Netty私有协议栈设计
消息定义
-
消息头
-
消息主体
图示:
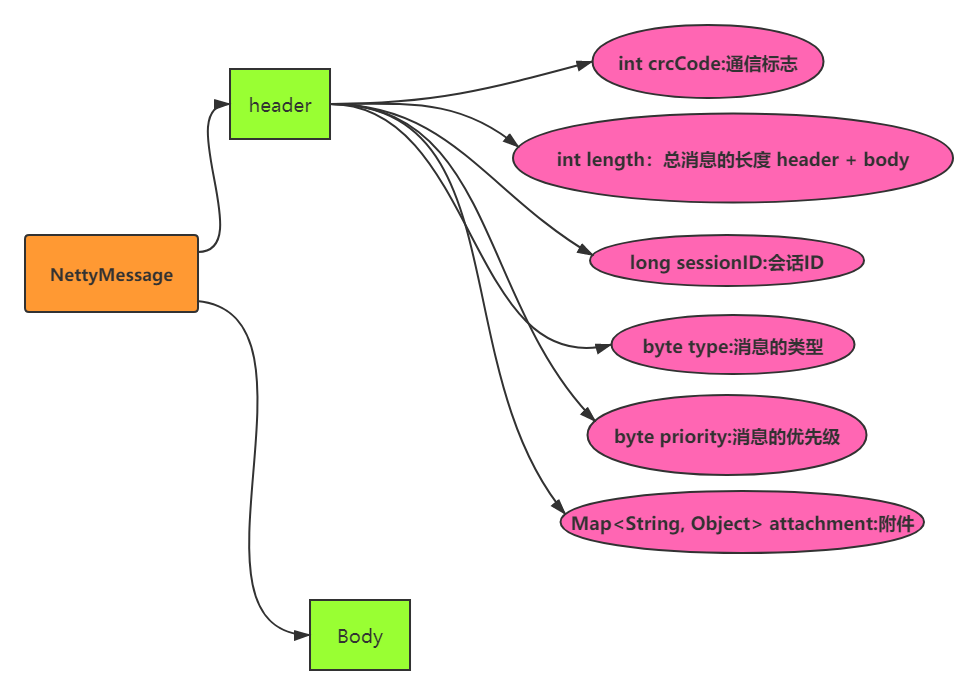
Header:
public class Header {
private int crcCode = 0xadaf0105; // 唯一的通信标志
private int length; // 总消息的长度 header + body
private long sessionID; // 会话ID
private byte type; // 消息的类型
private byte priority; // 消息的优先级 0~255
private Map<String, Object> attachment = new HashMap<String, Object>(); // 附件
// ...
}
NettyMessage
public class NettyMessage {
private Header header;
private Object body;
public final Header getHeader() {
return header;
}
public final void setHeader(Header header) {
this.header = header;
}
public final Object getBody() {
return body;
}
public final void setBody(Object body) {
this.body = body;
}
/*
* (non-Javadoc)
*
* @see java.lang.Object#toString()
*/
public String toString() {
return "NettyMessage [header=" + header + "]";
}
}
编解码设计
选择Marshaller作为Java对象序列化和反序列化的工具
MarshallingCodeCFactory工厂生成具体对象
public class MarshallingCodeCFactory {
public static Marshaller buildMarshalling() throws IOException {
//首先通过Marshalling工具类的精通方法获取Marshalling实例对象 参数serial标识创建的是java序列化工厂对象。
final MarshallerFactory marshallerFactory = Marshalling.getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial");
//创建了MarshallingConfiguration对象,配置了版本号为5
final MarshallingConfiguration configuration = new MarshallingConfiguration();
configuration.setVersion(5);
Marshaller marshaller = marshallerFactory.createMarshaller(configuration);
return marshaller;
}
public static Unmarshaller buildUnMarshalling() throws IOException {
final MarshallerFactory marshallerFactory = Marshalling.getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial");
final MarshallingConfiguration configuration = new MarshallingConfiguration();
configuration.setVersion(5);
Unmarshaller unmarshaller = marshallerFactory.createUnmarshaller(configuration);
return unmarshaller;
}
}
辅助Marshaller工作的两个类:
public class ChannelBufferByteOutput implements ByteOutput {
private final ByteBuf buffer;
/**
* Create a new instance which use the given {@link ByteBuf}
*/
public ChannelBufferByteOutput(ByteBuf buffer) {
this.buffer = buffer;
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
// Nothing to do
}
@Override
public void flush() throws IOException {
// nothing to do
}
@Override
public void write(int b) throws IOException {
buffer.writeByte(b);
}
@Override
public void write(byte[] bytes) throws IOException {
buffer.writeBytes(bytes);
}
@Override
public void write(byte[] bytes, int srcIndex, int length) throws IOException {
buffer.writeBytes(bytes, srcIndex, length);
}
/**
* Return the {@link ByteBuf} which contains the written content
*
*/
ByteBuf getBuffer() {
return buffer;
}
}
public class ChannelBufferByteInput implements ByteInput {
private final ByteBuf byteBuf;
public ChannelBufferByteInput(ByteBuf byteBuf) {
this.byteBuf = byteBuf;
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
if (byteBuf.isReadable()) {
return byteBuf.readByte() & 0xff;
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public int read(byte[] bytes) throws IOException {
return read(bytes, 0 , bytes.length);
}
@Override
public int read(byte[] dst, int dstIndex, int length) throws IOException {
int available = available();
if (available == 0) {
return -1;
}
length = Math.min(available, length);
byteBuf.readBytes(dst, dstIndex, length);
return length;
}
@Override
public int available() throws IOException {
return byteBuf.readableBytes();
}
@Override
public long skip(long bytes) throws IOException {
int readable = byteBuf.readableBytes();
if (readable < bytes) {
bytes = readable;
}
byteBuf.readerIndex((int) (byteBuf.readerIndex() + bytes));
return bytes;
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
}
}
编码器
处理流程:
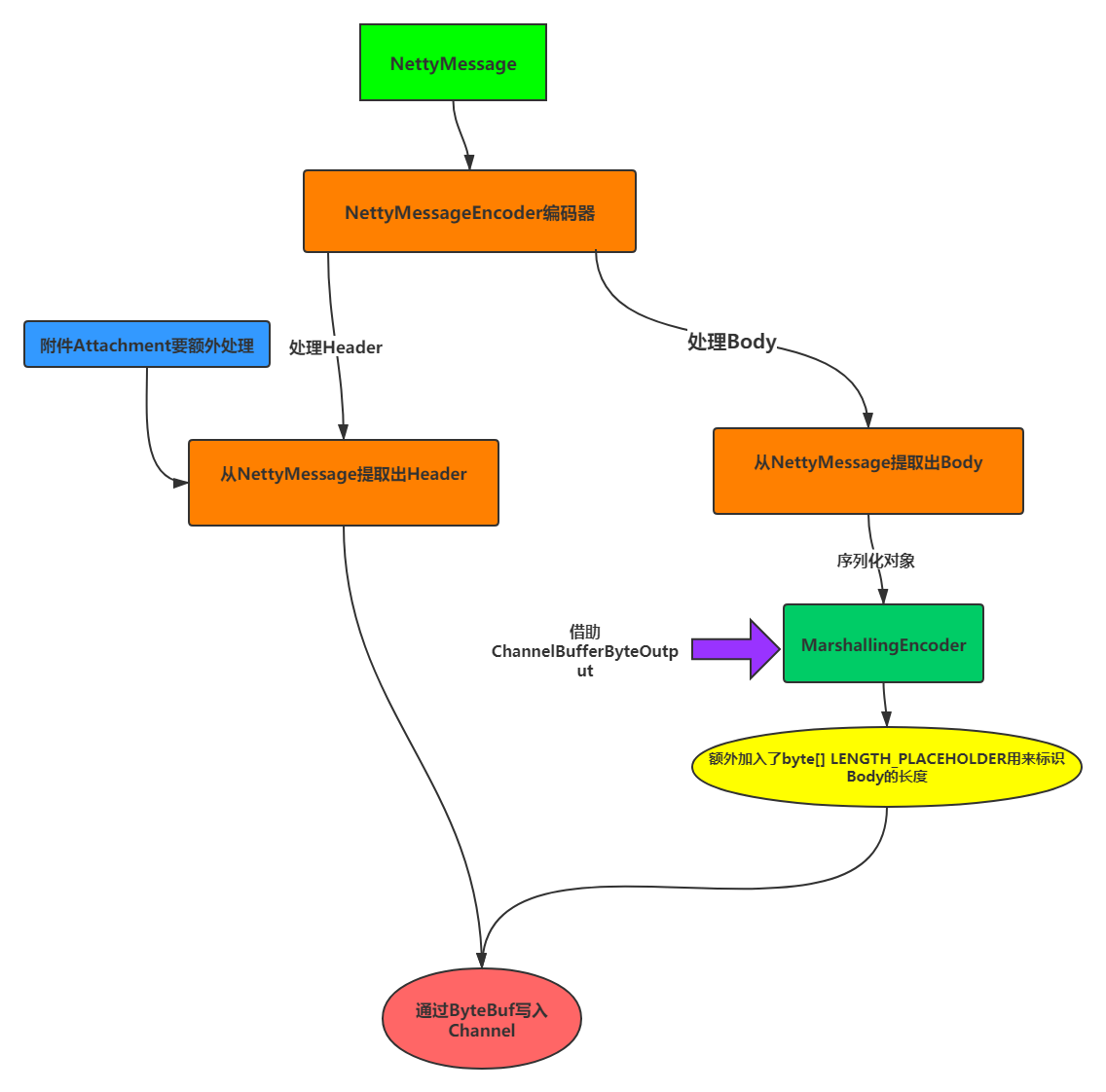
MarshallingEncoder:
public class MarshallingEncoder {
//空白占位: 用于预留设置 body的数据包长度
private static final byte[] LENGTH_PLACEHOLDER = new byte[4];
private Marshaller marshaller;
public MarshallingEncoder() throws IOException {
this.marshaller = MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshalling();
}
public void encode(Object body, ByteBuf out) throws IOException {
try {
//必须要知道当前的数据位置是哪: 起始数据位置
//长度属性的位置索引
int lengthPos = out.writerIndex();
//占位写操作:先写一个4个字节的空的内容,记录在起始数据位置,用于设置内容长度
out.writeBytes(LENGTH_PLACEHOLDER);
ChannelBufferByteOutput output = new ChannelBufferByteOutput(out);
marshaller.start(output);
marshaller.writeObject(body);
marshaller.finish();
//总长度(结束位置) - 初始化长度(起始位置) - 预留的长度 = body数据长度
int endPos = out.writerIndex();
out.setInt(lengthPos, endPos - lengthPos - 4);
} finally {
marshaller.close();
}
}
}
NettyMessageEncoder:
public class NettyMessageEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<NettyMessage> {
private MarshallingEncoder marshallingEncoder;
public NettyMessageEncoder() throws IOException {
this.marshallingEncoder = new MarshallingEncoder();
}
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, NettyMessage message, ByteBuf sendBuf) throws Exception {
if(message == null || message.getHeader() == null){
throw new Exception("编码失败,没有数据信息!");
}
//Head:
Header header = message.getHeader();
sendBuf.writeInt(header.getCrcCode());//校验码
sendBuf.writeInt(header.getLength());//总长度
sendBuf.writeLong(header.getSessionID());//会话id
sendBuf.writeByte(header.getType());//消息类型
sendBuf.writeByte(header.getPriority());//优先级
//对附件信息进行编码
//编码规则为:如果attachment的长度为0,表示没有可选附件,则将长度 编码设置为0
//如果attachment长度大于0,则需要编码,规则:
//首先对附件的个数进行编码
sendBuf.writeInt((header.getAttachment().size())); //附件大小
String key = null;
byte[] keyArray = null;
Object value = null;
//然后对key进行编码,先编码长度,然后再将它转化为byte数组之后编码内容
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> param : header.getAttachment()
.entrySet()) {
key = param.getKey();
keyArray = key.getBytes("UTF-8");
sendBuf.writeInt(keyArray.length);//key的字符编码长度
sendBuf.writeBytes(keyArray);
value = param.getValue();
marshallingEncoder.encode(value, sendBuf);
}
key = null;
keyArray = null;
value = null;
//Body:
Object body = message.getBody();
//如果不为空 说明: 有数据
if(body != null){
//使用MarshallingEncoder
this.marshallingEncoder.encode(body, sendBuf);
} else {
//如果没有数据 则进行补位 为了方便后续的 decoder操作
sendBuf.writeInt(0);
}
//最后我们要获取整个数据包的总长度 也就是 header + body 进行对 header length的设置
// TODO: 解释: 在这里必须要-8个字节 ,是因为要把CRC和长度本身占的减掉了
//(官方中给出的是:LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder中的lengthFieldOffset+lengthFieldLength)
//总长度是在header协议的第二个标记字段中
//第一个参数是长度属性的索引位置
sendBuf.setInt(4, sendBuf.readableBytes() - 8);
}
}
解码器
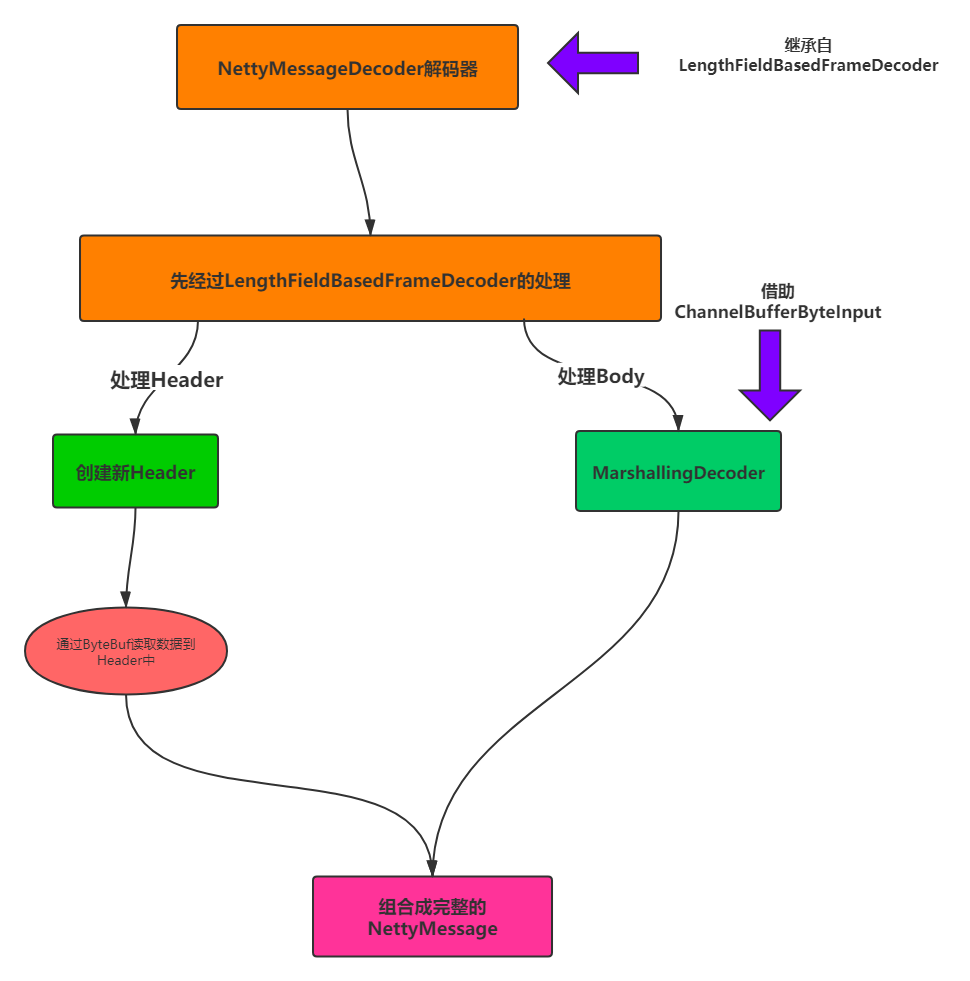
MarshallingDecoder
public class MarshallingDecoder {
private Unmarshaller unmarshaller;
public MarshallingDecoder() throws IOException {
this.unmarshaller = MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildUnMarshalling();
}
public Object decode(ByteBuf in) throws Exception {
try {
//1 首先读取4个长度(实际body内容长度)
int bodySize = in.readInt();
//2 获取实际body的缓冲内容
int readIndex = in.readerIndex();
ByteBuf buf = in.slice(readIndex, bodySize);
//3 转换
ChannelBufferByteInput input = new ChannelBufferByteInput(buf);
//4 读取操作:
this.unmarshaller.start(input);
Object ret = this.unmarshaller.readObject();
this.unmarshaller.finish();
//5 读取完毕以后, 更新当前读取起始位置:
//因为使用slice方法,原buf的位置还在readIndex上,故需要将位置重新设置一下
in.readerIndex(in.readerIndex() + bodySize);
return ret;
} finally {
this.unmarshaller.close();
}
}
}
NettyMessageDecoder
public class NettyMessageDecoder extends LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder {
private MarshallingDecoder marshallingDecoder;
/**
* 那减8应该是因为要把CRC和长度本身占的减掉了。
* @param maxFrameLength 第一个参数代表最大的序列化长度 1024*1024*5
* @param lengthFieldOffset 代表长度属性的偏移量 简单来说就是message中 总长度的起始位置(Header中的length属性的起始位置) 本例中为4
* @param lengthFieldLength 代表长度属性的长度 整个属性占多长(length属性为int,占4个字节) 4
* @throws IOException
*/
public NettyMessageDecoder(int maxFrameLength, int lengthFieldOffset, int lengthFieldLength) throws IOException {
super(maxFrameLength, lengthFieldOffset, lengthFieldLength);
this.marshallingDecoder = new MarshallingDecoder();
}
@Override
protected Object decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in) throws Exception {
//1 调用父类(LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder)方法:
ByteBuf frame = (ByteBuf)super.decode(ctx, in);
if(frame == null){
return null;
}
NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage();
Header header = new Header();
header.setCrcCode(frame.readInt()); //crcCode ----> 添加通信标记认证逻辑
header.setLength(frame.readInt()); //length
header.setSessionID(frame.readLong()); //sessionID
header.setType(frame.readByte()); //type
header.setPriority(frame.readByte()); //priority
int size = frame.readInt();
//附件个数大于0,则需要解码操作
if (size > 0) {
Map<String, Object> attch = new HashMap<String, Object>(size);
int keySize = 0;
byte[] keyArray = null;
String key = null;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
keySize = frame.readInt();
keyArray = new byte[keySize];
frame.readBytes(keyArray);
key = new String(keyArray, "UTF-8");
attch.put(key, marshallingDecoder.decode(frame));
}
keyArray = null;
key = null;
//解码完成放入attachment
header.setAttachment(attch);
}
message.setHeader(header);
//对于ByteBuf来说,读一个数据,就会少一个数据,所以读完header,剩下的应该就是body了
if(frame.readableBytes() > 4) { //大于4个字节,肯定就有数据了(4个字节是内容长度的占位)
message.setBody(marshallingDecoder.decode(frame));
}
return message;
}
}
握手消息请求的发送以及处理
图示:
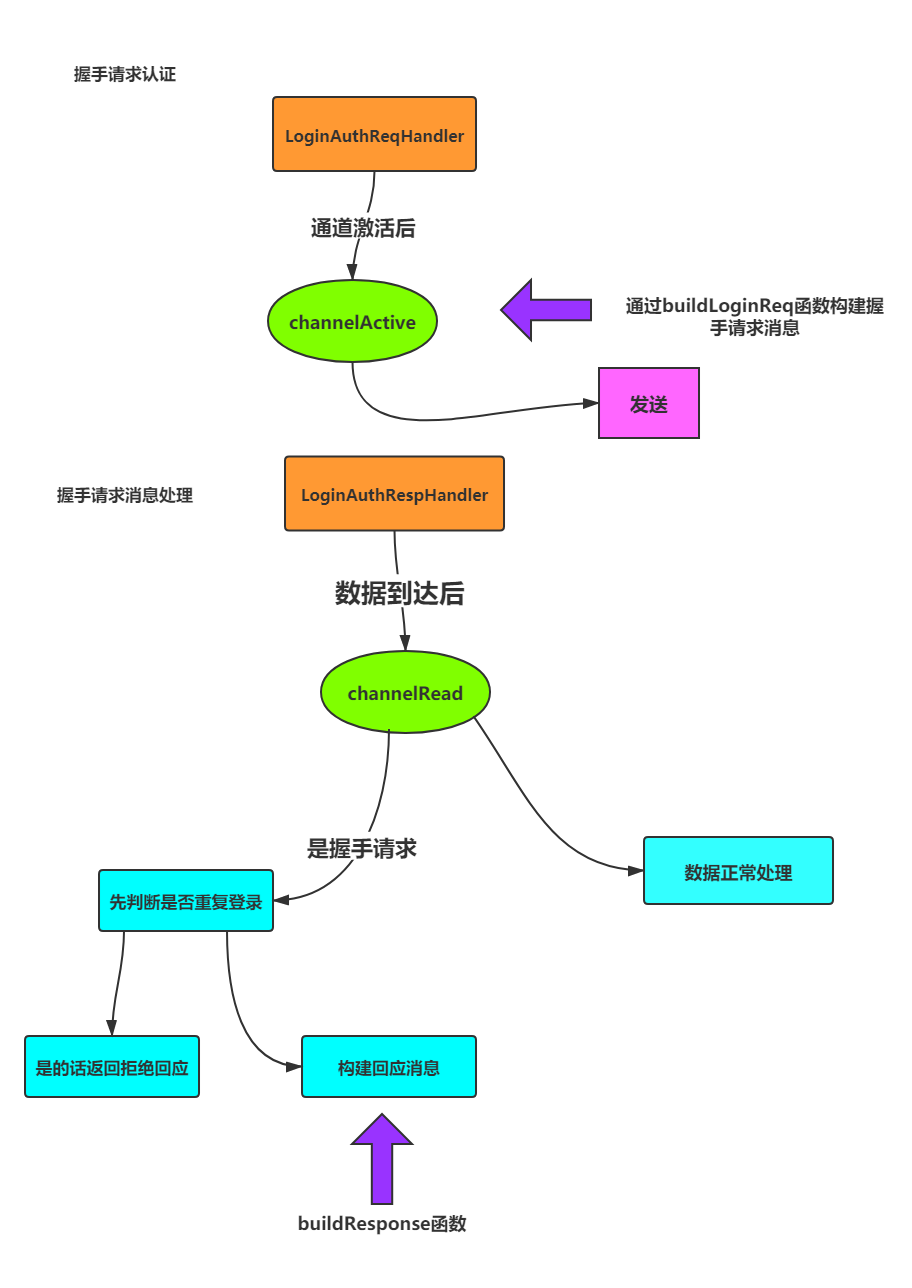
握手请求:
LoginAuthReqHandler
public class LoginAuthReqHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoginAuthReqHandler.class);
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
LOGGER.info("通道激活,握手请求认证..................");
ctx.writeAndFlush(buildLoginReq());
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
NettyMessage message = (NettyMessage) msg;
if (message.getHeader() != null && message.getHeader().getType() == MessageType.LOGIN_RESP.value()) {
byte loginResult = (byte) message.getBody();
if (loginResult != ResultType.SUCCESS.value()) {
ctx.close();
} else {
System.out.println("Login is OK : " + message);
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
} else {
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}
private NettyMessage buildLoginReq() {
NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage();
Header header = new Header();
header.setType(MessageType.LOGIN_REQ.value());
message.setHeader(header);
return message;
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause);
}
}
服务端处理:
LoginAuthRespHandler
public class LoginAuthRespHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoginAuthRespHandler.class);
/**
* 考虑到安全,链路的建立需要通过基于IP地址或者号段的黑白名单安全认证机制,本例中,多个IP通过逗号隔开
*/
private Map<String, Boolean> nodeCheck = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Boolean>();
private String[] whitekList = { "127.0.0.1", "192.168.56.1" };
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
NettyMessage message = (NettyMessage) msg;
// 判断消息是否为握手请求消息
if (message.getHeader() != null && message.getHeader().getType()
== MessageType.LOGIN_REQ.value()) {
String nodeIndex = ctx.channel().remoteAddress().toString();
NettyMessage loginResp = null;
if (nodeCheck.containsKey(nodeIndex)) {
LOGGER.error("重复登录,拒绝请求!");
loginResp = buildResponse(ResultType.FAIL);
} else {
InetSocketAddress address = (InetSocketAddress) ctx.channel().remoteAddress();
String ip = address.getAddress().getHostAddress();
boolean isOK = false;
for (String WIP : whitekList) {
if (WIP.equals(ip)) {
isOK = true;
break;
}
}
loginResp = isOK ? buildResponse(ResultType.SUCCESS) : buildResponse(ResultType.FAIL);
if (isOK)
nodeCheck.put(nodeIndex, true);
}
LOGGER.info("The login response is : {} body [{}]",loginResp,loginResp.getBody());
ctx.writeAndFlush(loginResp);
} else {
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}
/**
* 服务端接到客户端的握手请求消息后,如果IP校验通过,返回握手成功应答消息给客户端,应用层成功建立链路,否则返回验证失败信息。消息格式如下:
* 1.消息头的type为4
* 2.可选附件个数为0
* 3.消息体为byte类型的结果,0表示认证成功,1表示认证失败
*/
private NettyMessage buildResponse(ResultType result) {
NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage();
Header header = new Header();
header.setType(MessageType.LOGIN_RESP.value());
message.setHeader(header);
message.setBody(result.value());
return message;
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
nodeCheck.remove(ctx.channel().remoteAddress().toString());// 删除缓存
ctx.close();
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause); }
}
心跳检测
图示:
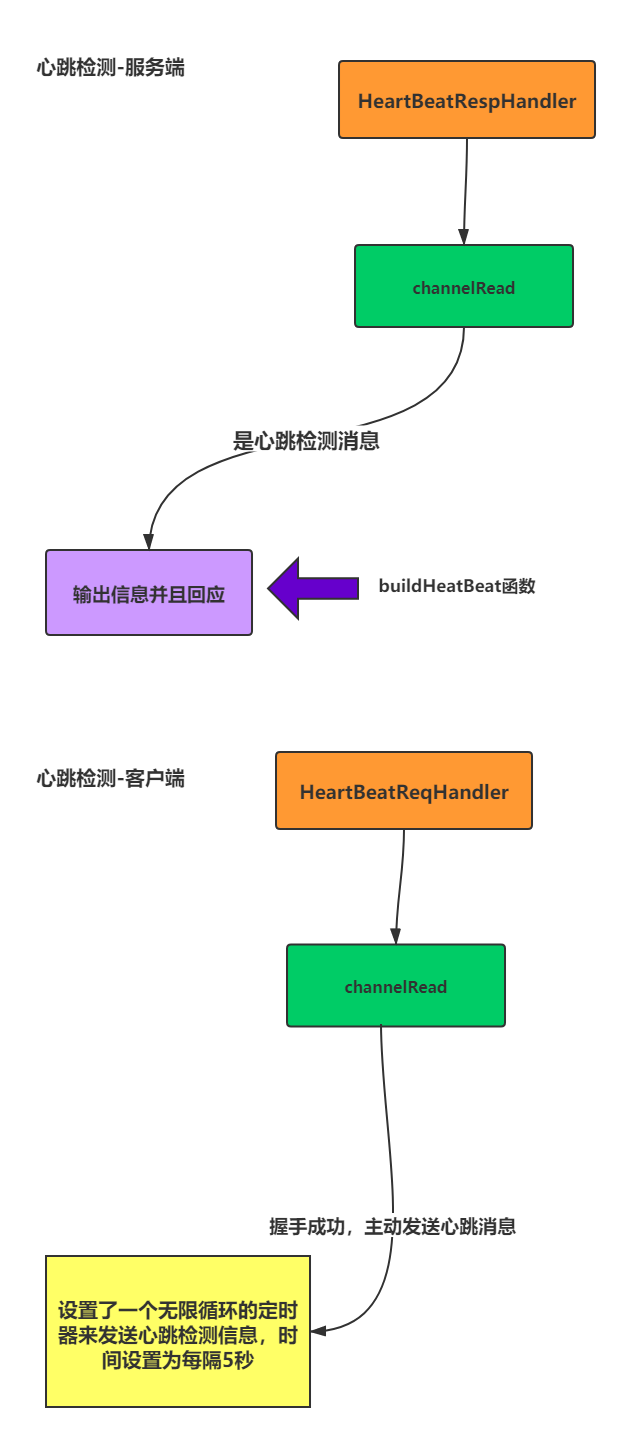
HeartBeatReqHandler
客户端发送:
public class HeartBeatReqHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HeartBeatReqHandler.class);
private volatile ScheduledFuture<?> heartBeat;
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
NettyMessage message = (NettyMessage) msg;
// 握手成功,主动发送心跳消息
if (message.getHeader() != null && message.getHeader().getType() == MessageType.LOGIN_RESP.value()) {
heartBeat = ctx.executor().scheduleAtFixedRate(new HeartBeatReqHandler.HeartBeatTask(ctx), 0, 5000,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else if (message.getHeader() != null && message.getHeader().getType() == MessageType.HEARTBEAT_RESP.value()) {
LOGGER.info("Client receive server heart beat message : ---> {}", message);
} else
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
private class HeartBeatTask implements Runnable {
private final ChannelHandlerContext ctx;
public HeartBeatTask(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
this.ctx = ctx;
}
@Override
public void run() {
NettyMessage heatBeat = buildHeatBeat();
LOGGER.info("Client send heart beat messsage to server : ---> {}", heatBeat);
ctx.writeAndFlush(heatBeat);
}
private NettyMessage buildHeatBeat() {
NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage();
Header header = new Header();
header.setType(MessageType.HEARTBEAT_REQ.value());
message.setHeader(header);
return message;
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
//断连期间,心跳定时器停止工作,不再发送心跳请求信息
if (heartBeat != null) {
heartBeat.cancel(true);
heartBeat = null;
}
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause); }
}
服务端处理:
public class HeartBeatRespHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HeartBeatRespHandler.class);
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
NettyMessage message = (NettyMessage) msg;
// 判断是否 是心跳检测消息
if (message.getHeader() != null && message.getHeader().getType() ==
MessageType.HEARTBEAT_REQ.value()) {
LOGGER.info("Receive client heart beat message : ---> {} " ,message);
NettyMessage heartBeat = buildHeatBeat();
LOGGER.info("Send heart beat response message to client : ---> {}" ,heartBeat);
ctx.writeAndFlush(heartBeat);
} else {
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}
// 生成心跳检测消息
private NettyMessage buildHeatBeat() {
NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage();
Header header = new Header();
header.setType(MessageType.HEARTBEAT_RESP.value());
message.setHeader(header);
return message;
}
}
最后
以上就是清脆雪糕最近收集整理的关于Netty私有协议栈设计Netty私有协议栈设计的全部内容,更多相关Netty私有协议栈设计Netty私有协议栈设计内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复