前言
本文档主要介绍android平台下bluetooth的应用层软件,先介绍bluetooth应用层的框架,接着分别介绍Bluedroid层软件、Bluetooth应用程序(Bluetooth.apk),Bluetooth framework层,最后完整分析一些蓝牙的操作流程。基于android 5.1的平台,涉及的bluetooth硬件为realtek的蓝牙。文档主要针对蓝牙的初学者,提供基础的学习指导。
1 Bluetooth应用层框架介绍
要介绍android平台bluetooth应用层的软件,首先介绍一下bluetooth的应用层整体框架,如图1为android下的bluetooth的框架。
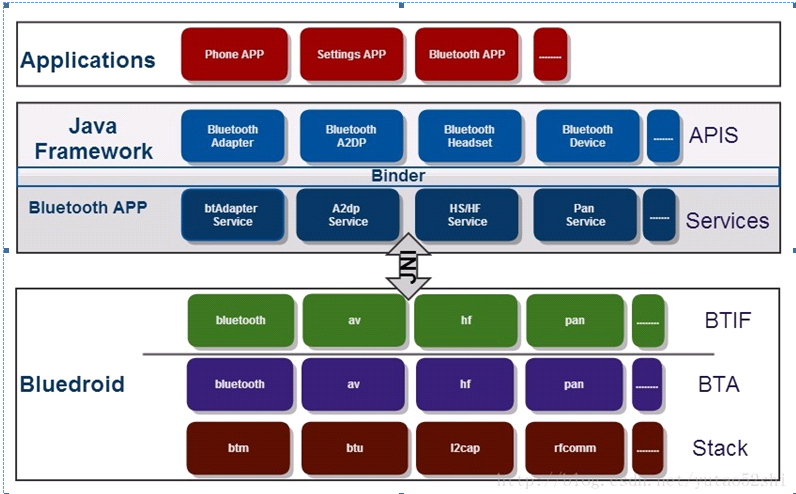
图1 bluetooth应用层框架
Applications:Android蓝牙应用程序,就是使用蓝牙的API的程序;
java Framework:提供给应用使用的API,我们平时使用的BluetoothAdapter,BluetoothDevice,BluetoothSocket等;
BluetoothAPP:这个应该也是属于java framework范畴,不过由于它比较特殊,所以独立出来,提供所有的上层服务以及与Bluedroid底层进行交互。其中btAdapter主要提供蓝牙的基本操作,比如enable, disable, discovery, pair, unpair, createRfcomm等,其他的就都是Profile的各自的Service了;
Bluedroid:蓝牙协议栈,提供所有蓝牙的实际操作,开关蓝牙,蓝牙的管理,搜索管理,链路管理,各种profile的实现,包括HCI,ACL,SCO,L2CAP,各种profile等;
这里Bluedroid分为三部分:
BTIF(Bluetooth Interface):提供所有Bluetooth.apk需要的API(使用HAL)
BTA(Bluetooth Application):蓝牙应用,一般指蓝牙的Profile的Bluedroid实现。
Stack:实现所有蓝牙底层的操作,其中还要分为btm(Bluetooth manager),btu(Bluetooth Upper Layer)等。
2 Bluedroid软件介绍
在第一节的bluetooth应用层框架图中,已可看到bluedroid的一个架构,但bluedroid与底层的接口就没表示出来。图2为bluedroid各层交互的框架图。
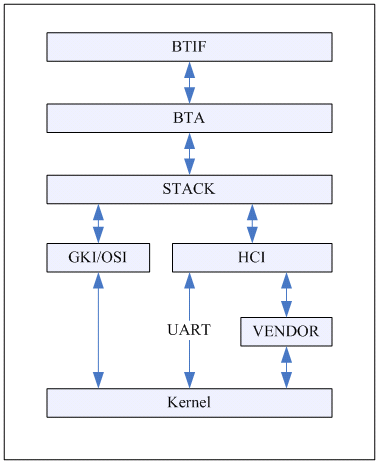
图2 bluedroid框架图
下面再看一下bluedroid下的目录结构及每个目录的功能。
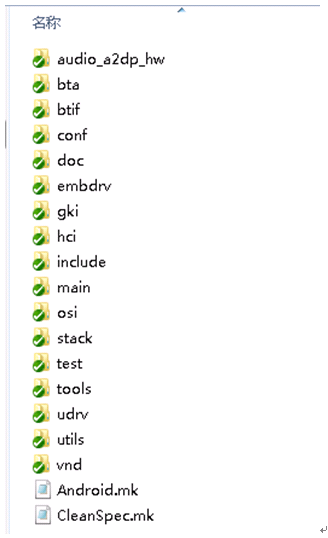
图3 bluedroid目录结构
audio_a2dp_hw: Implements hal for bluedroid a2dp audio device。 a2dp在bluedroid中的hal层实现。它通过socket与stack通信(通信机制实现参考udv目录下的uipc);
bta:buetooth application layer,实现应用层的一些接口,但都由Btif层进行管理和调用。
Ag:audio gateway (AG) subsystem of BTA
Ar:implementation for the audio/video registration module.
Av:implementation of the API for the advanced audio/video (AV)
* subsystem of BTA, Broadcom’s Bluetooth application layer for mobile
* phones.
Dm:API implementation file for the BTA device manager
Fs: implementation file for the file system call-in functions. //phone
Gattr: the GATT server and client implementation
Hh:host hid
btif:all BTIF functions accessed from main bluetooth HAL(与android的Bluetooth apk的jni层通信的接口,真正的为app提供interface的接口);
conf:是Bluedroid的一些配置文件;
embdrv: 主要负责sbc编码,SBC是由蓝牙特别兴趣组(SIG)提出的一种用于蓝牙设备标准音频编解码器的高效编码方法。在蓝牙技术的A2DP的音频数据规格中,SBC是用来保持互连能力的一个十分重要的音频数据编码方法,它是MP3和MPEG-4 AAC的规定选项;
gki/osi:general kernel interface/os interface,针对os的移植层,包括多任务和timer实现,实际就是为stack代码提供一个抽象的多任务和时间控制环境,达到可移植的目的;
hci:host control interface,实现hci的协议,并连接stack层与底层通信的实现;
main:处理配置信息,各个模块的初始化,连接btif与hci,提供btif控制hci的接口;
stack: 协议栈代码,各种profile;
udrv:代码作用是跟a2dp端进行socket通信,处理命令和a2dp数据pcm流,media task调用这里的接口,实际就是跟audio_a2dp_hw 的audio hal通信;
utils:杂项,很简单,目前就是提高a2dp任务优先级的函数;
vnd: vendor specific feature for BLE;
其中还有一个bt vendor没包含在bluedroid中,对于realtek的蓝牙,都是使用相同的bluedroid,但不同的蓝牙模块有不同的bt vendor库,该vendor库的功能是给蓝牙模块上、掉电,打开、关闭、配置串口,download fw(usb接口蓝牙的download fw在驱动内实现)。
2.1 Bluedroid对上层接口
Bluedroid与上层有多个接口, bluedroidbtifsrcbluetooth.c为一个主要接口,负责蓝牙的开关及基本控制, bluedroidaudio_a2dp_hwaudio_a2dp_hw.c专门针对a2dp的控制,还有部分profile也提供一些接口,这些接口为不同profile的独立接口。其中bluetooth.c实现一系列接口,由上层调用来控制蓝牙,同时在初始化的时候,上层会传递过来一个回调接口,当bluedroid有消息或结果需要通知上层时,就通过该回调接口。但像蓝牙的opp、hid等profile的数据就不是通过接口传递的,都是创建socket接口来交互数据的。
bluedroidbtifsrcbluetooth.c
static const bt_interface_t bluetoothInterface = {
sizeof(bluetoothInterface),
init,
enable,
disable,
get_recv_byte,
get_send_byte,
cleanup,
get_adapter_properties,
get_adapter_property,
set_adapter_property,
get_remote_device_properties,
get_remote_device_property,
set_remote_device_property,
get_remote_service_record,
get_remote_services,
start_discovery,
cancel_discovery,
create_bond,
remove_bond,
cancel_bond,
get_connection_state,
pin_reply,
ssp_reply,
get_profile_interface,
dut_mode_configure,
dut_mode_send,
#if BLE_INCLUDED == TRUE
le_test_mode,
#else
NULL,
#endif
config_hci_snoop_log,
set_os_callouts,
read_energy_info,
};
hardwarelibhardwareincludehardwarebluetooth.h
typedef struct { /* 蓝牙接口结构体定义 */
/** set to sizeof(bt_interface_t) */
size_t size;
/**
* Opens the interface and provides the callback routines
* to the implemenation of this interface.
*/
int (*init)(bt_callbacks_t* callbacks );
/** Enable Bluetooth. */
int (*enable)(void);
/** Disable Bluetooth. */
int (*disable)(void);
/** Get Bluetooth recv */
int (*get_recv_byte)(void);
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
int (*read_energy_info)();
} bt_interface_t;
bluedroidbtifsrcbluetooth.c
static int init(bt_callbacks_t* callbacks ) /* 初始化时,上层传递下来的回调接口结构体 */
{
ALOGI(“init”);
/* sanity check */
if (interface_ready() == TRUE)
return BT_STATUS_DONE;
/* store reference to user callbacks */
Bt_hal_cbacks = callbacks;
/* add checks for individual callbacks ? */
bt_utils_init();
/* init btif */
btif_init_bluetooth();
return BT_STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
hardwarelibhardwareincludehardwarebluetooth.h
/** Bluetooth DM callback structure. */ /* 回调结构体 */
typedef struct {
/** set to sizeof(bt_callbacks_t) */
size_t size;
adapter_state_changed_callback adapter_state_changed_cb;
adapter_properties_callback adapter_properties_cb;
remote_device_properties_callback remote_device_properties_cb;
device_found_callback device_found_cb;
discovery_state_changed_callback discovery_state_changed_cb;
pin_request_callback pin_request_cb;
ssp_request_callback ssp_request_cb;
bond_state_changed_callback bond_state_changed_cb;
acl_state_changed_callback acl_state_changed_cb;
callback_thread_event thread_evt_cb;
dut_mode_recv_callback dut_mode_recv_cb;
le_test_mode_callback le_test_mode_cb;
energy_info_callback energy_info_cb;
} bt_callbacks_t;
其中在get_profile_interface函数中会返回各种profile提供的接口。
bluedroidbtifsrcbluetooth.c
static const void* get_profile_interface (const char *profile_id)
{
ALOGI("get_profile_interface %s", profile_id);
/* sanity check */
if (interface_ready() == FALSE)
return NULL;
/* check for supported profile interfaces */
if (is_profile(profile_id, BT_PROFILE_HANDSFREE_ID))
return btif_hf_get_interface();
if (is_profile(profile_id, BT_PROFILE_HANDSFREE_CLIENT_ID))
return btif_hf_client_get_interface();
if (is_profile(profile_id, BT_PROFILE_SOCKETS_ID)) /* rfcomm使用 */
return btif_sock_get_interface();
if (is_profile(profile_id, BT_PROFILE_PAN_ID))
return btif_pan_get_interface();
if (is_profile(profile_id, BT_PROFILE_ADVANCED_AUDIO_ID))
return btif_av_get_src_interface();
if (is_profile(profile_id, BT_PROFILE_ADVANCED_AUDIO_SINK_ID))
return btif_av_get_sink_interface();
if (is_profile(profile_id, BT_PROFILE_HIDHOST_ID))
return btif_hh_get_interface();
if (is_profile(profile_id, BT_PROFILE_HEALTH_ID))
return btif_hl_get_interface();
if (is_profile(profile_id, BT_PROFILE_MAP_CLIENT_ID))
return btif_mce_get_interface();
#if ( BTA_GATT_INCLUDED == TRUE && BLE_INCLUDED == TRUE)
if (is_profile(profile_id, BT_PROFILE_GATT_ID))
return btif_gatt_get_interface();
#endif
if (is_profile(profile_id, BT_PROFILE_AV_RC_ID))
return btif_rc_get_interface();
if (is_profile(profile_id, BT_PROFILE_AV_RC_CTRL_ID))
return btif_rc_ctrl_get_interface();
return NULL;
}
下面为使用rfcomm通信时的使用的接口:
bluedroidbtifsrcbtif_sock.c
static btsock_interface_t sock_if = {
sizeof(sock_if),
btsock_listen,
btsock_connect
};
btsock_interface_t *btif_sock_get_interface()
{
return &sock_if;
}
audio_a2dp_hw.c的接口就没有看到回调函数,但audio_a2dp_hw.c中创建了2个socket接口,一个用于控制命令,一个用于a2dp数据的传输。
bluedroidaudio_a2dp_hwaudio_a2dp_hw.c
static int adev_open(const hw_module_t* module, const char* name,
hw_device_t** device)
{
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
adev->device.get_parameters = adev_get_parameters;
adev->device.get_input_buffer_size = adev_get_input_buffer_size;
adev->device.open_output_stream = adev_open_output_stream;
adev->device.close_output_stream = adev_close_output_stream;
adev->device.open_input_stream = adev_open_input_stream;
adev->device.close_input_stream = adev_close_input_stream;
adev->device.dump = adev_dump;
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
static struct hw_module_methods_t hal_module_methods = {
.open = adev_open,
};
struct audio_module HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.version_major = 1,
.version_minor = 0,
.id = AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "A2DP Audio HW HAL",
.author = "The Android Open Source Project",
.methods = &hal_module_methods,
},
};
bluedroidaudio_a2dp_hwaudio_a2dp_hw.c
static int adev_open_input_stream(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
audio_io_handle_t handle,
audio_devices_t devices,
struct audio_config *config,
struct audio_stream_in **stream_in,
audio_input_flags_t flags __unused,
const char *address __unused,
audio_source_t source __unused)
{
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
in->stream.common.set_parameters = in_set_parameters;
in->stream.common.get_parameters = in_get_parameters;
in->stream.common.add_audio_effect = in_add_audio_effect;
in->stream.common.remove_audio_effect = in_remove_audio_effect;
in->stream.set_gain = in_set_gain;
in->stream.read = in_read; /* 该函数会打开data socket */
in->stream.get_input_frames_lost = in_get_input_frames_lost;
/* initialize a2dp specifics */
a2dp_stream_common_init(&in->common);
*stream_in = &in->stream;
a2dp_dev->input = in;
a2dp_open_ctrl_path(&in->common);
bluedroidaudio_a2dp_hwaudio_a2dp_hw.c
static void a2dp_open_ctrl_path(struct a2dp_stream_common *common)
{
int i;
/* retry logic to catch any timing variations on control channel */
for (i = 0; i < CTRL_CHAN_RETRY_COUNT; i++)
{
/* connect control channel if not already connected */
if ((common->ctrl_fd = skt_connect(A2DP_CTRL_PATH, common->buffer_sz)) > 0)
{
bluedroidaudio_a2dp_hwaudio_a2dp_hw.c
static ssize_t in_read(struct audio_stream_in *stream, void* buffer,
size_t bytes)
{
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
/* only allow autostarting if we are in stopped or standby */
if ((in->common.state == AUDIO_A2DP_STATE_STOPPED) ||
(in->common.state == AUDIO_A2DP_STATE_STANDBY))
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&in->common.lock);
if (start_audio_datapath(&in->common) < 0)
bluedroidaudio_a2dp_hwaudio_a2dp_hw.c
static int start_audio_datapath(struct a2dp_stream_common *common)
{
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
/* connect socket if not yet connected */
if (common->audio_fd == AUDIO_SKT_DISCONNECTED)
{
common->audio_fd = skt_connect(A2DP_DATA_PATH, common->buffer_sz);2.2 Bluedroid中HCI层接口
Hci层处于bluedroid架构的最下面,向下与bt-vendor、内核交互,向上与bluedroid核心层交互。
2.2.1 Bluedroid中HCI与bt-vendor接口
Bluedroid与下层的交互接口全由hci目录的代码实现,在vendor.c文件中加载bt-vendor库,使用bt-vendor提供的接口,并把一个回调结构体传递给bt-vendor。
bluedroidhcisrcvendor.c
static const char *VENDOR_LIBRARY_NAME = "libbt-vendor.so"; /* 固定的bt-vendor库名 */
bool vendor_open(const uint8_t *local_bdaddr) {
assert(lib_handle == NULL);
lib_handle = dlopen(VENDOR_LIBRARY_NAME, RTLD_NOW);
if (!lib_handle) {
ALOGE("%s unable to open %s: %s", __func__, VENDOR_LIBRARY_NAME, dlerror());
goto error;
}
vendor_interface = (bt_vendor_interface_t *)dlsym(lib_handle, VENDOR_LIBRARY_SYMBOL_NAME);
if (!vendor_interface) {
ALOGE("%s unable to find symbol %s in %s: %s", __func__, VENDOR_LIBRARY_SYMBOL_NAME, VENDOR_LIBRARY_NAME, dlerror());
goto error;
}
/* 调用bt-vendor的初始化并传递回调结构体 */
int status = vendor_interface->init(&vendor_callbacks, (unsigned char *)local_bdaddr);
bluedroidhciincludebt_vendor_lib.h
typedef struct { /* bt-vendor提供的3个接口 */
/** Set to sizeof(bt_vndor_interface_t) */
size_t size;
/**
* Caller will open the interface and pass in the callback routines
* to the implemenation of this interface.
*/
int (*init)(const bt_vendor_callbacks_t* p_cb, unsigned char *local_bdaddr);
/** Vendor specific operations */
int (*op)(bt_vendor_opcode_t opcode, void *param);
/** Closes the interface */
void (*cleanup)(void);
} bt_vendor_interface_t;
bluedroidhcisrcvendor.c
static const bt_vendor_callbacks_t vendor_callbacks = { /* hci传递给bt-vendor的回调结构体 */
sizeof(vendor_callbacks),
firmware_config_cb,
sco_config_cb,
low_power_mode_cb,
sco_audiostate_cb,
buffer_alloc,
buffer_free,
transmit_cb,
epilog_cb
};
Bt-vendor库中,init和cleanup函数只是做开始时初始化及退出时清理的工作,主要工作都在op函数中实现。
modulesrtl8723bslibbtsrcbt_vendor_rtk.c
static int op(bt_vendor_opcode_t opcode, void *param)
{
switch(opcode)
{
case BT_VND_OP_POWER_CTRL:
…… /* 省略中间代码 */ /* 控制蓝牙模块的上掉电 */
break;
case BT_VND_OP_FW_CFG:
/* uart接口蓝牙加载fw */
/* usb接口蓝牙fw在驱动中加载,蓝牙上电时就自动加载,这里直接返回成功 */
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
break;
case BT_VND_OP_SCO_CFG:
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
break;
case BT_VND_OP_USERIAL_OPEN:
/* 打开uart口,把打开的fd传回给hci层。无论是uart接口蓝牙,还是usb接口蓝牙(usb接口蓝牙在驱动层虚拟出一个uart口),对bt-vendor层都是打开一个串口,所以从bluedroid层看,与底层的数据收发就是对uart口的收发 */
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
break;
case BT_VND_OP_USERIAL_CLOSE:
…… /* 省略中间代码 */ /* 关闭uart口 */
break;
case BT_VND_OP_GET_LPM_IDLE_TIMEOUT:
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
break;
case BT_VND_OP_LPM_SET_MODE:
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
break;
case BT_VND_OP_LPM_WAKE_SET_STATE:
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
break;
case BT_VND_OP_EPILOG:
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
break;
}
bluedroidhcisrcuserial.c
bool userial_open(userial_port_t port) {
/* hci层调用bt-vendor层打开uart口,返回uart口句柄,hci层对数据的收发就使用该句柄 */
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
int num_ports = vendor_send_command(BT_VND_OP_USERIAL_OPEN, &fd_array);
if (num_ports != 1) {
ALOGE("%s opened wrong number of ports: got %d, expected 1.", __func__, num_ports);
goto error;
}
userial_cb.fd = fd_array[0];2.2.2 Bluedroid中HCI层协议
Hci层有两个功能,一个为实现hci层协议,就是所见的h4、h5协议,另一个为连接stack层与bt-vendor层,实现stack层与硬件的通信传递。
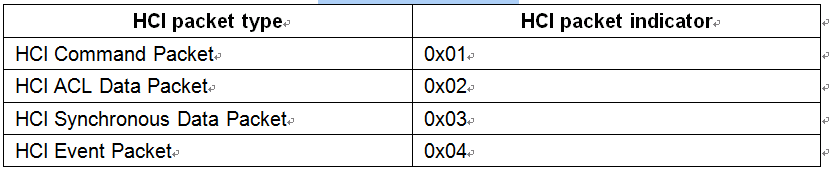
HCI有4种分组类型(有资料介绍通过uart传输时,还有错误消息分组和协商分组,但从现在的代码看,都没有使用了,只是增加了厂商自定义的操作码,用于发送错误消息或协商通信等),分组类型如表1,4种分组的数据格式如图4~图7。
表1 HCI封包类型
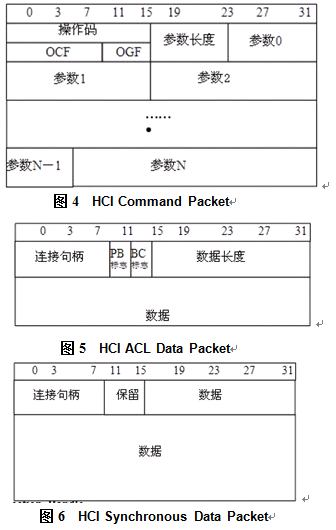
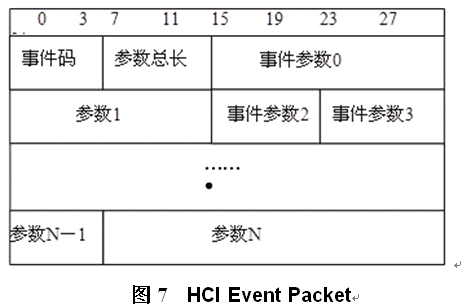
HCI本身的分组是不带包类型识别头的,在传输的时候就需要双方能识别出传输的分组类型,h4的协议就是在hci分组前增加一个字节的用于区别分组类型,现在使用的boardcom的蓝牙就是使用h4协议通过uart传输。从上面的各种分组结构看,都没有唯一的识别标志,在通过uart传输时,由于共用一个通道,就有数据同步问题,否则就无法找到分组头及解析数据分组。所以h4协议使用uart传输时,就需要有Error Recovery机制,只要通信双方有一个丢失同步,就需要进行同步恢复。如果h4协议使用usb传输,就不会存在该问题,usb通过不同的端点传输不同的分组类型,并且usb协议可以保证分组的完整。由于h4使用uart传输存在同步问题,后面有了h5协议,h5协议其实就是把h4协议的包重新封装一下,加入字符转换来实现唯一的分组头、分组尾标识,同时加入完整性校验,这样,即使一个分组数据出错了,下一个分组数据还是能正确解析的,不需要什么同步恢复机制。H5的封包如图8~图10。
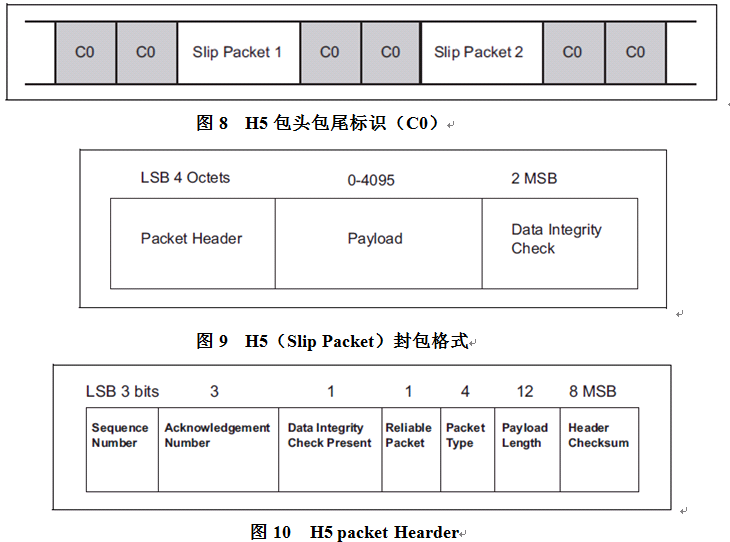
从上面可以看出,H5协议比H4协议在可靠性方面有增强,但同时需要处理的工作量也增多了,所以H5的传输效率会比H4低一些。
H4或H5的协议都提供相同的使用接口,HCI层实际使用哪种协议,现在bluedroid的做法是在代码编译的时候就固定的,如下面代码所示。
bluedroidhcisrcbt_hci_bdroid.c
static int init(const bt_hc_callbacks_t* p_cb, unsigned char *local_bdaddr)
{
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
vendor_open(local_bdaddr); /* 加载bt-vendor库 */
utils_init();
#ifdef HCI_USE_MCT
extern tHCI_IF hci_mct_func_table;
p_hci_if = &hci_mct_func_table;
#elif defined HCI_USE_RTK_H5
extern tHCI_IF hci_h5_func_table;
p_hci_if = &hci_h5_func_table; /* 使用h5协议 */
#else
extern tHCI_IF hci_h4_func_table;
p_hci_if = &hci_h4_func_table; /* 使用h4协议 */
#endif
bluedroidhciincludehci.h
typedef struct { /* h4,h5的结构体 */
tHCI_INIT init;
tHCI_CLEANUP cleanup;
tHCI_SEND send; /* 发送接口 */
tHCI_SEND_INT send_int_cmd; /* 为厂商专用发送接口 */
tHCI_ACL_DATA_LEN_HDLR get_acl_max_len;
#ifdef HCI_USE_MCT
tHCI_RCV evt_rcv;
tHCI_RCV acl_rcv;
#else
tHCI_RCV rcv; /* 接收接口 */
#endif
} tHCI_IF;2.2.3 Bluedroid中HCI与核心层接口
Hci层与bluedroid的核心层的交互接口,也是通过把接口封装在一个结构体提供给核心层,同时核心层提供一个回调的结构体。
bluedroidhcisrcbt_hci_bdroid.c
static const bt_hc_interface_t bluetoothHCLibInterface = {
sizeof(bt_hc_interface_t),
init, /* 加载bt-vendor库,选择使用的hci层协议 */
set_power, /* 蓝牙上掉电控制 */
lpm,
preload, /* 打开uart,加载fw */
postload,
transmit_buf, /* 发送数据 */
logging,
cleanup,
tx_hc_cmd,
};
const bt_hc_interface_t *bt_hc_get_interface(void) /* 获取hci接口的结构体 */
{
return &bluetoothHCLibInterface;
}
bluedroidmainbte_main.c
static void bte_main_in_hw_init(void)
{
if ( (bt_hc_if = (bt_hc_interface_t *) bt_hc_get_interface())
== NULL)
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
static void bte_hci_enable(void)
{
APPL_TRACE_DEBUG("%s", __FUNCTION__);
preload_start_wait_timer();
if (bt_hc_if)
{
/* 初始化hci接口,传递回调结构体 */
int result = bt_hc_if->init(&hc_callbacks, btif_local_bd_addr.address);
bluedroidhciincludebt_hci_lib.h
typedef struct {
/** set to sizeof(bt_hc_callbacks_t) */
size_t size;
/* notifies caller result of preload request */
preload_result_cb preload_cb;
/* notifies caller result of postload request */
postload_result_cb postload_cb;
/* notifies caller result of lpm enable/disable */
lpm_result_cb lpm_cb;
/* notifies hardware on host wake state */
hostwake_ind_cb hostwake_ind;
/* buffer allocation request */
alloc_mem_cb alloc;
/* buffer deallocation request */
dealloc_mem_cb dealloc;
/* notifies stack data is available */
data_ind_cb data_ind; /* hci层往上提交数据接口 */
/* notifies caller when a buffer is transmitted (or failed) */
tx_result_cb tx_result;
} bt_hc_callbacks_t;2.2.4 Bluedroid中HCI层流程例子
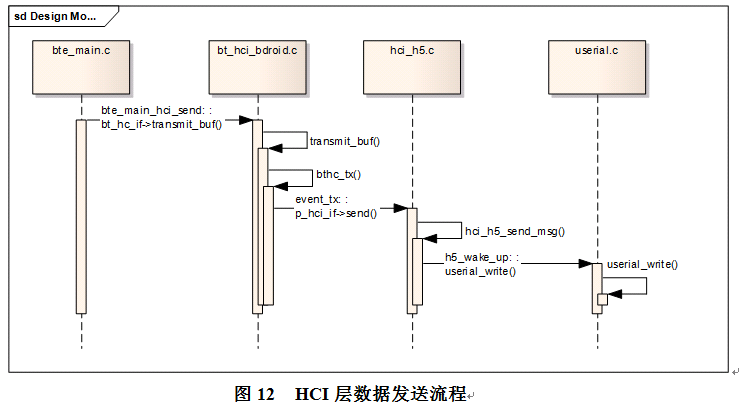
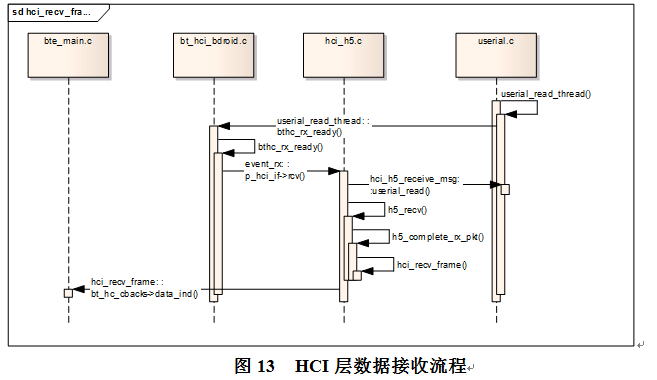
如图11为HCI层初始化的流程,包含接口的初始化,给蓝牙上电,打开串口,加载fw,由于加载fw过程涉及多重回调,没放到下面的框图。
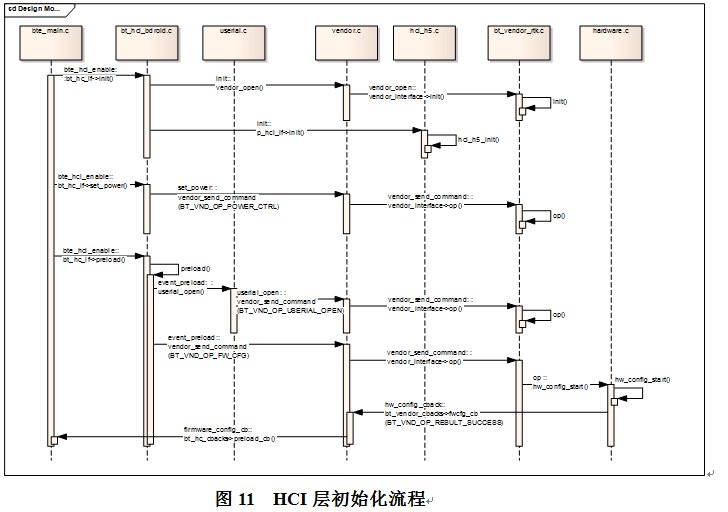
2.3 Bluedroid的核心层
Bluedroid的核心层负责蓝牙的管理,蓝牙协议的处理,状态的管理等,整个核心层的运行都是由事件驱动的,由上层发送的事件,底层处理结果的事件,底层接收数据的事件,底层状态变化的事件,加上定时器的超时事件,维护着整个核心层的正常运行。由于蓝牙核心层还不能很好理清流程及整理一个直观的框图,这里没给出核心层的架构图,后面从代码流程及整体的运行流程从侧面了解一下核心层的架构。
2.3.1 Bluedroid核心层的启动
Bluedroid的整个功能及运行,都是从enable Bluetooth开始,到disable Bluetooth结束。
bluedroidbtifsrcbluetooth.c
static int init(bt_callbacks_t* callbacks )
{
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
bt_utils_init();
/* init btif */
btif_init_bluetooth();
return BT_STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
bluedroidbtifsrcbtif_core.c
bt_status_t btif_init_bluetooth()
{
UINT8 status;
btif_config_init(); /* 配置初始化 */
bte_main_boot_entry(); /* Entry point for BTE chip/stack initialization */
/* As part of the init, fetch the local BD ADDR */
memset(&btif_local_bd_addr, 0, sizeof(bt_bdaddr_t));
btif_fetch_local_bdaddr(&btif_local_bd_addr);
/* start btif task */
status = GKI_create_task(btif_task, BTIF_TASK, BTIF_TASK_STR,
(UINT16 *) ((UINT8 *)btif_task_stack + BTIF_TASK_STACK_SIZE),
sizeof(btif_task_stack));
if (status != GKI_SUCCESS)
return BT_STATUS_FAIL;
return BT_STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
bluedroidbtifsrcbluetooth.c
static int enable( void )
{
ALOGI("enable");
/* sanity check */
if (interface_ready() == FALSE)
return BT_STATUS_NOT_READY;
return btif_enable_bluetooth();
}
bluedroidbtifsrcbtif_core.c
bt_status_t btif_enable_bluetooth(void)
{
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
/* Create the GKI tasks and run them */
bte_main_enable();
return BT_STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
bluedroidmainbte_main.c
void bte_main_enable()
{
APPL_TRACE_DEBUG("%s", __FUNCTION__);
/* Initialize BTE control block */
BTE_Init();
lpm_enabled = FALSE;
GKI_create_task((TASKPTR)btu_task, BTU_TASK, BTE_BTU_TASK_STR,
(UINT16 *) ((UINT8 *)bte_btu_stack + BTE_BTU_STACK_SIZE),
sizeof(bte_btu_stack));
bte_hci_enable(); /* 初始化hci层接口,上一节内容 */
GKI_run();
}
bluedroidstackbtubtu_task.c
BTU_API UINT32 btu_task (UINT32 param) /* 初始化工作及进行消息处理 */
{
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
/* Initialize the mandatory core stack control blocks
(BTU, BTM, L2CAP, and SDP)
*/
btu_init_core();
/* Initialize any optional stack components */
BTE_InitStack();
#if (defined(BTU_BTA_INCLUDED) && BTU_BTA_INCLUDED == TRUE)
bta_sys_init();
#endif
/* Initialise platform trace levels at this point as BTE_InitStack() and bta_sys_init()
* reset the control blocks and preset the trace level with XXX_INITIAL_TRACE_LEVEL
*/
#if ( BT_USE_TRACES==TRUE )
BTE_InitTraceLevels();
#endif
/* Send a startup evt message to BTIF_TASK to kickstart the init procedure */
GKI_send_event(BTIF_TASK, BT_EVT_TRIGGER_STACK_INIT);
prctl(PR_SET_NAME, (unsigned long)"BTU TASK", 0, 0, 0);
raise_priority_a2dp(TASK_HIGH_BTU);
/* Wait for, and process, events */
for (;;)
bluedroidbtifsrcbtif_core.c
void btif_enable_bluetooth_evt(tBTA_STATUS status, BD_ADDR local_bd)
{ /* Bluetooth enable完成时收到事件,会调用该函数 */
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
bte_main_postload_cfg();
#if (defined(HCILP_INCLUDED) && HCILP_INCLUDED == TRUE)
bte_main_enable_lpm(TRUE);
#endif
/* add passing up bd address as well ? */
/* callback to HAL */
if (status == BTA_SUCCESS)
{
/* initialize a2dp service */
btif_av_init();
/* init rfcomm & l2cap api */
btif_sock_init();
/* init pan */
btif_pan_init();
/* load did configuration */
bte_load_did_conf(BTE_DID_CONF_FILE);
bluedroidbtifsrcbtif_av.c
bt_status_t btif_av_init()
{
if (btif_av_cb.sm_handle == NULL)
{
if (btif_a2dp_start_media_task() != GKI_SUCCESS)
return BT_STATUS_FAIL;
btif_enable_service(BTA_A2DP_SERVICE_ID);
/* Also initialize the AV state machine */
btif_av_cb.sm_handle = btif_sm_init((const btif_sm_handler_t*)btif_av_state_handlers, BTIF_AV_STATE_IDLE);
btif_a2dp_on_init();
bluedroidbtifsrcbtif_media_task.c
int btif_a2dp_start_media_task(void)
{
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
/* start a2dp media task */
retval = GKI_create_task((TASKPTR)btif_media_task, A2DP_MEDIA_TASK,
A2DP_MEDIA_TASK_TASK_STR,
(UINT16 *) ((UINT8 *)a2dp_media_task_stack + A2DP_MEDIA_TASK_STACK_SIZE),
sizeof(a2dp_media_task_stack));前面说到整个蓝牙核心层由事件驱动,所有事件的处理全部由3个task来完成。
btu_task:处理发送给上层的事件,定时器超时事件,部分上层发送下来的事件,同时也会把部分事件转给btif_task处理;
btif_task:主要用于蓝牙协议处理,处理协议状态的流转,根据不同状态调用不同的处理函数;
btif_media_task:用于a2dp的控制及音频处理;
2.3.2 Bluedroid核心层部分profile的流程
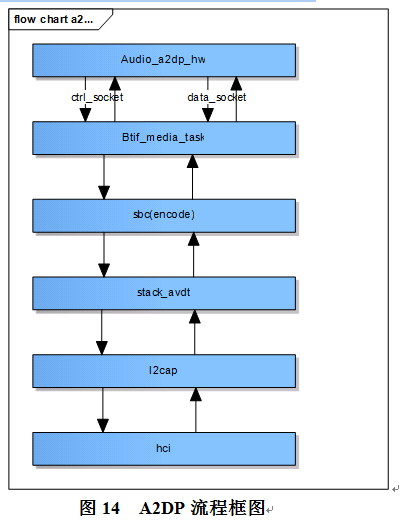
对于A2DP的流程,只给出概要框图,如下图所示。
对于opp文件传输,在bluedroid层就是使用rfcomm协议,rfcomm协议实质就是在两个蓝牙设备之间提供一条逻辑的数据通道,上层只需要使用rfcomm提供的链路就可以在两个蓝牙设备之间传递数据。Opp文件传输过程,先是两个设备进行连接,然后建立一条rfcomm通道,同时创建rfcomm与上层传输数据的socket,后面就可以进行数据传输,设备的连接、rfcomm通道的建立在后面介绍。
对于蓝牙鼠标、蓝牙键盘这些输入设备,使用的是hid(human interface Device)profile,建立连接后,注册一个uhid(dev_path = “/dev/uhid”)设备,把输入设备发送过来的数据发给uhid设备,由内核的hid驱动负责进行输入事件的处理,下图给出一个输入数据的流程框图。
3 Bluetooth应用程序介绍(Bluetooth.apk)
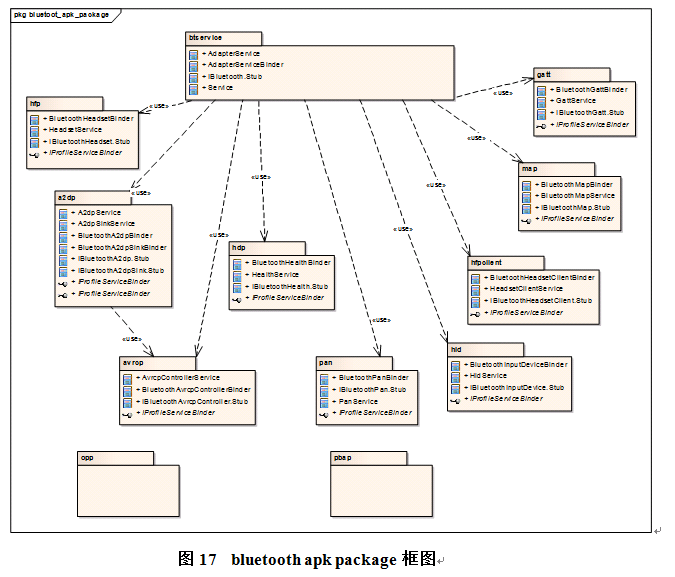
Bluetooth应用程序的主要功能是负责蓝牙状态的管理,连接bluedroid,提供各种蓝牙服务。其中btservice提供蓝牙基本服务,各个profile提供自身独立的服务,除了opp和pabp自成一体外,其它的profile由btservice管理。
3.1 Bluetooth应用程序框图及对外的接口
由于opp与pbap实质都是文件传输,但涉及UI交互操作等,作为两个相对独立的service存在,后面给出opp的一个框架。
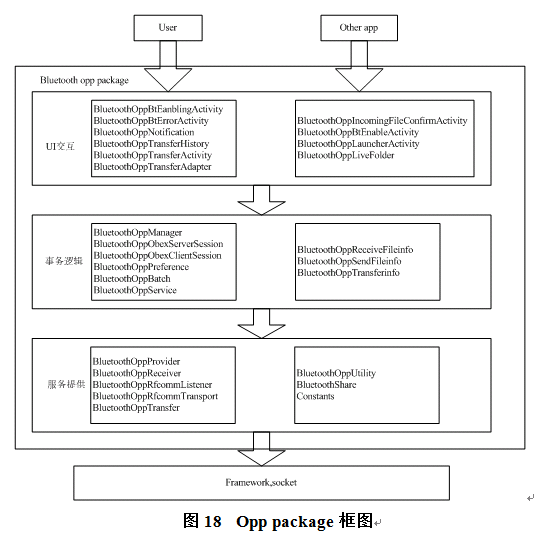
3.2 Bluetooth应用程序与bluedroid的接口
Bluetooth app与bluedroid通过jni接口交互,bluetooth app在开始时加载bluedroid库(bluetooth.default.so),使用bluedroid提供的操作接口,同时在调用bluedroid接口提供的init函数时,传递回调结构体给bluedroid。
packagesappsbluetoothjnicom_android_bluetooth_btservice_AdapterService.cpp
jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM *jvm, void *reserved)
{
…… /* 省略中间代码 */
if ((status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_btservice_AdapterService(e)) < 0) {
ALOGE("jni adapter service registration failure, status: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
if ((status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_hfp(e)) < 0) {
ALOGE("jni hfp registration failure, status: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
if ((status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_hfpclient(e)) < 0) {
ALOGE("jni hfp client registration failure, status: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
if ((status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_a2dp(e)) < 0) {
ALOGE("jni a2dp source registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
if ((status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_a2dp_sink(e)) < 0) {
ALOGE("jni a2dp sink registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
if ((status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_avrcp(e)) < 0) {
ALOGE("jni avrcp target registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
if ((status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_avrcp_controller(e)) < 0) {
ALOGE("jni avrcp controller registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
if ((status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_hid(e)) < 0) {
ALOGE("jni hid registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
if ((status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_hdp(e)) < 0) {
ALOGE("jni hdp registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
if ((status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_pan(e)) < 0) {
ALOGE("jni pan registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
if ((status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_gatt(e)) < 0) {
ALOGE("jni gatt registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
packagesappsbluetoothjnicom_android_bluetooth_btservice_AdapterService.cpp
static JNINativeMethod sMethods[] = { /* 各个Native接口 */
/* name, signature, funcPtr */
{"classInitNative", "()V", (void *) classInitNative},
{"initNative", "()Z", (void *) initNative},
{"cleanupNative", "()V", (void*) cleanupNative},
{"enableNative", "()Z", (void*) enableNative},
{"disableNative", "()Z", (void*) disableNative},
{"getRecvByteNative", "()I", (void*) getRecvByteNative},
{"getSendByteNative", "()I", (void*) getSendByteNative},
{"setAdapterPropertyNative", "(I[B)Z", (void*) setAdapterPropertyNative},
{"getAdapterPropertiesNative", "()Z", (void*) getAdapterPropertiesNative},
{"getAdapterPropertyNative", "(I)Z", (void*) getAdapterPropertyNative},
{"getDevicePropertyNative", "([BI)Z", (void*) getDevicePropertyNative},
{"setDevicePropertyNative", "([BI[B)Z", (void*) setDevicePropertyNative},
{"startDiscoveryNative", "()Z", (void*) startDiscoveryNative},
{"cancelDiscoveryNative", "()Z", (void*) cancelDiscoveryNative},
{"createBondNative", "([BI)Z", (void*) createBondNative},
{"removeBondNative", "([B)Z", (void*) removeBondNative},
{"cancelBondNative", "([B)Z", (void*) cancelBondNative},
{"getConnectionStateNative", "([B)I", (void*) getConnectionStateNative},
{"pinReplyNative", "([BZI[B)Z", (void*) pinReplyNative},
{"sspReplyNative", "([BIZI)Z", (void*) sspReplyNative},
{"getRemoteServicesNative", "([B)Z", (void*) getRemoteServicesNative},
{"getRemoteMasInstancesNative", "([B)Z", (void*) getRemoteMasInstancesNative},
{"connectSocketNative", "([BI[BII)I", (void*) connectSocketNative},
{"createSocketChannelNative", "(ILjava/lang/String;[BII)I",
(void*) createSocketChannelNative},
{"configHciSnoopLogNative", "(Z)Z", (void*) configHciSnoopLogNative},
{"alarmFiredNative", "()V", (void *) alarmFiredNative},
{"readEnergyInfo", "()I", (void*) readEnergyInfo},
};
int register_com_android_bluetooth_btservice_AdapterService(JNIEnv* env)
{
return jniRegisterNativeMethods(env, "com/android/bluetooth/btservice/AdapterService",
sMethods, NELEM(sMethods));
}
packagesappsbluetoothjnicom_android_bluetooth_btservice_AdapterService.cpp
static bool initNative(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj) {
ALOGV("%s:",__FUNCTION__);
sJniAdapterServiceObj = env->NewGlobalRef(obj);
sJniCallbacksObj = env->NewGlobalRef(env->GetObjectField(obj, sJniCallbacksField));
if (sBluetoothInterface) {
int ret = sBluetoothInterface->init(&sBluetoothCallbacks); /* 传递给bluedroid的回调接口 */3.3 Bluetooth 的状态图
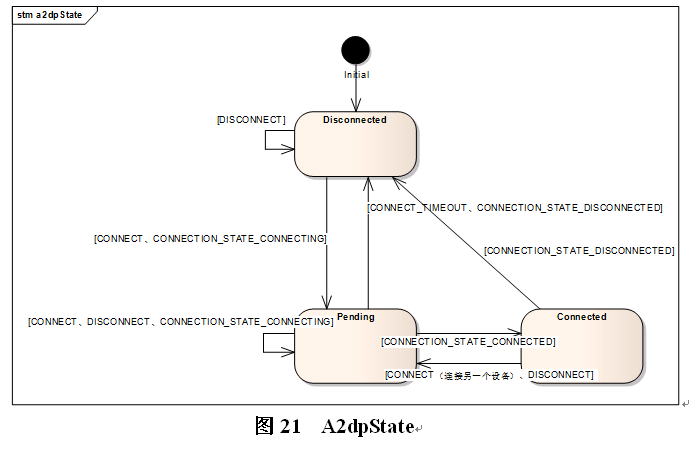
整个bluetooth存在多个状态机,除了有维护蓝牙开关的状态机及设备配对状态,还有部分profile使用状态机维护设备的连接状态。
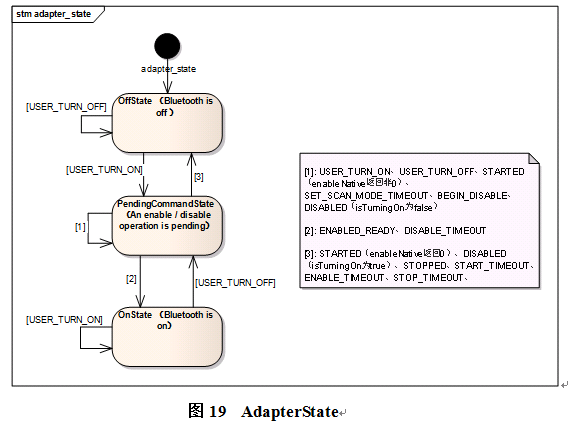
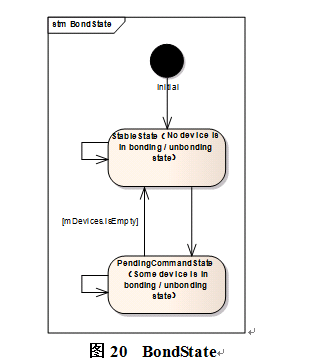
蓝牙Bond状态说明:
/**
* Indicates the remote device is not bonded (paired).
* <p>There is no shared link key with the remote device, so communication
* (if it is allowed at all) will be unauthenticated and unencrypted.
*/
public static final int BOND_NONE = 10;
/**
* Indicates bonding (pairing) is in progress with the remote device.
*/
public static final int BOND_BONDING = 11;
/**
* Indicates the remote device is bonded (paired).
* <p>A shared link keys exists locally for the remote device, so
* communication can be authenticated and encrypted.
* <p><i>Being bonded (paired) with a remote device does not necessarily
* mean the device is currently connected. It just means that the pending
* procedure was completed at some earlier time, and the link key is still
* stored locally, ready to use on the next connection.
* </i>
*/
public static final int BOND_BONDED = 12;例如:
两台平板配对,配对完成后,处于已配对状态,但还不是连接的状态,当需要传输文件时,才建立连接,文件传输完成后,连接会断开。
当平板与蓝牙耳机或蓝牙输入设备(蓝牙鼠标、键盘)配对时,配对完成后,马上会建立连接,这是由于蓝牙耳机或输入设备随时有数据传输。
3.4 Bluetooth 部分操作的流程图
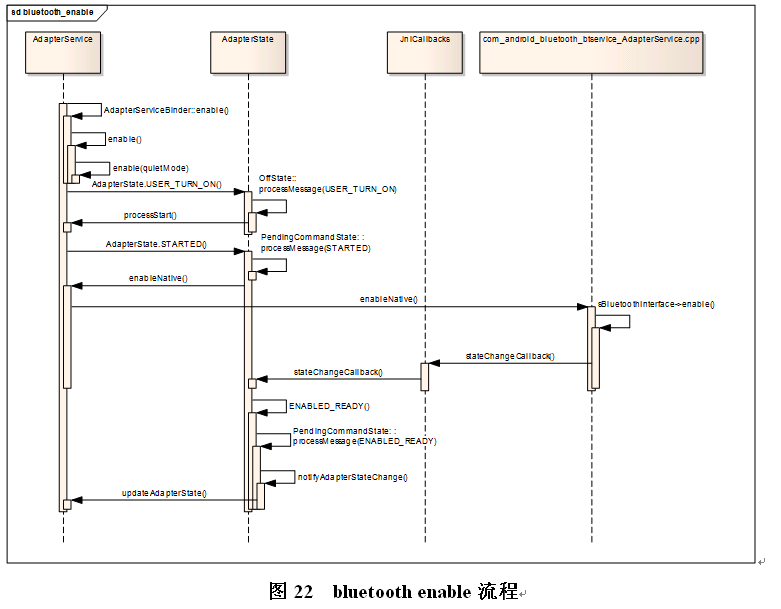
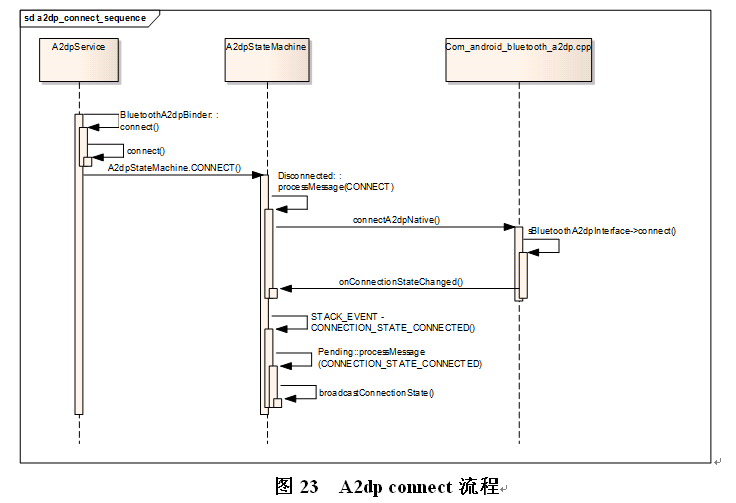
4 Bluetooth framework层介绍
Bluetooth framework层的作用只要是连接bluetooth service,为其它应用提供使用蓝牙的接口,起连接上下层的作用,没有太多的逻辑,下面只给出概要框图,不做过多描述。
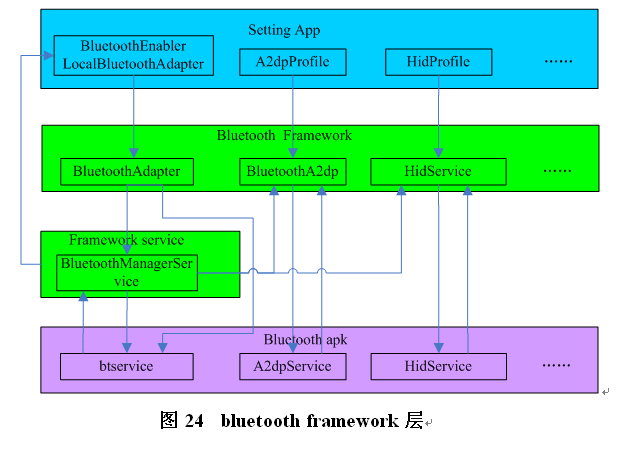
最后
以上就是淡定蜡烛最近收集整理的关于Android下bluedroid、bluetooth apk介绍前言1 Bluetooth应用层框架介绍2 Bluedroid软件介绍3 Bluetooth应用程序介绍(Bluetooth.apk)4 Bluetooth framework层介绍的全部内容,更多相关Android下bluedroid、bluetooth内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复