项目场景:
See also: Serial receiver and datapath
We want to add parity checking to the serial receiver. Parity checking adds one extra bit after each data byte. We will use odd parity, where the number of 1s in the 9 bits received must be odd. For example, 101001011 satisfies odd parity (there are 5 1s), but 001001011 does not.
Change your FSM and datapath to perform odd parity checking. Assert the done signal only if a byte is correctly received and its parity check passes. Like the serial receiver FSM, this FSM needs to identify the start bit, wait for all 9 (data and parity) bits, then verify that the stop bit was correct. If the stop bit does not appear when expected, the FSM must wait until it finds a stop bit before attempting to receive the next byte.
You are provided with the following module that can be used to calculate the parity of the input stream (It’s a TFF with reset). The intended use is that it should be given the input bit stream, and reset at appropriate times so it counts the number of 1 bits in each byte.
module parity (
input clk,
input reset,
input in,
output reg odd);
always @(posedge clk)
if (reset) odd <= 0;
else if (in) odd <= ~odd;
endmodule
Note that the serial protocol sends the least significant bit first, and the parity bit after the 8 data bits.
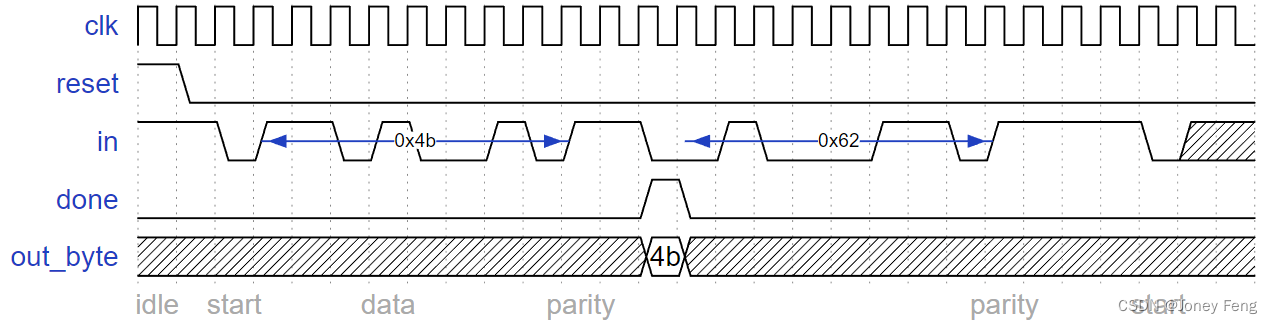
Some timing diagrams
No framing errors. Odd parity passes for first byte, fails for second byte.
问题描述
请参见:串行接收器和数据路径。
我们想在串行接收器中添加奇偶校验。奇偶校验在每个数据字节后增加一个额外的位。我们将使用奇数奇偶校验,其中接收的9位中的1的数量必须为奇数。例如,101001011满足奇偶校验(有5个1),而001001011不满足奇偶校验。
修改FSM和数据路径为奇偶校验。只有当一个字节被正确接收并且其奇偶校验通过时,才断言完成的信号。像串行接收FSM一样,这个FSM需要识别起始位,等待所有9位(数据和校验位),然后验证停止位是否正确。如果停止位没有出现,FSM必须等待,直到它找到一个停止位,然后再尝试接收下一个字节。
您可以使用以下模块来计算输入流的奇偶校验(它是一个带复位的TFF)。预期的用途是,应该给它输入位流,并在适当的时间重置,以便它计算每个字节中1位的数量。
module parity (
input clk,
input reset,
input in,
output reg odd);
always @(posedge clk)
if (reset) odd <= 0;
else if (in) odd <= ~odd;
endmodule
注意,串行协议先发送最低有效位,然后发送校验位。
一些时间图
没有框架的错误。奇偶校验对第一个字节通过,对第二个字节失败。
原因分析:
像串行接收FSM一样,这个FSM需要识别起始位,等待所有9位(数据和校验位),然后验证停止位是否正确。如果停止位没有出现,FSM必须等待,直到它找到一个停止位,然后再尝试接收下一个字节。
首先要寻找起始位0,找到起始位后依次识别8位数据位和1位奇偶校验位,再次就是寻找停止位1。通过FSM有限状态机明确状态跳转的条件,通过对状态的判断可以得出done信号的状态转换条件,通过移位寄存器可以对识别到的八位数据进行存储,再结合奇偶校验函数odd可以判断识别到的八位数据是不是我们需要的数据。
解决方案:
module top_module(
input clk,
input in,
input reset, // Synchronous reset
output [7:0] out_byte,
output done
); //
reg [3:0] state;
reg [3:0] next_state;
parameter IDEL = 4'd0;
parameter START = 4'd1;
parameter B1 = 4'd2;
parameter B2 = 4'd3;
parameter B3 = 4'd4;
parameter B4 = 4'd5;
parameter B5 = 4'd6;
parameter B6 = 4'd7;
parameter B7 = 4'd8;
parameter B8 = 4'd9;
parameter STOP = 4'd10;
parameter SEARCH = 4'd11;
parameter PARITY = 4'd12;
reg [7:0] data_reg;
always@(*)
case(state)
IDEL :next_state <= (!in) ? START : IDEL;
START :next_state <= B1;
B1 :next_state <= B2;
B2 :next_state <= B3;
B3 :next_state <= B4;
B4 :next_state <= B5;
B5 :next_state <= B6;
B6 :next_state <= B7;
B7 :next_state <= B8;
B8 :next_state <= PARITY;
PARITY :next_state <= (in) ? STOP : SEARCH;
SEARCH :next_state <= (in) ? IDEL : SEARCH;
STOP :next_state <= (!in) ? START : IDEL ;
default:next_state <= IDEL;
endcase
always@(posedge clk)
if(reset)
state <= IDEL;
else
state <= next_state;
always@(posedge clk)
if(reset)
data_reg <= 8'd0;
else
case(next_state)
B1: data_reg[0] <= in;
B2: data_reg[1] <= in;
B3: data_reg[2] <= in;
B4: data_reg[3] <= in;
B5: data_reg[4] <= in;
B6: data_reg[5] <= in;
B7: data_reg[6] <= in;
B8: data_reg[7] <= in;
PARITY: data_reg <= data_reg;
STOP: data_reg <= data_reg;
default: data_reg <= 8'd0;
endcase
//assign done = (odd == 1'b1);
always@(posedge clk)
if(reset)
done <= 1'b0;
else if((next_state == STOP) && (odd == 1'b1))
done <= 1'b1;
else
done <= 1'b0;
// Modify FSM and datapath from Fsm_serialdata
always@(posedge clk)
if(reset)
out_byte <= 8'd0;
else if((next_state == STOP) && (odd == 1'b1))
out_byte <= data_reg;
else
out_byte <= 8'd0;
// New: Add parity checking.
wire odd,reset_p;
assign reset_p = (next_state == START || reset == 1'b1);
parity parity_inst
(
. clk (clk ),
. reset (reset_p ),
. in (in),
. odd (odd )
);
endmodule
最后
以上就是高大巨人最近收集整理的关于Serial receiver with parity checking(Fsm serialdp)项目场景:问题描述原因分析:解决方案:的全部内容,更多相关Serial内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复