float占用32位,double占用64位,decimal占128位。
decimal的底数是10,是十进制的。由4个整数(Int32)组成
编译器标准都遵照IEEE制定的浮点数表示法来进行float,double运算。这种结构是一种科学计数法,用符号、指数和
尾数来表示,底数定为2——即把一个浮点数表示为尾数乘以2的指数次方再添上符号。下面是具体的规格:
符号位 阶码 尾数 长度
float 1 8 23 32
double 1 11 52 64
decimal的底数是10,是十进制的。有4个Int32整数组成。低low、中middle、高high、【符号位和小数位数】组成的一个整数。decimal的底数是10。【注意decimal的根脚与double的根脚不同。decimal是10,double和float是2】
Decimal转化为4个Int逻辑:将decimal去除小数点【不考虑正负号】后如 1234.5678M 整数部分是12345678。将去除小数点后的数字【12345678】转化为二进制。
因整数部分由96位组成,二进制左侧填充0(如果不够96位),使其凑够96位。这96位二进制 每隔32位 对应低low、中middle、高high三个整数。
第四个整数二进制格式形如:[X符号位]000 0000|000 [XXXXX就是几位小数,最多28位小数]|0000 0000|0000 0000。符号位:负数为1正数为0,【XXXXX】scale含有几位小数【小数点后有几位】,如有19位小数就是[10011]
一、下面用测试程序测试,源程序如下:
参考decimal源码:https://referencesource.microsoft.com/#mscorlib/system/decimal.cs,b39b204a56d1fbee
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AnalyzeDoubleAndDecimalDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.SetWindowSize(150, 40);
TestDoubleToBinary();
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("......下面测试Decimal转二进制数......");
TestDecimalToBinary();
Console.ReadLine();
}
/// <summary>
/// 双精度浮点数Double转二进制示例
/// float和double的底数是2
/// </summary>
static void TestDoubleToBinary()
{
//解析双精度double和小数Decimal的二进制表示
//double共64位 其中符号位S占1位,指数位E占11位,尾数位M占52位
double d = 12345678908888.0040625;
//整数进行除基取余
long partialInteger = 12345678908888L;
Stack<long> stack = new Stack<long>();
while (partialInteger != 0)
{
long cur = partialInteger % 2;
stack.Push(cur);
partialInteger = partialInteger / 2;
}
//整数部分的二进制字符串
string partialIntegerBinary = string.Join("", stack);
Console.WriteLine($"整数部分【{12345678908888}】的二进制显示:{partialIntegerBinary}");
//小数部分
double partialDecimal = 0.0040625;
int scale = 32;
int index = 0;
Queue<int> queue = new Queue<int>();
while (index < scale)
{
int cur = (int)(partialDecimal * 2);
queue.Enqueue(cur);
partialDecimal = partialDecimal * 2 - cur;
if (partialDecimal == 0)
{
break;
}
index++;
}
//小数部分的二进制字符串
string partialDecimalBinary = string.Join("", queue);
Console.WriteLine($"小数部分【{0.0040625}】的二进制显示:{partialDecimalBinary}");
string mergeBinary = partialIntegerBinary + "." + partialDecimalBinary;
Console.WriteLine($"合并后的二进制为:{mergeBinary}");
//科学表示法:将小数点移动到第一位的后面
string scienceBinary = mergeBinary.Remove(partialIntegerBinary.Length, 1).Insert(1, ".");
//指数,最大幂级:就是2的多少次方
int exponentNum = partialIntegerBinary.Length - 1;
Console.WriteLine($"科学表示法为({scienceBinary})×2的【{exponentNum}】次方");
//double的阶码,一共11位,因为指数可以为负,为了便于计算,规定都先加上1023
int exponent = 1023 + exponentNum;
//阶码需要凑够11位,不够的话左边填充0
string exponentBinary = Convert.ToString(exponent, 2).PadLeft(11, '0');
//【因科学表示法的开始一定是"1.",故尾数部分去除掉"1."】尾数部分:去除scienceBinary开始的"1.",也就是字符串从索引2开始。并凑够52位【不够的话右边填充0】
string partialMantissa = scienceBinary.Substring(2).PadRight(52, '0');//尾数位占用52位
//符号位:浮点数小于0为1,浮点数大于0为0
string partialSign = (d < 0 ? "1" : "0");
//1符号位+11阶码位+52尾数位=64位
string total64Binary = partialSign + exponentBinary + partialMantissa;
Console.WriteLine($"整体拼接64位二进制为:{total64Binary}");
byte[] buffer = new byte[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
buffer[i] = Convert.ToByte(total64Binary.Substring(8 * i, 8), 2);
}
Console.WriteLine($"double数【{d}】由8个字节组成,依次为:{string.Join(",", buffer)}");
byte[] bufferConverter = BitConverter.GetBytes(d);
Console.WriteLine($"【使用BitConverter】double数【{d}】由8个字节组成,依次为:{string.Join(",", bufferConverter)}");
Console.WriteLine($"将bufferConverter数组反转后为{string.Join(",", bufferConverter.Reverse())}");
Console.WriteLine($"将bufferConverter数组反转后 与 buffer完全一致。因本操作系统是低字节在前:【{BitConverter.IsLittleEndian}】");
}
/// <summary>
/// 十进制小数Decimal转二进制示例
/// decimal的底数是10。【注意decimal的根脚与double的根脚不同。decimal是10,double和float是2】
/// Decimal转化为4个Int逻辑:将decimal去除小数点后如 1234.5678M 整数部分是12345678。将去除小数点后的数字【12345678】转化为二进制。
/// 因整数部分由96位组成,二进制左侧填充0(如果不够96位),使其凑够96位。这96位二进制 每隔32位 对应低low、中middle、高high三个整数。
/// 第四个整数二进制格式形如:[X符号位]000 0000|000 [XXXXX就是几位小数,最多28位小数]|0000 0000|0000 0000。符号位:负数为1正数为0,【XXXXX】scale含有几位小数【小数点后有几位】,如有19位小数就是[10011]
/// </summary>
static void TestDecimalToBinary()
{
/*
The low, middle, high, and flags fields contain the representation of the Decimal value.
The lo, mid, and hi fields contain the 96-bit integer part of the Decimal. 【96位数字】
Bits 0-15 (the lower word) of the flags field are unused and must be zero;
bits 16-23 contain must contain a value between 0 and 28, indicating the power of 10 to divide the 96-bit integer part by to produce the Decimal value;
bits 24-30 are unused and must be zero; and finally bit 31 indicates the sign of the Decimal value, 0 meaning positive and 1 meaning negative.
NOTE: Do not change the order in which these fields are declared. The native methods in this class rely on this particular order.
*/
//decimal的源码查看:https://referencesource.microsoft.com/#mscorlib/system/decimal.cs,b39b204a56d1fbee
decimal m = 1234567890.1015625M;
//整数进行除基取余
long partialInteger = 1234567890L;
Stack<long> stack = new Stack<long>();
while (partialInteger != 0)
{
long cur = partialInteger % 10;
stack.Push(cur);
partialInteger = partialInteger / 10;
}
//整数部分的二进制字符串
string partialIntegerBinary = string.Join("", stack);
Console.WriteLine($"整数部分【不考虑正负符号】【{1234567890}】的十进制显示:{partialIntegerBinary}");
//小数部分
decimal partialDecimal = 0.1015625M;
int scale = 64;
int index = 0;
Queue<int> queue = new Queue<int>();
while (index < scale)
{
int cur = (int)(partialDecimal * 10);
queue.Enqueue(cur);
partialDecimal = partialDecimal * 10 - cur;
if (partialDecimal == 0)
{
break;
}
index++;
}
//小数部分的十进制字符串
string partialDecimalBinary = string.Join("", queue);
Console.WriteLine($"小数部分【{0.1015625}】的十进制显示:{partialDecimalBinary}");
string mergeBinary = partialIntegerBinary + partialDecimalBinary;
Console.WriteLine($"【去除小数点】合并后的十进制为:{mergeBinary}");
long threeInts = (long)decimal.Parse(mergeBinary);
//整数进行除基取余
stack = new Stack<long>();
while (threeInts != 0)
{
decimal cur = threeInts % 2;
stack.Push((long)cur);
threeInts = threeInts / 2;
}
//整数部分的二进制字符串
string partialThreeIntegerBinary = string.Join("", stack);
Console.WriteLine($"【高、中、低】整数部分【{mergeBinary}】的二进制显示:{partialThreeIntegerBinary}");
//低low、中midddle、高high 共有96位
string bits96 = partialThreeIntegerBinary.PadLeft(96, '0');
Console.WriteLine($"拼接成96位二进制为{bits96}");
int[] threeIntBits = new int[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
threeIntBits[i] = Convert.ToInt32(bits96.Substring(32 * i, 32), 2);
}
Console.WriteLine($"【高high、中midddle、低low】拼接的三个整数是{string.Join(",", threeIntBits)}");
//最后一个Int的由[X符号位,负数为1,正数为0]000 0000|000 [XXXXX就是几位小数,最多28位小数]|0000 0000|0000 0000
int scaleNum = partialDecimalBinary.Length;//小数位数,含有几位小数
string lastIntBinary = (m < 0 ? "1" : "0") + "0".PadRight(7, '0') + Convert.ToString(scaleNum, 2).PadLeft(8, '0') + "0".PadRight(16, '0') ;
Console.WriteLine($"最后一个整数的二进制表示为{lastIntBinary.Insert(24," ").Insert(16, " ").Insert(8, " ")}");
byte[] bufferLastInt = new byte[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
bufferLastInt[i] = Convert.ToByte(lastIntBinary.Substring(i * 8, 8), 2);
}
Console.WriteLine($"最后一个整数的数值为{Convert.ToInt32(lastIntBinary, 2)},对应的4个字节依次为{string.Join(",", bufferLastInt)}");
Console.WriteLine($"decimal数【{m}】由4个整数组成.n其中【低32位整数low】=【{threeIntBits[2]}】,【中32位整数middle】=【{threeIntBits[1]}】,【高32位整数high】=【{threeIntBits[0]}】,【符号和小数位数组成的整数flagAndScale】=【{Convert.ToInt32(lastIntBinary, 2)}】");
int[] bufferConverterInts = decimal.GetBits(m);
Console.WriteLine($"【使用GetBits】decimal数【{m}】由4个整数组成,依次为:{string.Join(",", bufferConverterInts)}");
byte[] bufferConverter = bufferConverterInts.SelectMany(numInt => BitConverter.GetBytes(numInt)).ToArray();
Console.WriteLine($"【使用BitConverter】decimal数【{m}】由16个字节组成,依次为:{string.Join(",", bufferConverter)}");
}
}
}
二、程序运行如图:
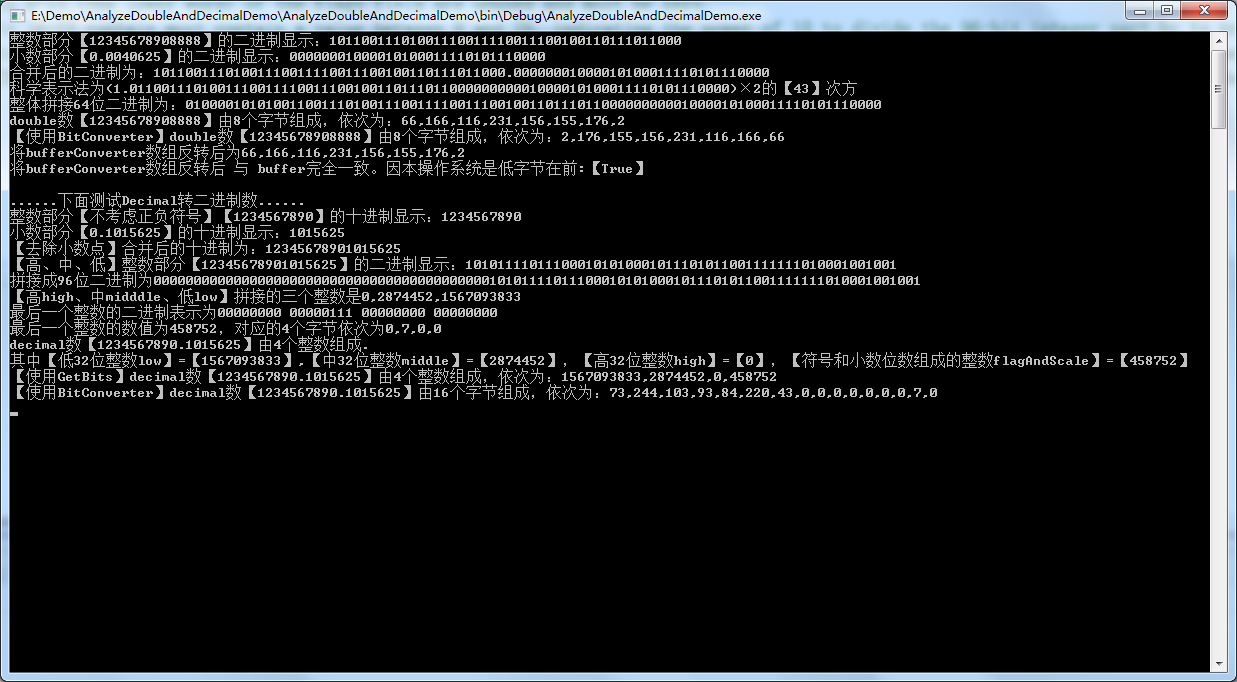
最后
以上就是个性小懒猪最近收集整理的关于C#Double和Decimal的二进制表示的全部内容,更多相关C#Double和Decimal内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复