1. Undirected graphical models(Markov random fields)
-
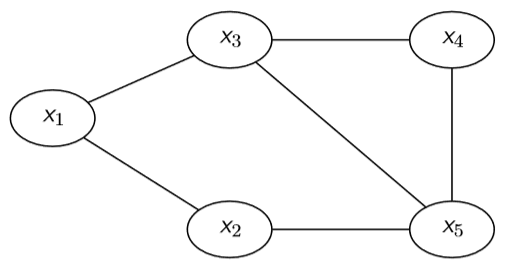
节点表示随机变量,边表示与节点相关的势函数
p x ( x ) ∝ φ 12 ( x 1 , x 2 ) φ 13 ( x 1 , x 3 ) φ 25 ( x 2 , x 5 ) φ 345 ( x 3 , x 4 , x 5 ) p_{mathbf{x}}(mathbf{x}) propto varphi_{12}left(x_{1}, x_{2}right) varphi_{13}left(x_{1}, x_{3}right) varphi_{25}left(x_{2}, x_{5}right) varphi_{345}left(x_{3}, x_{4}, x_{5}right) px(x)∝φ12(x1,x2)φ13(x1,x3)φ25(x2,x5)φ345(x3,x4,x5)
-
clique:全连接的节点集合
-
maximal clique:不是其他 clique 的真子集
**Theorem (Hammersley-Clifford) **: A strictly positive distribution p x ( x ) > 0 p_{mathsf{x}}(mathbf{x})>0 px(x)>0 satisfies the graph separation property of undirected graphical models if and only if it can be represented in the factorized form
p x ( x ) ∝ ∏ A ∈ C ψ x A ( x A ) p_{mathsf{x}}(mathbf{x}) propto prod_{mathcal{A} in mathcal{C}} psi_{mathbf{x}_{mathcal{A}}}left(mathbf{x}_{mathcal{A}}right) px(x)∝A∈C∏ψxA(xA)
- conditional independence: x A 1 ⊥ x A 2 ∣ x A 3 mathbf{x}_{mathcal{A}_{1}} perp mathbf{x}_{mathcal{A}_{2}} | mathbf{x}_{mathcal{A}_{3}} xA1⊥xA2∣xA3
2. Directed graphical models(Bayesian network)
-
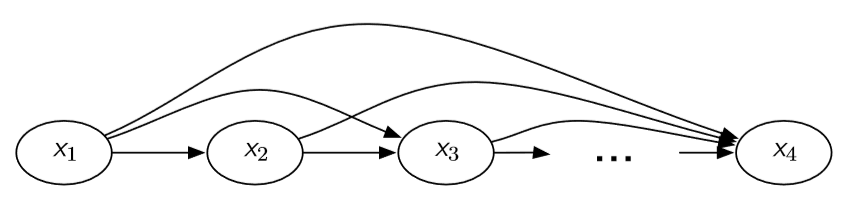
节点表示随机变量,有向边表示条件关系
p x 1 , … , x n = p x 1 ( x 1 ) p x 2 ∣ × 1 ( x 2 ∣ x 1 ) ⋯ p x n ∣ x 1 , … , x n − 1 ( x n ∣ x 1 , … , x n − 1 ) p_{mathrm{x}_{1}, ldots, mathrm{x}_{n}}=p_{mathrm{x}_{1}}left(x_{1}right) p_{mathrm{x}_{2} | times_{1}}left(x_{2} | x_{1}right) cdots p_{mathrm{x}_{n} | x_{1}, ldots, x_{n-1}}left(x_{n} | x_{1}, ldots, x_{n-1}right) px1,…,xn=px1(x1)px2∣×1(x2∣x1)⋯pxn∣x1,…,xn−1(xn∣x1,…,xn−1)
-
Directed acyclic graphs (DAG)
-
Fully-connected DAG
-
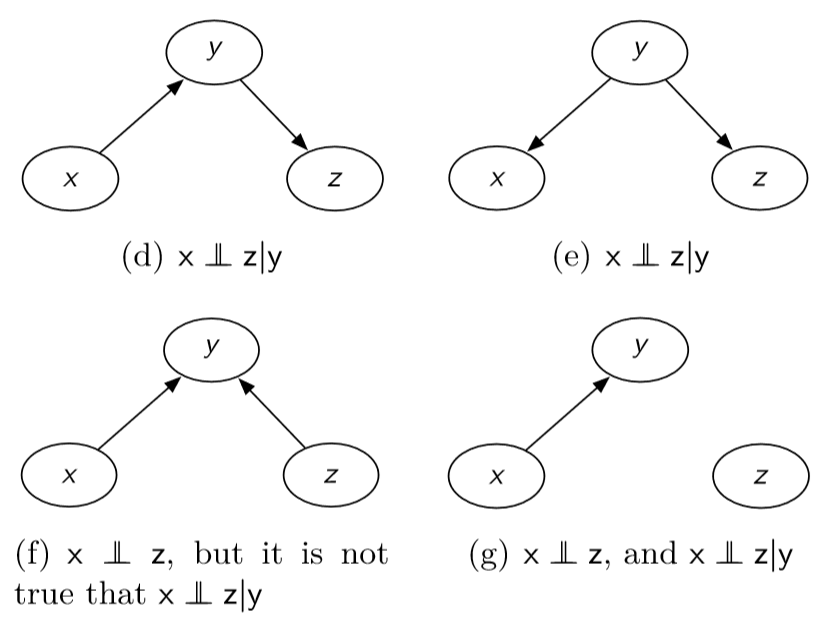
conditional independence: x A 1 ⊥ x A 2 ∣ x A 3 mathbf{x}_{mathcal{A}_{1}} perp mathbf{x}_{mathcal{A}_{2}} | mathbf{x}_{mathcal{A}_{3}} xA1⊥xA2∣xA3
-
Bayes ball algorithm
- primary shade: A 3 mathcal{A_3} A3 中的节点
- secondary shade: primary shade 的节点,以及 secondary shade 的父节点
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-8UKlSiFL-1580777349196)(C:Users1AppDataRoamingTyporatypora-user-images1574319393095.png)]
3. Factor graph
-
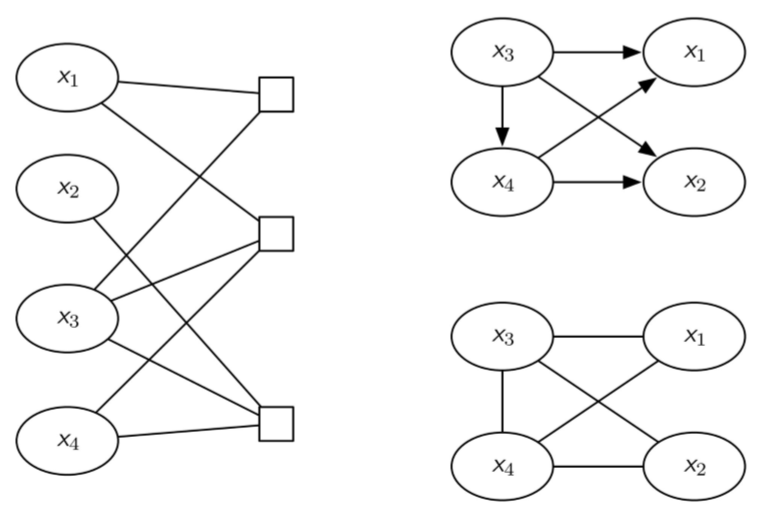
有 variable nodes 和 factor nodes,是 bipartitie graph
p x ( x ) ∝ ∏ j f j ( x f j ) p_{mathbf{x}}(mathbf{x}) propto prod_{j} f_{j}left(mathbf{x}_{f_{j}}right) px(x)∝j∏fj(xfj)
-
因子图比 directed graph 和 undirected graph 的表示能力更强,比如 p ( x ) = 1 Z ϕ 12 ( x 1 , x 2 ) ϕ 13 ( x 1 , x 3 ) ϕ 23 ( x 2 , x 3 ) p(x)=frac{1}{Z}phi_{12}(x_1,x_2)phi_{13}(x_1,x_3)phi_{23}(x_2,x_3) p(x)=Z1ϕ12(x1,x2)ϕ13(x1,x3)ϕ23(x2,x3)
-
因子图可以与 DAG 相互转化(根据 x 1 , . . . , x n x_1,...,x_n x1,...,xn 依次根据 conditional independence 决定父节点),DAG又可以转化为 undirected graph
4. Measuring goodness of graphical representations
- 给定分布 D 和图 G,他们之间没必要有联系
- C I ( D ) CI(D) CI(D):the set of conditional independencies satisfied by D D D
- C I ( G ) CI(G) CI(G): the set of all conditional independencies implied by G G G
- I-map: C I ( G ) ⊂ C I ( D ) C I(mathcal{G}) subset C I(D) CI(G)⊂CI(D)
- D-map: : C I ( G ) ⊃ C I ( D ) C I(mathcal{G}) supset C I(D) CI(G)⊃CI(D)
- P-map: C I ( G ) = C I ( D ) C I(mathcal{G}) = C I(D) CI(G)=CI(D)
- minimal I-map: Aminimal I-mapisanI-mapwiththepropertythatremovinganysingle edge would cause the graph to no longer be an I-map.
Remarks: G 中去掉一个边会使该 map 中有更多的 conditional independence,也即 C I ( G ) CI(G) CI(G) 更大,更不易满足 I-map条件。I-map 可以表示分布 D,但是 D-map 不能
其他内容请看:
统计推断(一) Hypothesis Test
统计推断(二) Estimation Problem
统计推断(三) Exponential Family
统计推断(四) Information Geometry
统计推断(五) EM algorithm
统计推断(六) Modeling
统计推断(七) Typical Sequence
统计推断(八) Model Selection
统计推断(九) Graphical models
统计推断(十) Elimination algorithm
统计推断(十一) Sum-product algorithm
最后
以上就是欣慰电灯胆最近收集整理的关于统计推断(九) Graphical models的全部内容,更多相关统计推断(九)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复