文章目录
- 前言
- 一、参考论文
- 二、HBP简介
- 三、基于pytorch的实现
- 1.NetModel.py
- 2.CUB200.py
- 3.Train.py
- 4.main.py
- 四、训练结果
- 五、问题与改进
- 总结
前言
本文记录了学习BCNN的一种改进方法——HBP的过程,并给出了基于pytorch的代码。欢迎大家交流指正。
一、参考论文
Bilinear CNN Models for Fine-grained Visual Recognition,CVPR2015 BCNN
Hierarchical Bilinear Pooling for Fine-Grained Visual Recognition,ECCV2018 HBP
二、HBP简介
参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/47608165(略作修改)
在细粒度图像分类中,双线性池化(bilinear pooling)的模型已经被证明是有效的,然而,先前的大多方法忽略了这样一个事实:层间部分特征交互和细粒度特征学习是相互关联的并且可以相互加强。根据这一问题,作者提出一种新的模型结构。(1)提出了一种可跨层的双线性池化方法,用来捕获层间部分特征的关系。(2)提出一种集成多个跨层双线性特征的分层双线性池化框架,增强模型的表示能力。
跨层双线性池化方法和传统的双线性池化方法相比,没有增加额外的训练参数,并且具有更强的表示能力。所以,作者提出分层双线性池化结构(HBP),通过级联多个跨层双线性池化模块来包含更多的卷积层特征。HBP模型的输出为
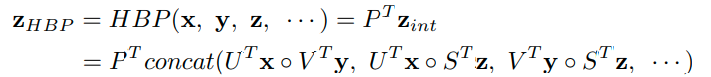
Hierarchical Bilinear Pooling 比 Bilinear Pooling多的就是层之间的交互,具体是这样实现的:以最简单的结构举例,假设两个CNN都采用VGG-16结构,去掉VGG的全连接层,卷积层最后三层定义为relu5_1, relu5_2, relu5_3,Bilinear Pooling 就是将CNN1的relu5_3和CNN2的relu5_3做了Bilinear Pooling操作,得到的结果进行分类。而Hierarchical Bilinear Pooling是relu5_3 * relu5_2,relu5_3 * relu5_1,relu5_2 * relu5_1,得到三组特征,并将这些特征拼接在一起,最后进行分类。
三、基于pytorch的实现
1.NetModel.py
参考:https://github.com/luyao777/HBP-pytorch
HBP实现代码如下:
import torch
import torchvision
import torch.nn.functional
class HBP(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
torch.nn.Module.__init__(self, pretrained)
# Convolution and pooling layers of VGG-16.
self.features = torchvision.models.vgg16(pretrained=pretrained).features
self.features_conv5_1 = torch.nn.Sequential(*list(self.features.children())[:-5])
self.features_conv5_2 = torch.nn.Sequential(*list(self.features.children())[-5:-3])
self.features_conv5_3 = torch.nn.Sequential(*list(self.features.children())[-3:-1])
self.bilinear_proj_1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(512, 8192, kernel_size=1, bias=True)
self.bilinear_proj_2 = torch.nn.Conv2d(512, 8192, kernel_size=1, bias=True)
self.bilinear_proj_3 = torch.nn.Conv2d(512, 8192, kernel_size=1, bias=True)
# Linear classifier.
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(8192 * 3, 200)
if pretrained:
# Freeze all previous layers.
for param in self.features_conv5_1.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
for param in self.features_conv5_2.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
for param in self.features_conv5_3.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
# Initialize the fc layers.
torch.nn.init.xavier_normal_(self.fc.weight.data)
if self.fc.bias is not None:
torch.nn.init.constant_(self.fc.bias.data, val=0)
def hbp_1_2(self, conv1, conv2):
N = conv1.size()[0]
proj_1 = self.bilinear_proj_1(conv1)
proj_2 = self.bilinear_proj_2(conv2)
assert (proj_1.size() == (N, 8192, 28, 28))
X = proj_1 * proj_2
assert (X.size() == (N, 8192, 28, 28))
X = torch.sum(X.view(X.size()[0], X.size()[1], -1), dim=2)
X = X.view(N, 8192)
X = torch.sign(X) * torch.sqrt(torch.abs(X) + 1e-5)
X = torch.nn.functional.normalize(X)
return X
def hbp_1_3(self, conv1, conv3):
N = conv1.size()[0]
proj_1 = self.bilinear_proj_1(conv1)
proj_3 = self.bilinear_proj_3(conv3)
assert (proj_1.size() == (N, 8192, 28, 28))
X = proj_1 * proj_3
assert (X.size() == (N, 8192, 28, 28))
X = torch.sum(X.view(X.size()[0], X.size()[1], -1), dim=2)
X = X.view(N, 8192)
X = torch.sign(X) * torch.sqrt(torch.abs(X) + 1e-5)
X = torch.nn.functional.normalize(X)
return X
def hbp_2_3(self, conv2, conv3):
N = conv2.size()[0]
proj_2 = self.bilinear_proj_2(conv2)
proj_3 = self.bilinear_proj_3(conv3)
assert (proj_2.size() == (N, 8192, 28, 28))
X = proj_2 * proj_3
assert (X.size() == (N, 8192, 28, 28))
X = torch.sum(X.view(X.size()[0], X.size()[1], -1), dim=2)
X = X.view(N, 8192)
X = torch.sign(X) * torch.sqrt(torch.abs(X) + 1e-5)
X = torch.nn.functional.normalize(X)
return X
def forward(self, X):
N = X.size()[0]
assert X.size() == (N, 3, 448, 448)
X_conv5_1 = self.features_conv5_1(X)
X_conv5_2 = self.features_conv5_2(X_conv5_1)
X_conv5_3 = self.features_conv5_3(X_conv5_2)
X_branch_1 = self.hbp_1_2(X_conv5_1, X_conv5_2)
X_branch_2 = self.hbp_1_3(X_conv5_1, X_conv5_3)
X_branch_3 = self.hbp_2_3(X_conv5_2, X_conv5_3)
X_branch = torch.cat([X_branch_1, X_branch_2, X_branch_3], dim=1)
assert X_branch.size() == (N, 8192 * 3)
X = self.fc(X_branch)
assert X.size() == (N, 200)
return X
2.CUB200.py
数据集准备代码如下:
import os
import pickle
import numpy as np
import PIL.Image
import torch.utils.data
class CUB200(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, file_path, train=True, transform=None, target_transform=None):
self.file_path = file_path
self.train = train
self.transform = transform
self.target_transform = target_transform
if not (os.path.isfile(os.path.join(self.file_path, 'processed/train.pkl'))
and os.path.isfile(os.path.join(self.file_path, 'processed/test.pkl'))):
self.process()
if self.train:
print('Read the training dataset...')
self.train_data, self.train_labels = pickle.load(
open(os.path.join(self.file_path, 'processed/train.pkl'), 'rb'))
print('Read successfully!')
else:
print('Read the test dataset...')
self.test_data, self.test_labels = pickle.load(
open(os.path.join(self.file_path, 'processed/test.pkl'), 'rb'))
print('Read successfully!')
def __getitem__(self, index):
if self.train:
image, label = self.train_data[index], self.train_labels[index]
else:
image, label = self.test_data[index], self.test_labels[index]
# Transform to PIL.Image format
image = PIL.Image.fromarray(image)
if self.transform is not None:
image = self.transform(image)
if self.target_transform is not None:
label = self.target_transform(label)
return image, label
def __len__(self):
if self.train:
return len(self.train_data)
else:
return len(self.test_data)
def process(self):
image_path = os.path.join(self.file_path, 'images/')
id_and_path = np.genfromtxt(os.path.join(self.file_path, 'images.txt'), dtype=str)
id_and_isTrain = np.genfromtxt(os.path.join(self.file_path, 'train_test_split.txt'), dtype=int)
train_data = []
train_labels = []
test_data = []
test_labels = []
print('Data preprocessing, storage files')
# pbar = tqdm(total=len(id_and_path))
for id in range(len(id_and_path)):
image = PIL.Image.open(os.path.join(image_path, id_and_path[id, 1]))
label = int(id_and_path[id, 1][:3]) - 1
# Converts gray scale to RGB
if image.getbands()[0] == 'L':
image = image.convert('RGB')
np_image = np.array(image)
image.close()
if id_and_isTrain[id, 1] == 1:
train_data.append(np_image)
train_labels.append(label)
else:
test_data.append(np_image)
test_labels.append(label)
# pbar.update(1)
# pbar.close()
# Store as a.pkl file
pickle.dump((train_data, train_labels), open(os.path.join(self.file_path, 'processed/train.pkl'), 'wb'))
pickle.dump((test_data, test_labels), open(os.path.join(self.file_path, 'processed/test.pkl'), 'wb'))
3.Train.py
训练代码如下(已修改):
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim
import torch.utils.data
import torchvision
import os
import NetModel
import CUB200
# base_lr = 0.1
# batch_size = 24
num_epochs = 200
weight_decay = 1e-8
num_classes = 200
cub200_path = 'E:/DataSets/CUB_200_2011/'
save_model_path = 'model_saved'
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
fc = 1
ft = 2
def train(mode, Model, model_path, base_lr, batch_size):
# load the network.
model = Model
model = model.to(device)
param_to_optim = []
if mode == fc:
# Load the fc parameter.
for param in model.parameters():
if not param.requires_grad:
continue
param_to_optim.append(param)
elif mode == ft:
# Load the saved model.
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(os.path.join(save_model_path,
model_path),
map_location=lambda storage, loc: storage))
# Load all parameters.
param_to_optim = model.parameters()
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(param_to_optim, lr=base_lr, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=weight_decay)
# If the incoming value does not increase for 3 consecutive times, the learning rate will be reduced by 0.1 times
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, mode='max', factor=0.1, patience=3, verbose=True)
# Calculate the mean and variance of each channel of sample data,
# run it only once, and record the corresponding value
# get_statistic()
# Mean and variance of CUB_200 dataset are [0.4856, 0.4994, 0.4324], [0.1817, 0.1811, 0.1927]
# Set up the data preprocessing process
train_transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose([torchvision.transforms.Resize(448),
torchvision.transforms.CenterCrop(448),
torchvision.transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
torchvision.transforms.Normalize([0.4856, 0.4994, 0.4324],
[0.1817, 0.1811, 0.1927])])
test_transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose([torchvision.transforms.Resize(448),
torchvision.transforms.CenterCrop(448),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
torchvision.transforms.Normalize([0.4856, 0.4994, 0.4324],
[0.1817, 0.1811, 0.1927])])
train_data = CUB200.CUB200(cub200_path, train=True, transform=train_transform)
test_data = CUB200.CUB200(cub200_path, train=False, transform=test_transform)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=test_data, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
print('Start training ...')
best_acc = 0.
best_epoch = 0
end_patient = 0
training_accuracy = []
testing_accuracy = []
epochs = []
size = len(train_loader.dataset)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
correct = 0
total = 0
epoch_loss = 0.
for i, (images, labels) in enumerate(train_loader):
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
epoch_loss += loss
_, prediction = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
correct += (prediction == labels).sum().item()
total += labels.size(0)
if i % 50 == 49:
print('Epoch %d: Iter %d/%d, Loss %g' % (epoch + 1, (i + 1)*batch_size, size, loss))
train_acc = 100 * correct / total
print('Testing on test dataset...')
test_acc = test_accuracy(model, test_loader)
print('Epoch [{}/{}] Loss: {:.4f} Train_Acc: {:.4f} Test1_Acc: {:.4f}'
.format(epoch + 1, num_epochs, epoch_loss, train_acc, test_acc))
scheduler.step(test_acc)
training_accuracy.append(train_acc)
testing_accuracy.append(test_acc)
epochs.append(epoch)
if test_acc > best_acc:
if mode == fc:
model_file = os.path.join(save_model_path, 'CUB_200_train_fc_epoch_%d_acc_%g.pth' %
(best_epoch, best_acc))
if os.path.isfile(model_file):
os.remove(os.path.join(save_model_path, 'CUB_200_train_fc_epoch_%d_acc_%g.pth' %
(best_epoch, best_acc)))
end_patient = 0
best_acc = test_acc
best_epoch = epoch + 1
print('The accuracy is improved, save model')
torch.save(model.state_dict(), os.path.join(save_model_path,
'CUB_200_train_fc_epoch_%d_acc_%g.pth' %
(best_epoch, best_acc)))
elif mode == ft:
model_file = os.path.join(save_model_path, 'CUB_200_train_ft_epoch_%d_acc_%g.pth' %
(best_epoch, best_acc))
if os.path.isfile(model_file):
os.remove(os.path.join(save_model_path, 'CUB_200_train_ft_epoch_%d_acc_%g.pth' %
(best_epoch, best_acc)))
end_patient = 0
best_acc = test_acc
best_epoch = epoch + 1
print('The accuracy is improved, save model')
torch.save(model.state_dict(), os.path.join(save_model_path,
'CUB_200_train_ft_epoch_%d_acc_%g.pth' %
(best_epoch, best_acc)))
else:
end_patient += 1
print('Impatient: ', end_patient)
# If the accuracy of the 10 iteration is not improved, the training ends
if end_patient >= 10:
break
print('After the training, the end of the epoch %d, the accuracy %g is the highest' % (best_epoch, best_acc))
print('epochs:', epochs)
print('training accuracy:', training_accuracy)
print('testing accuracy:', testing_accuracy)
def test_accuracy(model, test_loader):
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
correct = 0
total = 0
for images, labels in test_loader:
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
_, prediction = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
correct += (prediction == labels).sum().item()
total += labels.size(0)
model.train()
return 100 * correct / total
def get_statistic():
train_data = CUB200.CUB200(cub200_path, train=True, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor())
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=1, shuffle=False)
print('Calculate the mean and variance of the data')
mean = torch.zeros(3)
std = torch.zeros(3)
for X, _ in train_loader:
for d in range(3):
mean[d] += X[:, d, :, :].mean()
std[d] += X[:, d, :, :].std()
mean.div_(len(train_data))
std.div_(len(train_data))
print(mean)
print(std)
4.main.py
fc mode:训练HBP和分类全连接层
ft mode: fine-tuning微调模型
import Train
import NetModel
fc = 1
fc_base_lr = 0.1
fc_batch_size = 6
ft = 2
ft_base_lr = 0.001
ft_batch_size = 4
model = NetModel.HBP(pretrained=True)
model_path = ''
base_lr = 0.1
batch_size = 24
mode = fc
if mode == fc:
base_lr = fc_base_lr
batch_size = fc_batch_size
elif mode == ft:
base_lr = ft_base_lr
batch_size = ft_batch_size
# Train.get_statistic()
Train.train(mode=mode, Model=model, model_path=model_path, base_lr=base_lr, batch_size=batch_size)
四、训练结果
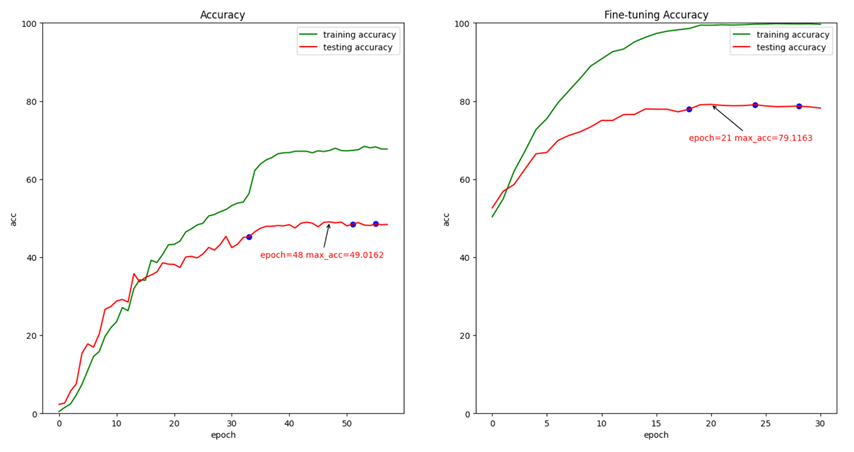
仅训练了HBP和全连接层后,最高准确度可达79.6859%。
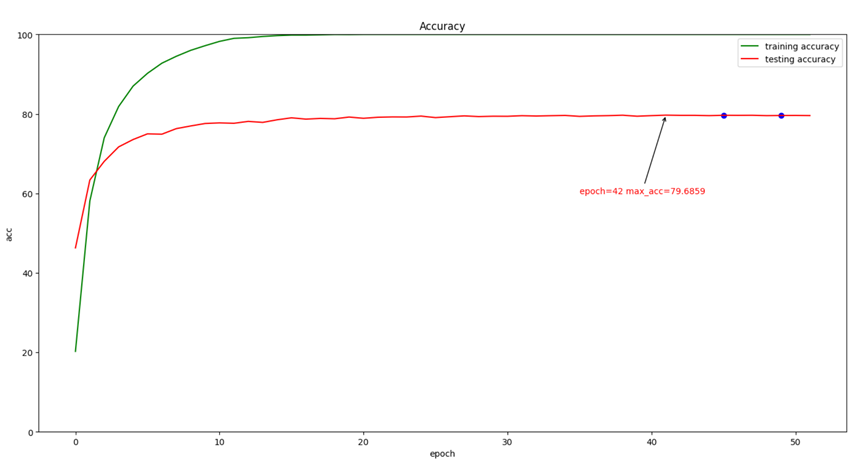
后来分析训练结果,才意识到在fc mode训练到第22个epoch时,training accuarcy已经达到100%了,而且loss已经很小且基本不下降了,所以继续训练的意义已经不大了。
(可以看出,在训练10个epoch之后,testing accuarcy就增长的很慢了,如果觉得训练时间过长,可减小Train.py中的patience和end_patient。)
与论文中的87.15%的准确度来说,我的模型泛化能力还是较差的。
# 47行
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, mode='max', factor=0.1, patience=3, verbose=True)
# 144行
if end_patient >= 10:
break
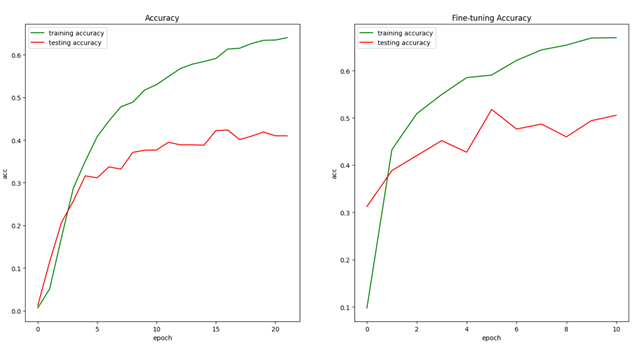
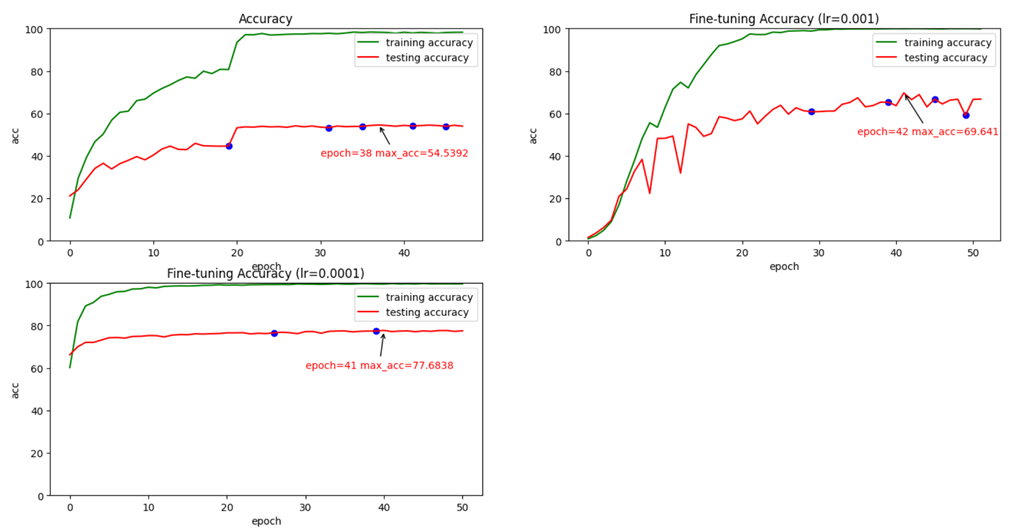
对比
VGG16:
ResNet34:
ResNet34+BCNN:
五、问题与改进
目前只进行了fc mode的训练,由于在batch size比8大的时候出现了RuntimeError: Unable to find a valid cuDNN algorithm to run convolution、CUDA out of memory的问题,所以我不得不将batch size降到了6。
参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33866063/article/details/121009069
考虑到fine-tuning训练参数的激增,如果不进行其他改进,我将无法进行ft训练。
随后,我咨询了学长,他的做法如下:
如果想要更大的batch_size但是电脑的显存或内存不够的话,一般我是这样解决的,每一次迭代会将loss.backward(),然后optimizer.step()根据回传的梯度更新网络,那么我可以跑两个batch,再做梯度更新,也就是第一次backward()之后不optimizer.step() 同时也不optimizer.zero_grad(),等到第二个batch backward之后再做梯度更新和清零。一些知识补充:因为backward计算后,默认会释放计算图(bp算法会需要这些信息),而这些计算图就是网络计算的一些中间结果,那么一次回传计算完梯度后,它会将这些梯度保留在模型每一层的属性里,计算图得到释放,你又有显存(内存)可以用,再跑下一个batch梯度一样回传,存到模型的每一层属性里,然后再更新就可以了,记得将两次回传的loss平均,这部分你可以自己想想怎么平均比较合理能够达到跟原来一个batch一样的效果。
总结
上文介绍了HBP的原理和实现,同时给出了基于pytorch的代码和初步训练结果。接下来,我将根据学长建议进行改进并对模型进行进一步的改进并作微调训练。
欢迎大家给出建议,交流指正~
最后
以上就是精明百合最近收集整理的关于细粒度分类:Hierarchical Bilinear Pooling(HBP),分级双线性池化(一)前言一、参考论文二、HBP简介三、基于pytorch的实现四、训练结果五、问题与改进总结的全部内容,更多相关细粒度分类:Hierarchical内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。


![[西瓜书]——第三章部分编程答案](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg12.png)
![matlab中bilinear函数,【Bilinear interpolation】双线性插值详解(转)[组图]](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg13.png)




发表评论 取消回复