动态规划-避障道走法计算(AvoidRoads):
从右下坐标(0,0)出发,走到右上角的坐标。其中黑色粗体道路表示道路无法通行。只可以往右或上走,求走法可能。
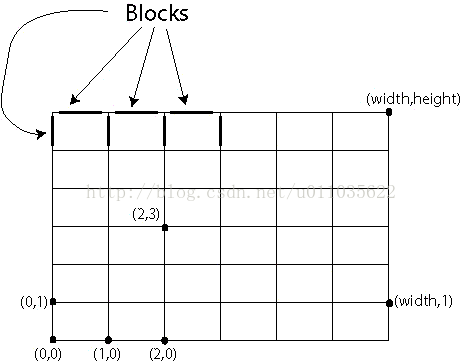
输入
width
height
n
x1 y1 x2 y2
其中前两个数分别表示宽度和高度。
n表示不可通道路的数量。
x1 y1 x2 y2 表示从(x1,y1)到(x2,y2)的道路不可通。
示例:
width = 6
length = 6
n = 2
0 0 0 1
6 6 5 6
Return :252
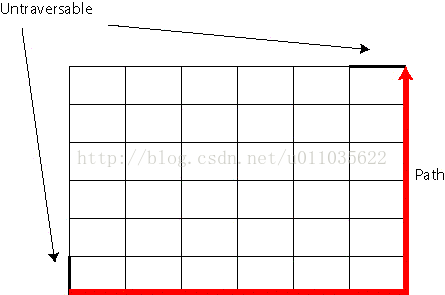
更多示例:
35
31
0
Returns: 6406484391866534976
2
2
3
{"0 0 1 0", "1 2 2 2", "1 1 2 1"}
Returns: 0
开始是用暴力搜索的方法,通过递归遍历全部,代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
static long count = 0;
public static void findback(int x ,int y ,int mark[][]){
System.out.println(count);
if (x == mark.length-1 &&y == mark.length-1) {//已到达右上角终点的情况。
count++;
return;
}
if (mark[x][y] == 0) { //两条路都可以走。
if (x != mark.length-1) {//判断是否到达右边界
findback(x+1,y,mark);
}
if (y != mark.length-1) {//判断是否到达上边界
findback(x,y+1,mark);
}
}
if (mark[x][y] == 5 && y != mark.length-1) {//右路封了,只能往上走,同时判断是否为上边界。
findback(x,y+1,mark);
}
if (mark[x][y] == 3 && x != mark.length-1) {//上路封了,只能往右走,同时判断是否为右边界。
findback(x+1,y,mark);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int X = sc.nextInt()+1;
int Y = sc.nextInt()+1;
int side = Math.max(X, Y);
int[][] mark = new int[side][side];
int N = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int x1 =sc.nextInt();
int y1 =sc.nextInt();
int x2 =sc.nextInt();
int y2 =sc.nextInt();
if (Math.abs(x2-x1) == 1) {
int min = Math.min(x1, x2);
mark[min][y1] = 5;//代表只能向上
}
if (Math.abs(y2-y1) == 1) {
int min = Math.min(y1, y2);
mark[x1][min] = 3;//代表只能向右
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < mark.length; j++) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(mark[j]));
}
findback(0,0,mark);
System.out.println(count);
}
}
后来发现这样的方法不行,因为数据较大时完全不行。(其实应该早点看出来的。。)
问了个比较懂算法的同学,理解了一下编写规律和方法。记录如下:
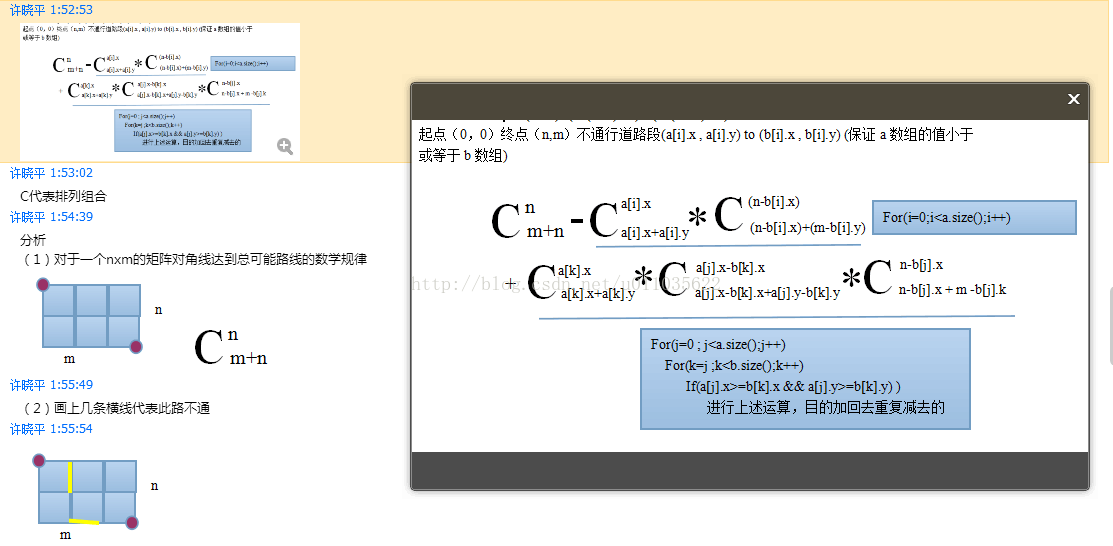

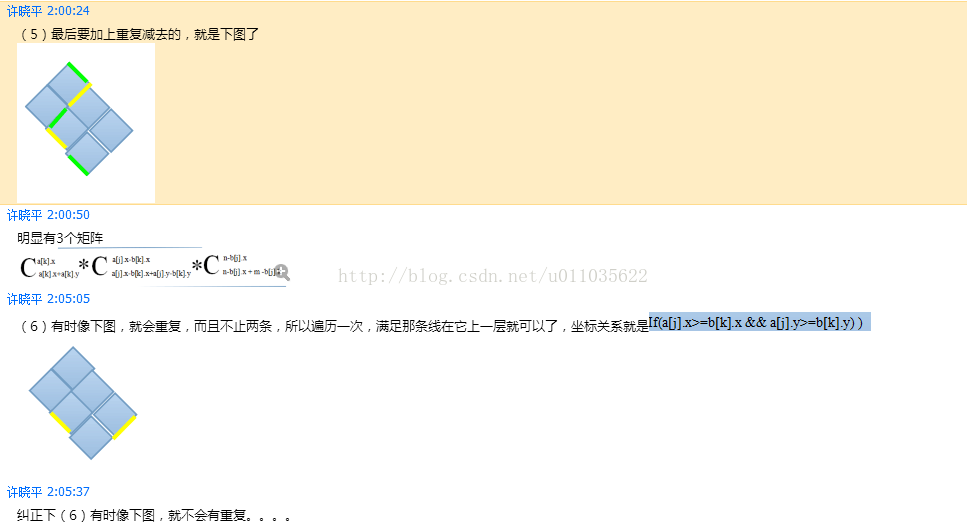
最后那几句话没怎么懂他在说什么,但是理解规律就大概知道该怎么编了~
代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
//排列组合算法。十分容易溢出。
public static Long C(Long X, Long Y) {
Long output = 1l;
for (Long i = X + Y; i > Y; i--) {
output *= i;
// System.out.println("1 parpered:"+output);
}
for (Long j = 1l; j <= X; j++) {
output /= j;
// System.out.println("2 parpered:"+output);
}
return output;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Long X = sc.nextLong();
Long Y = sc.nextLong();
int N = sc.nextInt();
Long[][] a = new Long[2][N];
Long[][] b = new Long[2][N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
Long x1 = sc.nextLong();
Long y1 = sc.nextLong();
Long x2 = sc.nextLong();
Long y2 = sc.nextLong();
a[0][i] = Math.min(x1, x2);//
a[1][i] = Math.min(y1, y2);//
b[0][i] = Math.max(x1, x2);//
b[1][i] = Math.max(y1, y2);//
}
//从左下到右上的通路的走法总数(无阻碍通道的情况)。
Long output = C(X, Y);
System.out.println("first:" + output);
//减去每条障碍通道所占有的通路可能 (相互之间会有重叠部分,所以后面要加回来。)
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
output -= C(a[0][i], a[1][i]) * C(X - b[0][i], Y - b[1][i]);
}
System.out.println("second:" + output);
//多减去的通路重叠那部分加回来(也就是交集的部分。)
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < N; j++) {
//类似冒泡的方法,让每两个阻碍道都有机会判断一次
//因为输入的大小顺序没有确定,所以要分下面两种情况,其他情况不会产生交集。
//目的是让右上的点减左下的点。
// i点在j点右上方
if ((a[0][i] >= b[0][j] && a[1][i] >= b[1][j])) {
output += C(Math.min(a[0][i], a[0][j]),
Math.min(a[1][i], a[1][j]))
* C(Math.abs(a[0][i] - b[0][j]),
Math.abs(a[1][i] - b[1][j]))//<<==事实上两种情况只有这里不同(为了区分这个因数的情况)。
* C(X - Math.max(b[0][j], b[0][i]),
Y - Math.max(b[0][j], b[1][i]));
}
// j点在i点右上方
if (((a[0][j] >= b[0][i] && a[1][j] >= b[1][i]))) {
output += C(Math.min(a[0][i], a[0][j]),
Math.min(a[1][i], a[1][j]))
* C(Math.abs(a[0][j] - b[0][i]),
Math.abs(a[1][j] - b[1][i]))//<<==事实上两种情况只有这里不同。
* C(X - Math.max(b[0][j], b[0][i]),
Y - Math.max(b[0][j], b[1][i]));
}
System.out.println("last parpered:" + output);
}
}
System.out.println("last:" + output);
}
}计算效率上没有问题,但数据存在问题,在计算阶乘时数据过大导致溢出。大概要通过字符串来拼接乘法。下次再编辑好了。
最后
以上就是慈祥蜜蜂最近收集整理的关于动态规划-避障道走法计算(AvoidRoads)的全部内容,更多相关动态规划-避障道走法计算(AvoidRoads)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复