Leetcode全排序-剪枝算法
编号47. 全排列2 剪枝
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列 nums ,按任意顺序 返回所有不重复的全排列。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,1,2]
输出:
[[1,1,2],
[1,2,1],
[2,1,1]]
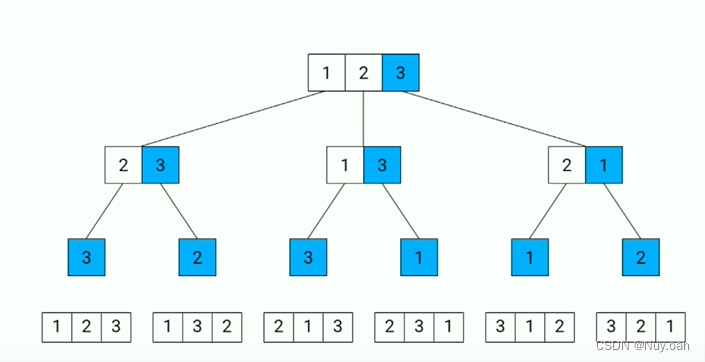
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums={1,2,1};
System.out.println(permuteUnique(nums));
}
public static List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);//不管什么数组都要先进行排序,好判断
List<List<Integer>> list=new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length];
dfs(nums,list,path,used);
return list;
}
private static void dfs(int[] nums, List<List<Integer>> list, List<Integer> path, boolean[] used) {
if (path.size()==nums.length){
list.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
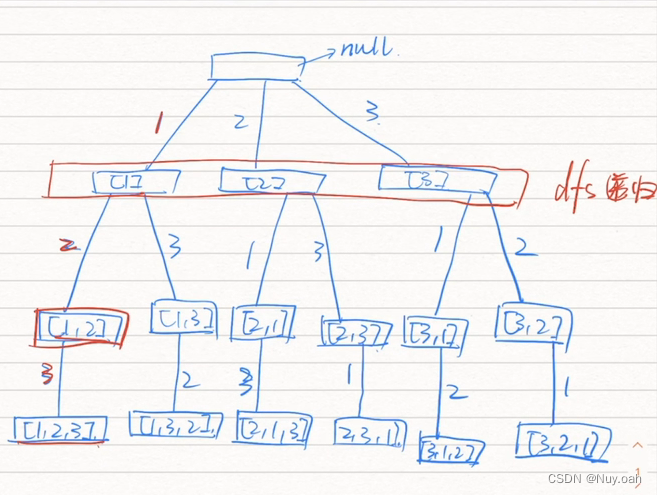
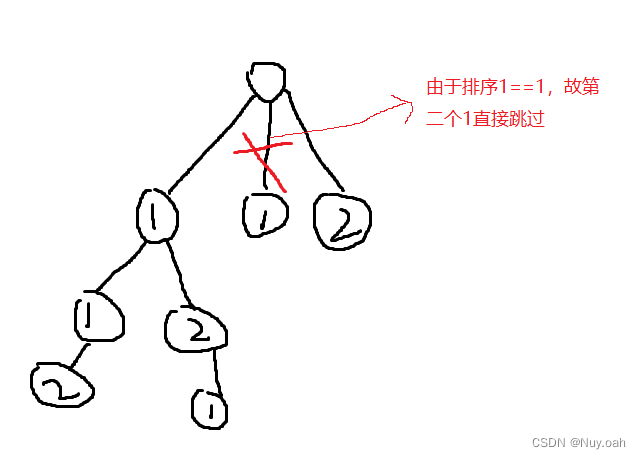
// 剪枝条件:i > 0 是为了保证 nums[i - 1] 有意义
//nums[i] == nums[i-1] 判断是不是重复的点,这也是排序是剪枝的前提的原因
// 写 !used[i - 1] 是因为 nums[i - 1] 在深度优先遍历的过程中刚刚被撤销选择,也就是重置为false。
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (used[i]==true)
continue;
if (i>0&&nums[i]==nums[i-1]&&used[i-1]==false)
continue;
used[i]=true;
path.add(nums[i]);
dfs(nums,list,path,used);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
used[i]=false;
}
}
46.全排列
和47差不多,47只是46的一种特殊情况
public static List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> list=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if (nums.length==0)
return list;
List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] used=new boolean[nums.length];
dfs(list,nums,path,used);
return list;
}
static void dfs(List<List<Integer>> list,int[] nums, List<Integer> path, boolean[] used) {
if (path.size()==nums.length){
list.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (used[i]==true)
continue;
used[i]=true;
path.add(nums[i]);
dfs(list,nums,path,used);
System.out.println(path.size()-1);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
used[i]=false;
}
}
最后
以上就是烂漫冷风最近收集整理的关于Leetcode全排序-剪枝算法Leetcode全排序-剪枝算法的全部内容,更多相关Leetcode全排序-剪枝算法Leetcode全排序-剪枝算法内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复