input子系统架构总览
在网上能找到一些关于input子系统架构相关的示意图,大体表达的意思都差不多。

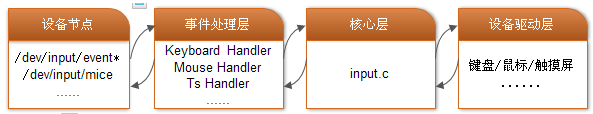
linux输入子系统(linux input subsystem)从上到下由三层实现,分别为:输入子系统事件处理层(EventHandler)、输入子系统核心层(InputCore)和输入子系统设备驱动层(driver)。
对于输入子系统设备驱动层而言,主要实现对硬件设备的读写访问,中断设置,并把硬件产生的事件转换为核心层定义的规范提交给事件处理层。
对于核心层而言,为设备驱动层提供了规范和接口。设备驱动层只要关心如何驱动硬件并获得硬件数据(例如按下的按键数据),然后调用核心层提供的接口,核心层会自动把数据提交给事件处理层。
对于事件处理层而言,则是用户编程的接口(设备节点),并处理驱动层提交的数据处理。
input子系统分为三层:
1、最上层:输入事件驱动层,evdev.c和mousedev.c和joydev.c属于这一层,对应 /dev/input/xxx;
2、中间层:输入核心层,input.c属于这一层;
3、最下层:输入设备驱动层,drivers/input/xxx 文件夹下;
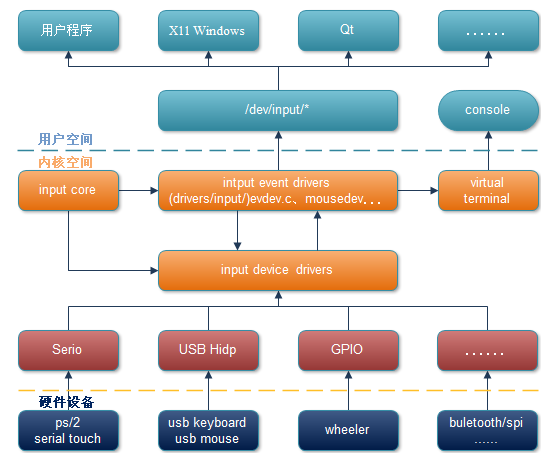
/dev/input目录下显示的是已经注册在内核中的设备编程接口,用户通过open这些设备文件来打开不同的输入设备进行硬件操作。
事件处理层为不同硬件类型提供了用户访问及处理接口。例如当我们打开设备/dev/input/mice时,会调用到事件处理层的Mouse Handler来处理输入事件,这也使得设备驱动层无需关心设备文件的操作,因为Mouse Handler已经有了对应事件处理的方法。
输入子系统由内核代码drivers/input/input.c构成,它的存在屏蔽了用户到设备驱动的交互细节,为设备驱动层和事件处理层提供了相互通信的统一界面。
输入核心层分析
输入核心层input.c,一、提供操作接口(中间层,不含具体的硬件操作以及具体的handler操作);二、承上启下,为驱动层提供输入设备注册接口,为事件层提供事件handler注册接口。因此重要的两个接口:int input_register_device(struct input_dev *dev) 和 int input_register_handler(struct input_handler *handler)
注意两者都会讲dev或handler加入到全局变量的链表中,且都会进行dev与handler之间的匹配。如下代码所示。
input_register_device中:
list_add_tail(&dev->node, &input_dev_list);
list_for_each_entry(handler, &input_handler_list, node)
input_attach_handler(dev, handler);
input_register_handler中:
list_add_tail(&handler->node, &input_handler_list);
list_for_each_entry(dev, &input_dev_list, node)
input_attach_handler(dev, handler);
因此解析一下input_attach_handler这个函数。
static int input_attach_handler(struct input_dev *dev, struct input_handler *handler)
{
const struct input_device_id *id;
int error;
id = input_match_device(handler, dev);
if (!id)
return -ENODEV;
error = handler->connect(handler, dev, id);
if (error && error != -ENODEV)
printk(KERN_ERR
"input: failed to attach handler %s to device %s, "
"error: %dn",
handler->name, kobject_name(&dev->dev.kobj), error);
return error;
}
input_match_device针对两者的这些能力进行比较,返回一个input_device_id类型的id_table,并通过handler中的connect函数指针(事件驱动层中定义)进行两者的绑定error = handler->connect(handler, dev, id);。
struct input_device_id {
kernel_ulong_t flags;
__u16 bustype;
__u16 vendor;
__u16 product;
__u16 version;
kernel_ulong_t evbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_EV_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];
kernel_ulong_t keybit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_KEY_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];
kernel_ulong_t relbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_REL_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];
kernel_ulong_t absbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_ABS_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];
kernel_ulong_t mscbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MSC_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];
kernel_ulong_t ledbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_LED_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];
kernel_ulong_t sndbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_SND_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];
kernel_ulong_t ffbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_FF_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];
kernel_ulong_t swbit[INPUT_DEVICE_ID_SW_MAX / BITS_PER_LONG + 1];
kernel_ulong_t driver_info;
};
handler->connect实际调用到evdev_connect(evdev.c为例),而evdev_connect中主要调用了device_initialize和device_add(相当于原来的device_create)创建了设备文件节点,以及调用核心层的input_register_handle去真正绑定输入设备和handler。
如下是input_register_handle的入参类型input_handle,对其的dev和handler分别赋值,最后注册到系统中。
struct input_handle {
void *private;
int open;
const char *name;
struct input_dev *dev;
struct input_handler *handler;
struct list_head d_node;
struct list_head h_node;
};
input_handler 与 id_table
每个事件驱动层都各自定义了struct input_handler类型的handler,如evdev中的evdev_handler、mousedev中的mousedev_handler等等。
static const struct input_device_id evdev_ids[] = {
{ .driver_info = 1 }, /* Matches all devices */
{ }, /* Terminating zero entry */
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(input, evdev_ids);
static struct input_handler evdev_handler = {
.event = evdev_event,
.connect = evdev_connect,
.disconnect = evdev_disconnect,
.fops = &evdev_fops,
.minor = EVDEV_MINOR_BASE,
.name = "evdev",
.id_table = evdev_ids,
};
static struct input_handler mousedev_handler = {
.event = mousedev_event,
.connect = mousedev_connect,
.disconnect = mousedev_disconnect,
.fops = &mousedev_fops,
.minor = MOUSEDEV_MINOR_BASE,
.name = "mousedev",
.id_table = mousedev_ids,
};
id_table是用来描述可匹配该handler的所有硬件能力表,即满足该表中的任意一种设备类型(主要看能力)即可匹配,如下是mousedev_handler的id_table。而evdev_handler中的id_table为空,即Matches all devices。
static const struct input_device_id mousedev_ids[] = {
{
.flags = INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_EVBIT |
INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_KEYBIT |
INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_RELBIT,
.evbit = { BIT_MASK(EV_KEY) | BIT_MASK(EV_REL) },
.keybit = { [BIT_WORD(BTN_LEFT)] = BIT_MASK(BTN_LEFT) },
.relbit = { BIT_MASK(REL_X) | BIT_MASK(REL_Y) },
}, /* A mouse like device, at least one button,
two relative axes */
{
.flags = INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_EVBIT |
INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_RELBIT,
.evbit = { BIT_MASK(EV_KEY) | BIT_MASK(EV_REL) },
.relbit = { BIT_MASK(REL_WHEEL) },
}, /* A separate scrollwheel */
{
.flags = INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_EVBIT |
INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_KEYBIT |
INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_ABSBIT,
.evbit = { BIT_MASK(EV_KEY) | BIT_MASK(EV_ABS) },
.keybit = { [BIT_WORD(BTN_TOUCH)] = BIT_MASK(BTN_TOUCH) },
.absbit = { BIT_MASK(ABS_X) | BIT_MASK(ABS_Y) },
}, /* A tablet like device, at least touch detection,
two absolute axes */
{
.flags = INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_EVBIT |
INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_KEYBIT |
INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_ABSBIT,
.evbit = { BIT_MASK(EV_KEY) | BIT_MASK(EV_ABS) },
.keybit = { [BIT_WORD(BTN_TOOL_FINGER)] =
BIT_MASK(BTN_TOOL_FINGER) },
.absbit = { BIT_MASK(ABS_X) | BIT_MASK(ABS_Y) |
BIT_MASK(ABS_PRESSURE) |
BIT_MASK(ABS_TOOL_WIDTH) },
}, /* A touchpad */
{
.flags = INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_EVBIT |
INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_KEYBIT |
INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_ABSBIT,
.evbit = { BIT_MASK(EV_KEY) | BIT_MASK(EV_ABS) },
.keybit = { [BIT_WORD(BTN_LEFT)] = BIT_MASK(BTN_LEFT) },
.absbit = { BIT_MASK(ABS_X) | BIT_MASK(ABS_Y) },
}, /* Mouse-like device with absolute X and Y but ordinary
clicks, like hp ILO2 High Performance mouse */
{ }, /* Terminating entry */
};
输入事件驱动层分析
主要关注的就是input_handler这个数据类型,特别是其中的一些成员函数。
上述已经对输入事件驱动层源码(以evdev.c为例)中的input_handler、evdev_connect、id_table进行过分析了。
硬件上报事件 evdev_event
其调用过程如下:
驱动层调用input_report_key等input_report_xxx接口(input.h中定义)->
input_event (input.c中定义)->
input_handle_event (input.c中定义)->
dev->event
evdev_event中填充了event.time、event.type、event.code、event.value这些应用层看到的事件信息,再在evdev_pass_event中将event放到了client->buffer中,且支持单发或多发(client_list)。
最后唤醒中断。
static void evdev_event(struct input_handle *handle,
unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
struct evdev *evdev = handle->private;
struct evdev_client *client;
struct input_event event;
struct timespec ts;
ktime_get_ts(&ts);
event.time.tv_sec = ts.tv_sec;
event.time.tv_usec = ts.tv_nsec / NSEC_PER_USEC;
event.type = type;
event.code = code;
event.value = value;
rcu_read_lock();
client = rcu_dereference(evdev->grab);
if (client)
evdev_pass_event(client, &event);
else
list_for_each_entry_rcu(client, &evdev->client_list, node)
evdev_pass_event(client, &event);
rcu_read_unlock();
wake_up_interruptible(&evdev->wait);
}
static void evdev_pass_event(struct evdev_client *client,
struct input_event *event)
{
/*
* Interrupts are disabled, just acquire the lock
*/
spin_lock(&client->buffer_lock);
wake_lock_timeout(&client->wake_lock, 5 * HZ);
client->buffer[client->head++] = *event;
client->head &= EVDEV_BUFFER_SIZE - 1;
spin_unlock(&client->buffer_lock);
if (event->type == EV_SYN)
kill_fasync(&client->fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
}
上报应用事件 evdev_read
evdev_read为struct file_operations 的evdev_fops的read方法,对应应用层cat或read函数。该函数主要是将client->buffer中的事件数据(上述硬件上报事件时保存的)通过copy_to_user上报到用户态的应用层。
wait_event_interruptible会阻塞等待事件中断,若有硬件上报事件时会被唤醒。
static ssize_t evdev_read(struct file *file, char __user *buffer,
size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
struct evdev_client *client = file->private_data;
struct evdev *evdev = client->evdev;
struct input_event event;
int retval;
if (count < input_event_size())
return -EINVAL;
if (client->head == client->tail && evdev->exist &&
(file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK))
return -EAGAIN;
retval = wait_event_interruptible(evdev->wait,
client->head != client->tail || !evdev->exist);
if (retval)
return retval;
if (!evdev->exist)
return -ENODEV;
while (retval + input_event_size() <= count &&
evdev_fetch_next_event(client, &event)) {
if (input_event_to_user(buffer + retval, &event))
return -EFAULT;
retval += input_event_size();
}
return retval;
}
static int evdev_fetch_next_event(struct evdev_client *client,
struct input_event *event)
{
int have_event;
spin_lock_irq(&client->buffer_lock);
have_event = client->head != client->tail;
if (have_event) {
*event = client->buffer[client->tail++];
client->tail &= EVDEV_BUFFER_SIZE - 1;
if (client->head == client->tail)
wake_unlock(&client->wake_lock);
}
spin_unlock_irq(&client->buffer_lock);
return have_event;
}
硬件驱动层
以button-smdkv210.c为例,该驱动实现为一个平台总线,那我们先分析其probe函数。
主要做的就是一下四件事:
- gpio_request // 申请GPIO,以及设置为高电平、输出模式
- input_allocate_device
- input_register_device // input_allocate_device 和 input_register_device 向inputCore注册输入设备
- timer // 设置并添加定时器
/* Scan timer init */
init_timer(&timer);
timer.function = s3cbutton_timer_handler;
timer.expires = jiffies + (HZ/100);
add_timer(&timer);
该定时器定时周期为(HZ / 100) = 1s / 100 = 10ms,s3cbutton_timer_handler作为定时器到了去执行的函数,而这个函数中则是去对每个按键对应的GPIO去做检查,是否状态与之前不一样了,若不一样了则上报值与事件(input_report_key)。
中断方式按键驱动
可以看出这个驱动是通过轮询写的,但是这种方式效率低下,一般我们采取中断来实现按键驱动。
在内核源码的Documentationinput目录下,有一个input-programming.txt的文档,描述了如何 Creating an input device driver,并且提供了一个The simplest example,就是一个按键驱动的demo。根据这个demo修改后,实现的中断方式按键驱动代码如下:
#include <linux/input.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <asm/irq.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <mach/gpio.h>
#include <mach/irqs.h> // arch/arm/mach-s5pv210/include/mach/irqs.h
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
/*
* X210:
*
* POWER -> EINT1 -> GPH0_1
* LEFT -> EINT2 -> GPH0_2
* DOWN -> EINT3 -> GPH0_3
* UP -> KP_COL0 -> GPH2_0
* RIGHT -> KP_COL1 -> GPH2_1
* MENU -> KP_COL3 -> GPH2_3 (KEY_A)
* BACK -> KP_COL2 -> GPH2_2 (KEY_B)
*/
#define BTN KEY_LEFT
#define BUTTON_IRQ IRQ_EINT2
static struct input_dev *button_dev;
static irqreturn_t button_interrupt(int irq, void *dummy)
{
int flag;
s3c_gpio_cfgpin(S5PV210_GPH0(2), S3C_GPIO_SFN(0x0)); // input
flag = gpio_get_value(S5PV210_GPH0(2));
s3c_gpio_cfgpin(S5PV210_GPH0(2), S3C_GPIO_SFN(0x0f)); // EINT2
input_report_key(button_dev, BTN, !flag);
input_sync(button_dev);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
static int __init button_init(void)
{
int error;
// request and set GPIO
error = gpio_request(S5PV210_GPH0(2), "GPH0_2");
if (error)
{
printk("button-x210: request gpio GPH0(2) failn");
return -EBUSY;
}
s3c_gpio_cfgpin(S5PV210_GPH0(2), S3C_GPIO_SFN(0x0f)); // EINT2
// request_irq
if (request_irq(BUTTON_IRQ, button_interrupt, 0, "button-x210", NULL)) {
printk(KERN_ERR "key-s5pv210.c: Can't allocate irq %dn", BUTTON_IRQ);
return -EBUSY;
}
button_dev = input_allocate_device();
if (!button_dev) {
printk(KERN_ERR "key-s5pv210.c: Not enough memoryn");
error = -ENOMEM;
goto err_free_irq;
}
button_dev->evbit[0] = BIT_MASK(EV_KEY);
button_dev->keybit[BIT_WORD(BTN)] = BIT_MASK(BTN);
//set_bit(EV_KEY, button_dev->evbit);
//set_bit(BTN, button_dev->keybit);
error = input_register_device(button_dev);
if (error) {
printk(KERN_ERR "key-s5pv210.c: Failed to register devicen");
goto err_free_dev;
}
return 0;
err_free_dev:
input_free_device(button_dev);
err_free_irq:
free_irq(BUTTON_IRQ, button_interrupt);
return error;
}
static void __exit button_exit(void)
{
input_unregister_device(button_dev);
free_irq(BUTTON_IRQ, NULL);
gpio_free(S5PV210_GPH0(2));
}
module_init(button_init);
module_exit(button_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("ericpa <ericpa@yeah.net>");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Keyboard driver for x210 button.");
MODULE_ALIAS("platform:x210-button");
最后
以上就是成就刺猬最近收集整理的关于【Linux驱动】input子系统与按键驱动的全部内容,更多相关【Linux驱动】input子系统与按键驱动内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复