整体导读:
尽管transformer体系结构已成为自然语言处理任务的实际标准,但其在计算机视觉中的应用仍然受到限制。在视觉上,注意力要么与卷积网络结合使用,要么用于替换卷积网络的某些组件,同时将其整体结构保持在适当的位置。2020年10月22日,谷歌人工智能研究院Alexey Dosovitskiy, Lucas Beyer等研究员将Transformer应用到图像识别上并在顶会“Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR)”上发表一篇题为“An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale”的文章。文章将图像切割成一个个图像块,组成序列化的数据输入Transformer执行图像分类任务。当对大量数据进行预训练并将其传输到多个中型或小型图像识别数据集(ImageNet、CIFAR-100、VTAB等)时,与目前的卷积网络相比,Vision Transformer(ViT)获得了出色的结果,同时所需的计算资源也大大减少。
论文名称:An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale
原文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2010.11929.pdf
会议名称:Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
论文创新点:
在模型设计中,文章尽可能地遵循原始的transformer,这样几乎可以立即使用可扩展的NLP transformer体系结构及其有效的实现。
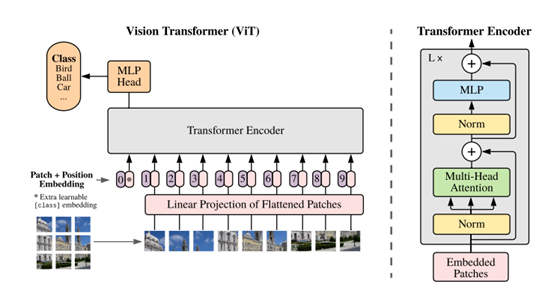


模型代码
import torch
from torch import nn, einsum
import torch.nn.functional as F
from einops import rearrange, repeat
from einops.layers.torch import Rearrange
# helpers
def pair(t):
return t if isinstance(t, tuple) else (t, t)
# classes
class PreNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, fn):
super().__init__()
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.fn = fn
def forward(self, x, **kwargs):
return self.fn(self.norm(x), **kwargs)
class FeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, hidden_dim, dropout=0.):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, dim),
nn.Dropout(dropout)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.net(x)
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, heads=8, dim_head=64, dropout=0.):
super().__init__()
inner_dim = dim_head * heads
project_out = not (heads == 1 and dim_head == dim)
self.heads = heads
self.scale = dim_head ** -0.5
self.attend = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
self.to_qkv = nn.Linear(dim, inner_dim * 3, bias=False)
self.to_out = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(inner_dim, dim),
nn.Dropout(dropout)
) if project_out else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
b, n, _, h = *x.shape, self.heads
qkv = self.to_qkv(x).chunk(3, dim=-1)
q, k, v = map(lambda t: rearrange(t, 'b n (h d) -> b h n d', h=h), qkv)
dots = einsum('b h i d, b h j d -> b h i j', q, k) * self.scale
attn = self.attend(dots)
out = einsum('b h i j, b h j d -> b h i d', attn, v)
out = rearrange(out, 'b h n d -> b n (h d)')
return self.to_out(out)
class Transformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, depth, heads, dim_head, mlp_dim, dropout=0.):
super().__init__()
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([])
for _ in range(depth):
self.layers.append(nn.ModuleList([
PreNorm(dim, Attention(dim, heads=heads, dim_head=dim_head, dropout=dropout)),
PreNorm(dim, FeedForward(dim, mlp_dim, dropout=dropout))
]))
def forward(self, x):
for attn, ff in self.layers:
x = attn(x) + x
x = ff(x) + x
return x
class ViT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, *, image_size, patch_size, num_classes, dim, depth, heads, mlp_dim, pool='cls', channels=3,
dim_head=64, dropout=0., emb_dropout=0.):
super().__init__()
image_height, image_width = pair(image_size)
patch_height, patch_width = pair(patch_size)
assert image_height % patch_height == 0 and image_width % patch_width == 0, 'Image dimensions must be divisible by the patch size.'
num_patches = (image_height // patch_height) * (image_width // patch_width)
patch_dim = channels * patch_height * patch_width
assert pool in {'cls', 'mean'}, 'pool type must be either cls (cls token) or mean (mean pooling)'
self.to_patch_embedding = nn.Sequential(
Rearrange('b c (h p1) (w p2) -> b (h w) (p1 p2 c)', p1=patch_height, p2=patch_width),
nn.Linear(patch_dim, dim),
)
self.pos_embedding = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, num_patches + 1, dim))
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, 1, dim))
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(emb_dropout)
self.transformer = Transformer(dim, depth, heads, dim_head, mlp_dim, dropout)
self.pool = pool
self.to_latent = nn.Identity()
self.mlp_head = nn.Sequential(
nn.LayerNorm(dim),
nn.Linear(dim, num_classes)
)
def forward(self, img):
x = self.to_patch_embedding(img)
b, n, _ = x.shape
cls_tokens = repeat(self.cls_token, '() n d -> b n d', b=b)
x = torch.cat((cls_tokens, x), dim=1)
x += self.pos_embedding[:, :(n + 1)]
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.transformer(x)
x = x.mean(dim=1) if self.pool == 'mean' else x[:, 0]
x = self.to_latent(x)
return self.mlp_head(x)
最后
以上就是鳗鱼睫毛最近收集整理的关于Vision Transformer:用于图像识别的Transformer的全部内容,更多相关Vision内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复