迭代器只是一個遍歷工具,它不是一個容器,意思就是儅集合調用iterator方法時,它不會把集合的元素裝起來再遍歷輸出,只是在原來集合的基礎上遍歷。如需創建Iterator對象,則必須有一個被迭代的集合。集合對象每次調用iterator()方法都得到一個全新的迭代器對象!

使用迭代器遍歷時常見的錯誤
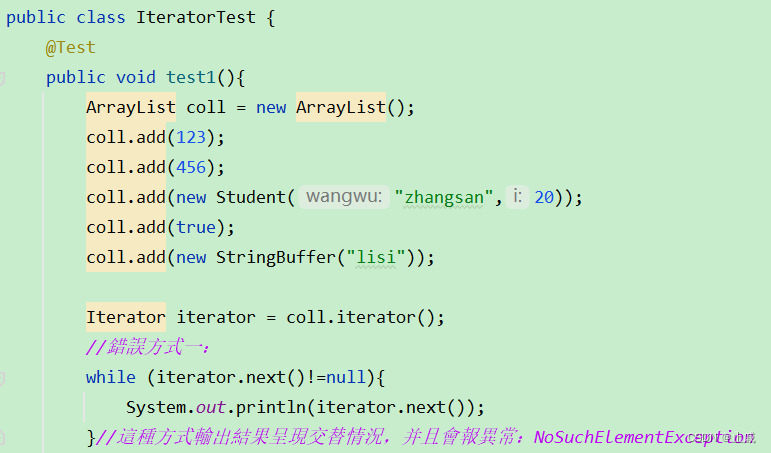
情形一:
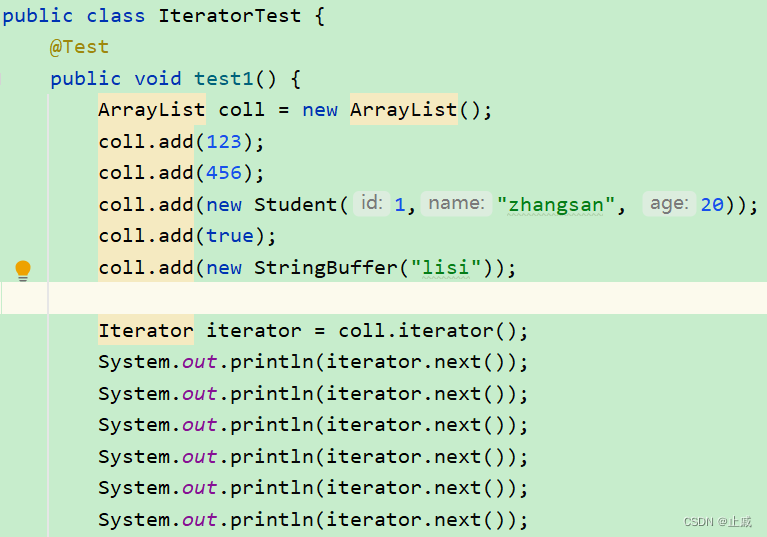
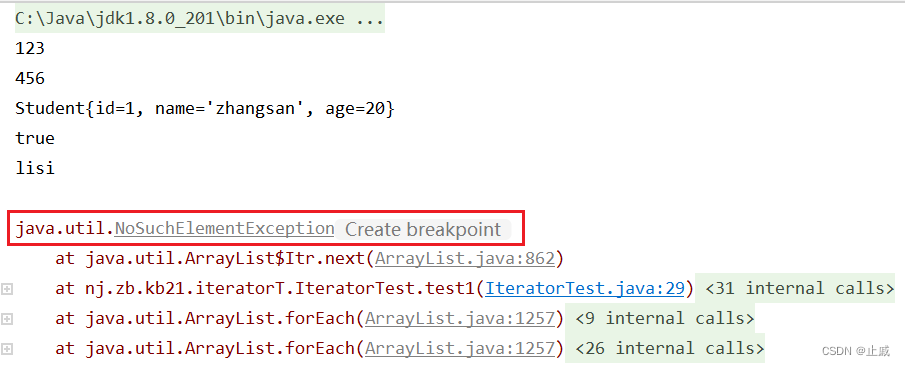
情形二:
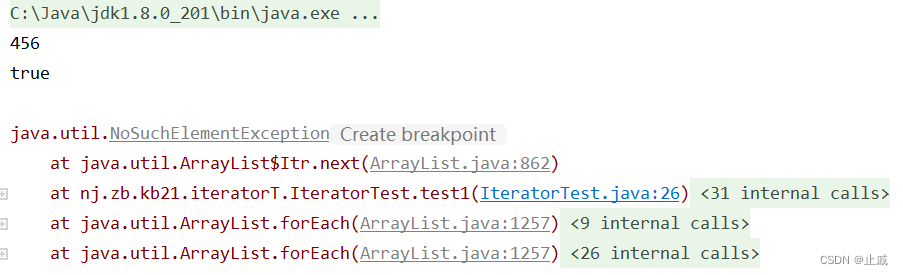

 迭代器Iterator接口内部定義了remove()方法,可以在遍歷的時候刪除集合中的元素。此方法不同於集合直接調用remove()。
迭代器Iterator接口内部定義了remove()方法,可以在遍歷的時候刪除集合中的元素。此方法不同於集合直接調用remove()。
Iterator.remove()方法
正確使用:

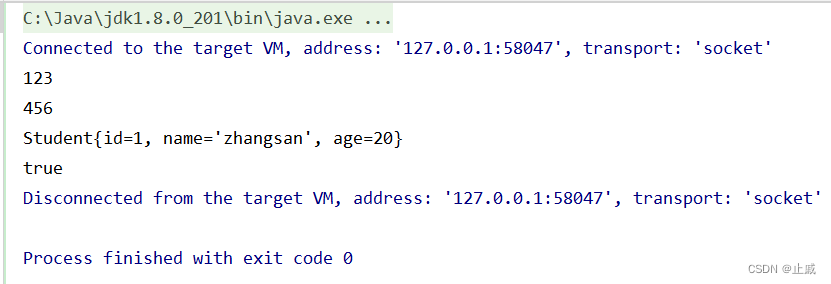
小練習:(答案見篇尾)
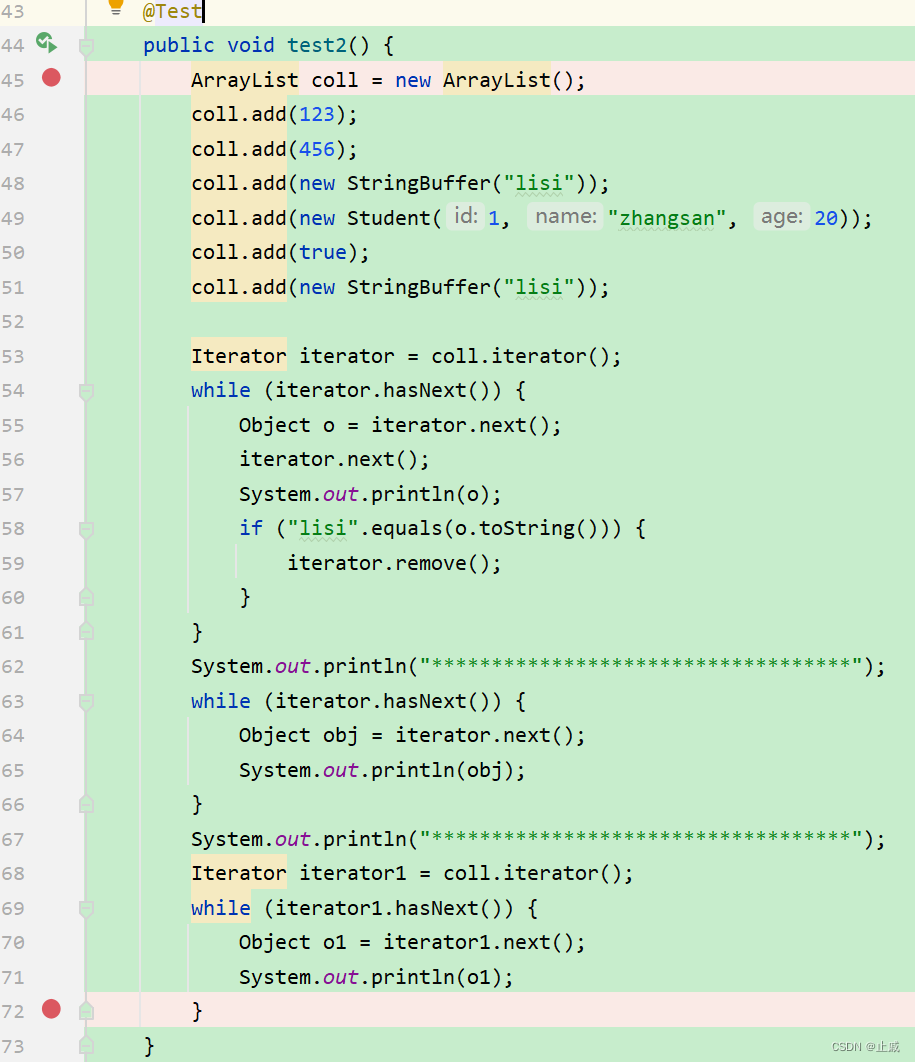
常見錯誤:
情形一:
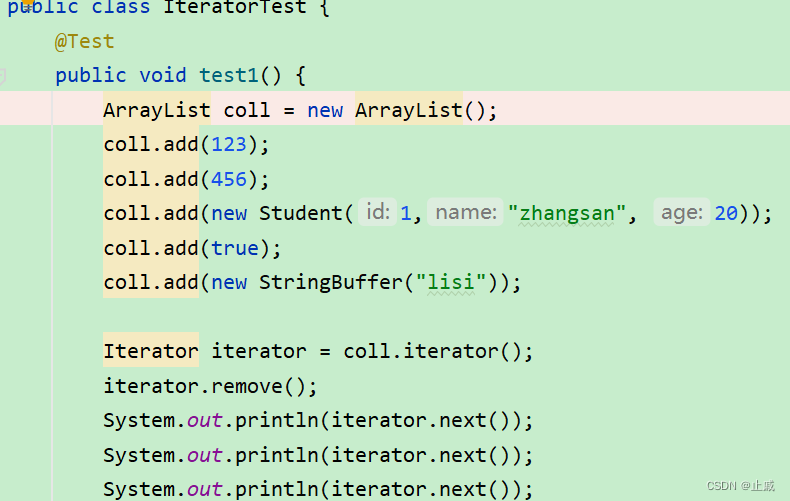

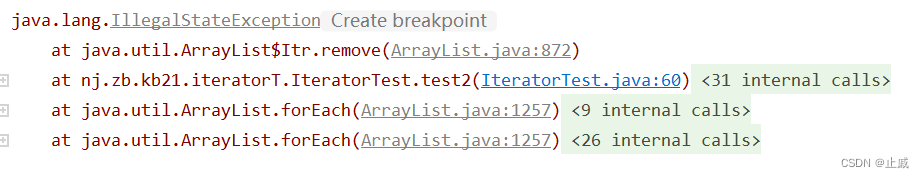
源碼:
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}情形二:

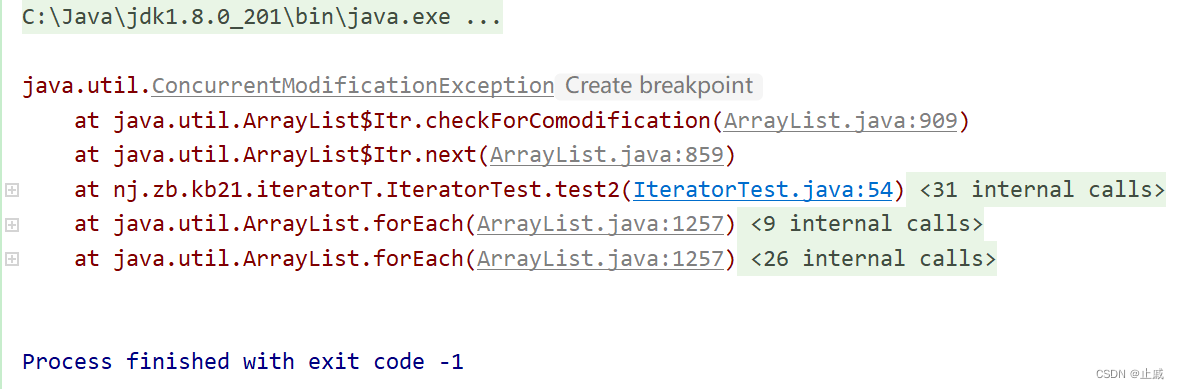 源碼:
源碼:
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}在iterator.next()方法源碼中,方法内首先調用了checkForComodification方法,該方法會判斷modCount是否等於expectedModCount,不等於就會抛出ConcurrentModificationException異常。
modCount是ArrayList的一個屬性,表示ArrayList對象的修改次數,ArrayList中有add、remove、clear、ensureCapacityInternal等方法可改變modCount的值。
在創建Iterator的時候會將modCount的值賦值給expectedModCount,在整個遍歷過程中expectedModCount的值保持不變。
一個遍歷中不能改變,另一個遍歷過程中可以修改,儅ArrayList對象一旦進行修改操作,就會使得modCount的值不等於expectedModCount的值,等執行到next()方法時,就會抛出上述異常。
注意:
- Iterator可以刪除集合的元素,但是是遍歷過程中通過迭代器對象的remove()方法,不是集合對象的remove()方法。
- 如果還未調用next()或上一次調用next()方法之後已經調用了remove()方法,再調用remove()都會報IllegalStateException。
- 多个线程的情況,多個綫程在同一容器中運行,很容易出現上面的異常,需要通過iterator遍歷過程加上鎖讓其同步。
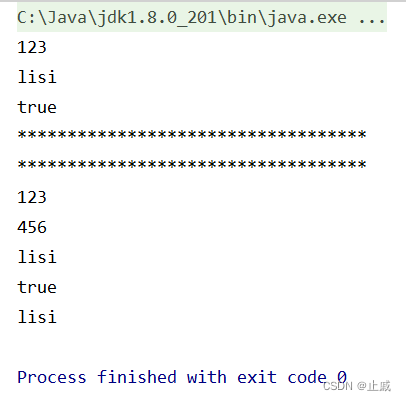
習題答案:
參考:
https://blog.csdn.net/tc1124692/article/details/97244905
https://blog.csdn.net/lkllkl123123/article/details/125918027
https://blog.csdn.net/scyatcs/article/details/9003295
https://www.cnblogs.com/snowater/p/8024776.html
最后
以上就是鲤鱼衬衫最近收集整理的关于迭代器Iterator的執行原理的全部内容,更多相关迭代器Iterator内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复