直接遍历、for循环遍历、foreach循换,迭代器....
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);//add尾插
//直接遍历
System.out.println(list);//AbstractCollection中重写了toString方法
System.out.println("==========================");
//for循环
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); ++i){
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println("n========================");
//foreach循环
for (Integer x: list) {
System.out.print(x+" ");
}
System.out.println("n========================");
//迭代器遍历--正向输出
ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext()){//1:boolean hasNext()判断集合中是否有元素,如果有元素可以迭代,就返回true。
System.out.print(it.next()+" ");//2: E next()返回迭代的下一个元素
}
System.out.println("n========================");
//迭代器遍历--反向输出
ListIterator<Integer> rit = list.listIterator(list.size());
while (rit.hasPrevious()){
System.out.print(rit.previous() +" ");
}
}结果:
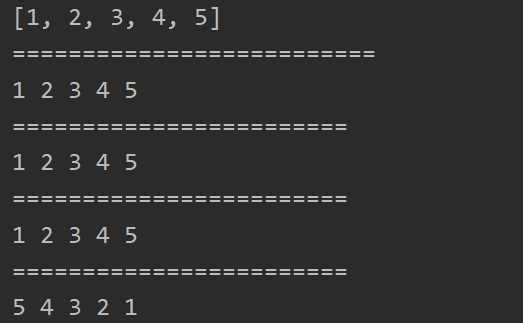
最后
以上就是专注老鼠最近收集整理的关于LinkedList的五种遍历方式的全部内容,更多相关LinkedList内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复