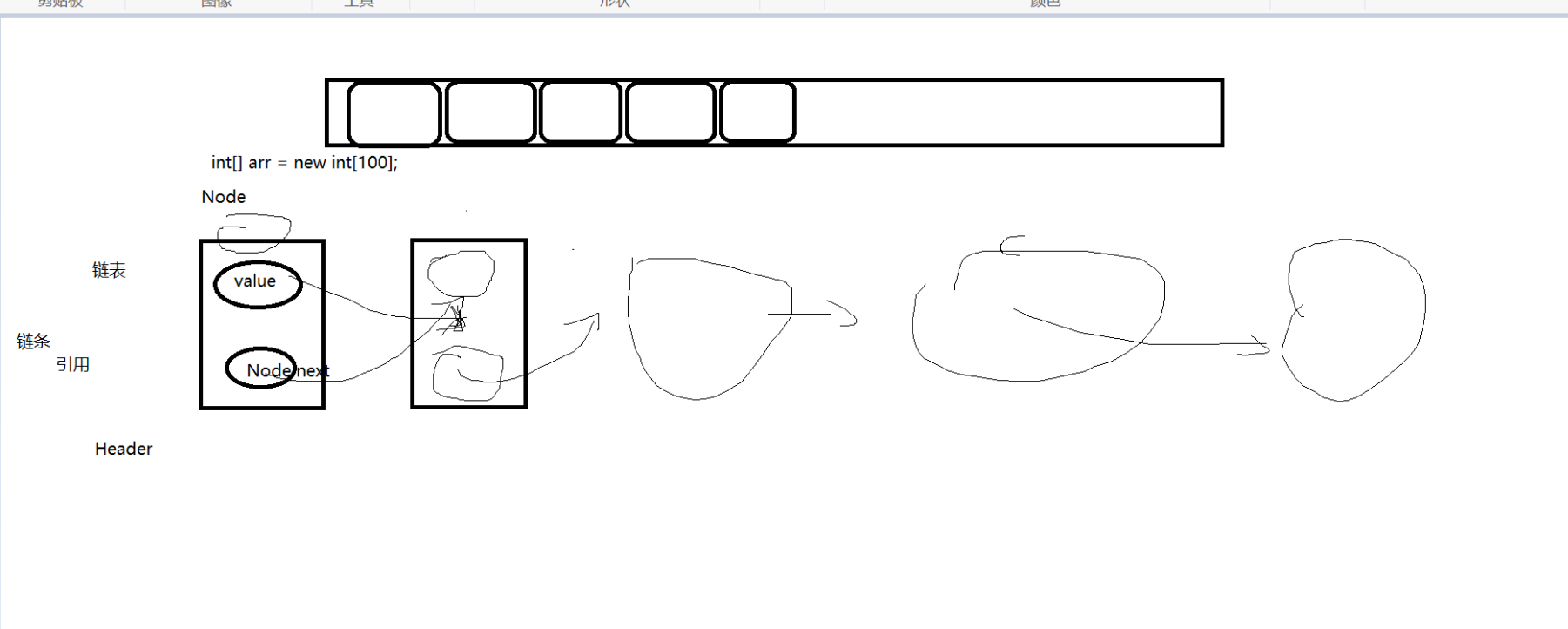
LinkedList,链表(类似自行车的链条),通过加入引用节点,往前或者往后,如果遍历找一个元素会根据首节点一个一个找,所以遍历的性能不如ArrayList,但可以随时更新,没有复制和扩容的问题,所以更新的性能更好。链表分为,单向,双向,环形链表(最后一个节点指向头),双向链表-->为了遍历时的效率,只查一半(移位运算:右移除2,左移除2),为了提高性能可以将linkedlisk,arraylist进行组装成一个大的list,将大的数据拆开,最后组装,数据分区分表。
Vector,与ArrayList类似,添加了一个同步的方法,与线程相关。
2、Set(无set,get方法,因为这个方法需要有序的,Collection也没有)
里面存的是不重复的元素,无序的,没有索引能使用增强for循环,但与之前list的实现方式不一样,虽然语法一样。
SortedSet接口-->有顺序的-->实现类:TreeSet(跟树型结构有关);HashSet类-->无序的。
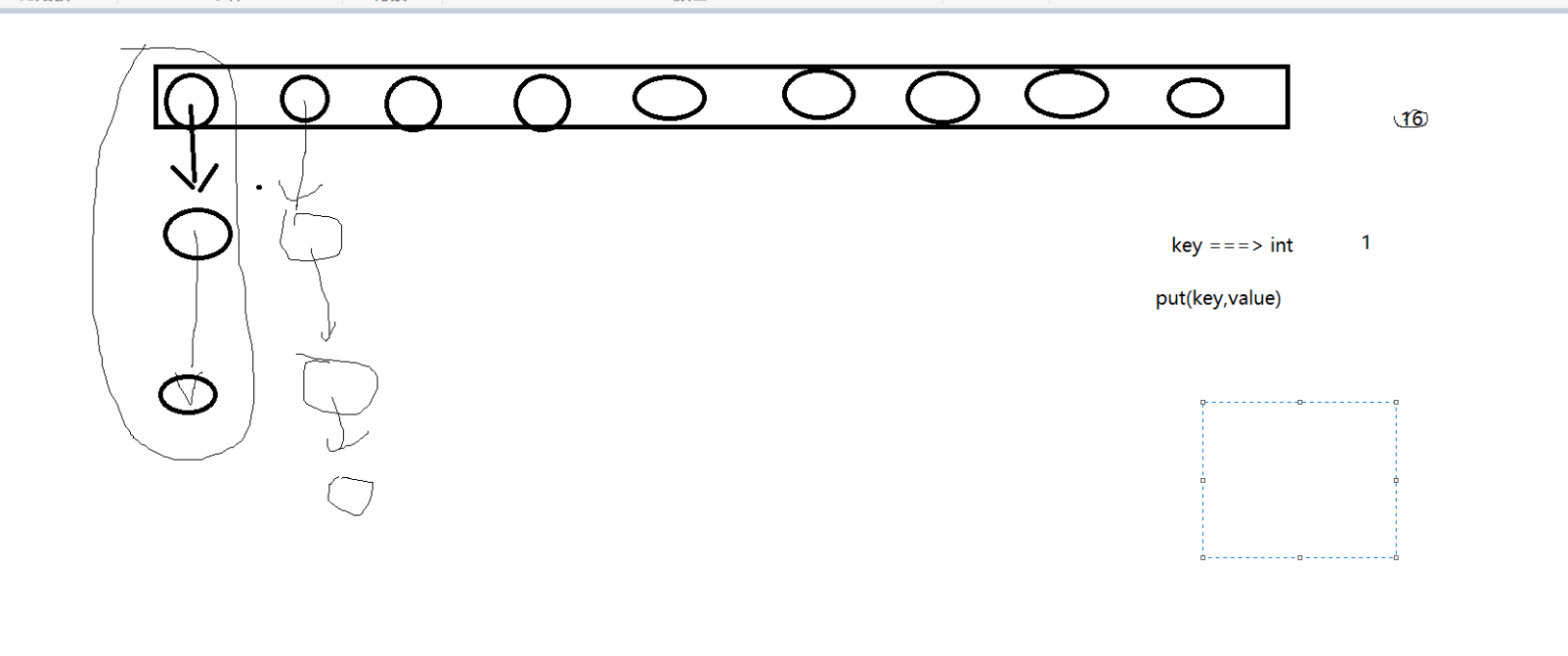
Map(映射)接口,与数据库的表类似,键值对通过key取值,value,key可以快速找到对应的值,定位value所在的位置。.get(key)取得value。
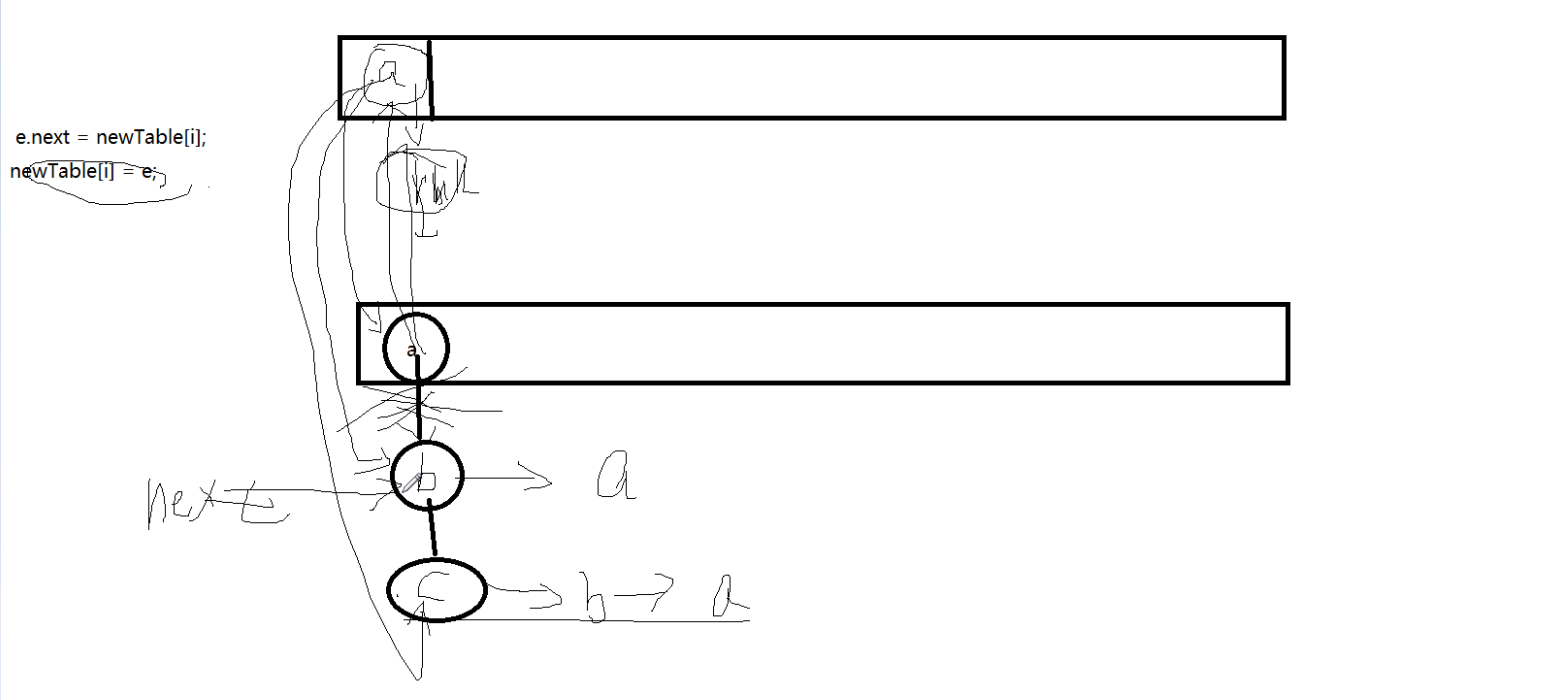
HashMap(无序的)头插法-->循环引用,put(key,value)value可以为数值,类等,若给值时,key相同,后面的会覆盖前面一个,因为key是唯一标识符,当key是自定义的类时,必须重写hashcode方法;equals值相等的两个类,hashcode方法必须一致,equals不同的,他们hashcode可以相等,也可以不相等。resize方法在jdk1.6有缺陷,TreeMap(有序的)。因为没听太明白,所以也写不出多少。
下面是一些老师画的结构图:
hashmap
课后,还有一个作业,写一个自己的MyLinkedList,我好像没写完整:
public classMyLinkedList {static intcount;staticMyNode header;publicMyLinkedList(){
header=null;
count=0;
}public intsize(){returncount;
}public Object get(intindex){if(index<0||index>=count){throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index"+index);
}if(index==0){returnheader.value;
}
MyNode temp=header;for(int i=0;i
temp=temp.next;
}returntemp.value;
}public voidadd(Object value){if(null==header){
header=newMyNode();
header.setValue(value);
}else{
MyNode temp=header;while(temp.next!=null){
temp=temp.next;
}
MyNode last= newMyNode();
last.setValue(value);
temp.setNext(last);
}
count++;
}public void remove(intindex){if(index<0||index>=count){throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index"+index);
}if(index==0){
header=header.next;
}
MyNode temp=header;
MyNode prev=header;for(int i=0;i
prev=temp;
temp=temp.next;
}
prev.next=temp.next;
count--;
}public void set(intindex,Object value){if(index<0||index>=count){throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index"+index);
}if(index==0){
header.setValue(value);
}
MyNode temp=header;for(int i=0;i
temp=temp.next;
}
temp.setValue(value);
}public intindexOf(Object value){for(int i=0;i
}
}else if(value.equals(get(i))){returni;
}
}return -1;
}public intlastindexOf(Object value){for(int i=count;i>0;i--){if(null==value){if(value==get(i)){returni;
}
}else if(value.equals(get(i))){returni;
}
}return -1;
}static classMyNode{privateMyNode prey;privateObject value;privateMyNode next;publicMyNode getPrey() {returnprey;
}public voidsetPrey(MyNode prey) {this.prey =prey;
}publicObject getValue() {returnvalue;
}public voidsetValue(Object value) {this.value =value;
}publicMyNode getNext() {returnnext;
}public voidsetNext(MyNode next) {this.next =next;
}
}
}
最后
以上就是聪明黑猫最近收集整理的关于java.util.map<>_java.util中的Collection,Map;的全部内容,更多相关java.util.map<>_java.util中内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复