文章目录
- strvcat(不推荐)垂直串联字符串
- ind2sub 索引值转换为下标
- squeeze
- gcd(求最大公约数)
- fullfile
- physconst
- typecast(在不更改基础数据的情况下转换数据类型)
- swapbytes(交换字节顺序)
- uigetfile(选择打开文件夹)
- groot(图形根对象)
- NAN(创建所有值均为 NaN 的数组)
- repmat(重复数组副本)
- patch(绘制一个或多个填充多边形区域)
- enumeration(枚举类)
- bitshift(移位)
- break和continue
- 复数矩阵的.'是求转置
- reshape/fftshift
- classdef
- isfield(确定输入是否为结构体数组字段)
- normrnd(生成正态随机数)
- rand (生成均匀分布的随机数)
strvcat(不推荐)垂直串联字符串
官网链接
function s=strvcat(varargin)
% https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/matlab/ref/strvcat.html
%STRVCAT Vertically concatenate character vectors or string scalars.
% S = STRVCAT(T1,T2,T3,..) forms the character matrix S containing the
% text T1,T2,T3,... as rows. Automatically pads each input
% with spaces in order to form a valid matrix. Each text parameter, Ti,
% can itself be a character matrix. This allows the creation of
% arbitrarily large character arrays. Empty character arrays or strings
% in the input are ignored.
% 形成字符矩阵S,T1,T2,T3,… 按行排列
% 每一行的长度一样,不足的用空格自动填充
% Ti可以是字符矩阵
% 输入中的空字符数组或字符串将被忽略
% S = STRVCAT(T), when T is a string array or cell array of character vectors,
% each element of T is passed as an input to STRVCAT. Empty character vectors in
% the input are ignored.
% 当 T 为字符向量元胞数组时,S = strvcat(T) 将 c 的每个元素作为输入传递给 strvcat
% 输入中的空字符向量将被忽略
% STRVCAT('Hello','Yes') is the same as ['Hello';'Yes '] except
% that the padding is done automatically.
%
% STRVCAT is not recommended. Use CHAR instead.
%
% See also STRING, PAD, CHAR, STRCAT
% Copyright 1984-2016 The MathWorks, Inc.
[varargin{:}] = convertStringsToChars(varargin{:});%将字符串数组转换为字符数组,其他数组不变
%convertStringsToChars,https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/matlab/ref/convertstringstochars.html
numinput = nargin;
if numinput == 1 && iscellstr(varargin{1}) %iscellstr,确定输入是否为字符向量元胞数组
varargin = (varargin{1});
end
% find the empty cells
notempty = ~cellfun('isempty',varargin);
% vertically concatenate the non-empty cells.
s = char(varargin{notempty});
ind2sub 索引值转换为下标
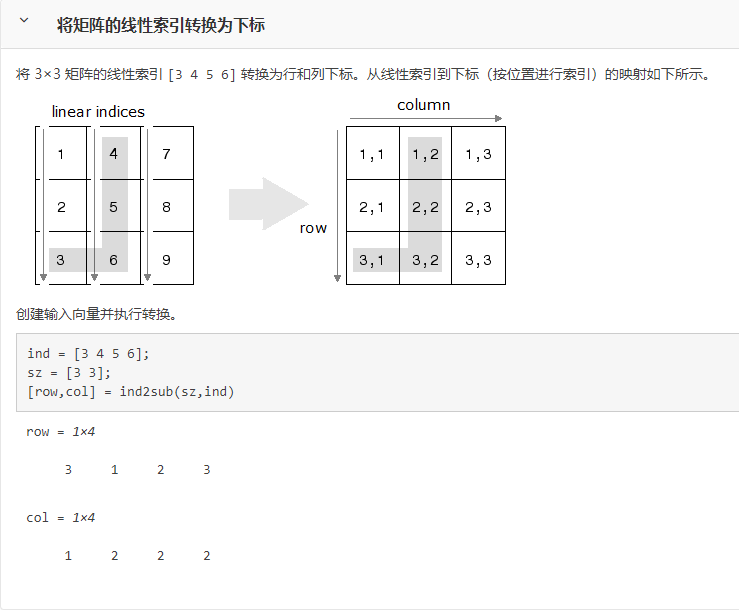
function [v1,v2,varargout] = ind2sub(siz,ndx)
%IND2SUB Multiple subscripts from linear index.
% IND2SUB is used to determine the equivalent subscript values
% corresponding to a given single index into an array.
% 把矩阵中某个元素的索引值转换为下标
% [I,J] = IND2SUB(SIZ,IND) returns the arrays I and J containing the
% equivalent row and column subscripts corresponding to the index
% matrix IND for a matrix of size SIZ.
% For matrices, [I,J] = IND2SUB(SIZE(A),FIND(A>5)) returns the same
% values as [I,J] = FIND(A>5).
%
% [I1,I2,I3,...,In] = IND2SUB(SIZ,IND) returns N subscript arrays
% I1,I2,..,In containing the equivalent N-D array subscripts
% equivalent to IND for an array of size SIZ.
%
% Class support for input IND:
% float: double, single
% integer: uint8, int8, uint16, int16, uint32, int32, uint64, int64
%
% See also SUB2IND, FIND.
% Copyright 1984-2015 The MathWorks, Inc.
nout = max(nargout,1);
siz = double(siz);
lensiz = length(siz);
if lensiz < nout
siz = [siz ones(1,nout-lensiz)];
elseif lensiz > nout
siz = [siz(1:nout-1) prod(siz(nout:end))];
end
if nout > 2
k = cumprod(siz);
for i = nout:-1:3,
vi = rem(ndx-1, k(i-1)) + 1;
vj = (ndx - vi)/k(i-1) + 1;
varargout{i-2} = double(vj);
ndx = vi;
end
end
if nout >= 2
vi = rem(ndx-1, siz(1)) + 1;
v2 = double((ndx - vi)/siz(1) + 1);
v1 = double(vi);
else
v1 = double(ndx);
end
squeeze
function b = squeeze(a)
%SQUEEZE Remove singleton dimensions.
% B = SQUEEZE(A) returns an array B with the same elements as
% A but with all the singleton dimensions removed. A singleton
% is a dimension such that size(A,dim)==1. 2-D arrays are
% unaffected by squeeze so that row vectors remain rows.
% 返回一个数组,其元素与输入数组 A 相同,但删除了长度为 1 的维度。例如,如果 A 是 3×1×2 数组,则 squeeze(A) 返回 3×2 矩阵。
% For example,
% squeeze(rand(2,1,3))
% is 2-by-3.
%
% See also SHIFTDIM.
% Copyright 1984-2010 The MathWorks, Inc.
if nargin==0
error(message('MATLAB:squeeze:NotEnoughInputs'));
end
if ~ismatrix(a)
siz = size(a);
siz(siz==1) = []; % Remove singleton dimensions.
siz = [siz ones(1,2-length(siz))]; % Make sure siz is at least 2-D
b = reshape(a,siz);
else
b = a;
end
gcd(求最大公约数)
function [g,c,d] = gcd(a,b)
%GCD Greatest common divisor.
% G = GCD(A,B) is the greatest common divisor of corresponding elements
% of A and B. The arrays A and B must contain integer values and must be
% the same size (or either can be scalar). GCD(0,0) is 0 by convention;
% all other GCDs are positive integers.
%
% [G,C,D] = GCD(A,B) also returns C and D so that G = A.*C + B.*D.
% These are useful for solving Diophantine equations and computing
% Hermite transformations.
%
% Class support for inputs A,B:
% float: double, single
% integer: uint8, int8, uint16, int16, uint32, int32, uint64, int64
%
% See also LCM.
% References:
% Knuth, Donald, The Art of Computer Programming, Vol. 2, Addison-Wesley:
% Reading MA, 1973. Section 4.5.2, Algorithms A and X.
%
% Thanks to John Gilbert for the original version
% Copyright 1984-2017 The MathWorks, Inc.
if ~isequal(size(a),size(b)) && ~isscalar(a) && ~isscalar(b)
error(message('MATLAB:gcd:InputSizeMismatch'))
end
if ~isreal(a) || ~isequal(round(a),a) || any(isinf(a(:))) || ...
~isreal(b) || ~isequal(round(b),b) || any(isinf(b(:)))
error(message('MATLAB:gcd:NonIntInputs'))
end
if ~isscalar(a)
siz = size(a);
else
siz = size(b);
end
a = a(:);
b = b(:);
if isinteger(a)
if ~(strcmp(class(a),class(b)) || (isa(b,'double') && isscalar(b)))
error(message('MATLAB:gcd:mixedIntegerTypes'))
end
classin = class(a);
if isa(b,'double') && (b > intmax(classin) || b < intmin(classin))
error(message('MATLAB:gcd:outOfRange'));
end
inttype = true;
elseif isinteger(b)
if ~(isa(a,'double') && isscalar(a))
error(message('MATLAB:gcd:mixedIntegerTypes'))
end
classin = class(b);
if a > intmax(classin) || a < intmin(classin)
error(message('MATLAB:gcd:outOfRange'));
end
inttype = true;
else
classin = superiorfloat(a,b);
largestFlint = flintmax(classin);
if any(abs(a) > largestFlint) || any(abs(b) > largestFlint)
warning(message('MATLAB:gcd:largestFlint'));
end
inttype = false;
end
if nargout <= 1
% intmin in signed integers requires special handling
iminIndex = [];
if inttype
imin = intmin(classin);
if imin < 0
iminIndex = xor(a == imin, b == imin);
end
end
u = max(abs(a),abs(b));
v = min(abs(a),abs(b));
u(iminIndex) = u(iminIndex)/2;
vnz = v>0;
while any(vnz)
t = rem(u,v);
u(vnz) = v(vnz);
v(vnz) = t(vnz);
vnz = v>0;
end
g = reshape(u,siz);
else
if inttype
if intmin(classin) == 0 % unsigned integers not supported
error(message('MATLAB:gcd:unsupportedType'));
end
end
len = prod(siz);
if issparse(a) || issparse(b)
u = spalloc(len,3,nnz(a)+len);
else
u = zeros(len,3,classin);
end
u(:,1) = 1;
u(:,3) = a;
if issparse(b)
v = spalloc(len,3,nnz(b)+len);
else
v = zeros(len,3,classin);
end
v(:,2) = 1;
v(:,3) = b;
vnz = v(:,3)~=0;
while any(vnz)
if inttype
q = idivide(u(:,3),v(:,3));
else
q = fix( u(:,3)./v(:,3));
end
t = u - v .* q;
u(vnz,:) = v(vnz,:);
v(vnz,:) = t(vnz,:);
vnz = v(:,3)~=0;
end
g = reshape(u(:,3),siz);
c = reshape(u(:,1),siz).*sign(g);
d = reshape(u(:,2),siz).*sign(g);
g = abs(g);
% correct overflow conditions in signed integers
if inttype
overflow1 = reshape(a == intmin(classin) & b == -1, siz);
overflow2 = reshape(a == -1 & b == intmin(classin), siz);
g(overflow1 | overflow2) = 1;
c(overflow1) = 0;
d(overflow1) = -1;
c(overflow2) = -1;
d(overflow2) = 0;
end
end
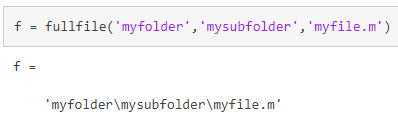
fullfile
f = fullfile(filepart1,...,filepartN) 根据指定的文件夹和文件名构建完整的文件设定。
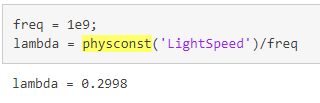
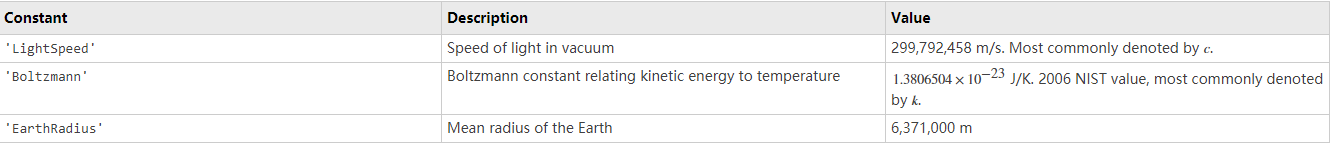
physconst
const = physconst(name) returns the value of the physical constant const
specified by the name argument.
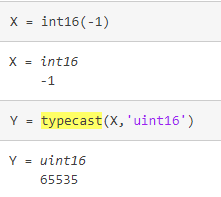
typecast(在不更改基础数据的情况下转换数据类型)
Y = typecast(X,type) 将 X 的位模式转换为 type 指定的数据类型,而不更改基础数据。
X 必须为由非复数数值组成的满标量或满向量。
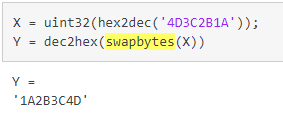
swapbytes(交换字节顺序)
Y = swapbytes(X) 将数组 X 中每个元素的字节排序从 little endian 转换为 big endian
(或相反)。输入数组的所有元素必须是完整的非复数数值元素。
uigetfile(选择打开文件夹)
[file,path] = uigetfile('C:DocumentsWork*.png',...
'Select an Image File')
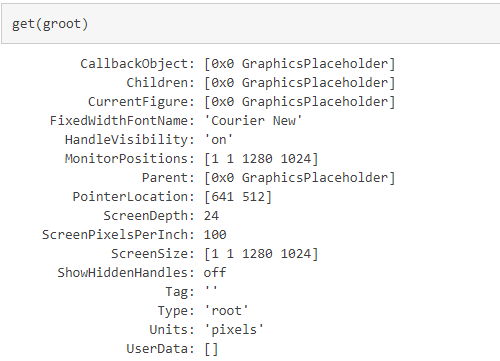
groot(图形根对象)
Root 对象是图形对象树的根。Root 属性包含有关图形环境和图形系统的当前状态的信息。
使用圆点表示法引用特定的对象和属性。
获取主显示画面的大小
get(groot, 'ScreenSize');
使用图形根对象为其他类型的对象设置根级别的默认值。例如,将以后所有图窗的默认颜色图设置为 summer 颜色图。
set(groot,'DefaultFigureColormap',summer)
NAN(创建所有值均为 NaN 的数组)
X = NaN(sz1,...,szN) 返回由 NaN 值组成的 sz1×...×szN 数组,
其中 sz1,...,szN 指示每个维度的大小。
例如:NaN(3,4) 返回一个 3×4 的矩阵。
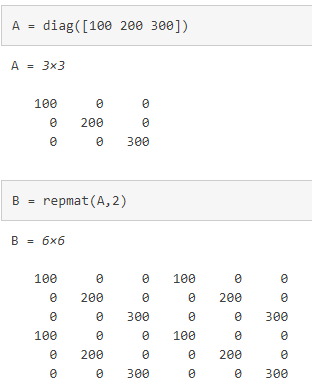
repmat(重复数组副本)
B = repmat(A,n) 返回一个数组,该数组在其行维度和列维度包含 A 的 n 个副本。
A 为矩阵时,B 大小为 size(A)*n。

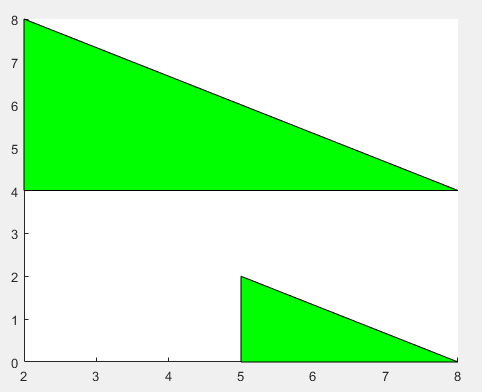
patch(绘制一个或多个填充多边形区域)
patch(X,Y,C) 使用 X 和 Y 的元素作为每个顶点的坐标,以绘制一个或多个填充多边形区域。
patch 以您指定顶点的顺序连接这些顶点。要创建一个多边形,请将 X 和 Y 指定为向量。
要创建多个多边形,请将 X 和 Y 指定为矩阵,其中每一列对应于一个多边形。
C 决定多边形的颜色。
通过将 x 和 y 指定为两列矩阵,创建两个多边形。每一列定义其中一个多边形的坐标。
x2 = [2 5; 2 5; 8 8];
y2 = [4 0; 8 2; 4 0];
patch(x2,y2,'green')
%2、2、8是第一个多边形的x坐标;5、5、8是第二个多边形的y坐标
%4、8、4是第二个多边形的x坐标;0、2、0是第三个多边形的y坐标
%没有明显的顺时针或者逆时针
enumeration(枚举类)
%通过向类定义中添加 enumeration 代码块可创建枚举类。
%例如,WeekDays 类列举一周中的工作日。
classdef WeekDays
enumeration
Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday
end
end
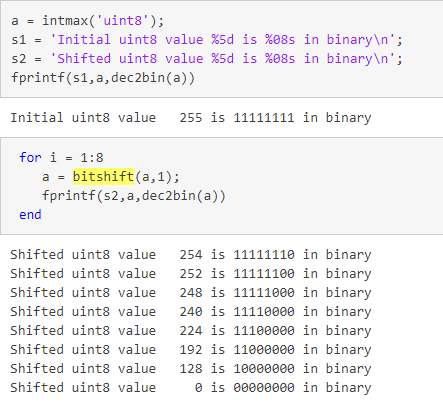
bitshift(移位)
noise = bitshift(AA,-4); % noise = AA/2^4
break和continue
close all;
clear all;
clc;
for ii = 1:3
for jj = 1:3
if ii == 1 && jj == 2
break;
end
disp(['ii = ',num2str(ii),' ,jj = ',num2str(jj),' ,aa = ',num2str(ii+jj)]);
end
end
for ii = 1:3
for jj = 1:3
if ii == 1 && jj == 2
continue;
end
disp(['ii = ',num2str(ii),' ,jj = ',num2str(jj),' ,bb = ',num2str(ii+jj)]);
end
end
结果
ii = 1 ,jj = 1 ,aa = 2
ii = 2 ,jj = 1 ,aa = 3
ii = 2 ,jj = 2 ,aa = 4
ii = 2 ,jj = 3 ,aa = 5
ii = 3 ,jj = 1 ,aa = 4
ii = 3 ,jj = 2 ,aa = 5
ii = 3 ,jj = 3 ,aa = 6
ii = 1 ,jj = 1 ,bb = 2
ii = 1 ,jj = 3 ,bb = 4
ii = 2 ,jj = 1 ,bb = 3
ii = 2 ,jj = 2 ,bb = 4
ii = 2 ,jj = 3 ,bb = 5
ii = 3 ,jj = 1 ,bb = 4
ii = 3 ,jj = 2 ,bb = 5
ii = 3 ,jj = 3 ,bb = 6
复数矩阵的.'是求转置

reshape/fftshift


classdef
classdef (Attributes) ClassName < SuperclassName
enumeration
EnumName
end
end
% 例如
classdef Assigned < int32
enumeration
Failed (0)
succeed (1)
end
end
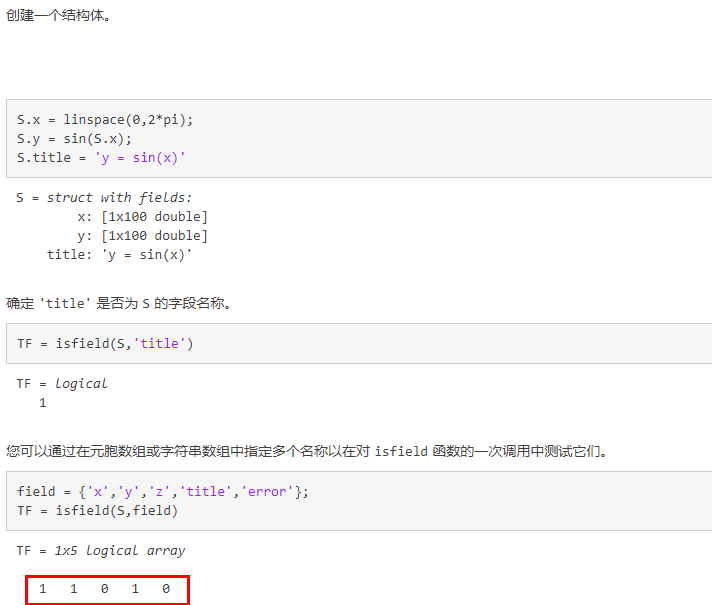
isfield(确定输入是否为结构体数组字段)
确定输入是否为结构体数组字段
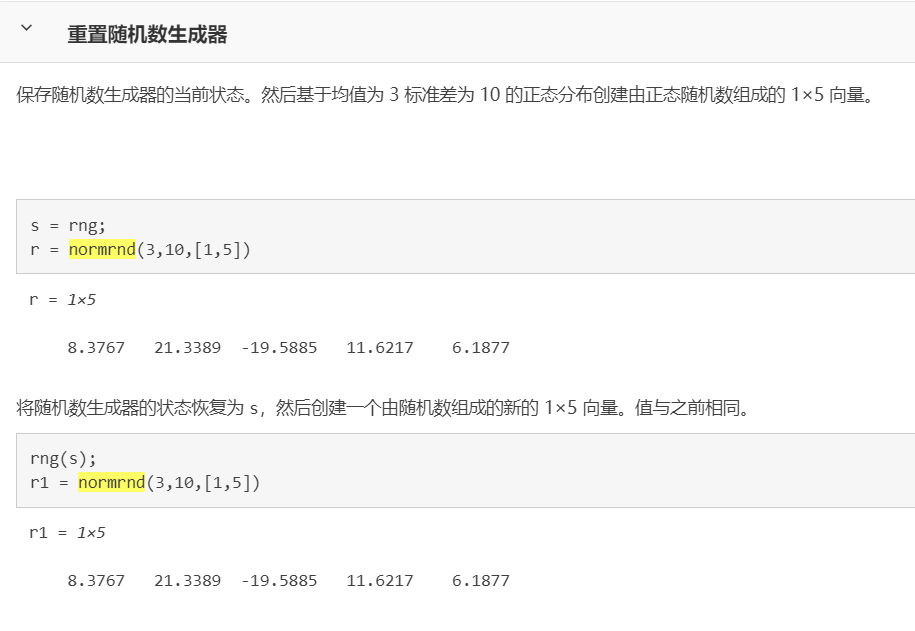
normrnd(生成正态随机数)
https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/stats/normrnd.html?searchHighlight=normrnd&s_tid=srchtitle
r = normrnd(mu,sigma) 从均值参数为 mu 和标准差参数为 sigma 的正态分布中生成随机数。
r = normrnd(mu,sigma,sz1,…,szN) 生成正态随机数数组,其中 sz1,…,szN 指示每个维度的大小。
示例
r = normrnd(mu,sigma,sz) 生成正态随机数数组,其中向量 sz 指定 size®。
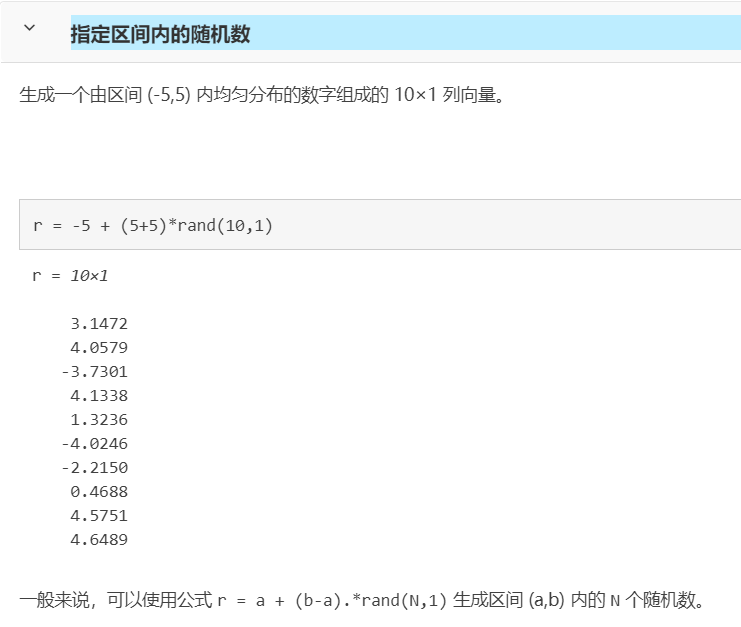
rand (生成均匀分布的随机数)
https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/matlab/ref/rand.html?s_tid=doc_ta
X = rand 返回一个在区间 (0,1) 内均匀分布的随机数。
X = rand(n) 返回一个 n×n 的随机数矩阵。
最后
以上就是忧虑发带最近收集整理的关于MATLAB笔记:一些自嵌函数/built-in functionstrvcat(不推荐)垂直串联字符串ind2sub 索引值转换为下标squeezegcd(求最大公约数)fullfilephysconsttypecast(在不更改基础数据的情况下转换数据类型)swapbytes(交换字节顺序)uigetfile(选择打开文件夹)groot(图形根对象)NAN(创建所有值均为 NaN 的数组)repmat(重复数组副本)patch(绘制一个或多个填充多边形区域)enumeration(枚举类)b的全部内容,更多相关MATLAB笔记:一些自嵌函数/built-in内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复